Содержание
- 2. Overview Mass Spectrometry in a Nutshell - Facts and Basics Mass Resolution and Mass Accuracy Fragmentation
- 4. Difference Between Spectrometric Methods: Ionization implies a chemical process induced by physical methods. The sample is
- 5. Structural Information by MS MW determination nominal accurate (elemental composition) Isotope pattern High resolution Fragmentation Fragmentation
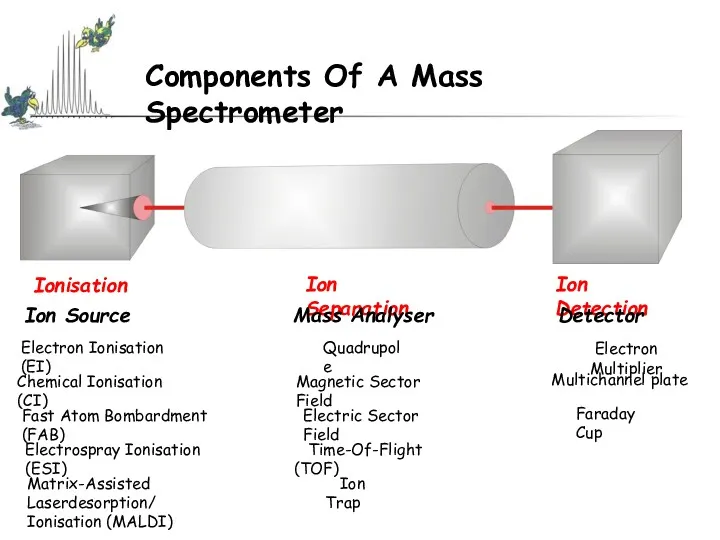
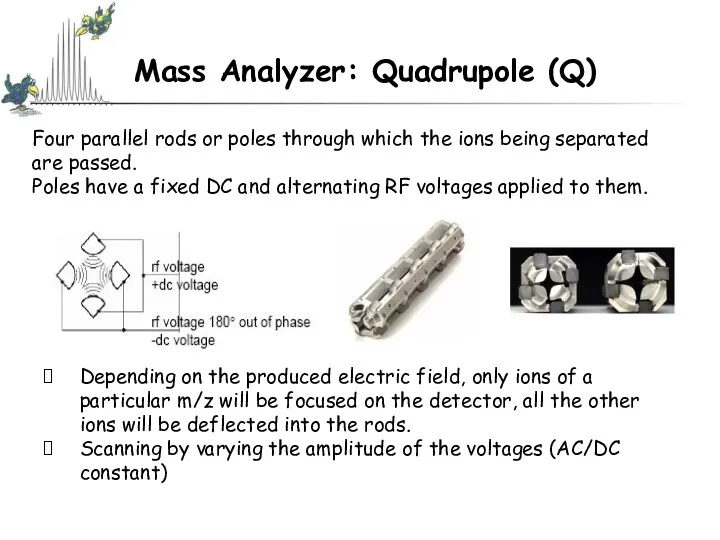
- 6. Components Of A Mass Spectrometer Ionisation Ion Detection Ion Separation Ion Source Mass Analyser Detector Electron
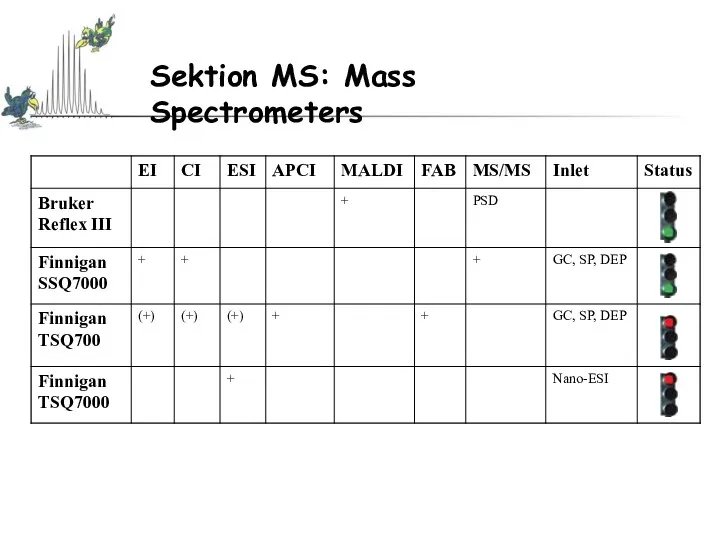
- 7. Sektion MS: Mass Spectrometers
- 8. Homepage „Sektion Massenspektrometrie“ http://www.uni-ulm.de/uni/fak/natwis/oc2/massenspektrometrie/index.htm FTP-Server for data collection (MALDI, EI, CI, FAB) like the NMR-service Server:
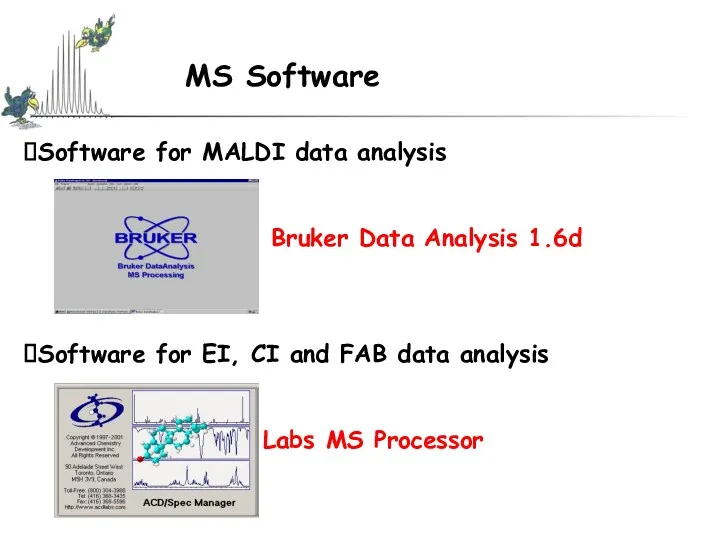
- 9. Software for MALDI data analysis Bruker Data Analysis 1.6d Software for EI, CI and FAB data
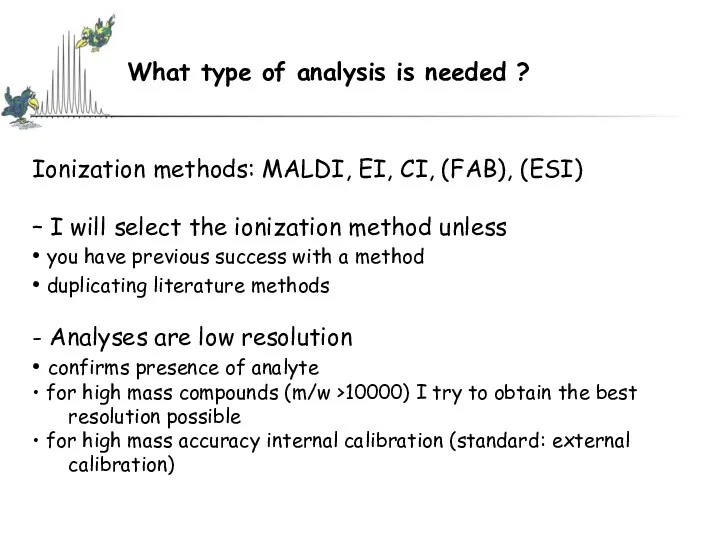
- 10. Ionization methods: MALDI, EI, CI, (FAB), (ESI) – I will select the ionization method unless •
- 11. Which MS method is best for the compound I want to analyze ? Molecular weigth? Solvent
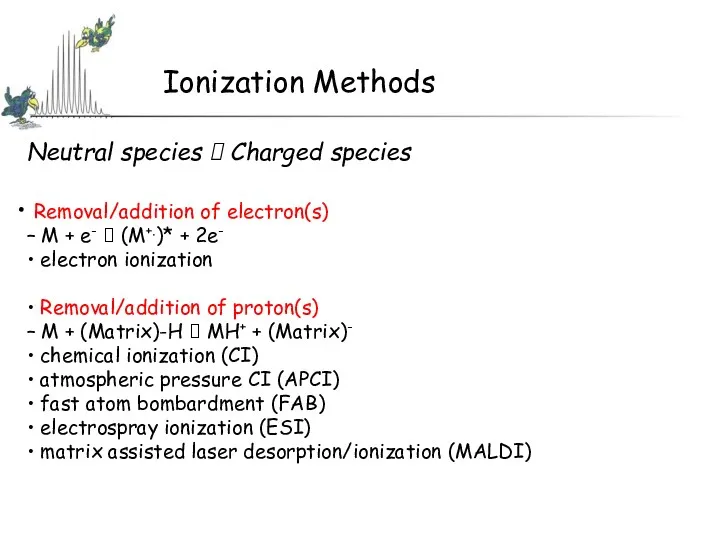
- 12. Ionization Methods Neutral species ? Charged species Removal/addition of electron(s) – M + e- ? (M+.)*
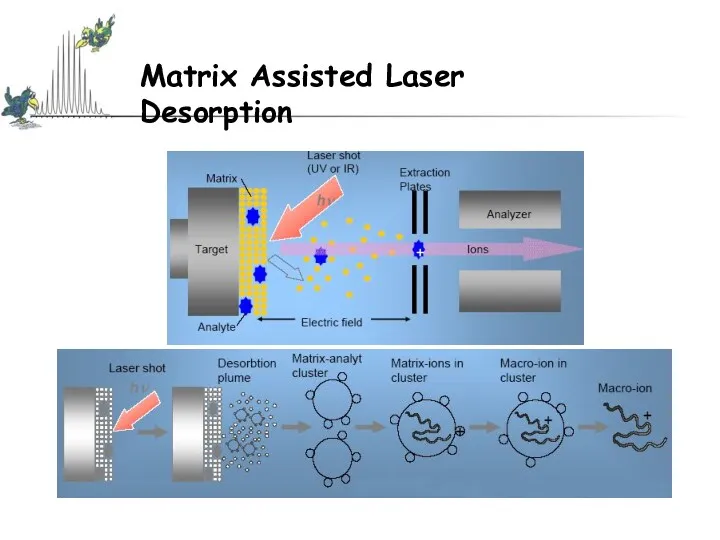
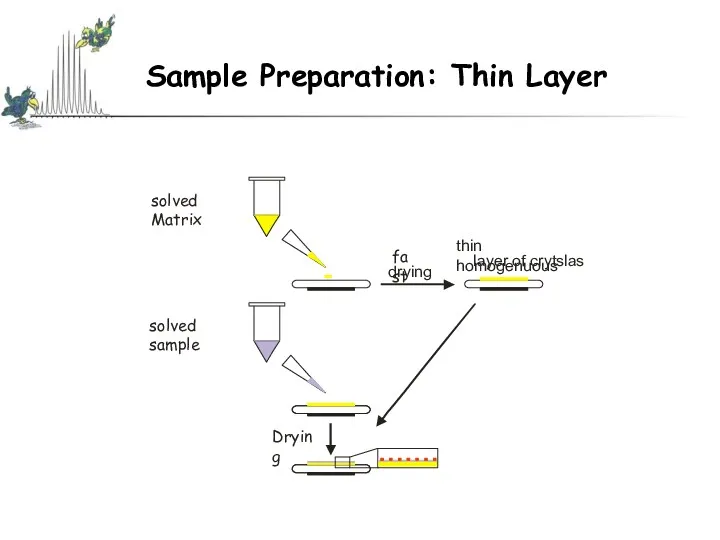
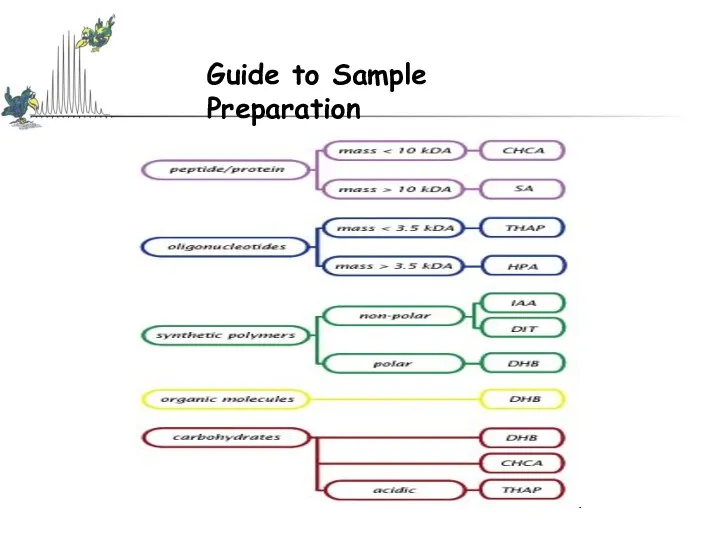
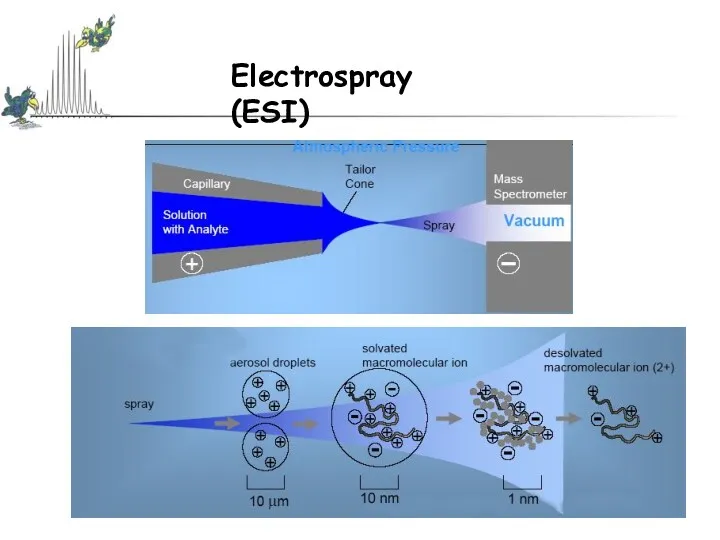
- 13. Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption
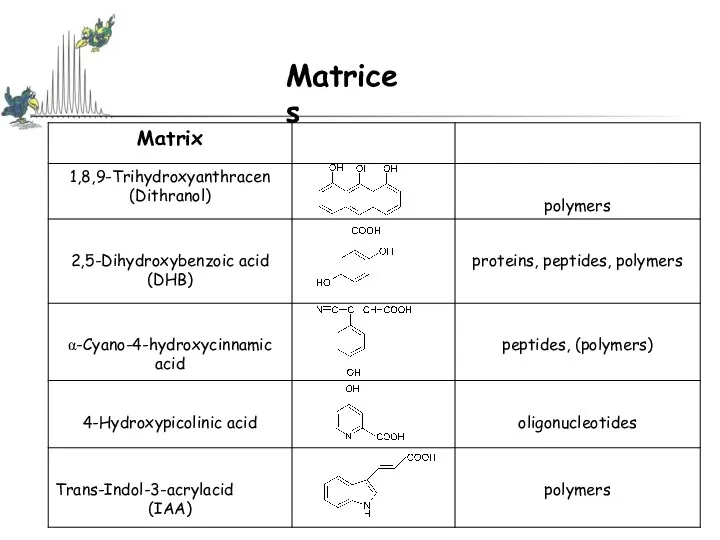
- 15. Matrices
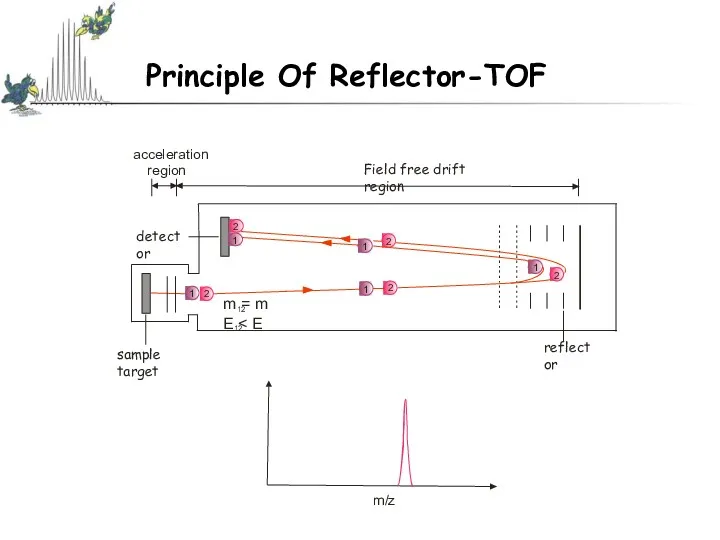
- 20. Principle Of Reflector-TOF
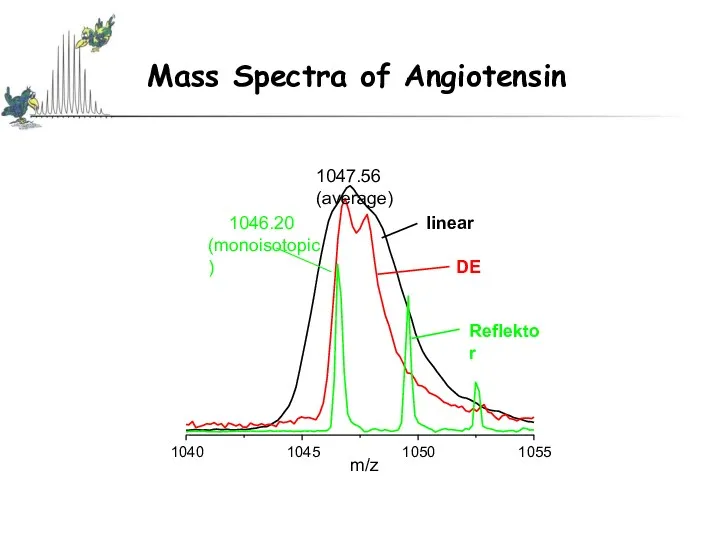
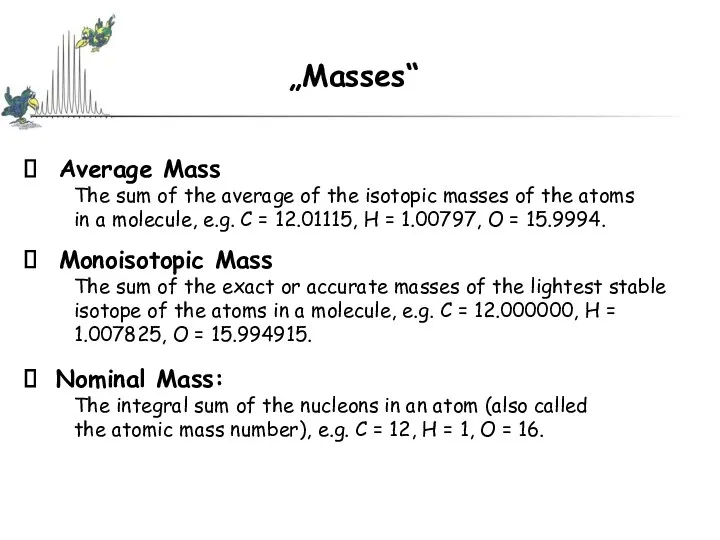
- 27. „Masses“ Average Mass The sum of the average of the isotopic masses of the atoms in
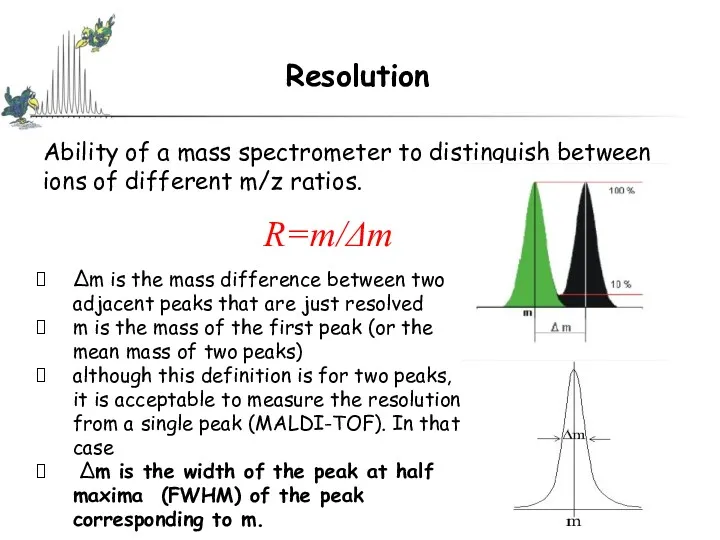
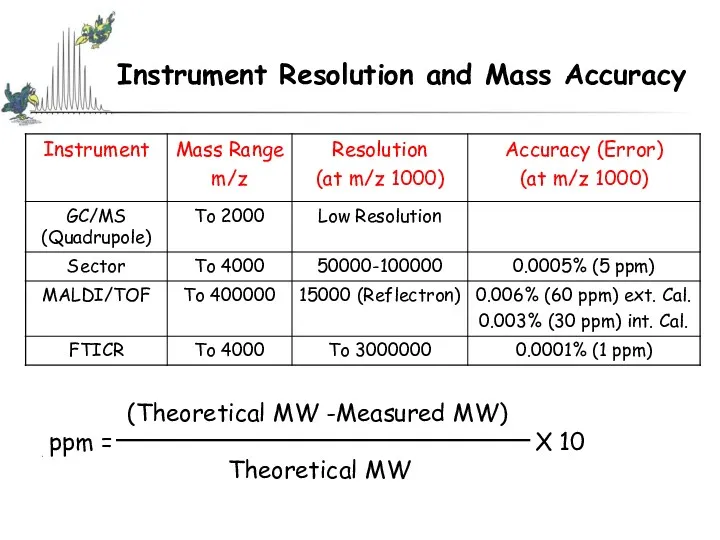
- 30. Instrument Resolution and Mass Accuracy (Theoretical MW -Measured MW) ppm = X 10 Theoretical MW
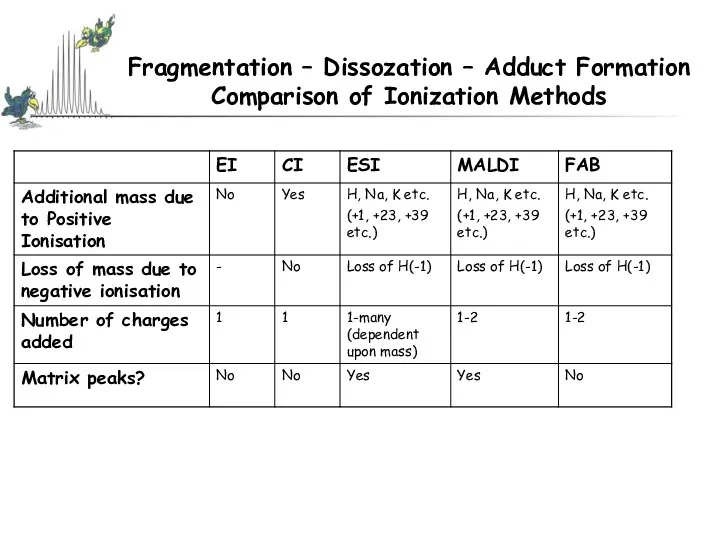
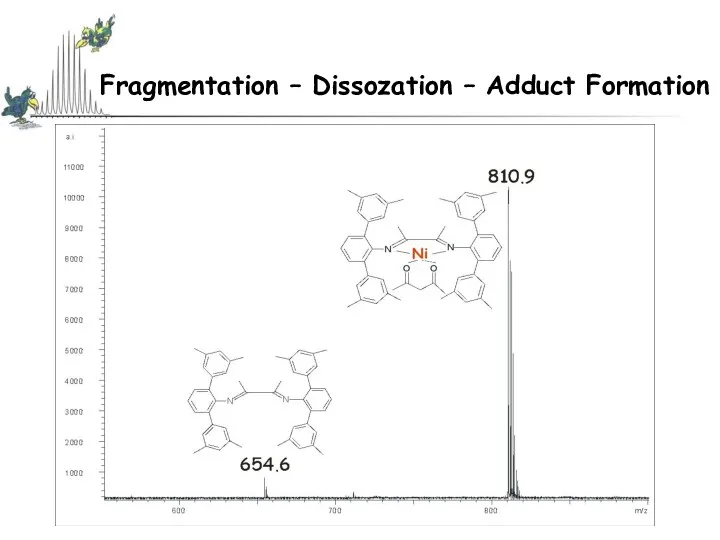
- 33. Fragmentation – Dissozation – Adduct Formation Comparison of Ionization Methods
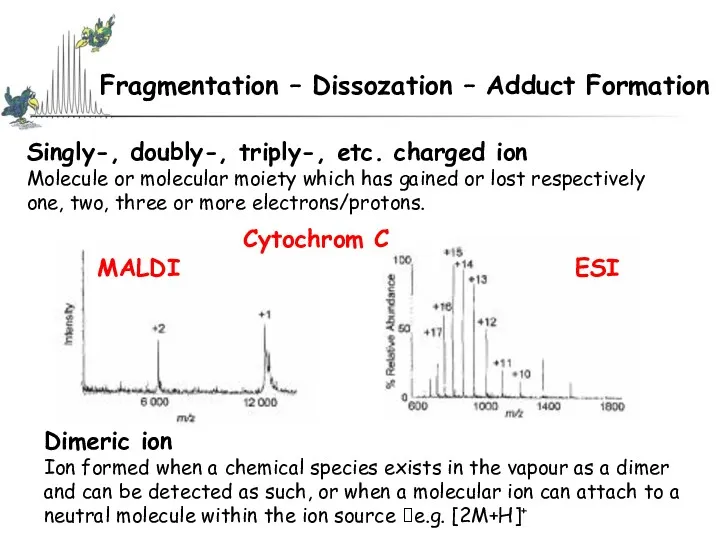
- 34. Singly-, doubly-, triply-, etc. charged ion Molecule or molecular moiety which has gained or lost respectively
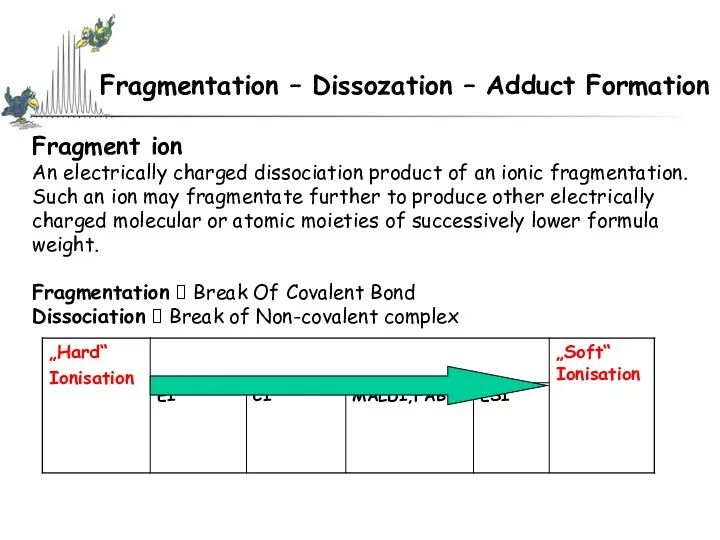
- 37. Fragment ion An electrically charged dissociation product of an ionic fragmentation. Such an ion may fragmentate
- 38. Fragment ion An electrically charged dissociation product of an ionic fragmentation. Such an ion may fragmentate
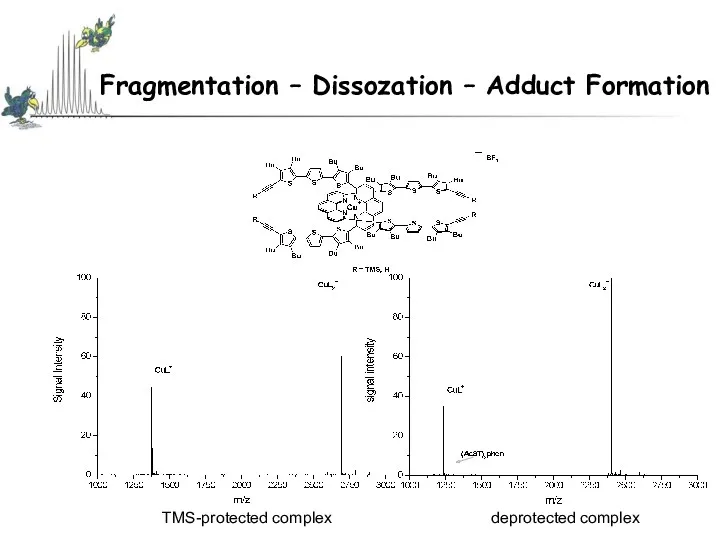
- 40. Fragmentation – Dissozation – Adduct Formation TMS-protected complex deprotected complex
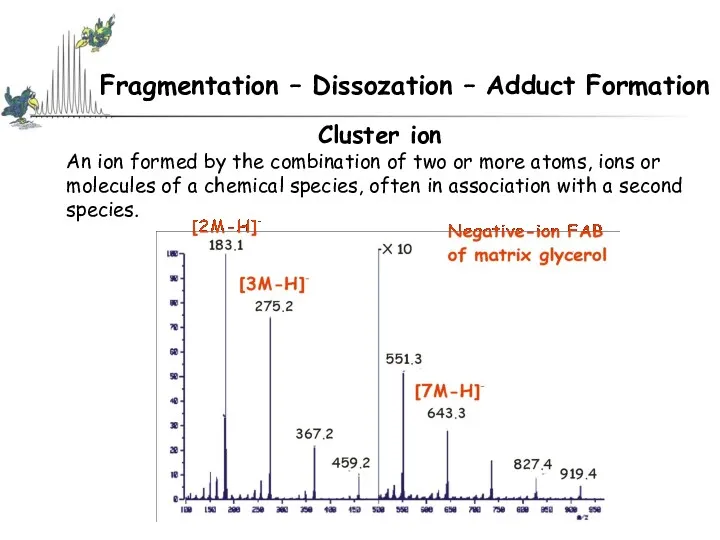
- 41. Fragmentation – Dissozation – Adduct Formation
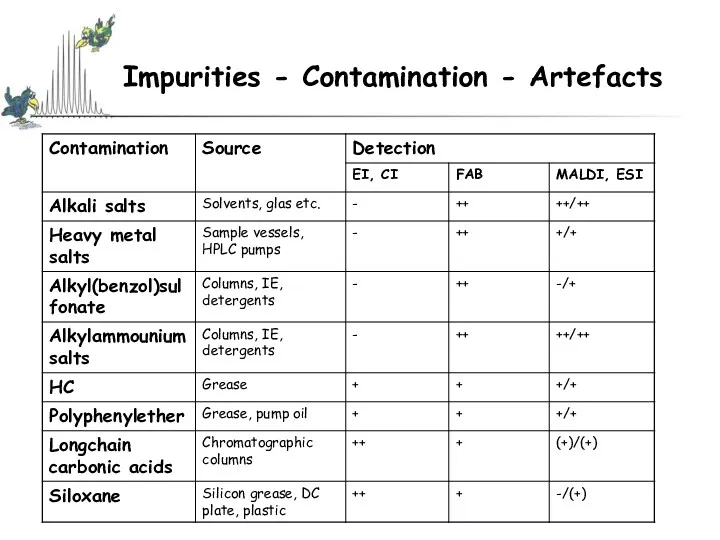
- 43. Impurities - Contamination - Artefacts
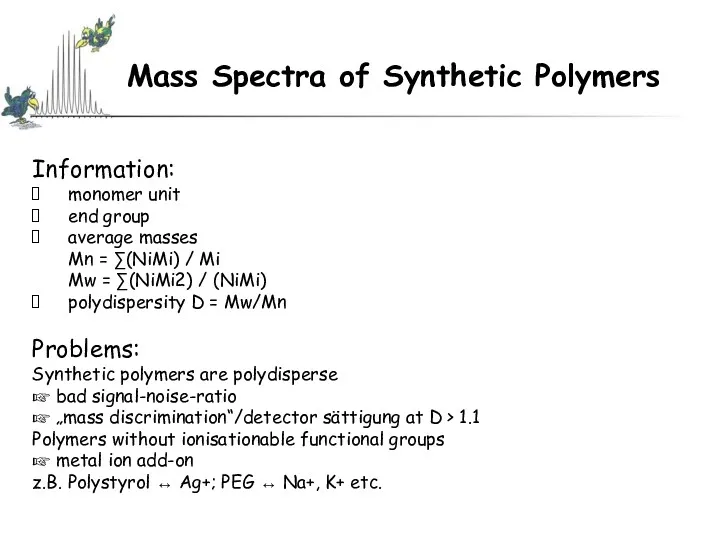
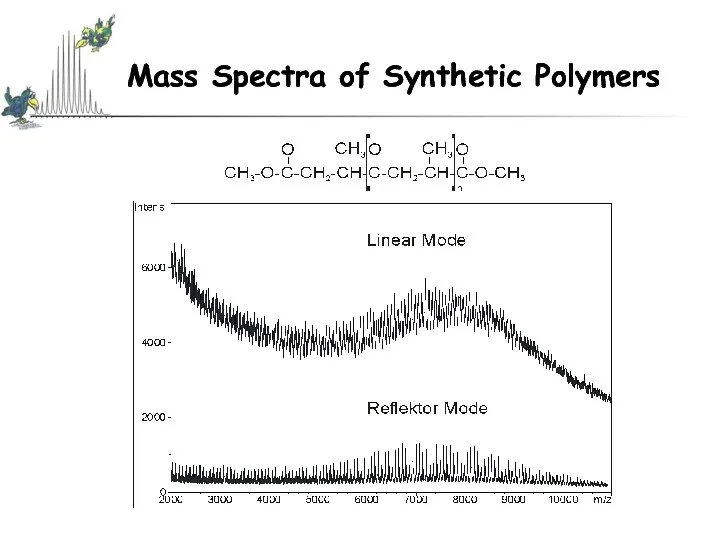
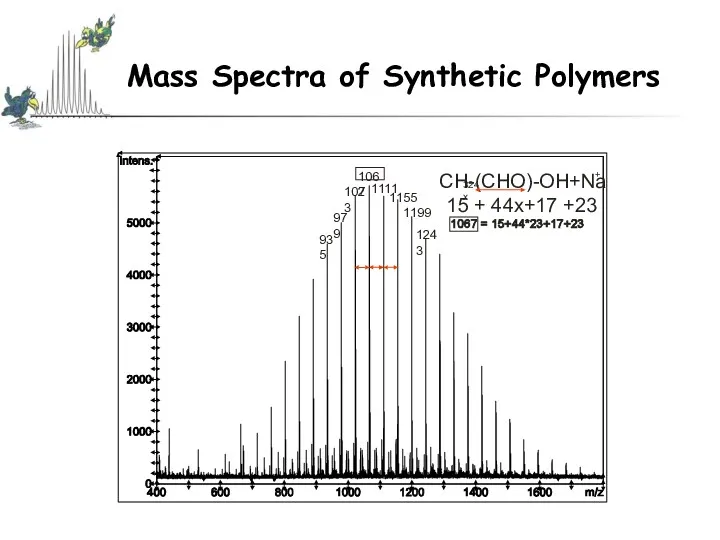
- 47. Mass Spectra of Synthetic Polymers Mass Spectra of Synthetic Polymers
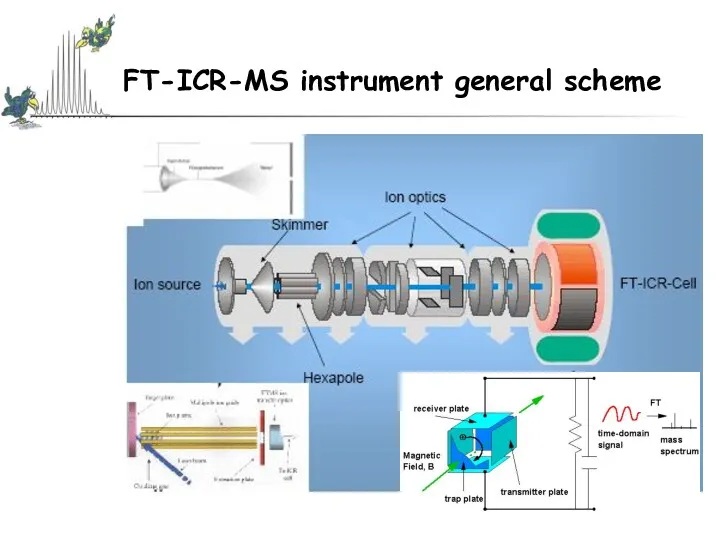
- 52. Fouriertransform-ICR: New Dimensions of High Performance Mass Spectrometry A high-frequency mass spectrometer in which the cyclotron
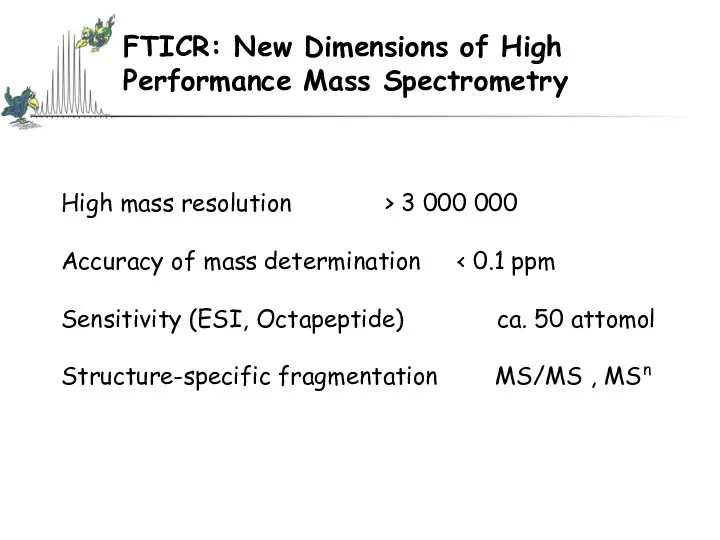
- 53. FTICR: New Dimensions of High Performance Mass Spectrometry High mass resolution > 3 000 000 Accuracy
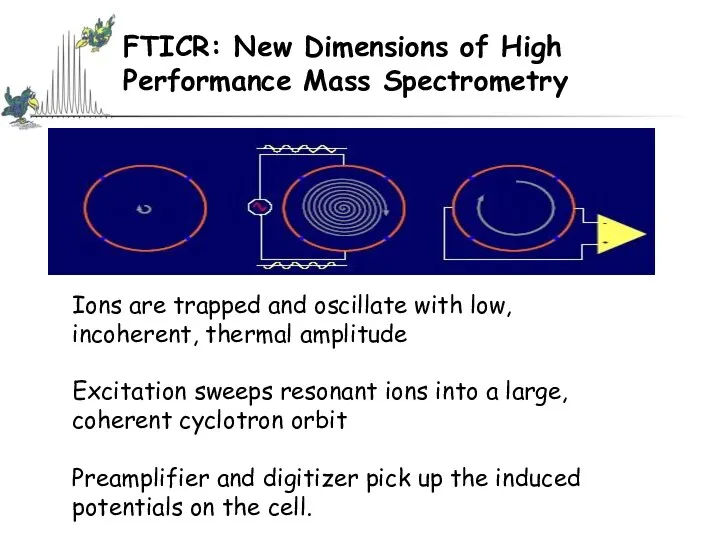
- 54. FTICR: New Dimensions of High Performance Mass Spectrometry Ions are trapped and oscillate with low, incoherent,
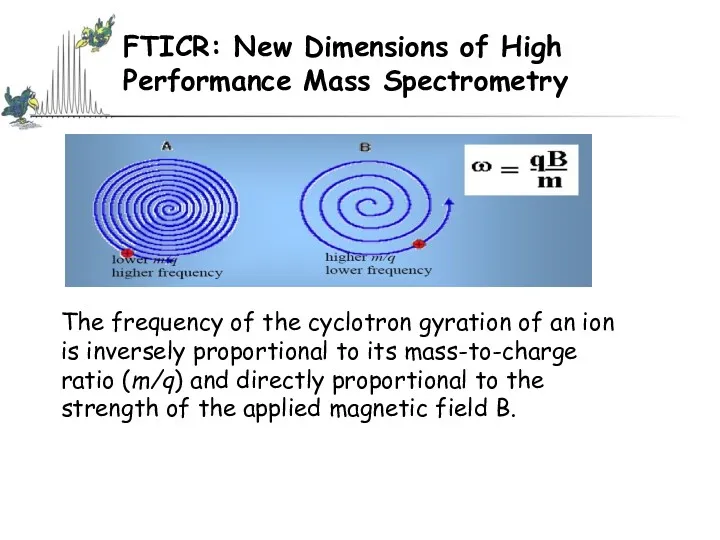
- 55. FTICR: New Dimensions of High Performance Mass Spectrometry The frequency of the cyclotron gyration of an
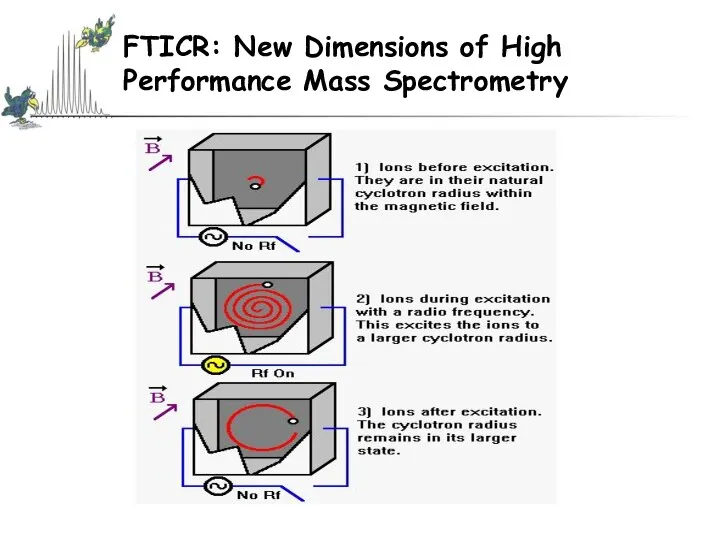
- 56. FTICR: New Dimensions of High Performance Mass Spectrometry
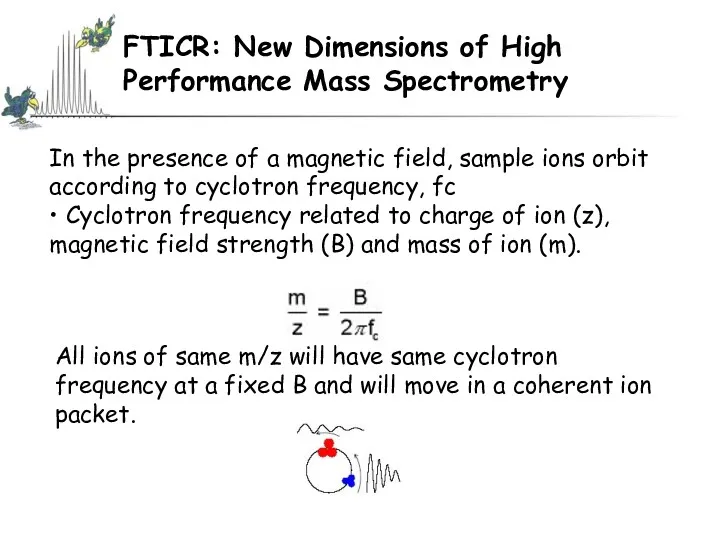
- 57. FTICR: New Dimensions of High Performance Mass Spectrometry In the presence of a magnetic field, sample
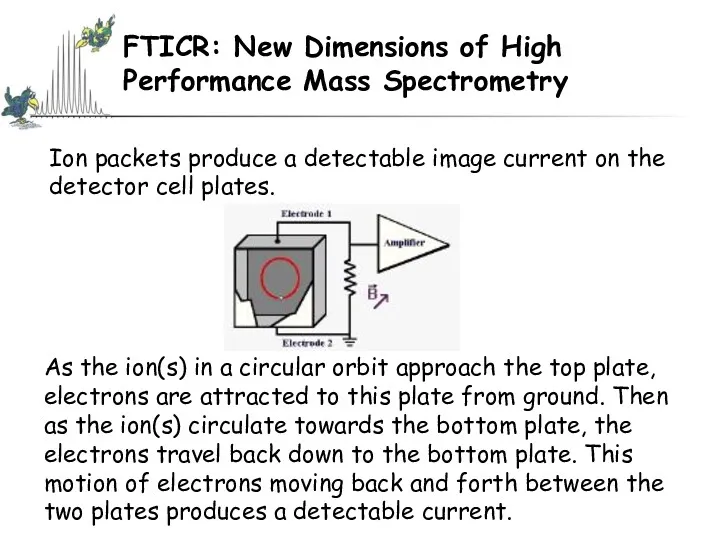
- 58. FTICR: New Dimensions of High Performance Mass Spectrometry Ion packets produce a detectable image current on
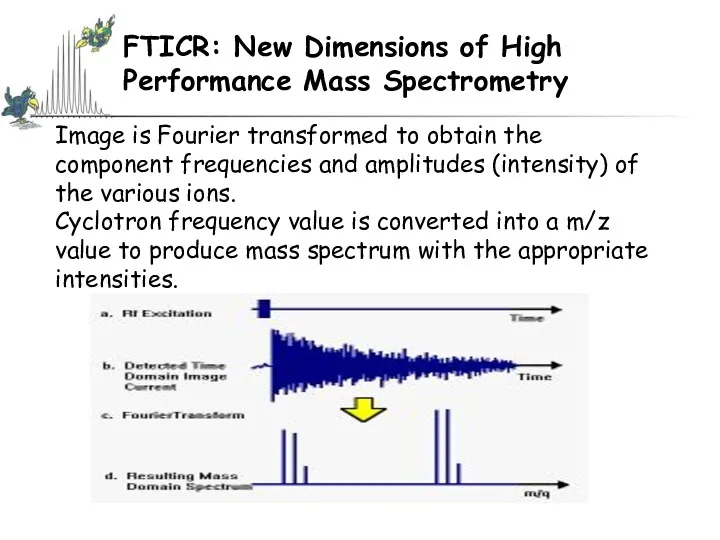
- 59. FTICR: New Dimensions of High Performance Mass Spectrometry Image is Fourier transformed to obtain the component
- 62. Скачать презентацию
















 Альфа-, бета- и гамма-излучение. Радиоактивность
Альфа-, бета- и гамма-излучение. Радиоактивность Электротехника и электроника. Трехфазные электрические цепи. (Лекция 8)
Электротехника и электроника. Трехфазные электрические цепи. (Лекция 8) Заттың тығыздығы
Заттың тығыздығы Урок – лабораторная работа Измерение сопротивления проводника при помощи амперметра и вольтметра.
Урок – лабораторная работа Измерение сопротивления проводника при помощи амперметра и вольтметра. Quick Quiz
Quick Quiz Математические модели и методы оптимизации процессов пространственного маневрирования морских подвижных объектов
Математические модели и методы оптимизации процессов пространственного маневрирования морских подвижных объектов Основы молекулярно-кинетической теории
Основы молекулярно-кинетической теории Элементы квантовой механики. Лекция № 4
Элементы квантовой механики. Лекция № 4 Последовательности и их параметры
Последовательности и их параметры Шкала электромагнитных волн
Шкала электромагнитных волн открытый урок-презентация на тему История Российской атомной энергетики
открытый урок-презентация на тему История Российской атомной энергетики Презентация по физике на тему _Шкала электромагнитных волн_
Презентация по физике на тему _Шкала электромагнитных волн_ Открытие протона и нейтрона
Открытие протона и нейтрона Диэлектрические потери
Диэлектрические потери Загадки
Загадки Реактивное движение
Реактивное движение Влагомаслоотделитель пневматической системы троллейбуса ЗИУ - 9
Влагомаслоотделитель пневматической системы троллейбуса ЗИУ - 9 Физика атомного ядра
Физика атомного ядра Основные понятия и законы теории электромагнитного поля и теории электрических цепей
Основные понятия и законы теории электромагнитного поля и теории электрических цепей Подшипники качения
Подшипники качения Отклонения и допуски на размеры детали. Размеры деталей на чертежах
Отклонения и допуски на размеры детали. Размеры деталей на чертежах Явление электромагнитной индукции. Уравнения Максвелла
Явление электромагнитной индукции. Уравнения Максвелла Структурна надійність
Структурна надійність Линзы. Построение изображений в линзах
Линзы. Построение изображений в линзах Плотность = масса : объем
Плотность = масса : объем Electrode processes
Electrode processes Восстановительный поезд
Восстановительный поезд Interest in the synthesis of metal nanoparticles by explosion
Interest in the synthesis of metal nanoparticles by explosion