Содержание
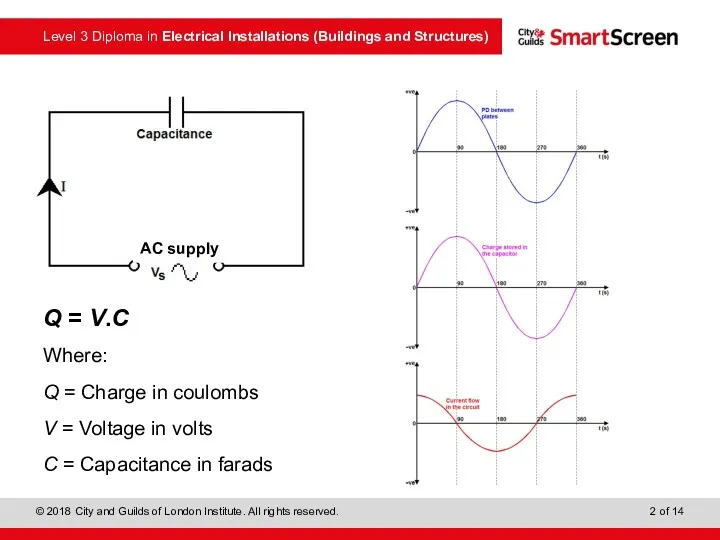
- 2. Q = V.C Where: Q = Charge in coulombs V = Voltage in volts C =
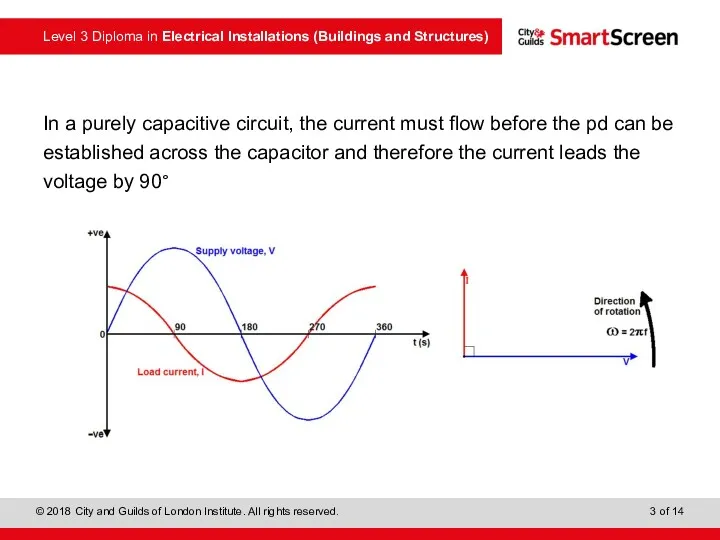
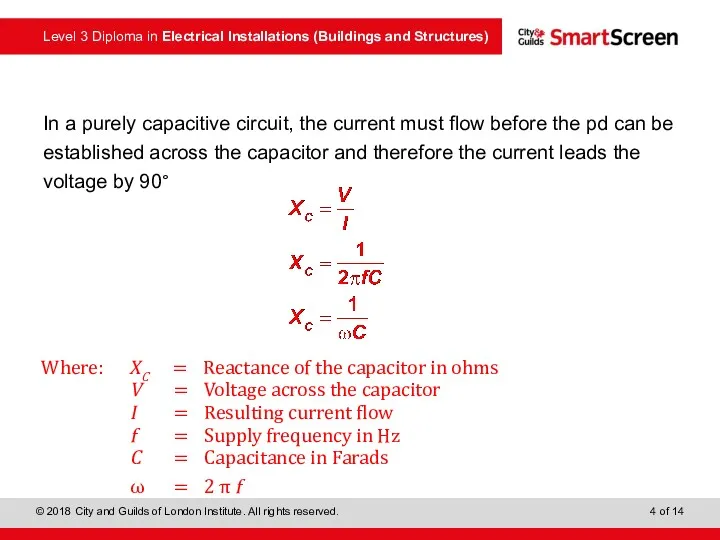
- 3. In a purely capacitive circuit, the current must flow before the pd can be established across
- 4. In a purely capacitive circuit, the current must flow before the pd can be established across
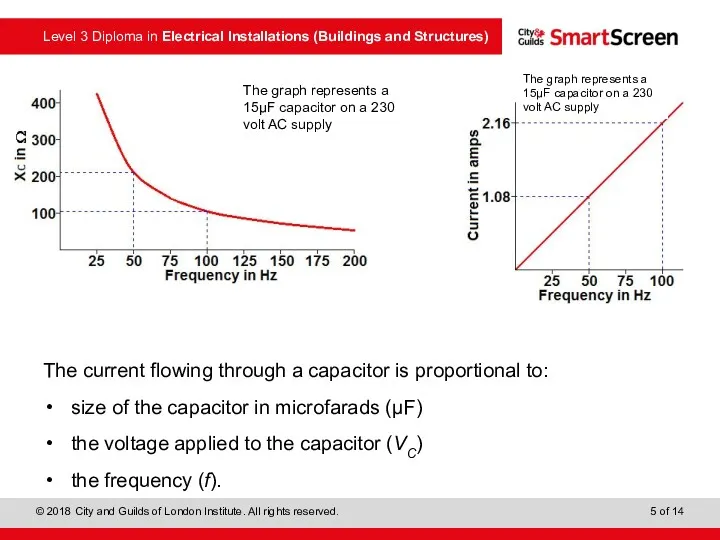
- 5. The current flowing through a capacitor is proportional to: size of the capacitor in microfarads (μF)
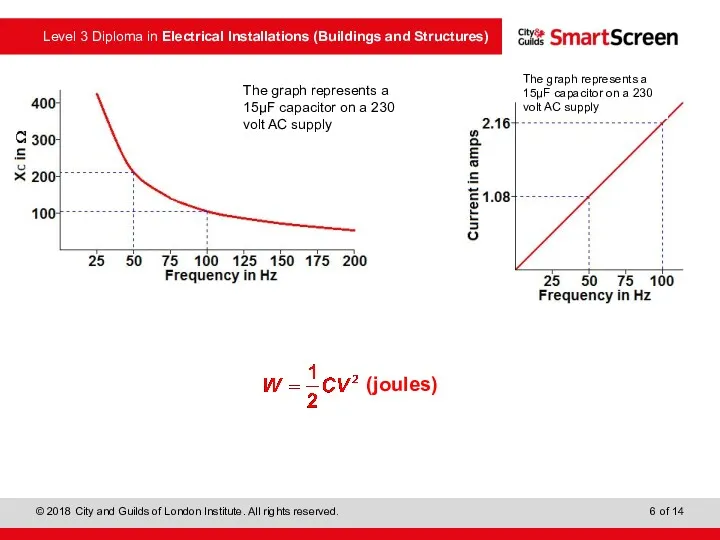
- 6. (joules)
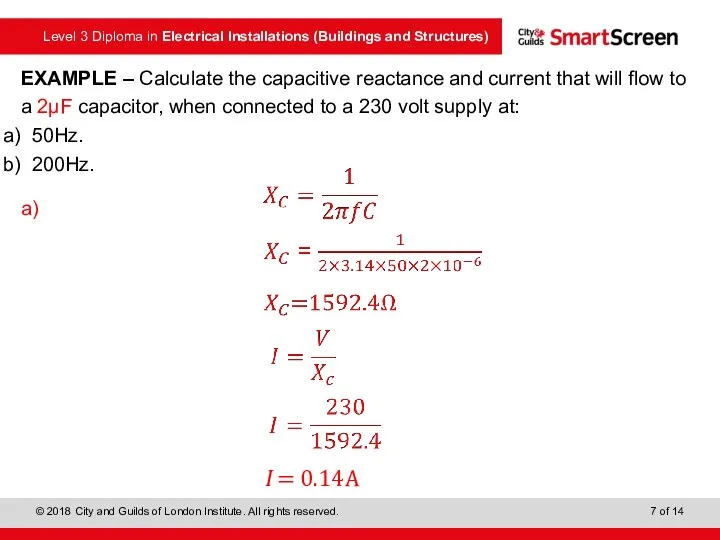
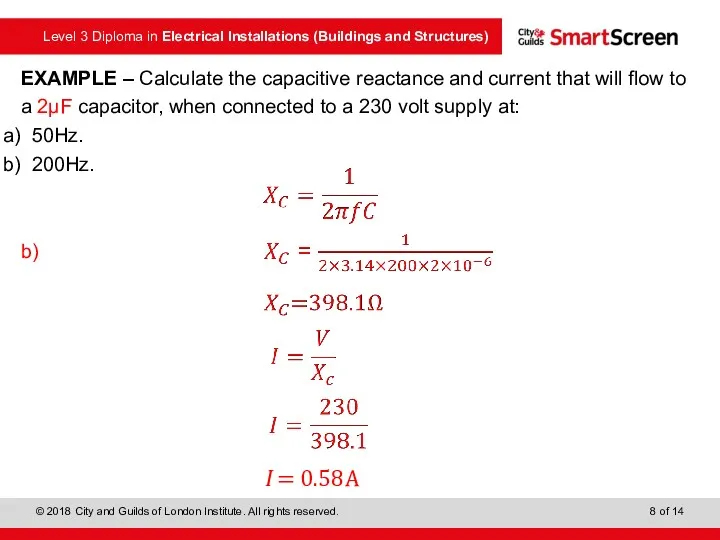
- 7. EXAMPLE – Calculate the capacitive reactance and current that will flow to a 2μF capacitor, when
- 8. EXAMPLE – Calculate the capacitive reactance and current that will flow to a 2μF capacitor, when
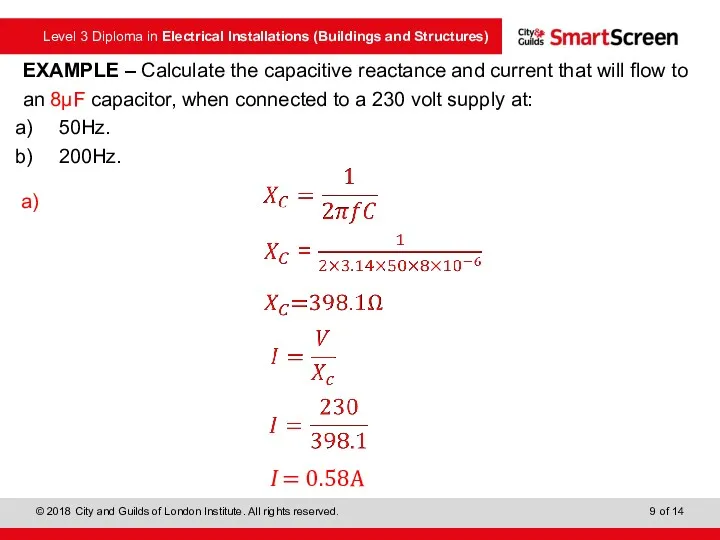
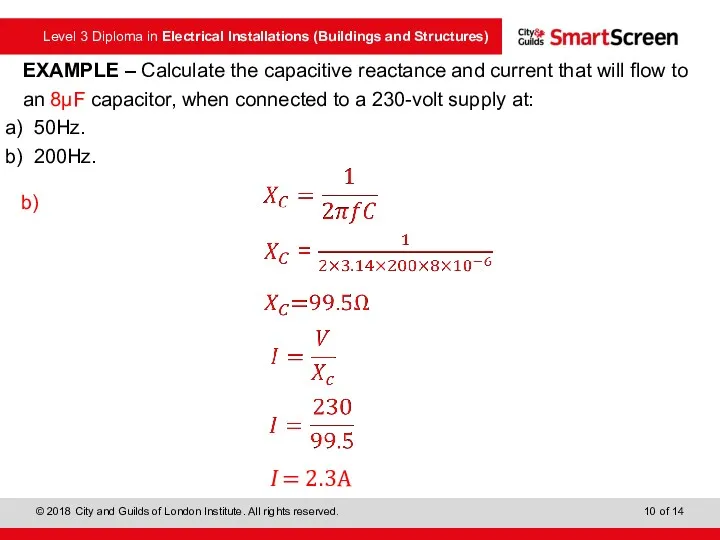
- 9. EXAMPLE – Calculate the capacitive reactance and current that will flow to an 8μF capacitor, when
- 10. EXAMPLE – Calculate the capacitive reactance and current that will flow to an 8μF capacitor, when
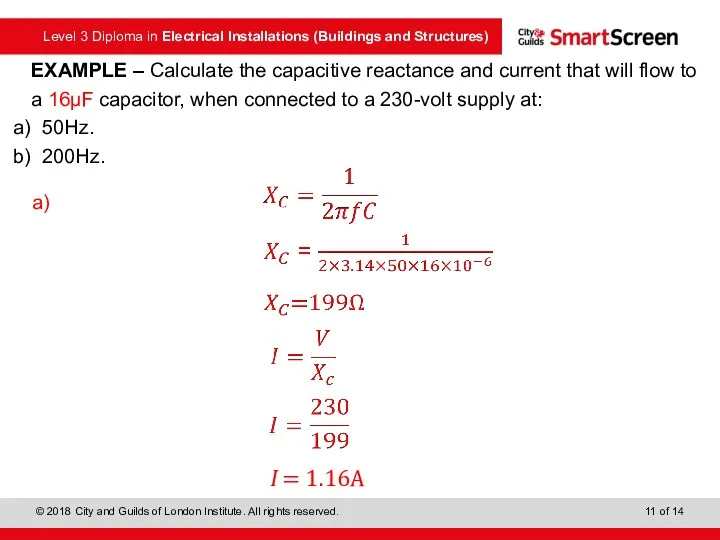
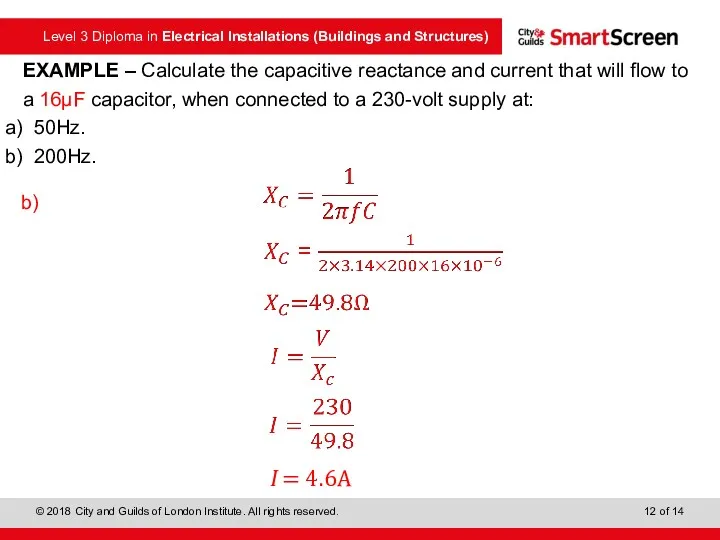
- 11. EXAMPLE – Calculate the capacitive reactance and current that will flow to a 16μF capacitor, when
- 12. EXAMPLE – Calculate the capacitive reactance and current that will flow to a 16μF capacitor, when
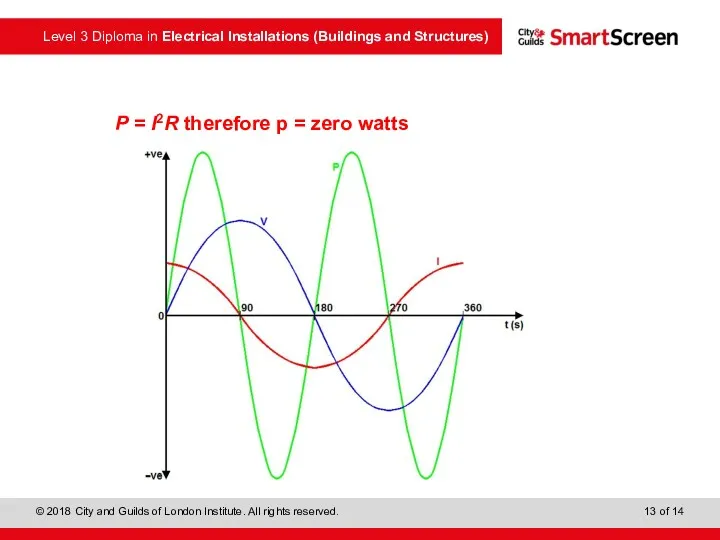
- 13. P = I2R therefore p = zero watts
- 15. Скачать презентацию
 Работа газа и пара при расширении
Работа газа и пара при расширении Энергия. Потенциальная и кинетическая энергия
Энергия. Потенциальная и кинетическая энергия Контур с током в магнитном поле
Контур с током в магнитном поле Восстановительный ремонт автомобилей CHERY
Восстановительный ремонт автомобилей CHERY Физбой. Интеллектуальная игра по физике
Физбой. Интеллектуальная игра по физике Инженерно-авиационное обеспечение безопасности полётов
Инженерно-авиационное обеспечение безопасности полётов Radiation safety training
Radiation safety training Теоретические основы преобразования энергии в тепловых двигателях
Теоретические основы преобразования энергии в тепловых двигателях Неравновесные носители заряда в полупроводниках
Неравновесные носители заряда в полупроводниках Законы отражения
Законы отражения Автотракторні двигуни. (Лекція 2)
Автотракторні двигуни. (Лекція 2) Выполнение судовых работ. Рулевые устройства
Выполнение судовых работ. Рулевые устройства Мир в магнитах. При поддержке туристической компании Колесница
Мир в магнитах. При поддержке туристической компании Колесница Типы моторов на машинках для стрижки волос. Их особенности, преимущества, недостатки
Типы моторов на машинках для стрижки волос. Их особенности, преимущества, недостатки Магнитное поле. Взаимодействие токов
Магнитное поле. Взаимодействие токов Свободное падение. (10 класс)
Свободное падение. (10 класс) Отчет по учебной практике. Радарный уровнемер Saab TankRadar RTG 3920
Отчет по учебной практике. Радарный уровнемер Saab TankRadar RTG 3920 Проектирование и производство изделий интегральной электроники. Фотолитография
Проектирование и производство изделий интегральной электроники. Фотолитография Проводники в электростатическом поле. Конденсаторы. Энергия электрического поля
Проводники в электростатическом поле. Конденсаторы. Энергия электрического поля Оборудование для ремонта рам, кузовов и кабин автомобилей
Оборудование для ремонта рам, кузовов и кабин автомобилей Электрическое напряжение. Единицы напряжения. Вольтметр. Измерение напряжения
Электрическое напряжение. Единицы напряжения. Вольтметр. Измерение напряжения Процесс сборки-сварки корпуса емкости дистиллятора Е-201
Процесс сборки-сварки корпуса емкости дистиллятора Е-201 Реактивное движение
Реактивное движение Действие магнитного поля на движущийся заряд
Действие магнитного поля на движущийся заряд Сферическое движение
Сферическое движение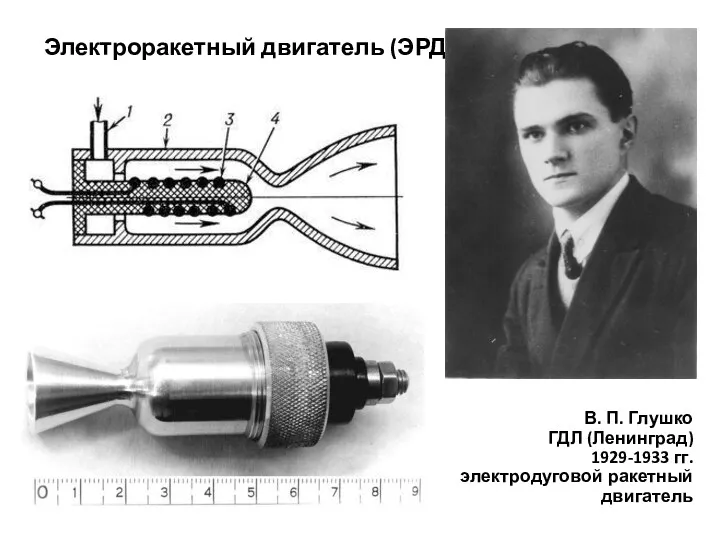 Ракетные двигатели
Ракетные двигатели Сила тока в различных участках параллельной цепи
Сила тока в различных участках параллельной цепи Статистический метод описания
Статистический метод описания