Содержание
- 2. A slow speed or medium speed Diesel engine is a high pressure propulsion plant with internal
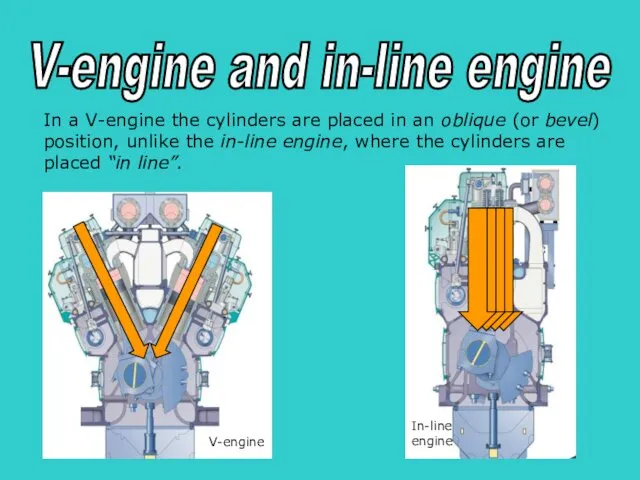
- 3. s V-engine and in-line engine In a V-engine the cylinders are placed in an oblique (or
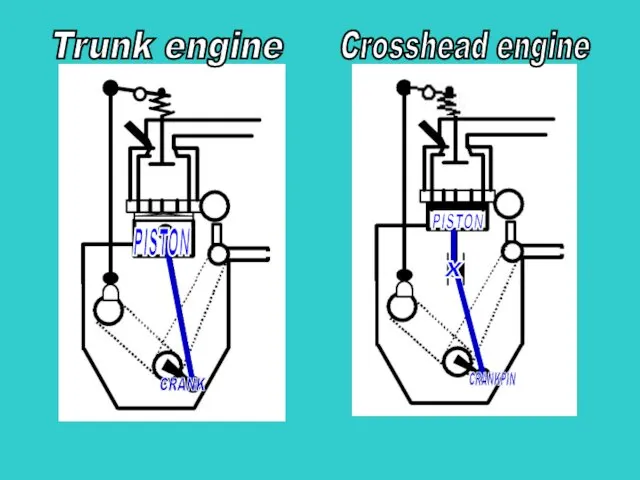
- 4. Trunk engine Crosshead engine PISTON CRANK S PISTON X CRANKPIN
- 5. s 2-stroke crosshead engine
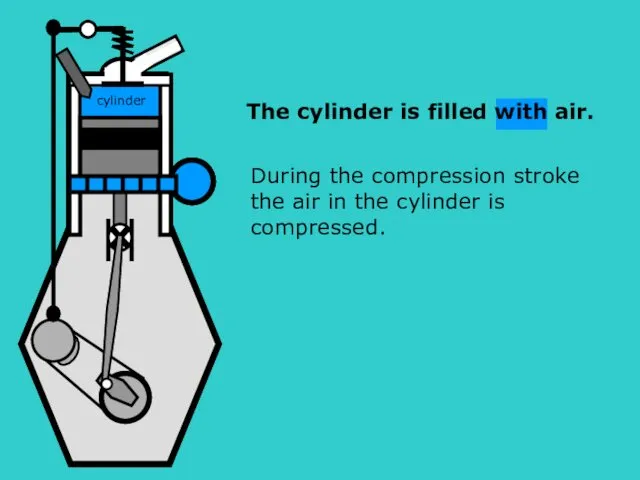
- 6. The cylinder is filled with air. S During the compression stroke the air in the cylinder
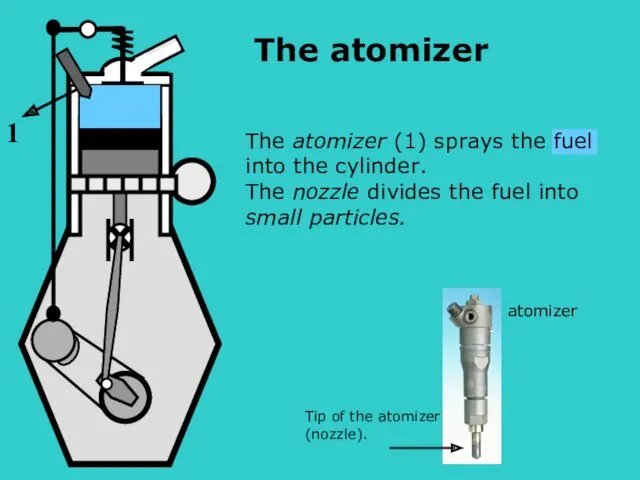
- 7. The atomizer (1) sprays the fuel into the cylinder. The nozzle divides the fuel into small
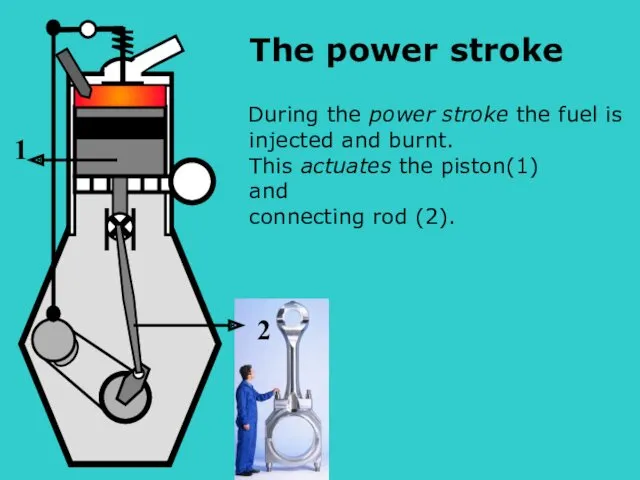
- 8. During the power stroke the fuel is injected and burnt. This actuates the piston(1) and connecting
- 9. The piston makes a reciprocating motion. Piston The piston
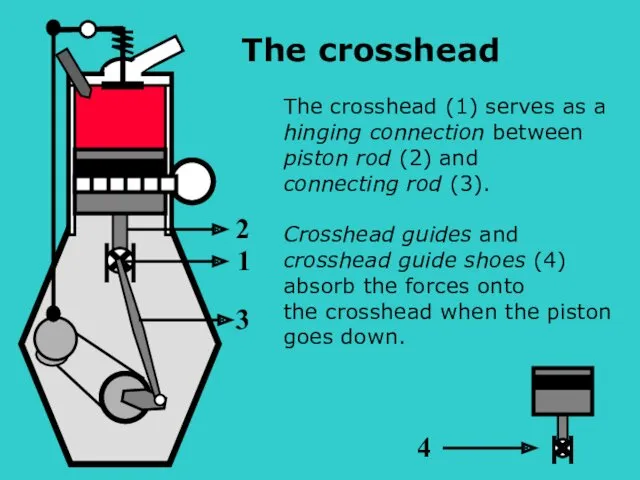
- 10. 1 2 3 The crosshead (1) serves as a hinging connection between piston rod (2) and
- 11. S 1 2 Crankshaft The crank (1)is connected to the crankshaft (2).
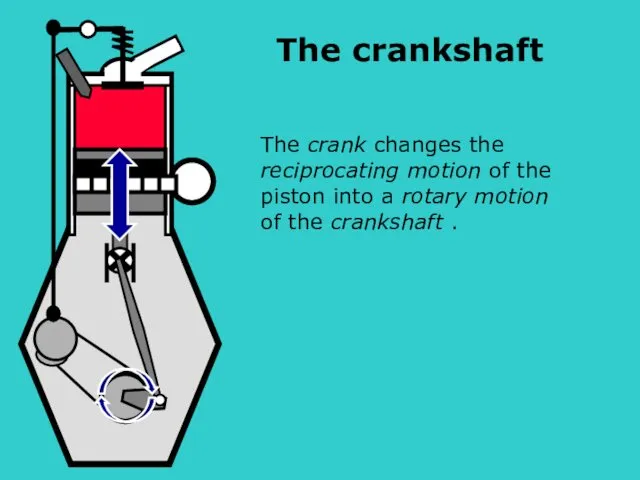
- 12. S The crank changes the reciprocating motion of the piston into a rotary motion of the
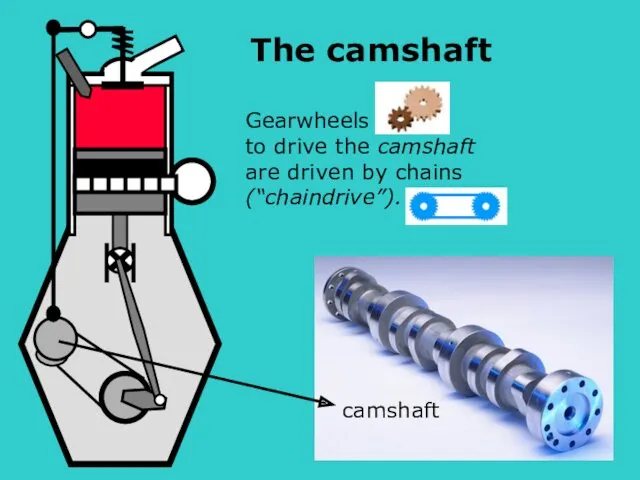
- 13. S Gearwheels to drive the camshaft are driven by chains (“chaindrive”). camshaft The camshaft
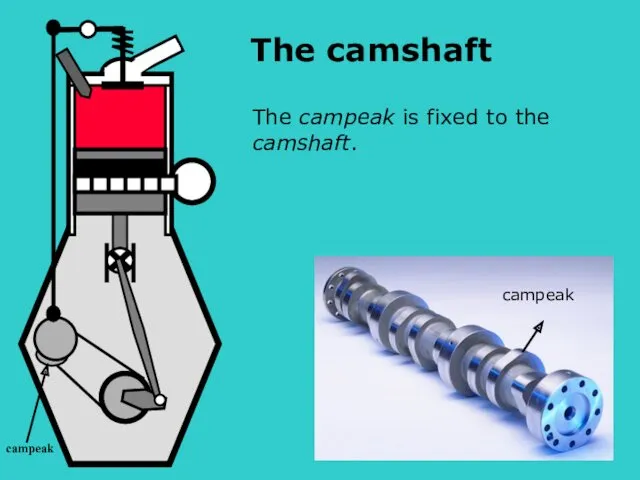
- 14. S The campeak is fixed to the camshaft. campeak campeak The camshaft
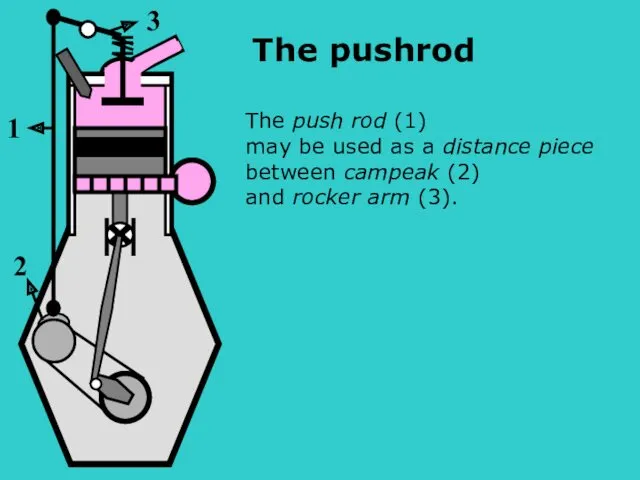
- 15. s The push rod (1) may be used as a distance piece between campeak (2) and
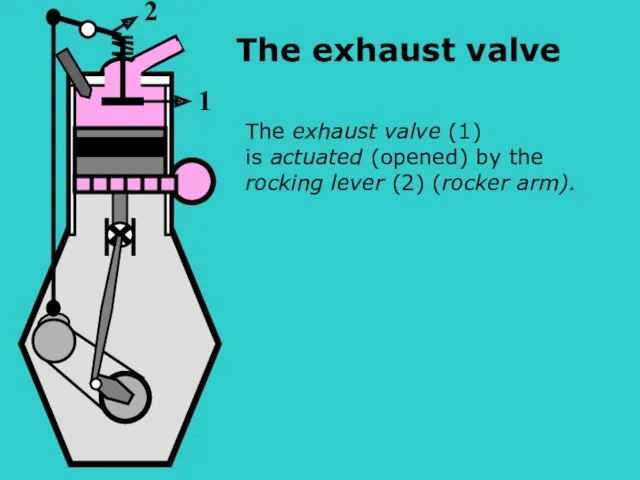
- 16. S The exhaust valve (1) is actuated (opened) by the rocking lever (2) (rocker arm). 2
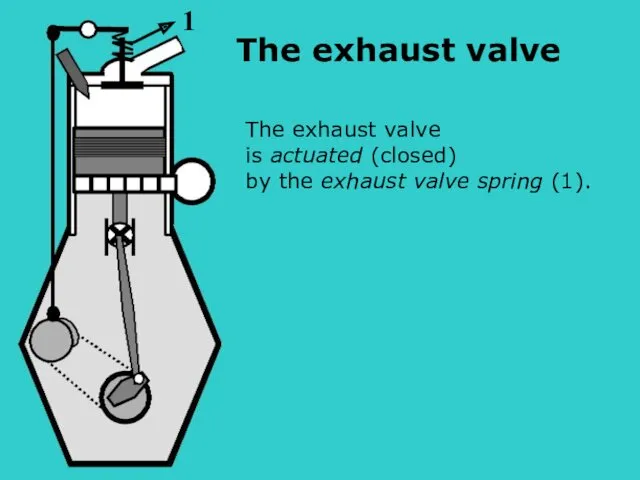
- 17. S The exhaust valve is actuated (closed) by the exhaust valve spring (1). 1 The exhaust
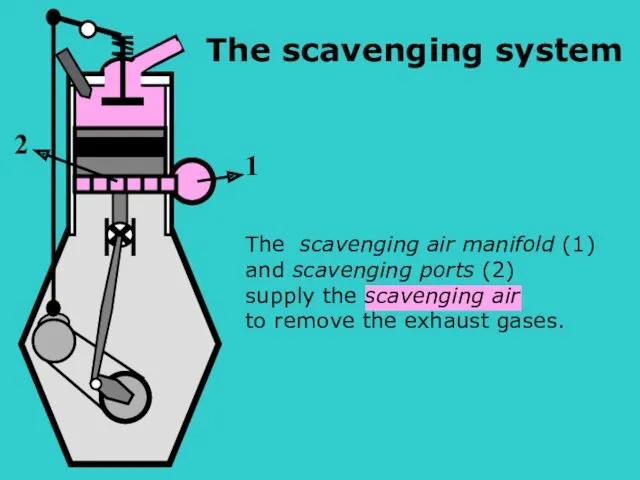
- 18. S The scavenging air manifold (1) and scavenging ports (2) supply the scavenging air to remove
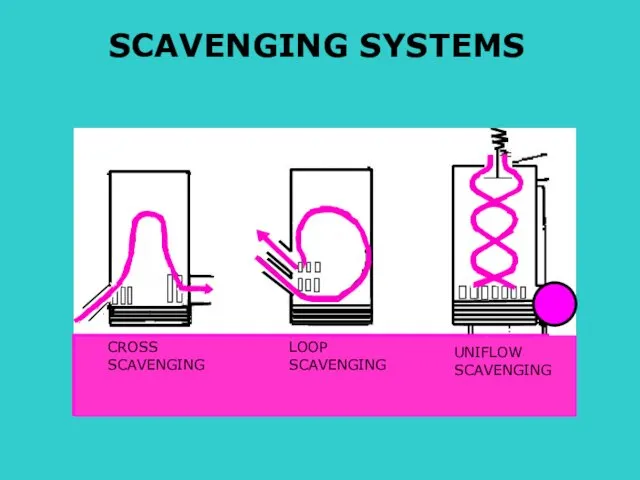
- 19. S CROSS SCAVENGING LOOP SCAVENGING UNIFLOW SCAVENGING
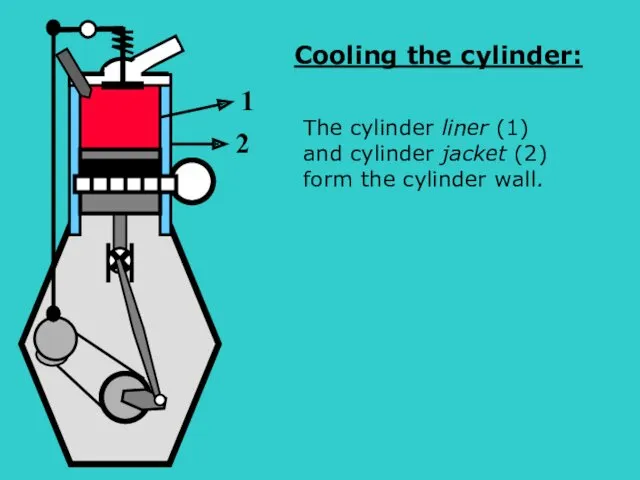
- 20. S The cylinder liner (1) and cylinder jacket (2) form the cylinder wall. 1 2 Cooling
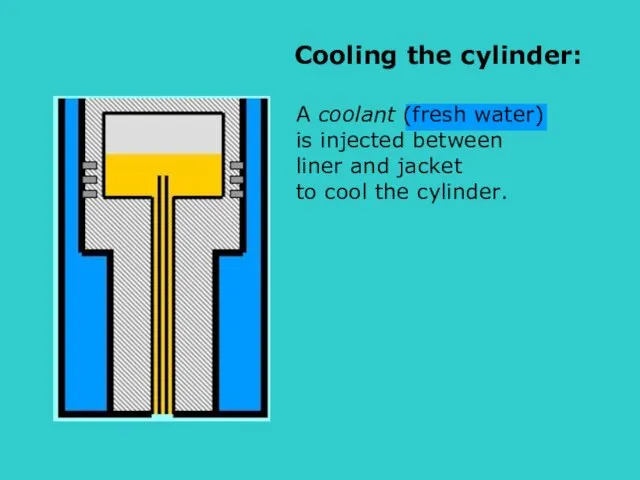
- 21. A coolant (fresh water) is injected between liner and jacket to cool the cylinder. s Cooling
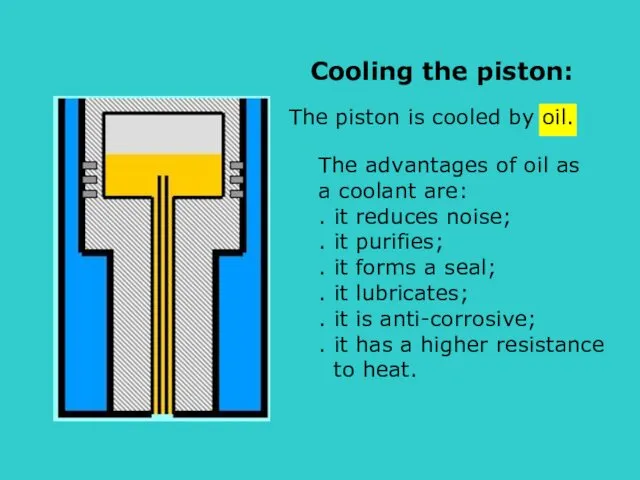
- 22. s Cooling the piston: The advantages of oil as a coolant are: . it reduces noise;
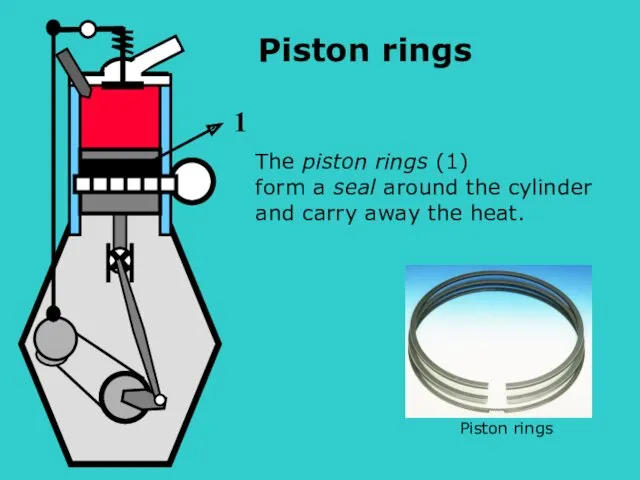
- 23. SO The piston rings (1) form a seal around the cylinder and carry away the heat.
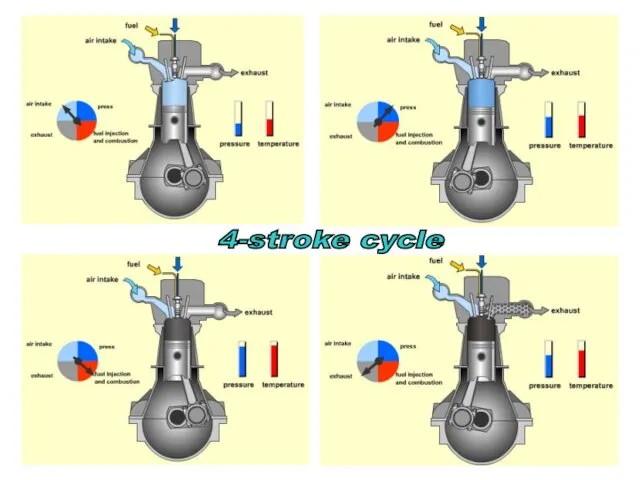
- 24. s 4-stroke cycle
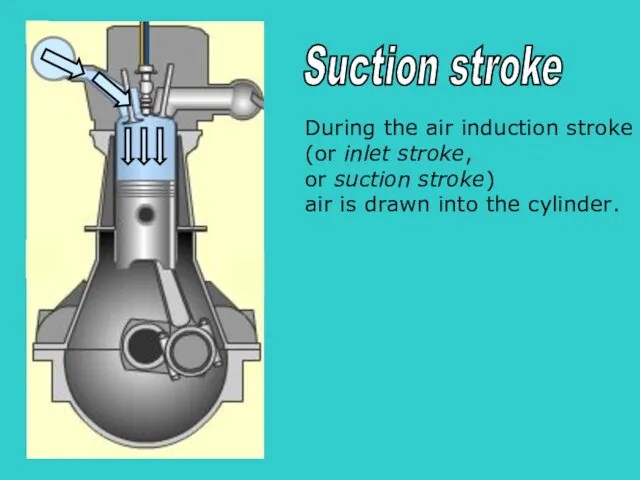
- 25. S During the air induction stroke (or inlet stroke, or suction stroke) air is drawn into
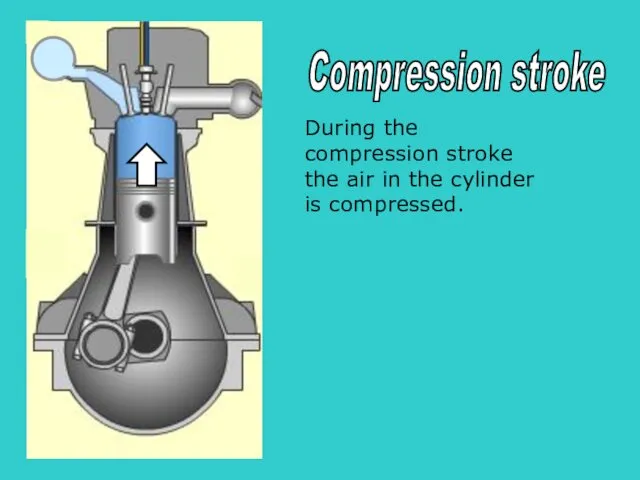
- 26. S During the compression stroke the air in the cylinder is compressed. Compression stroke
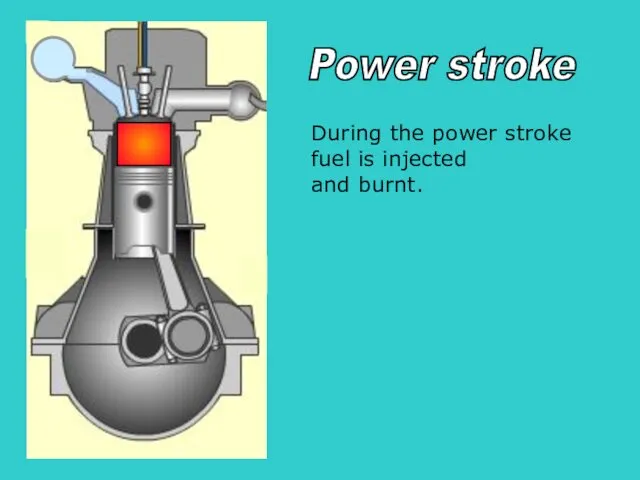
- 27. S During the power stroke fuel is injected and burnt. Power stroke
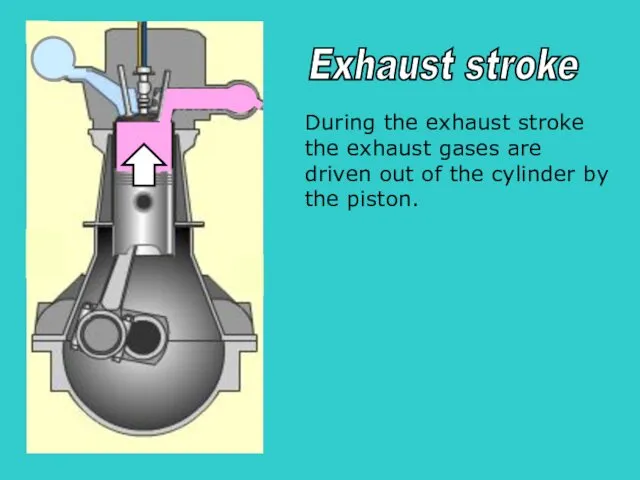
- 28. S During the exhaust stroke the exhaust gases are driven out of the cylinder by the
- 30. Скачать презентацию




 Молекулярно-кинетическая теория вещества
Молекулярно-кинетическая теория вещества Энергия и работа. Лекция 3
Энергия и работа. Лекция 3 Итоговый видео тест по курсу Физика-8
Итоговый видео тест по курсу Физика-8 Распространение колебаний в упругих средах. Продольные и поперечные волны
Распространение колебаний в упругих средах. Продольные и поперечные волны Transformer. What is it?
Transformer. What is it? Internal сombustion engine. The fuels and emissions control. Engine fuels
Internal сombustion engine. The fuels and emissions control. Engine fuels Телескоп
Телескоп Ворот. Лебёдка
Ворот. Лебёдка Закон сохранения импульса
Закон сохранения импульса Электромагнитная индукция. Явление электромагнитной индукции. Правило Ленца
Электромагнитная индукция. Явление электромагнитной индукции. Правило Ленца Жерсерік байланысын ұйымдастыру қағидасын түсіндіру
Жерсерік байланысын ұйымдастыру қағидасын түсіндіру Изображения и обозначение передач и их составных частей. (Лекция 5)
Изображения и обозначение передач и их составных частей. (Лекция 5) Искусственная радиоактивность
Искусственная радиоактивность Методы определения скорости света
Методы определения скорости света Соединения клеммовые, стяжными кольцами и конусные
Соединения клеммовые, стяжными кольцами и конусные Расчет силовых нагрузок на вал и построение эпюр изгибающих моментов и крутящего момента
Расчет силовых нагрузок на вал и построение эпюр изгибающих моментов и крутящего момента Материаловедение и технологии современных и перспективных материалов
Материаловедение и технологии современных и перспективных материалов Элементарные частицы
Элементарные частицы Лекция 4: Волновая оптика. Голография. Слоистые среды и фотонные кристаллы
Лекция 4: Волновая оптика. Голография. Слоистые среды и фотонные кристаллы Динамика вязкой жидкости
Динамика вязкой жидкости Сопла и диффузоры. Истечение жидкостей, паров и газов
Сопла и диффузоры. Истечение жидкостей, паров и газов Электрические явления. Уильям Гильберт. 8 класс
Электрические явления. Уильям Гильберт. 8 класс Интегрированный урок физики и французского языка Прогулки по Парижу (обощение мателиала по темам: плотность, масса, сила тяжести, вес, давление, Эйфелева башня - символ Парижа)
Интегрированный урок физики и французского языка Прогулки по Парижу (обощение мателиала по темам: плотность, масса, сила тяжести, вес, давление, Эйфелева башня - символ Парижа) Ремонт автомобилей. Ремонт корпусных деталей. (Тема 4.3)
Ремонт автомобилей. Ремонт корпусных деталей. (Тема 4.3) Припої. Загальні властивості
Припої. Загальні властивості Повітря і його функції
Повітря і його функції Презентация к уроку Закон всемирного тяготения
Презентация к уроку Закон всемирного тяготения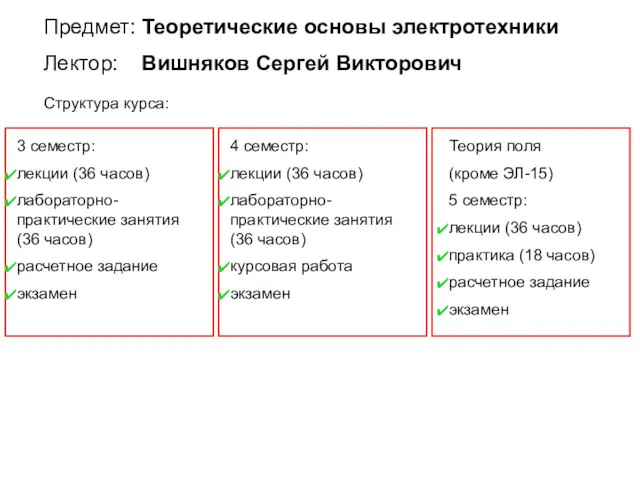 Теоретические основы электротехники
Теоретические основы электротехники