Содержание
- 2. Learning Objective After completing the module, the trainee will be able to … Explain drivetrain system
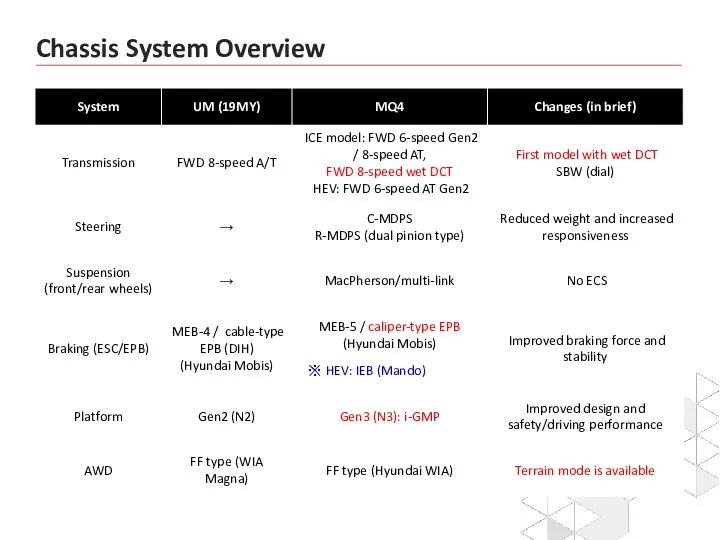
- 3. DL3 Transmission System Chassis System Overview
- 4. First Kia vehicle model with wet DCT (Engine: New R 2.2, Theta Ⅲ 2.5 T-GDI) First
- 5. 8 Speed DCT Lesson 1.
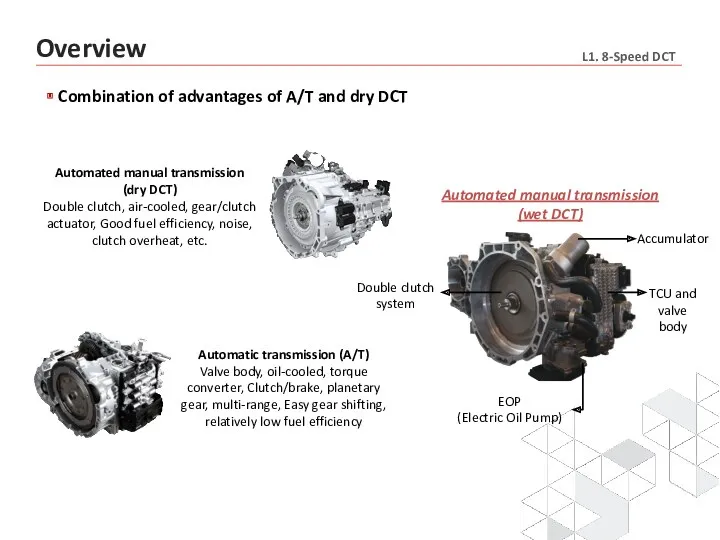
- 6. Combination of advantages of A/T and dry DCT Overview Automatic transmission (A/T) Valve body, oil-cooled, torque
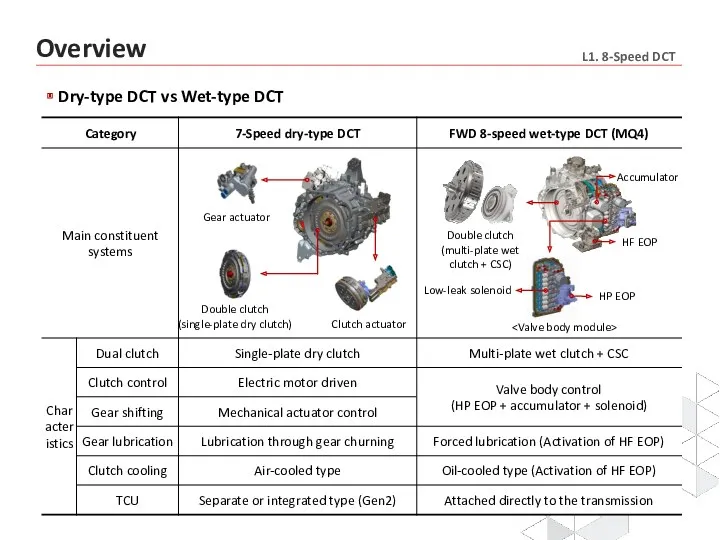
- 7. Dry-type DCT vs Wet-type DCT Gear actuator Double clutch (single-plate dry clutch) Clutch actuator Double clutch
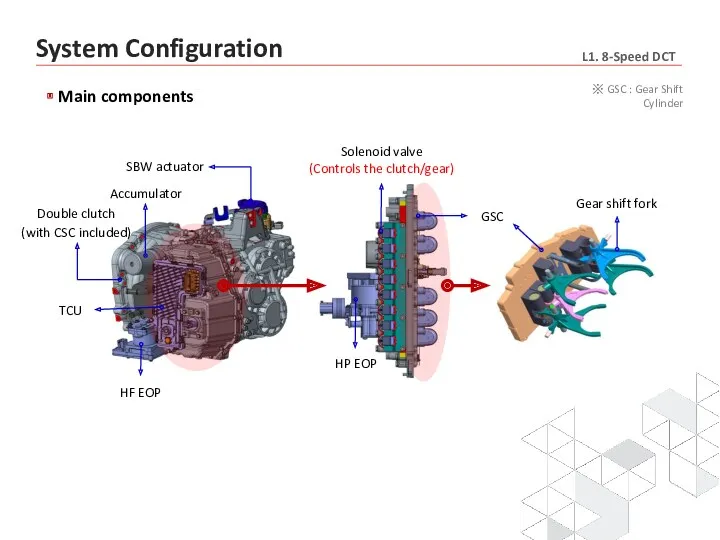
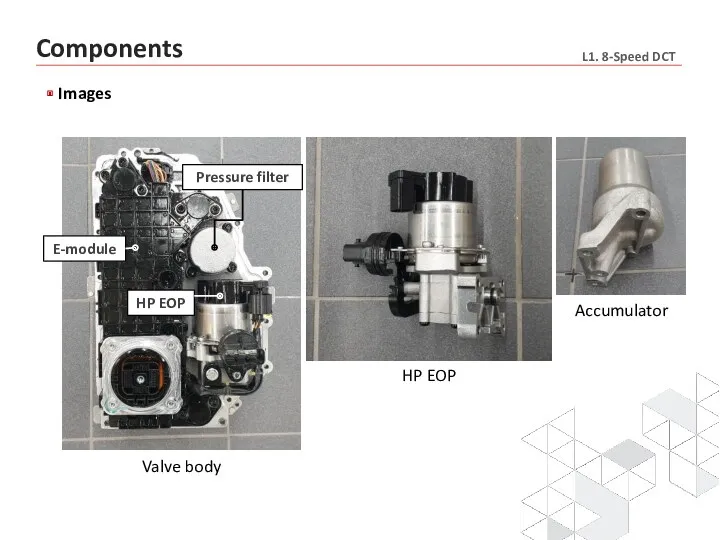
- 8. Main components Double clutch (with CSC included) SBW actuator Accumulator HF EOP HP EOP Solenoid valve
- 9. Wet double clutch - Multi-plate control through CSC control by hydraulic pressure Control oil feed hole
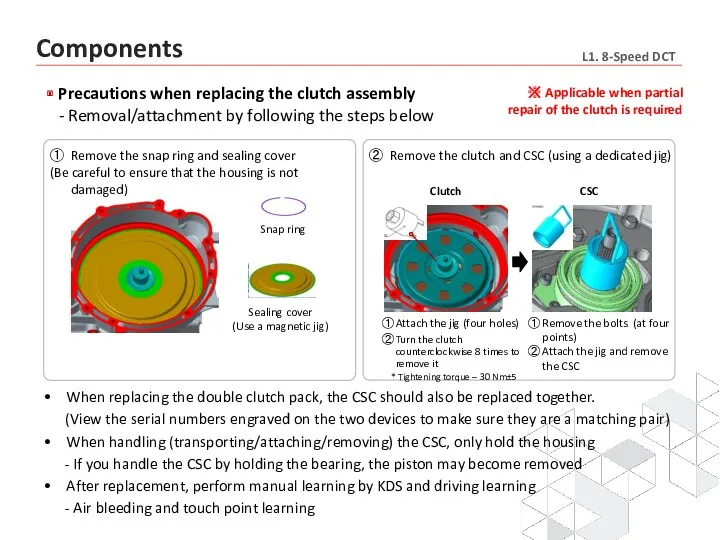
- 10. Precautions when replacing the clutch assembly - Removal/attachment by following the steps below ① Remove the
- 11. Hydraulic System and E-Module Components: Oil pressure sensor (x3), oil temperature sensor (x1), solenoid valve (x8),
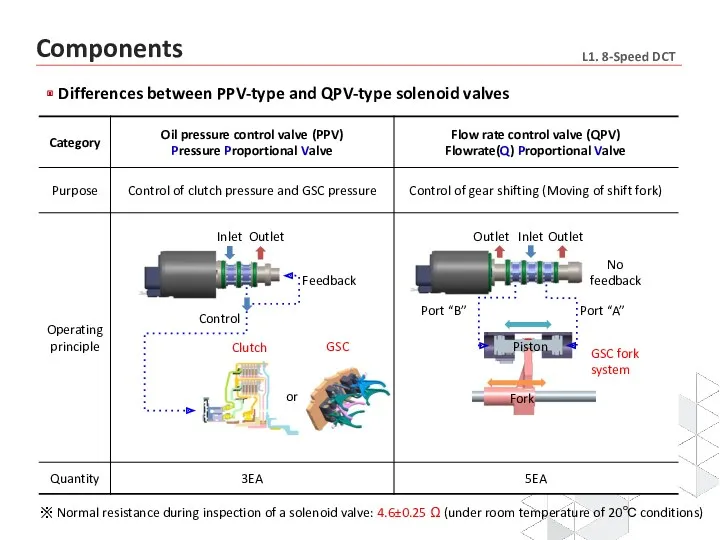
- 12. Differences between PPV-type and QPV-type solenoid valves Inlet Outlet Control Feedback Clutch Port “A” Port “B”
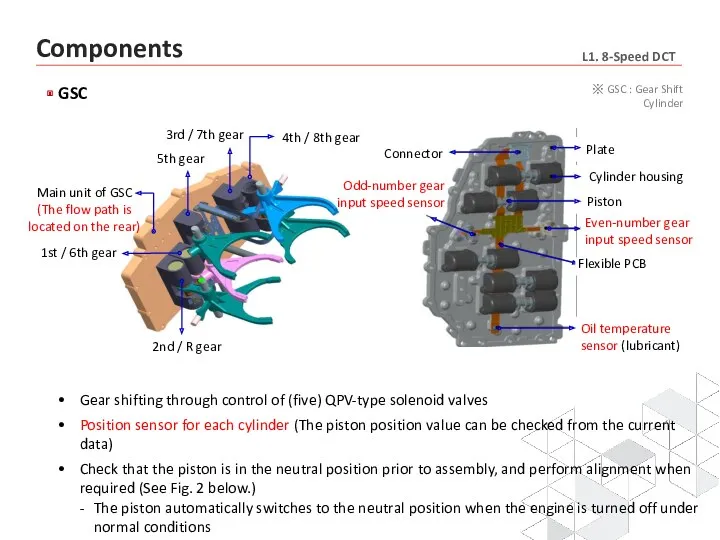
- 13. Gear shifting through control of (five) QPV-type solenoid valves Position sensor for each cylinder (The piston
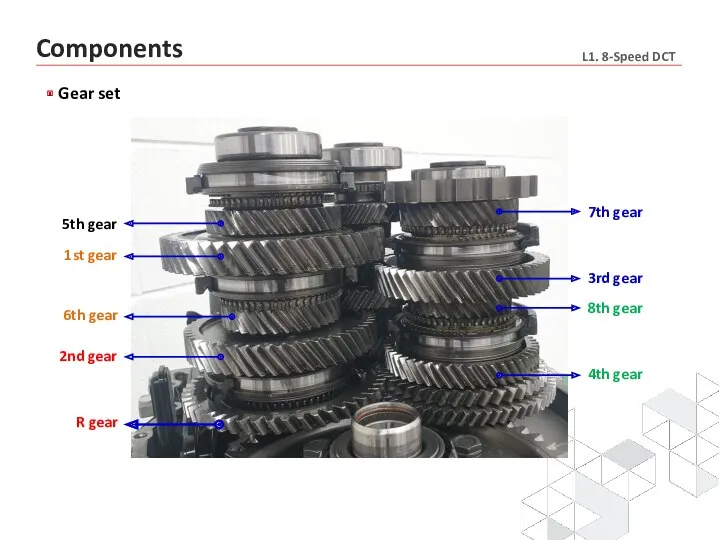
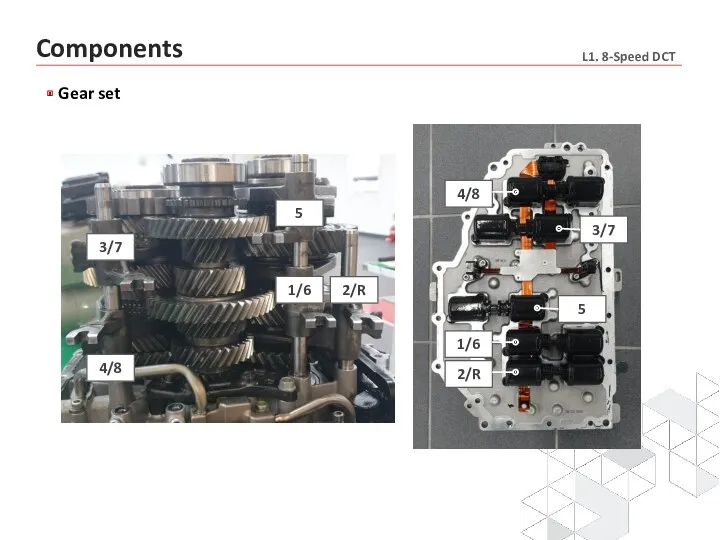
- 14. Components Gear set
- 15. Gear set 2/R 1/6 5 4/8 3/7 2/R 1/6 5 3/7 4/8 Components
- 16. ※ EOP: Electric Oil Pump EOP (x2) - EOP operates to supply necessary oil pressure and
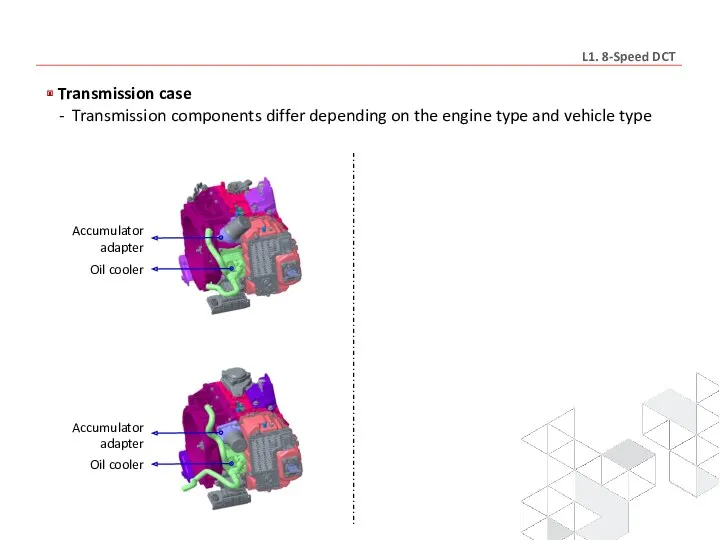
- 17. Transmission case - Transmission components differ depending on the engine type and vehicle type Control oil
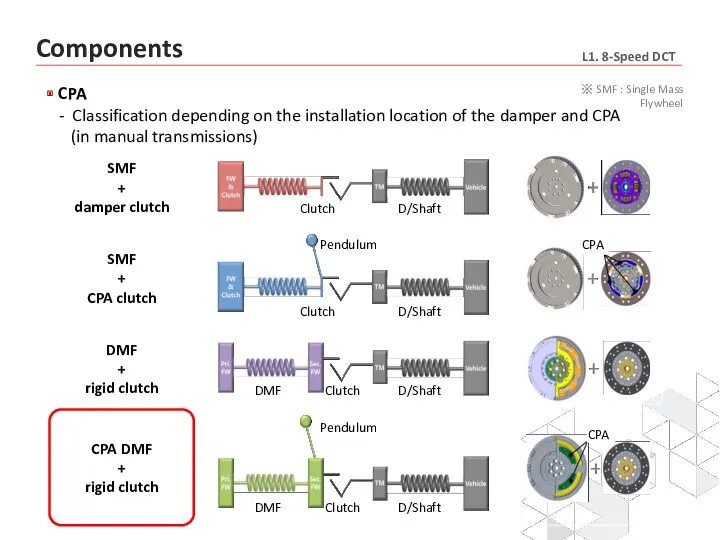
- 18. CPA - Reduces engine vibrations and booming CPA is installed on the torque converter damper clutch
- 19. CPA - Classification depending on the installation location of the damper and CPA (in manual transmissions)
- 20. Multi-plate wet clutch pack Odd gears Even gears Lubricant feed hole Control oil feed hole (left:
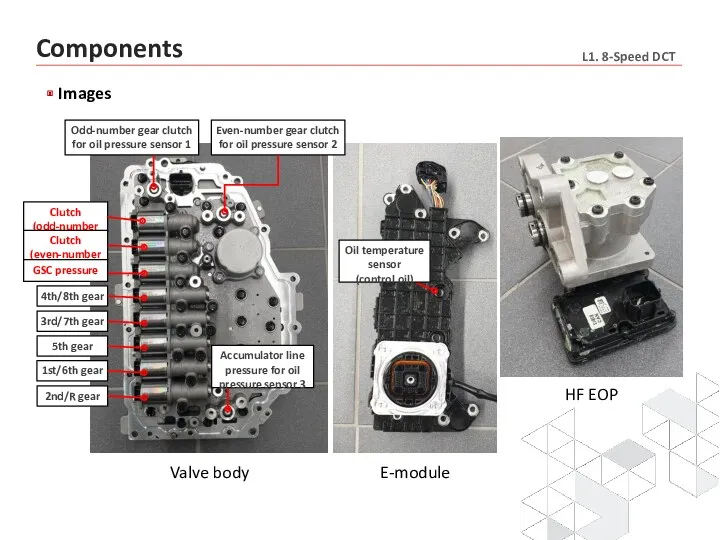
- 21. Components Images
- 22. Valve body E-module Odd-number gear clutch for oil pressure sensor 1 Even-number gear clutch for oil
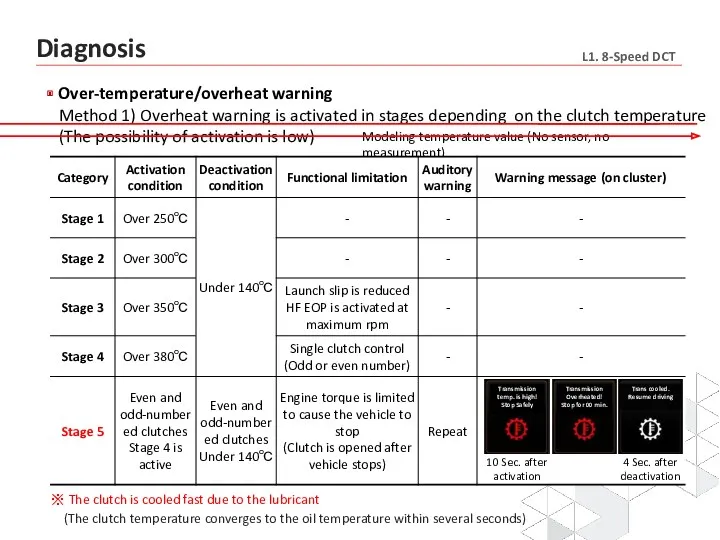
- 23. Over-temperature/overheat warning Method 1) Overheat warning is activated in stages depending on the clutch temperature (The
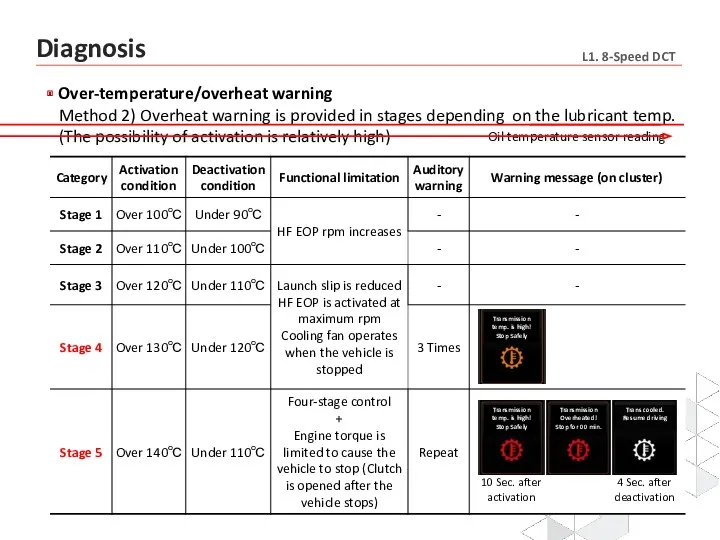
- 24. Over-temperature/overheat warning Method 2) Overheat warning is provided in stages depending on the lubricant temp. (The
- 25. TCU DTC (OBD1) – 1 *OBD1(Electrical fault) / OBD2(Mechanical fault) Diagnosis See the slide note!!
- 26. TCU DTC (OBD1) - 2 Diagnosis See the slide note!!
- 27. TCU DTC (OBD1) - 3 Diagnosis See the slide note!!
- 28. TCU DTC (OBD2) Diagnosis See the slide note!!
- 29. SBW Lesson 2.
- 30. Types and characteristics of shifters Shifters are classified largely as the SBC type and SBW type,
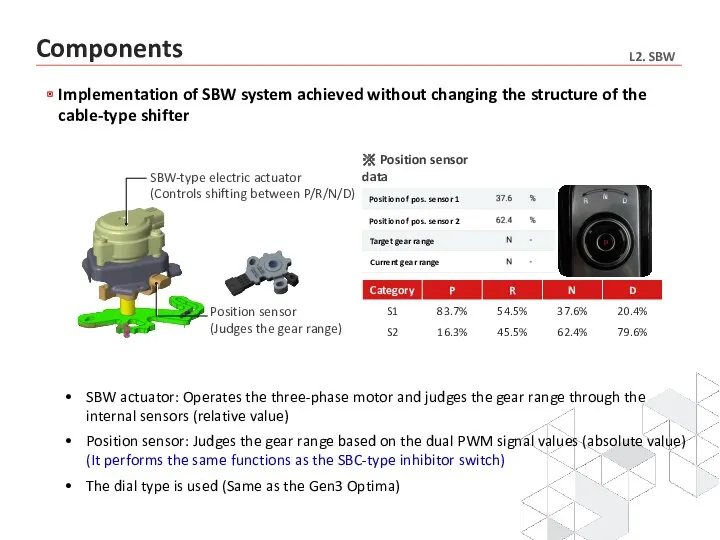
- 31. SBW actuator: Operates the three-phase motor and judges the gear range through the internal sensors (relative
- 32. Neutral Staying Mode - Keeps the power in “ACC” position and gear in “N” position while
- 33. Failsafe - Allows the vehicle to continue to run even when there is a failure in
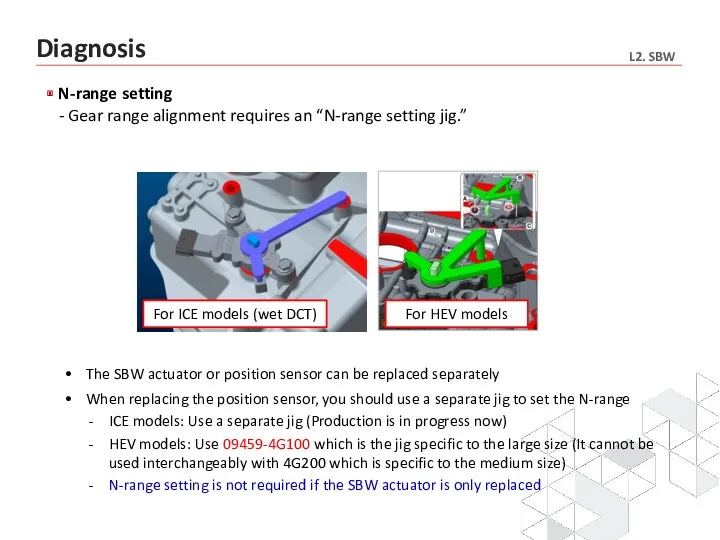
- 34. N-range setting - Gear range alignment requires an “N-range setting jig.” The SBW actuator or position
- 35. AWD Lesson 3.
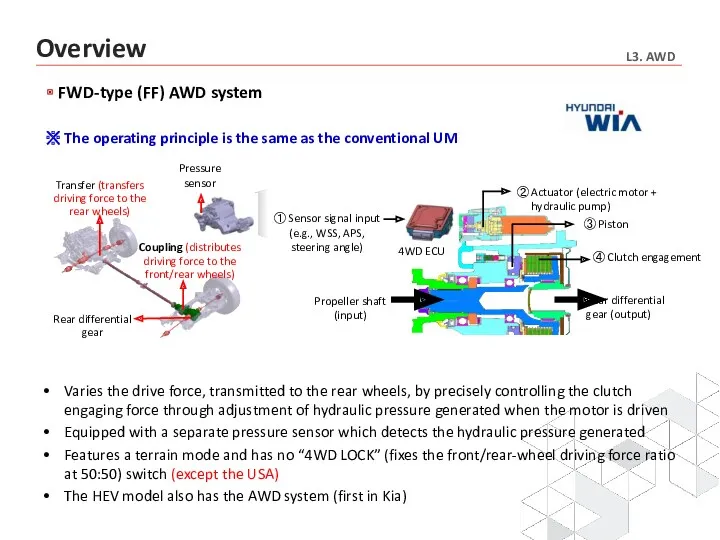
- 36. FWD-type (FF) AWD system Transfer (transfers driving force to the rear wheels) ※ The operating principle
- 38. Скачать презентацию
















 Шпоночные соединения. (Лекция 12)
Шпоночные соединения. (Лекция 12) Конденсированное состояние вещества
Конденсированное состояние вещества Игра Хочу всё знать!
Игра Хочу всё знать! Гидродинамика
Гидродинамика Cила тертя
Cила тертя Когда изобрели велосипед
Когда изобрели велосипед Интеллектуальная игра Физбой
Интеллектуальная игра Физбой Организация ТО и текущего ремонта легкового автомобиля Ford-escort 1.8 16V
Организация ТО и текущего ремонта легкового автомобиля Ford-escort 1.8 16V Пример использования метода преобразования сложнозамкнутых электрических сетей
Пример использования метода преобразования сложнозамкнутых электрических сетей Система впрыска VAG
Система впрыска VAG Презентация к уроку Криволинейное движение
Презентация к уроку Криволинейное движение Основы теплоэнергетики
Основы теплоэнергетики Техника безопасности при работе с электрическим током. Проблемы энергосбережения
Техника безопасности при работе с электрическим током. Проблемы энергосбережения Измерение аберраций оптических систем
Измерение аберраций оптических систем Сущность и назначение операции опиливания
Сущность и назначение операции опиливания Контрольная работа по теме Механическое движение. Взаимодействие тел
Контрольная работа по теме Механическое движение. Взаимодействие тел Семинарское занятие по теме основы электростатики, 10 класс
Семинарское занятие по теме основы электростатики, 10 класс Определение стоимости и расхода электроэнергии
Определение стоимости и расхода электроэнергии Масса тела
Масса тела Спектры и спектральные аппараты
Спектры и спектральные аппараты Автоматика и управление. Тема 3. Временные характеристики ЛСС. Лекция 3. Типовые входные сигналы
Автоматика и управление. Тема 3. Временные характеристики ЛСС. Лекция 3. Типовые входные сигналы Трехфазные цепи при соединении электроприемников звездой
Трехфазные цепи при соединении электроприемников звездой Система EDS (Elektronische Differentialsperre) для автомобилей
Система EDS (Elektronische Differentialsperre) для автомобилей Проектирование нанотехнологий
Проектирование нанотехнологий Электростатика
Электростатика ЛЕКЦИЯ-БЕСЕДА С ОБРАТНОЙ СВЯЗЬЮ В 10 КЛАССЕ ПО ТЕМЕ: ЭНЕРГИЯ - ВЗГЛЯД В БУДУЩЕЕ
ЛЕКЦИЯ-БЕСЕДА С ОБРАТНОЙ СВЯЗЬЮ В 10 КЛАССЕ ПО ТЕМЕ: ЭНЕРГИЯ - ВЗГЛЯД В БУДУЩЕЕ Естественное и искусственное освещение
Естественное и искусственное освещение Контроль параметрів радіовипромінювання. Радіоперешкоди
Контроль параметрів радіовипромінювання. Радіоперешкоди