Содержание
- 2. SIW plan : Smart-мақсат Lecture :Heterogeneous catalysis The basic concept of heterogeneous catalysis Adsorption theory of
- 3. Интерактивті тақта арқылы студенттерге гетерогенді катализ және оның механизмі мен себептері жайында түсіндіру, нақты жағдаяттарға пікірталас
- 4. PLAN: The basic concept of heterogeneous catalysis Adsorption theory of heterogeneous catalysis Stages of heterogeneous catalysis
- 5. Catalysis
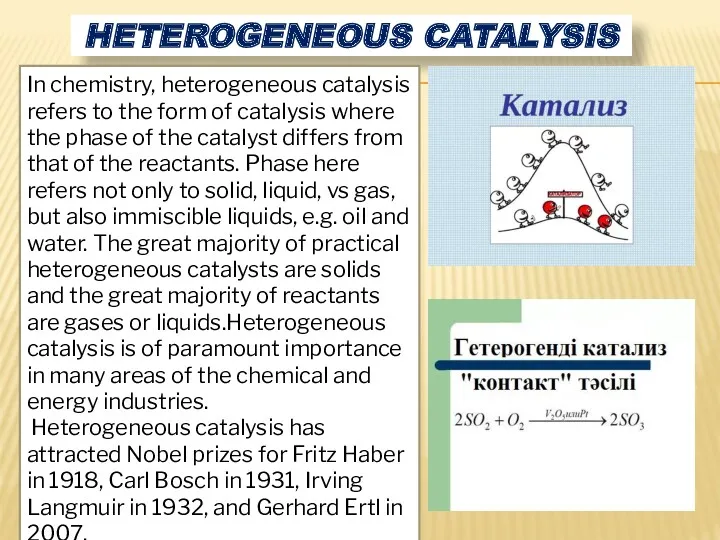
- 6. HETEROGENEOUS CATALYSIS In chemistry, heterogeneous catalysis refers to the form of catalysis where the phase of
- 7. Describes the catalytic processes that occur at the interface of the solid phase (catalyst) and the
- 8. Stages of heterogeneous catalysis
- 9. Reactive molecules diffuse to the surface of a solid. Diffusion Diffusion of ethylene and hydrogen molecules
- 10. The reacting molecules are first adsorbed physically, then enter into chemical reactions with active surface centers
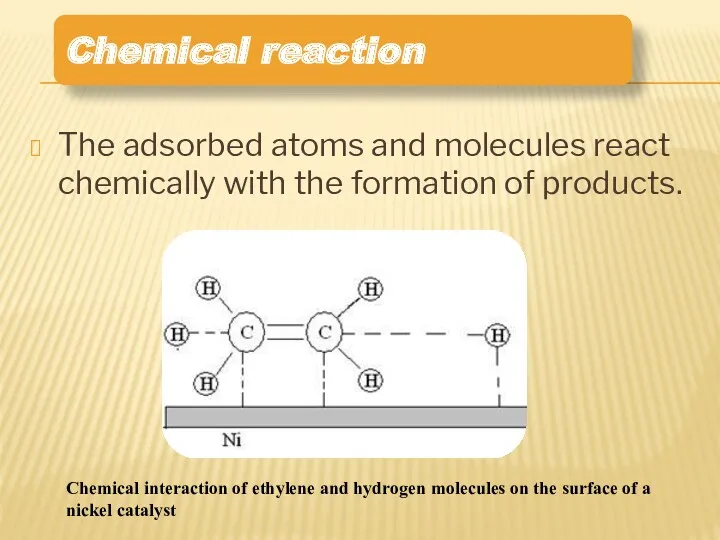
- 11. The adsorbed atoms and molecules react chemically with the formation of products. Chemical reaction Chemical interaction
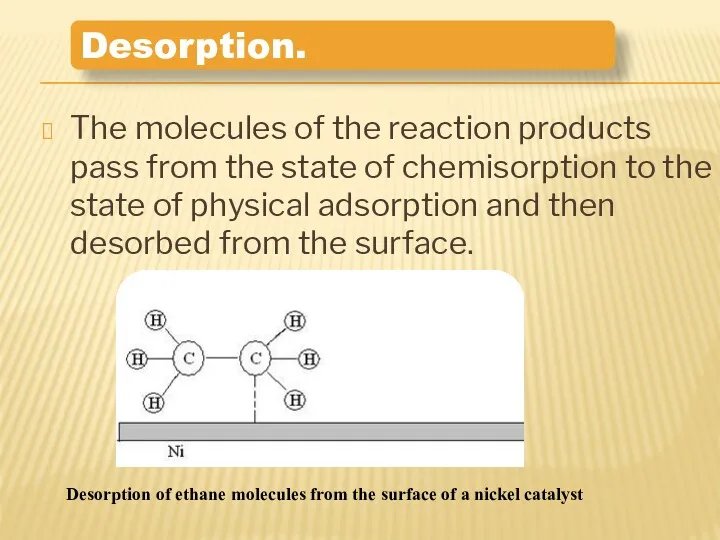
- 12. The molecules of the reaction products pass from the state of chemisorption to the state of
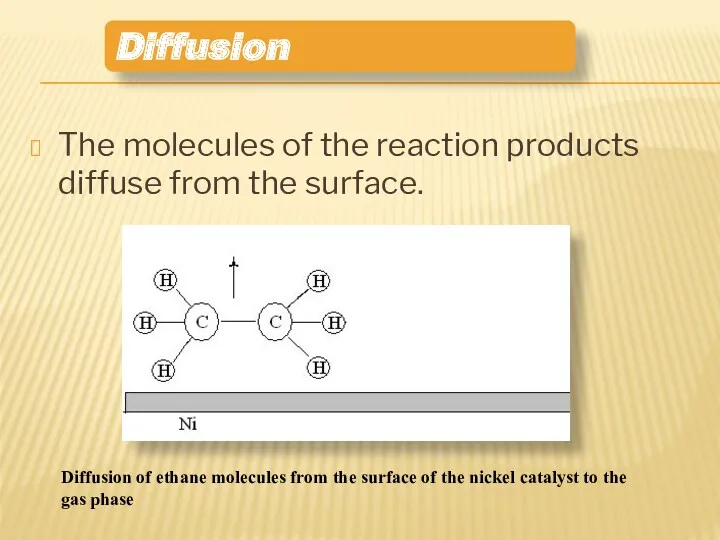
- 13. The molecules of the reaction products diffuse from the surface. Diffusion Diffusion of ethane molecules from
- 15. 10% Explanation show Analysis Summary Chart
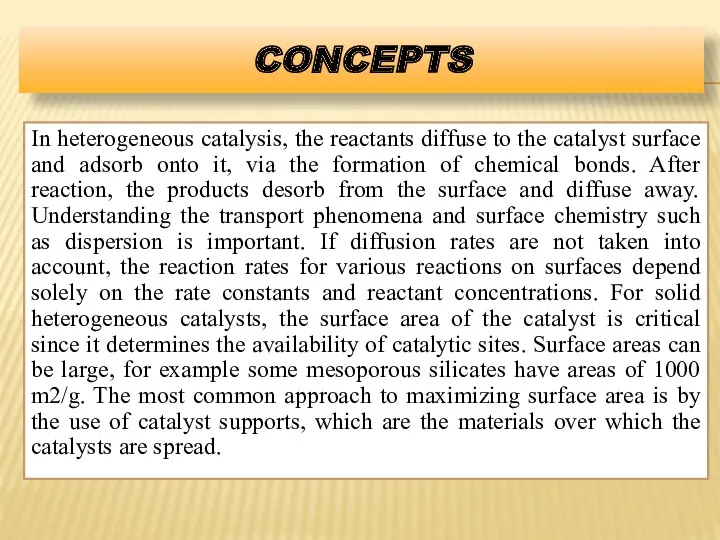
- 16. CONCEPTS In heterogeneous catalysis, the reactants diffuse to the catalyst surface and adsorb onto it, via
- 18. Скачать презентацию







 Кран машиниста поезда, с дистанционным управлением №130
Кран машиниста поезда, с дистанционным управлением №130 Правило буравчика, правило правой руки
Правило буравчика, правило правой руки Взаимодействие света с веществом. Лекция №8
Взаимодействие света с веществом. Лекция №8 Соединения с натягом
Соединения с натягом Постоянный ток. Занятие 1
Постоянный ток. Занятие 1 Механические колебания
Механические колебания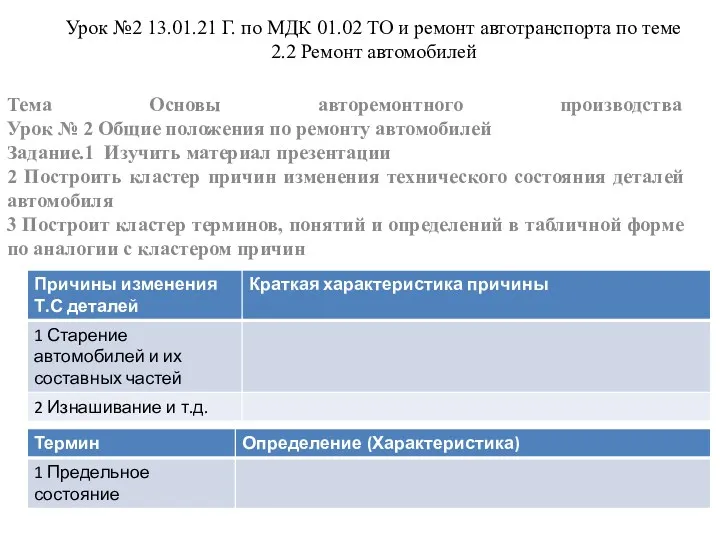 Ремонт автомобилей
Ремонт автомобилей Композиты - древний материал будущего
Композиты - древний материал будущего Устройство карбюраторных двигателей
Устройство карбюраторных двигателей Базирование по отверстиям под стыковые болты
Базирование по отверстиям под стыковые болты Основные положения молекулярно-кинетической теории. Размеры молекул
Основные положения молекулярно-кинетической теории. Размеры молекул Механическое движение
Механическое движение Статика. Виды равновесия. Равновесие тел имеющих площадь опоры. Законы равновесия. (10 класс)
Статика. Виды равновесия. Равновесие тел имеющих площадь опоры. Законы равновесия. (10 класс) Построение изображений, даваемых линзой (9 класс)
Построение изображений, даваемых линзой (9 класс) Задача силового анализа действующих на механизм
Задача силового анализа действующих на механизм Электричество. Цепи постоянного тока. Черные и серые ящики. Задачи региональных этапов
Электричество. Цепи постоянного тока. Черные и серые ящики. Задачи региональных этапов Electrical Charges
Electrical Charges Электромагнитные волны. Электромагнитное поле как особый вид материи
Электромагнитные волны. Электромагнитное поле как особый вид материи Определение массы Земли
Определение массы Земли Проект станции технического обслуживания автомобилей газель в г. Стерлитамак
Проект станции технического обслуживания автомобилей газель в г. Стерлитамак Излучение и спектры
Излучение и спектры Плотность вещества
Плотность вещества Давление твёрдых тел
Давление твёрдых тел Діелектрики та провідники в електростатичному полі
Діелектрики та провідники в електростатичному полі Презентация Зимние виды спорта
Презентация Зимние виды спорта Поршеньді компрессорларды жөндеу
Поршеньді компрессорларды жөндеу Растяжение и сжатие
Растяжение и сжатие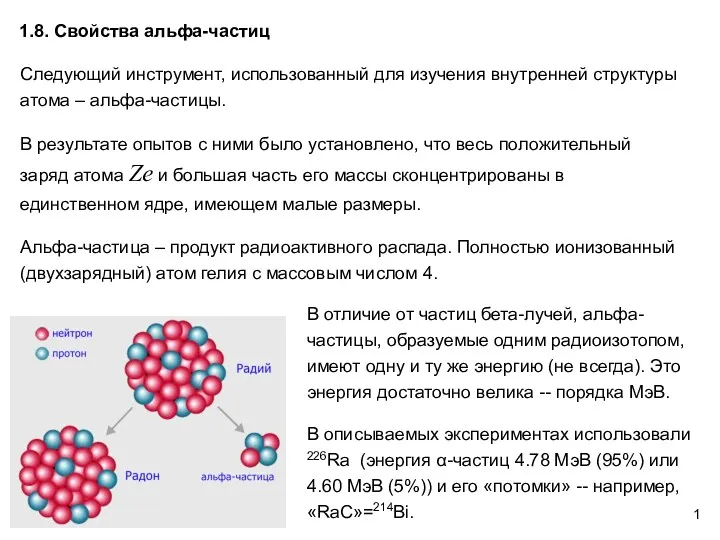 Свойства альфа-частиц. АФ1.8
Свойства альфа-частиц. АФ1.8