Содержание
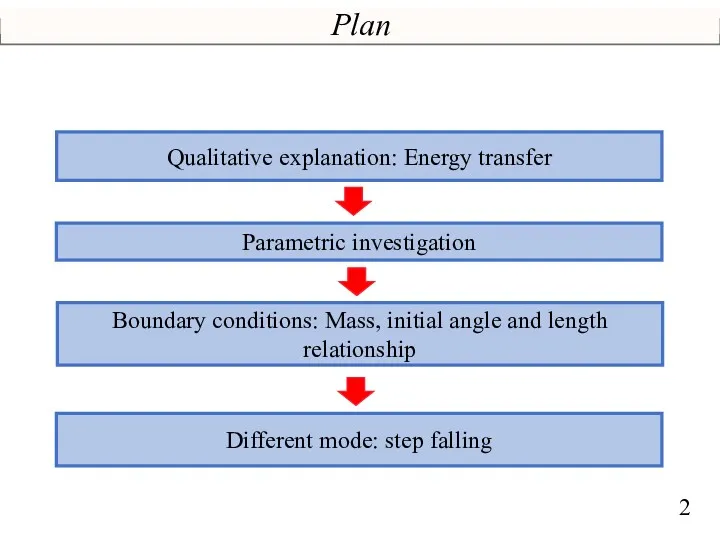
- 2. Plan Qualitative explanation: Energy transfer Boundary conditions: Mass, initial angle and length relationship Parametric investigation Different
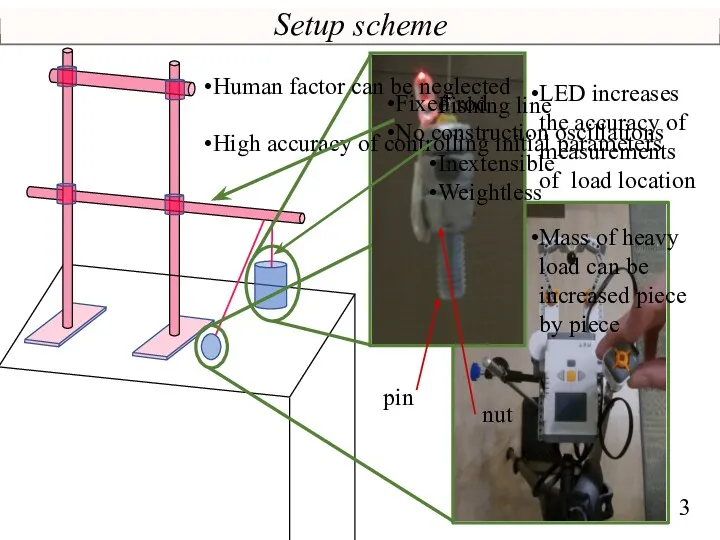
- 3. Setup scheme LED increases the accuracy of measurements of load location Mass of heavy load can
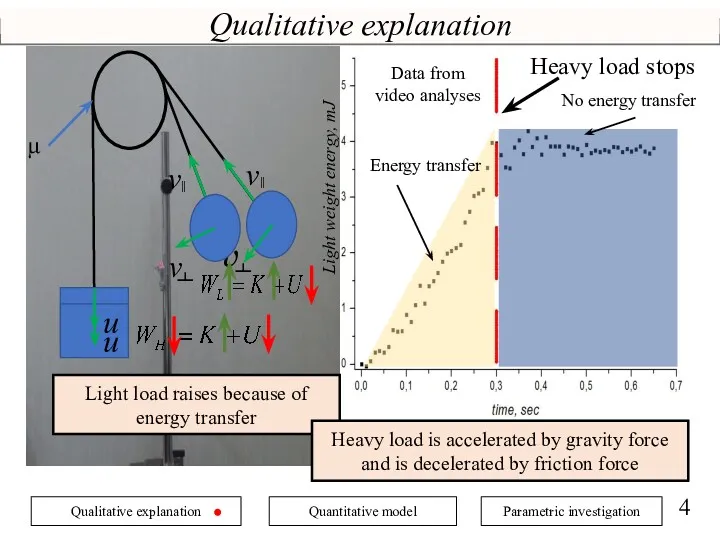
- 4. Qualitative explanation v ˫ μ Light load raises because of energy transfer Heavy load is accelerated
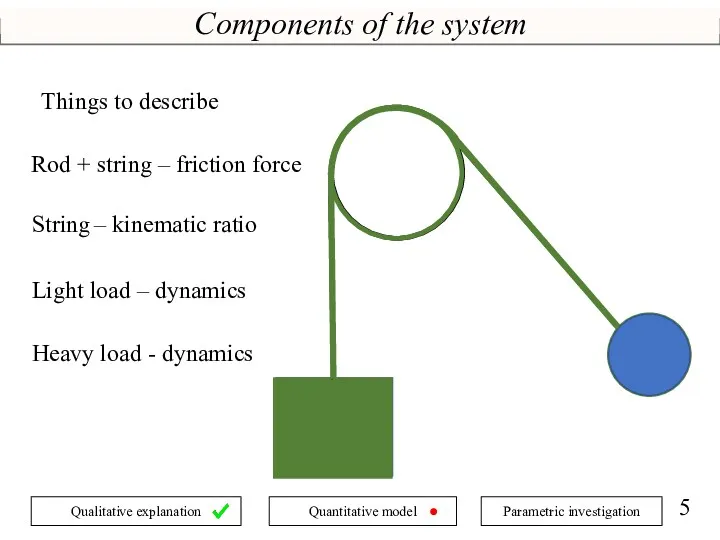
- 5. Components of the system Rod + string – friction force String – kinematic ratio Light load
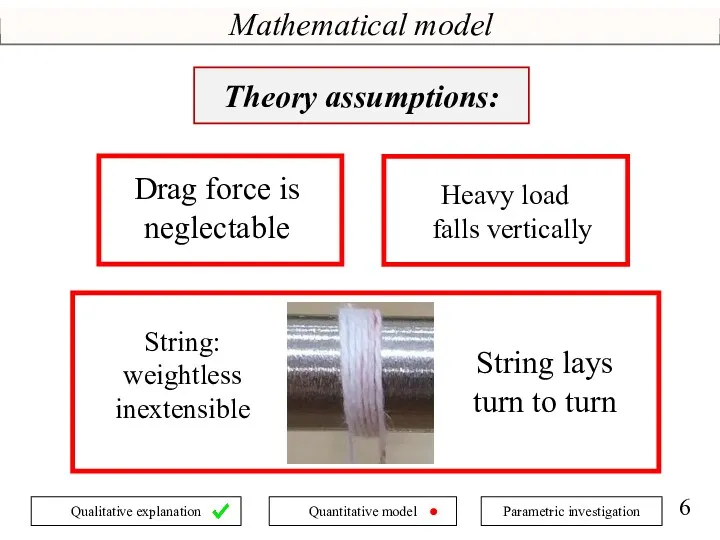
- 6. Mathematical model String lays turn to turn String: weightless inextensible Heavy load falls vertically Drag force
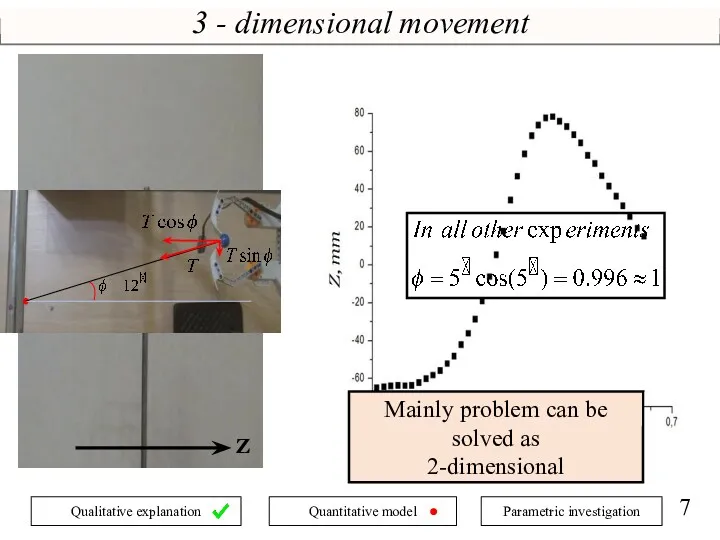
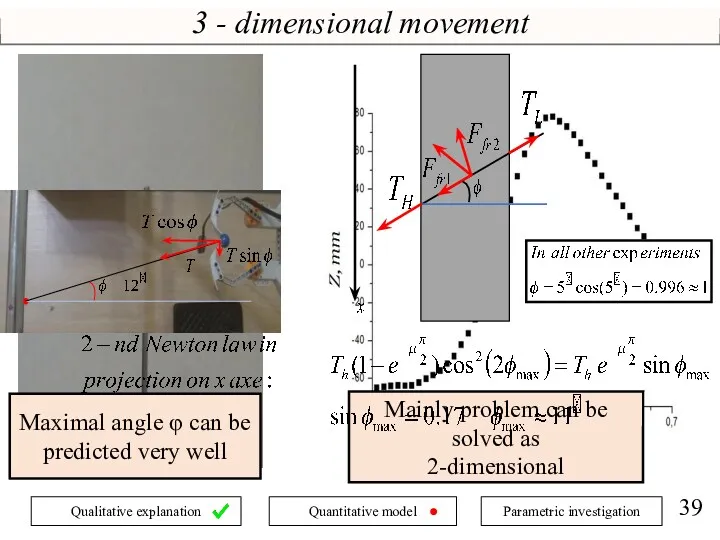
- 7. 3 - dimensional movement Z Mainly problem can be solved as 2-dimensional
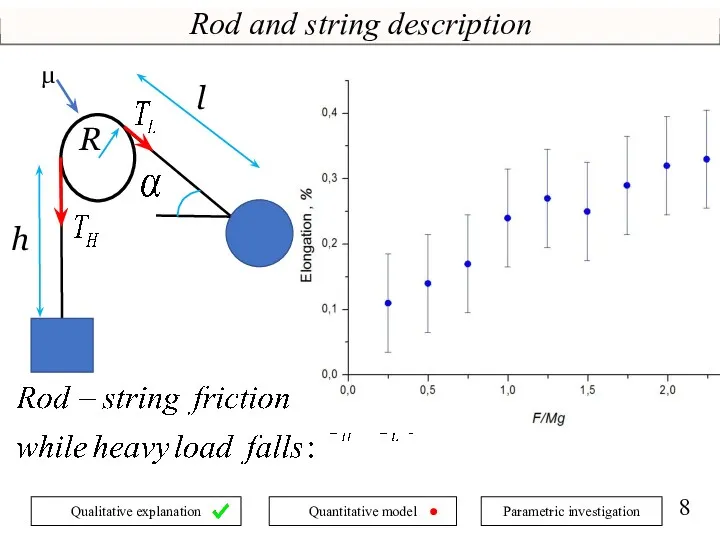
- 8. Rod and string description h R l μ
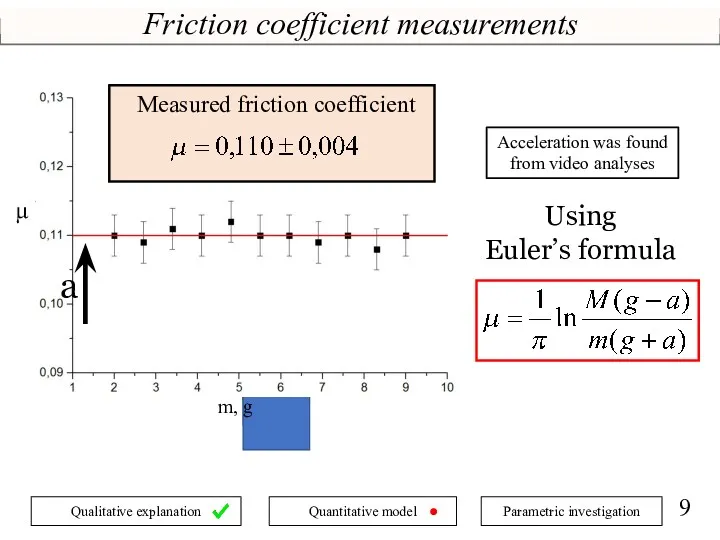
- 9. Friction coefficient measurements a π m M μ Using Euler’s formula m, g a Measured friction
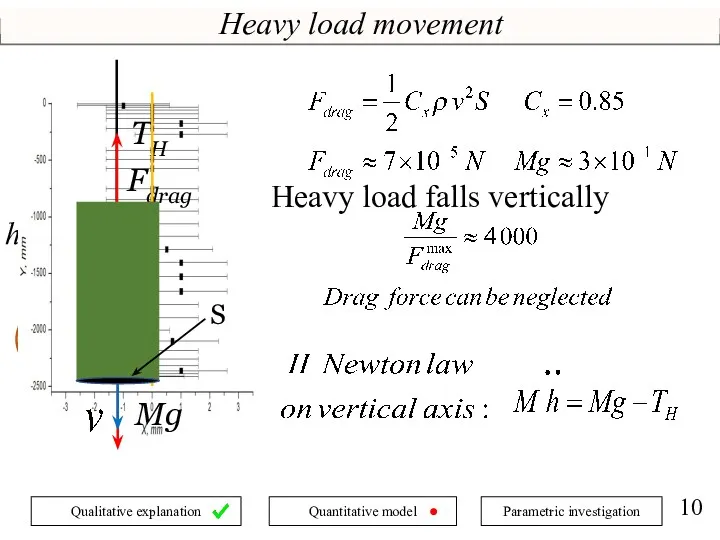
- 10. Heavy load movement h Heavy load falls vertically Fdrag TH Mg S
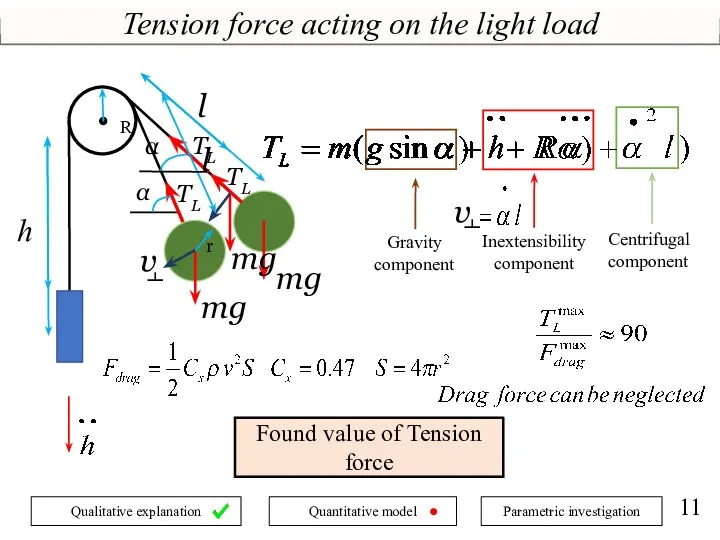
- 11. Tension force acting on the light load mg TL α h R l Inextensibility component Centrifugal
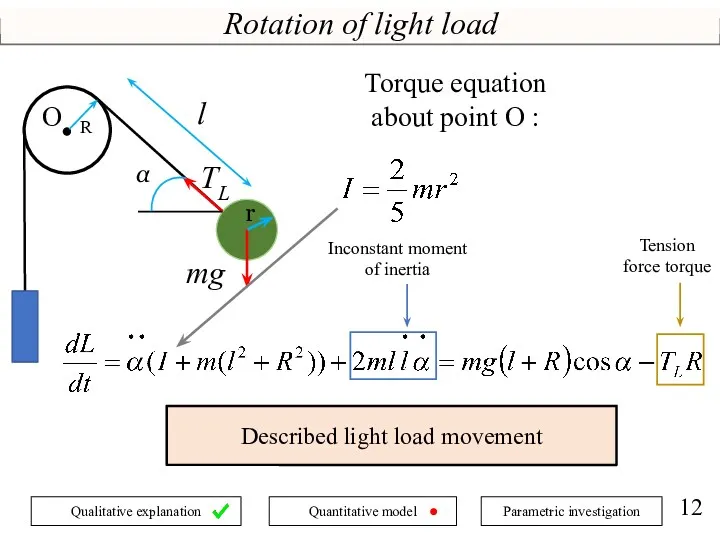
- 12. Rotation of light load Described light load movement mg TL α R О l Torque equation
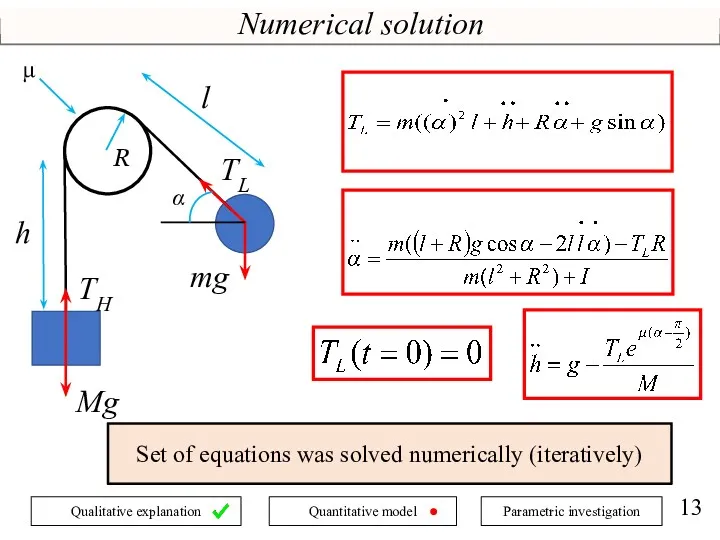
- 13. Numerical solution mg Mg TH TL R μ l h α Set of equations was solved
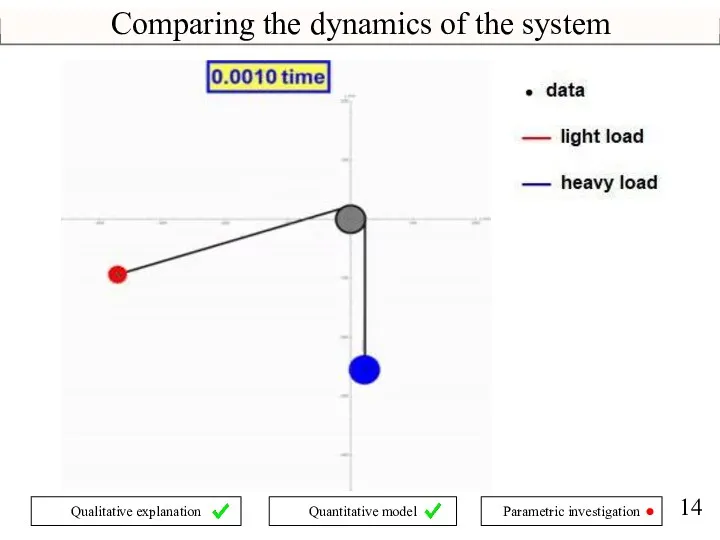
- 14. Comparing the dynamics of the system
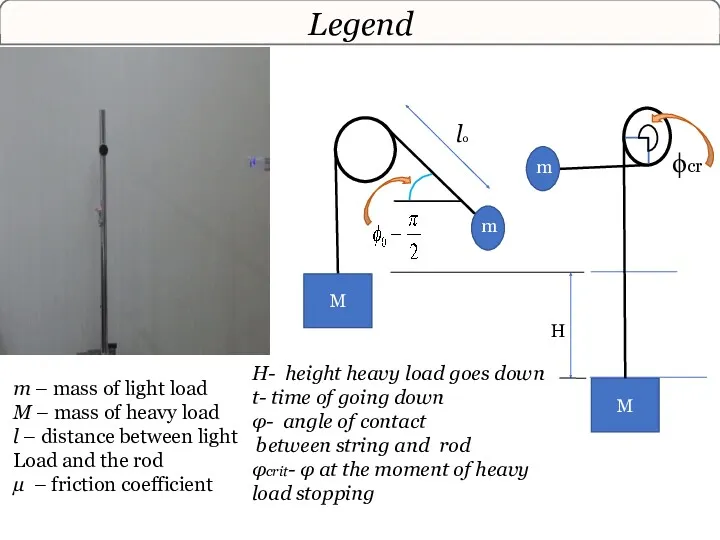
- 15. Legend l0 M M H m – mass of light load M – mass of heavy
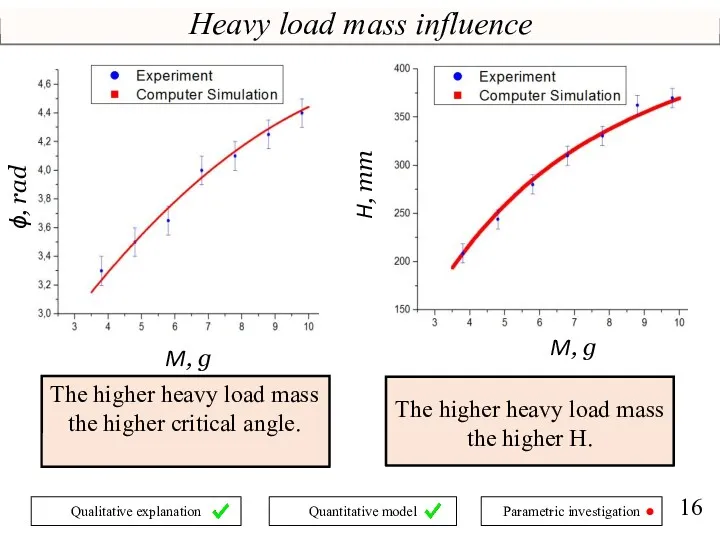
- 16. ϕ, rad M, g M, g H, mm Heavy load mass influence
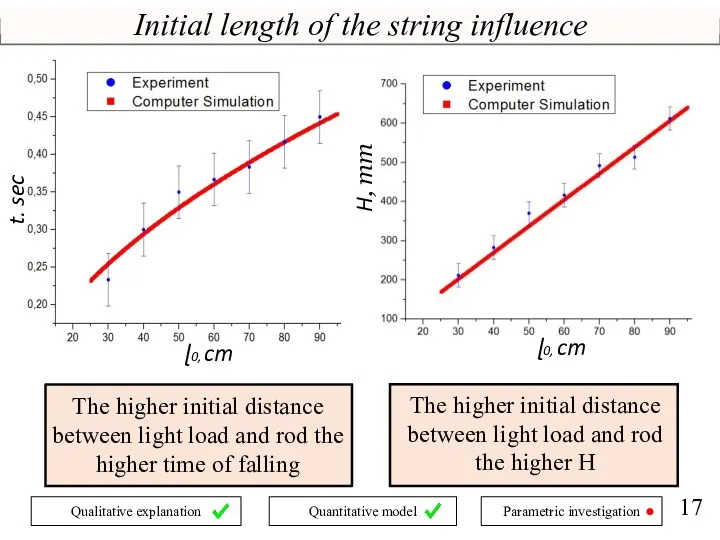
- 17. Initial length of the string influence H, mm t, sec ɭ0, cm ɭ0, cm
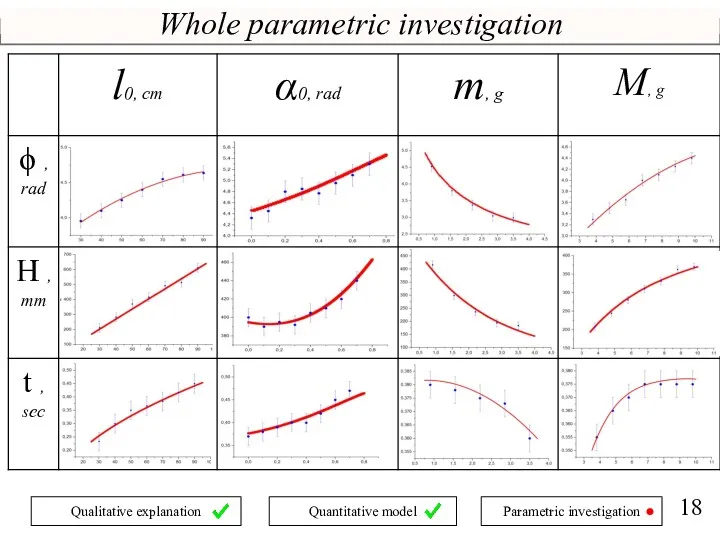
- 18. Whole parametric investigation
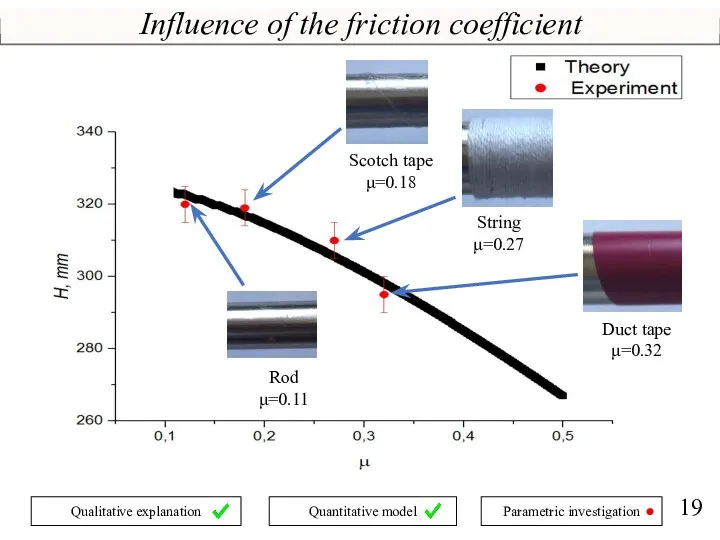
- 19. Influence of the friction coefficient Duct tape μ=0.32 String μ=0.27 Scotch tape μ=0.18 Rod μ=0.11
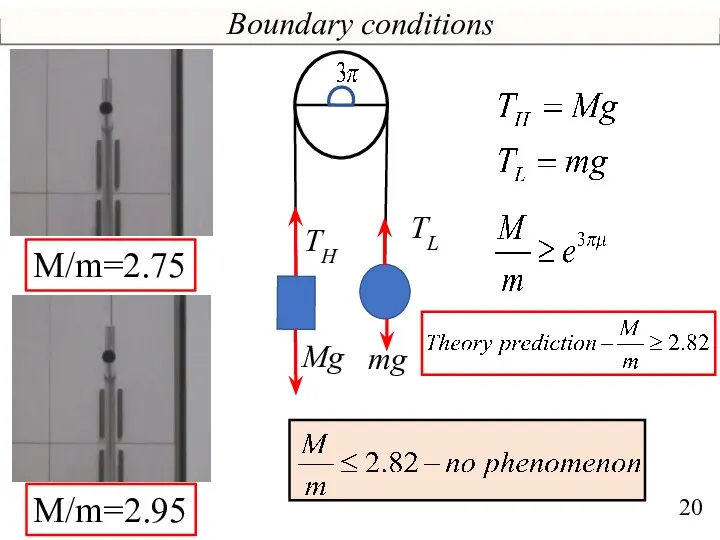
- 20. Boundary conditions M/m=2.75 TL TH Mg mg M/m=2.95
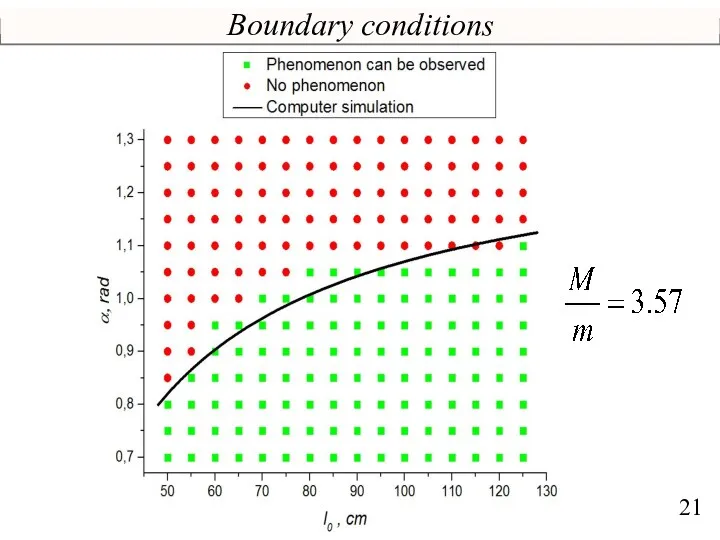
- 21. Boundary conditions
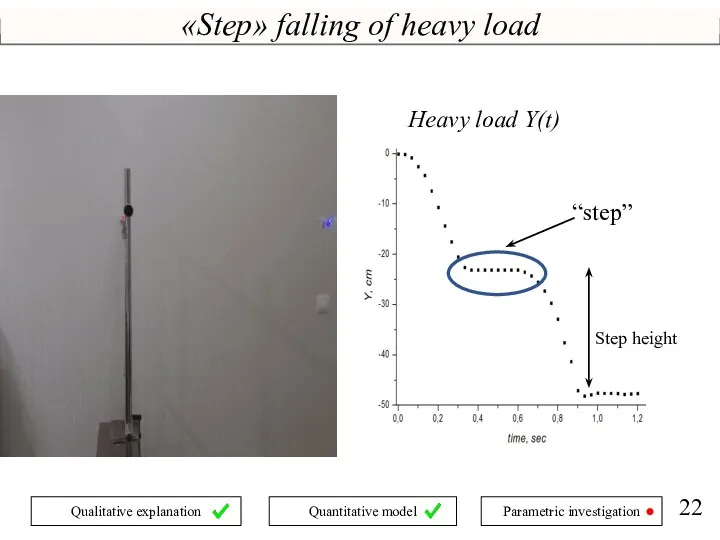
- 22. «Step» falling of heavy load “step” Step height Heavy load Y(t)
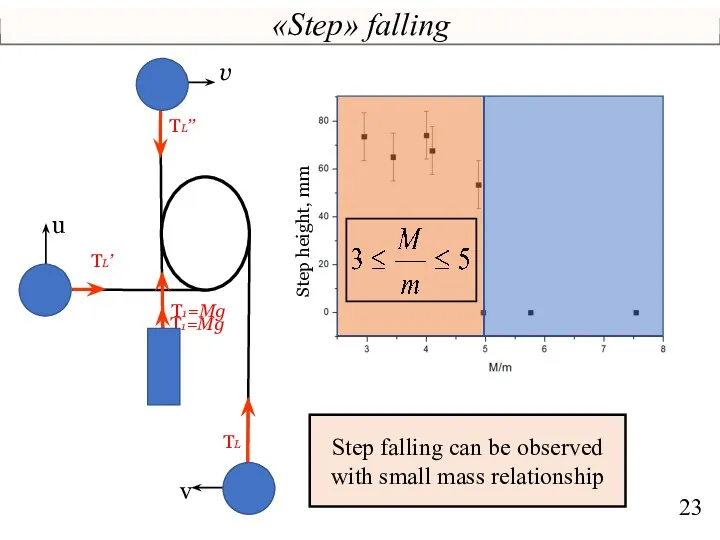
- 23. «Step» falling Т1=Mg ТL’ ТL Т1=Mg v u ТL’’ v Step height, mm
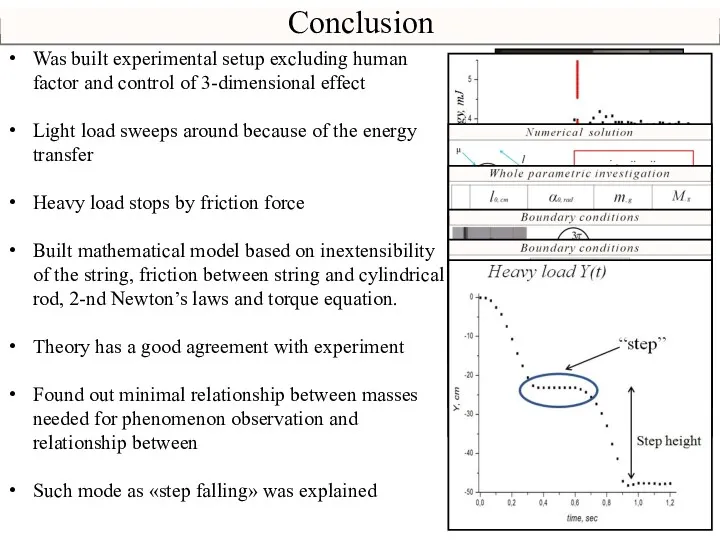
- 24. Conclusion Was built experimental setup excluding human factor and control of 3-dimensional effect Light load sweeps
- 25. Thank you for your attention! Also was investigated: Massive string Back sweeping Rod strike of light
- 26. Additional slides
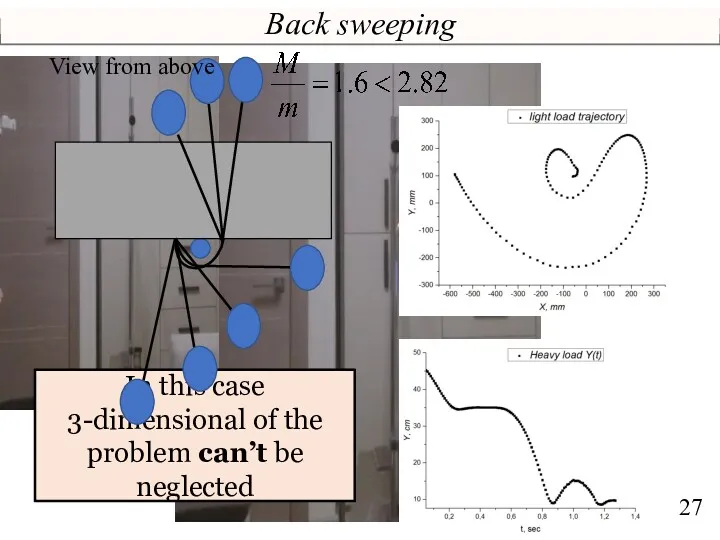
- 27. Back sweeping View from above
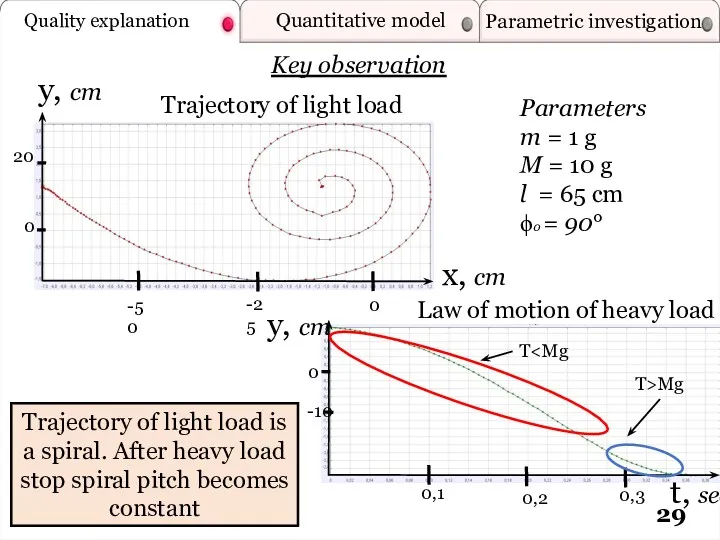
- 29. Quality explanation Quantitative model Parametric investigation y, cm t, sec y, cm x, cm Law of
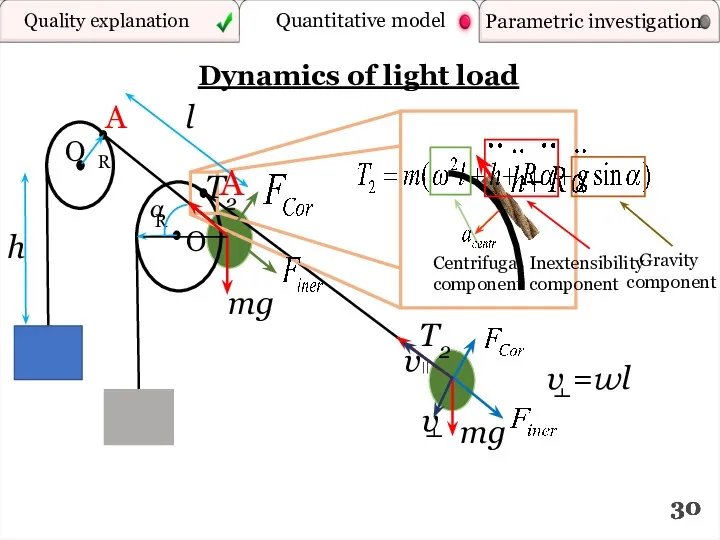
- 30. Dynamics of light load mg T2 R О mg T2 α h R О A l
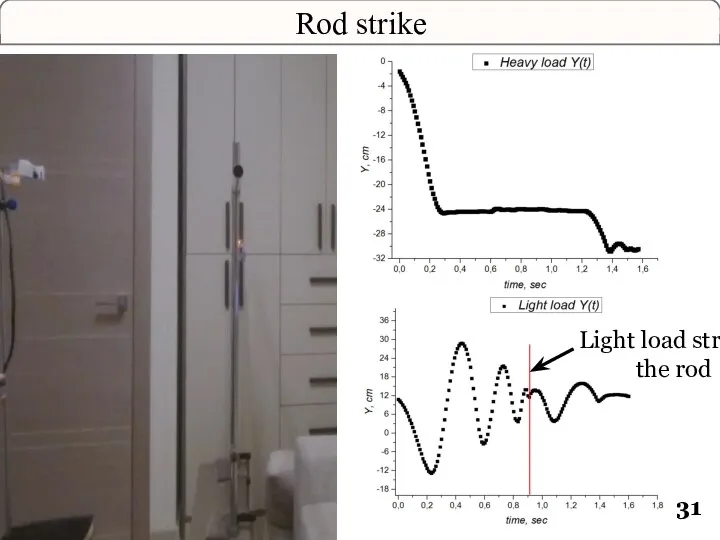
- 31. Rod strike Light load strikes the rod
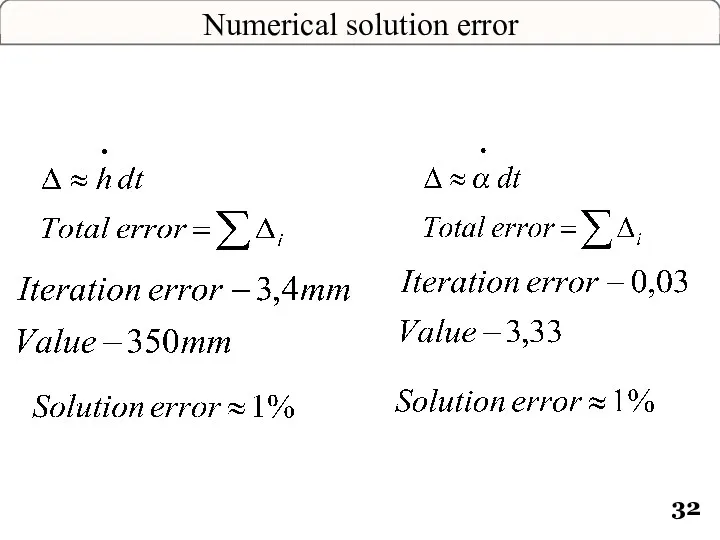
- 32. Numerical solution error
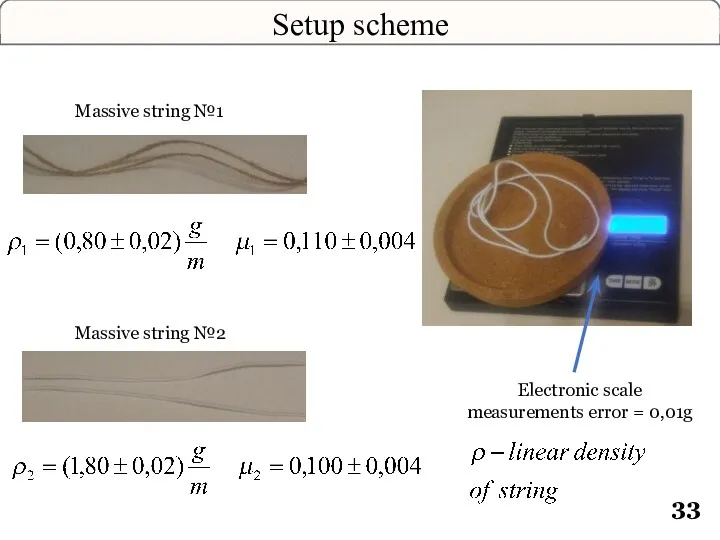
- 33. Setup scheme Electronic scale measurements error = 0,01g Massive string №1 Massive string №2
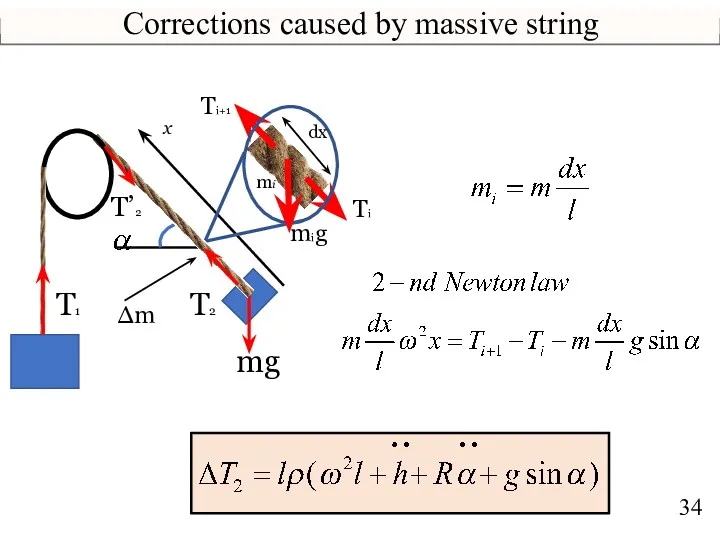
- 34. Corrections caused by massive string mg T2 x Δm Ti+1 Ti mig dx mi T1 T’2
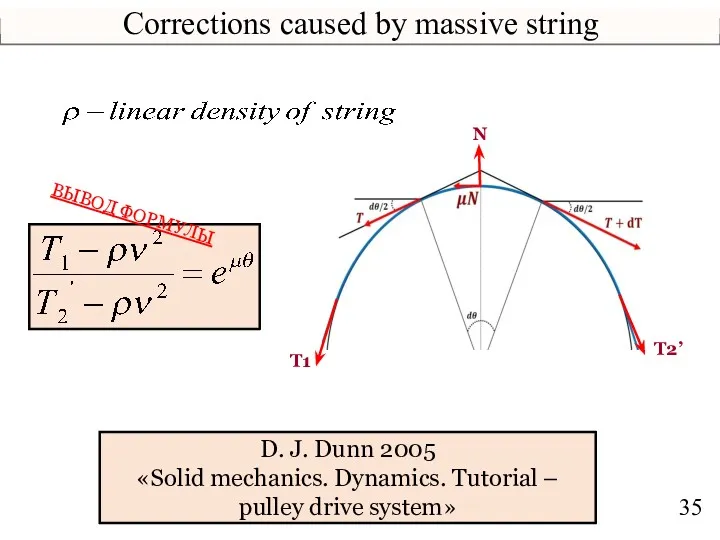
- 35. Corrections caused by massive string T1 T2’ N D. J. Dunn 2005 «Solid mechanics. Dynamics. Tutorial
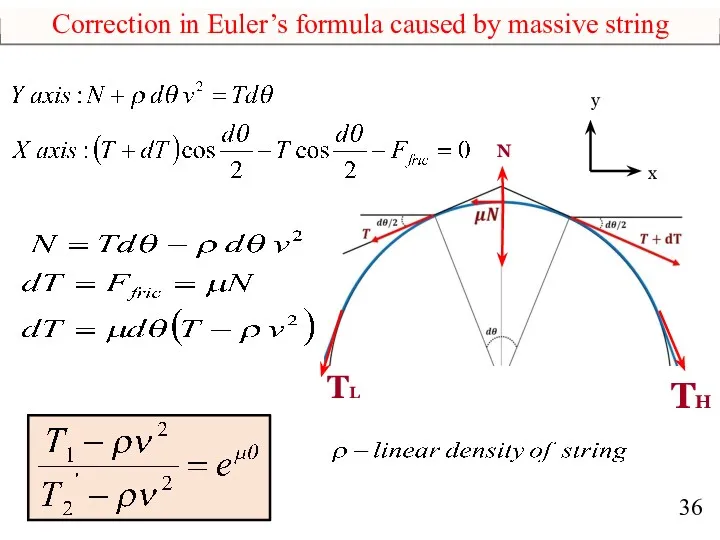
- 36. Correction in Euler’s formula caused by massive string TL N TH y x
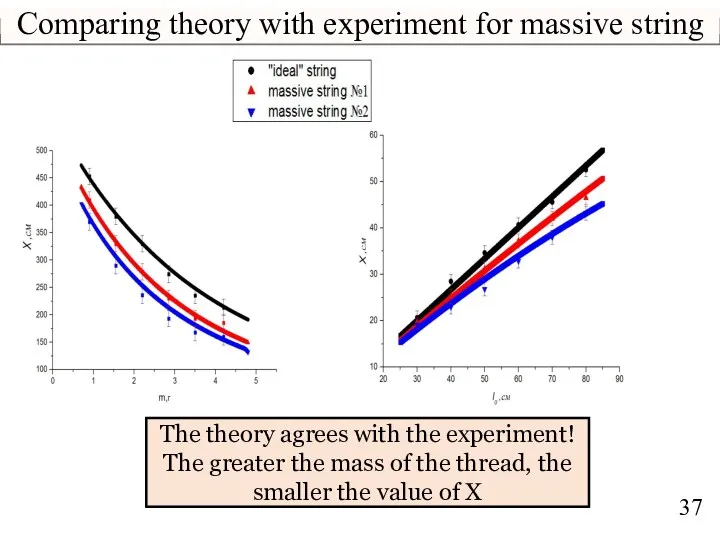
- 37. Comparing theory with experiment for massive string The theory agrees with the experiment! The greater the
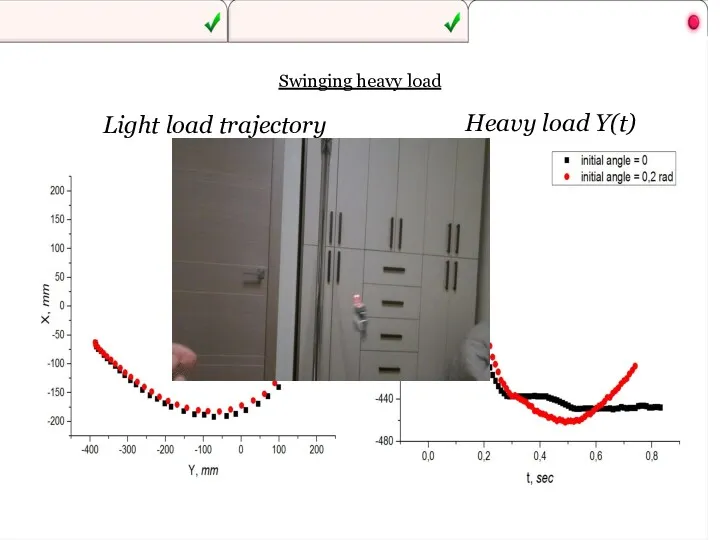
- 38. Swinging heavy load Heavy load Y(t) Light load trajectory
- 39. 3 - dimensional movement Z Mainly problem can be solved as 2-dimensional Maximal angle φ can
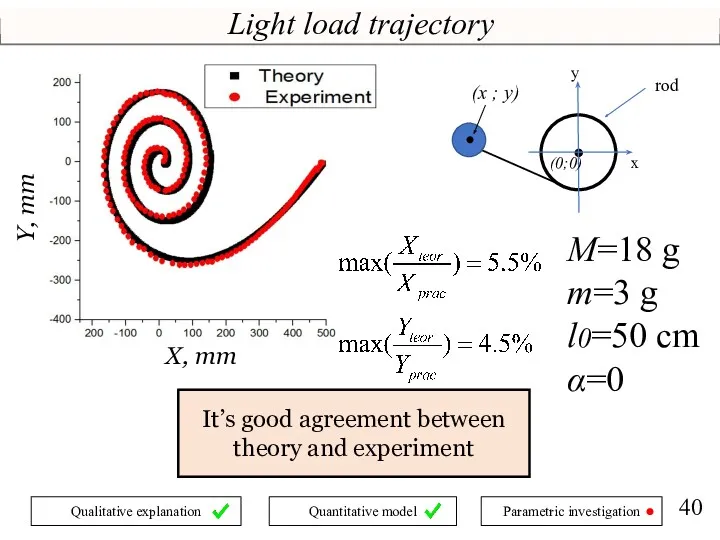
- 40. Light load trajectory X, mm It’s good agreement between theory and experiment M=18 g m=3 g
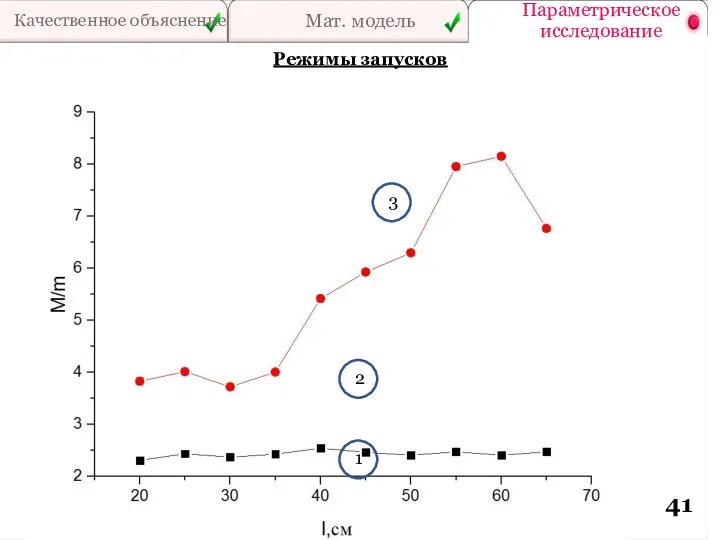
- 41. Качественное объяснение Мат. модель Параметрическое исследование Режимы запусков 1 2 3
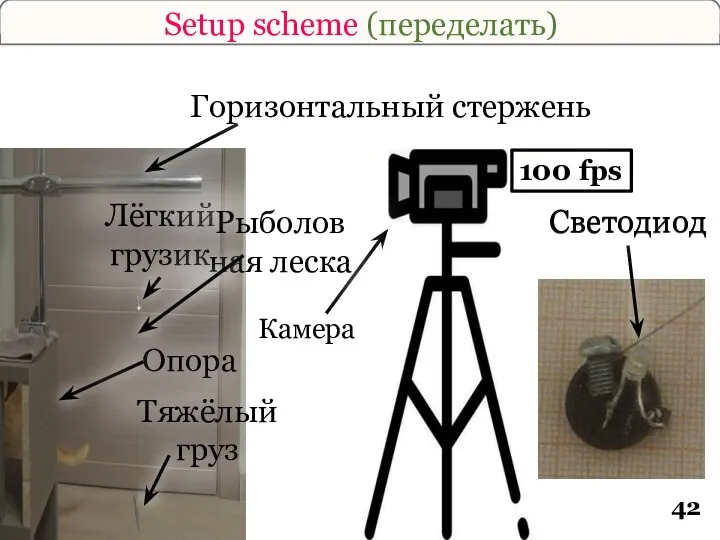
- 42. Setup scheme (переделать) Опора Светодиод Лёгкий грузик Тяжёлый груз Горизонтальный стержень Светодиод Камера 100 fps Рыболовная
- 44. Скачать презентацию



 система СИ
система СИ Пневматична система
Пневматична система Напряженность электрического поля. Урок физики в 10 классе
Напряженность электрического поля. Урок физики в 10 классе Механизм газораспределения автомобиля ВАЗ 2107
Механизм газораспределения автомобиля ВАЗ 2107 Тиристор деп төрт деңгейлі жартылай өткізгіш құрылғылардын
Тиристор деп төрт деңгейлі жартылай өткізгіш құрылғылардын Электроемкость. Конденсаторы
Электроемкость. Конденсаторы Удельная теплоёмкость
Удельная теплоёмкость презентация по теме Сила трения 7 класс
презентация по теме Сила трения 7 класс Лампа накаливания
Лампа накаливания Передача давления жидкостями и газами. Закон Паскаля
Передача давления жидкостями и газами. Закон Паскаля Скорость света
Скорость света Решение задач на применение законов Ньютона
Решение задач на применение законов Ньютона Сила тока. Закон Ома для участка цепи. Сопротивление. 10 класс
Сила тока. Закон Ома для участка цепи. Сопротивление. 10 класс Радиометрия и спектрометрия ионизирующих излучений. (Лекция 9)
Радиометрия и спектрометрия ионизирующих излучений. (Лекция 9) Инструкции по технике безопасности в кабинете физики.
Инструкции по технике безопасности в кабинете физики. От порядка к хаосу. Сценарии перехода к хаосу
От порядка к хаосу. Сценарии перехода к хаосу урок в 7 классе Давление твёрдых тел
урок в 7 классе Давление твёрдых тел Тепломассообмен. Поперечное обтекание одиночных труб и трубных пучков
Тепломассообмен. Поперечное обтекание одиночных труб и трубных пучков Основы атомной физики. Основы квантовой механики. Строение вещества
Основы атомной физики. Основы квантовой механики. Строение вещества Адаптация обучающихся в учебном пространстве предмета - физика
Адаптация обучающихся в учебном пространстве предмета - физика Своя игра. Физика. 7 класс.
Своя игра. Физика. 7 класс. Кристаллооптический анализ
Кристаллооптический анализ Биомеханика двигательных действий: составные движения в биокинематических цепях
Биомеханика двигательных действий: составные движения в биокинематических цепях Електростатичне поле
Електростатичне поле Электростатическое поле в вакууме. Принцип суперпозиции. Проводники в электростатическом поле
Электростатическое поле в вакууме. Принцип суперпозиции. Проводники в электростатическом поле Литий-ионные (Li-ion) аккумуляторы
Литий-ионные (Li-ion) аккумуляторы Заттың магниттік қасиеттері. Ақпараттың магниттік жазылуы
Заттың магниттік қасиеттері. Ақпараттың магниттік жазылуы Теплотехника. Основы теории тепло- и массообмена. (Лекция 11)
Теплотехника. Основы теории тепло- и массообмена. (Лекция 11)