Содержание
- 2. Mechanical waves Properties of mechanical waves: transmit energy (not mass) oscillators oscillate but do not move
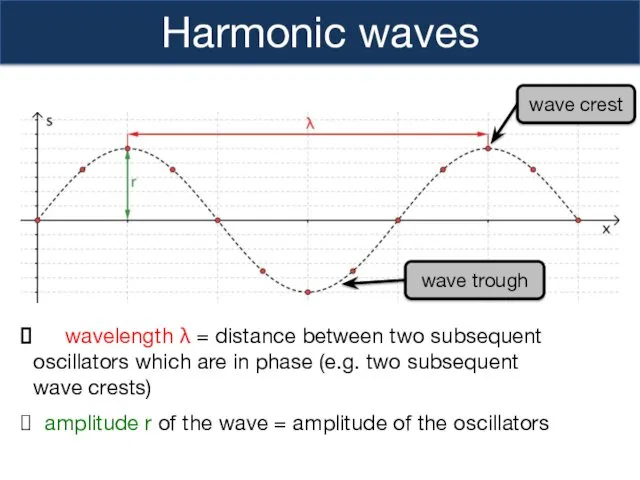
- 3. Harmonic waves wavelength λ = distance between two subsequent oscillators which are in phase (e.g. two
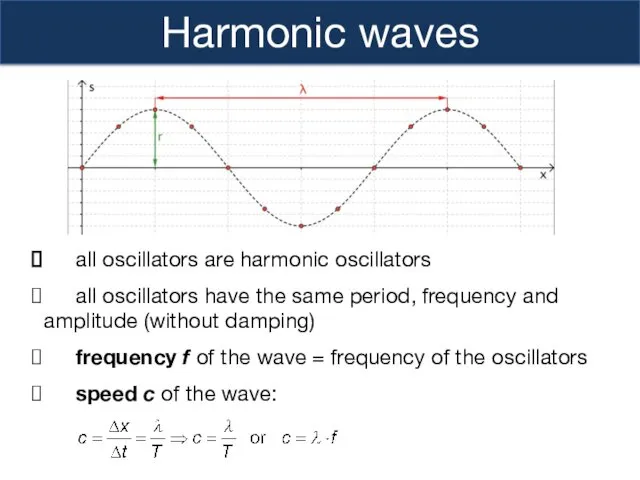
- 4. Harmonic waves all oscillators are harmonic oscillators all oscillators have the same period, frequency and amplitude
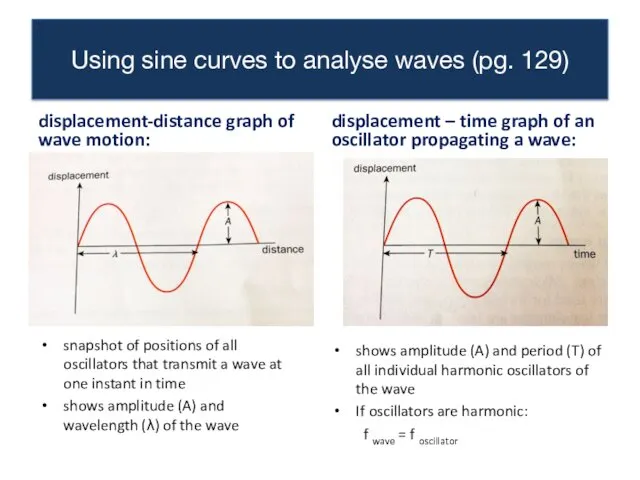
- 5. Using sine curves to analyse waves (pg. 129) displacement-distance graph of wave motion: displacement – time
- 6. Wavefronts (pg.123) imaginary lines which join identical points (oscillators) of several waves which are in phase
- 7. Energy and intensity (pg. 126-127)
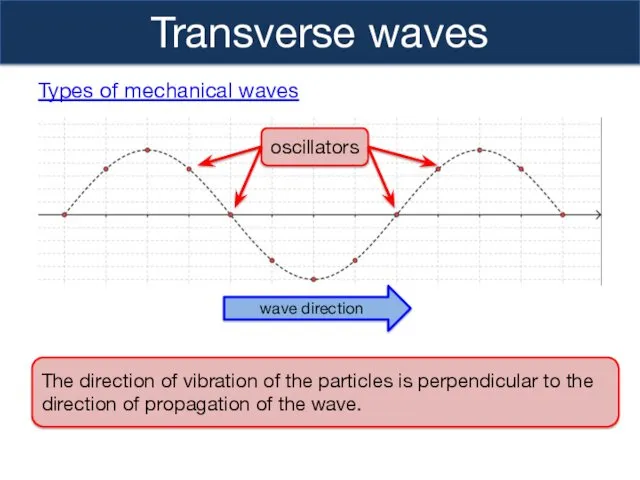
- 8. Transverse waves The direction of vibration of the particles is perpendicular to the direction of propagation
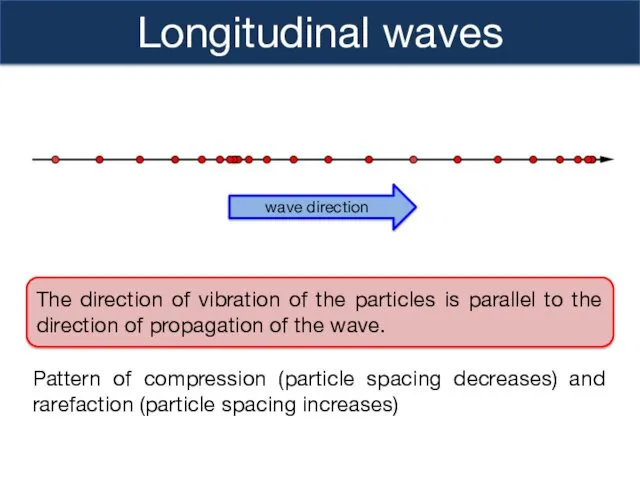
- 9. Longitudinal waves The direction of vibration of the particles is parallel to the direction of propagation
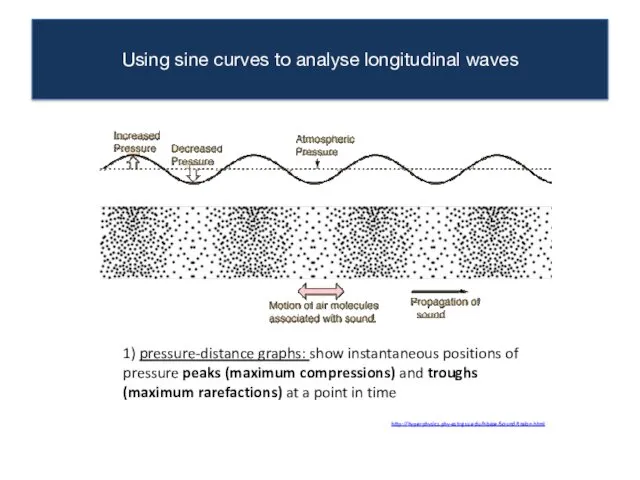
- 10. Using sine curves to analyse longitudinal waves 1) pressure-distance graphs: show instantaneous positions of pressure peaks
- 12. Скачать презентацию



 Припои и флюсы
Припои и флюсы Физика. Электростатика (продолжение)
Физика. Электростатика (продолжение) теоретические основы метрологического обеспечения
теоретические основы метрологического обеспечения Закон Кулона
Закон Кулона Решение неоднородного уравнения теплопроводности
Решение неоднородного уравнения теплопроводности Ременные передачи
Ременные передачи Использование системно-деятельностного подхода в преподавании физики
Использование системно-деятельностного подхода в преподавании физики Рупорные антенны. (Лекция 12)
Рупорные антенны. (Лекция 12) Основні положення теорії надійності. (Лекція 6)
Основні положення теорії надійності. (Лекція 6) Кинематический и силовой расчет привода винтового толкателя
Кинематический и силовой расчет привода винтового толкателя Элементы физики твердого тела. Статистика Бозе-Эйнштейна и Ферми-Дирака. Лекция 5
Элементы физики твердого тела. Статистика Бозе-Эйнштейна и Ферми-Дирака. Лекция 5 Дисперсия света
Дисперсия света Diesel and petrol power
Diesel and petrol power Строительная механика пластин. Изгиб пластин
Строительная механика пластин. Изгиб пластин Термодинамические системы и термодинамические параметры
Термодинамические системы и термодинамические параметры Оптика - раздел физики
Оптика - раздел физики РБМК (реактор большой мощности канальный). Лекция 8
РБМК (реактор большой мощности канальный). Лекция 8 Презентация по теме Внутренняя энергия и способы ее изменения8кл
Презентация по теме Внутренняя энергия и способы ее изменения8кл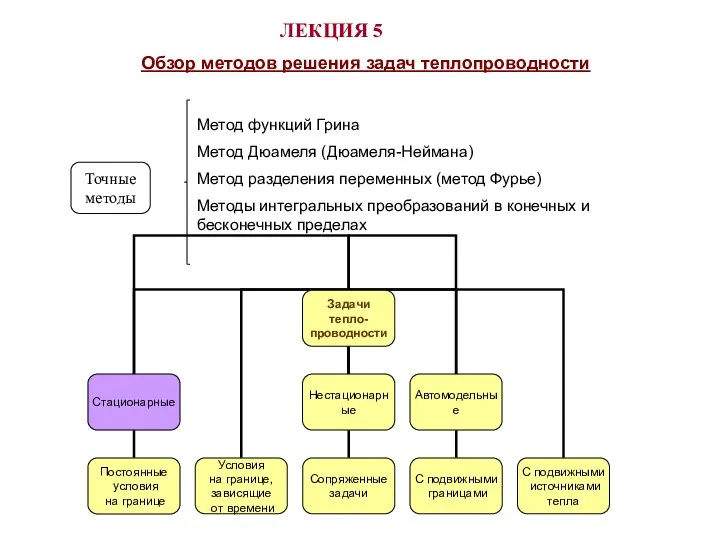 Обзор методов решения задач теплопроводности
Обзор методов решения задач теплопроводности Перемещение при прямолинейном движении
Перемещение при прямолинейном движении Нахождение удельной теплоты плавления льда в опытах по плавлению льда нагретыми металлическими цилиндрами
Нахождение удельной теплоты плавления льда в опытах по плавлению льда нагретыми металлическими цилиндрами Основы теории автоматического управления. Устойчивость САУ. Лекция 11
Основы теории автоматического управления. Устойчивость САУ. Лекция 11 КВН
КВН Структура и взаимодействие адронов
Структура и взаимодействие адронов Холодильные установки. Криогенные жидкости. Компрессоры
Холодильные установки. Криогенные жидкости. Компрессоры Кинематический расчет привода
Кинематический расчет привода Закон Паскаля. Сполучені посудини
Закон Паскаля. Сполучені посудини Сообщающиеся сосуды
Сообщающиеся сосуды