Содержание
- 2. SIMPLE PLAN ! THAT’S SO SIMPLE 1.Principles of molecular spectroscopy 2. Nuclear Shieldingand1H Chemical Shifts
- 3. Lets understand few things Electromagnetic Radiation – is propagated at the speed of light has properties
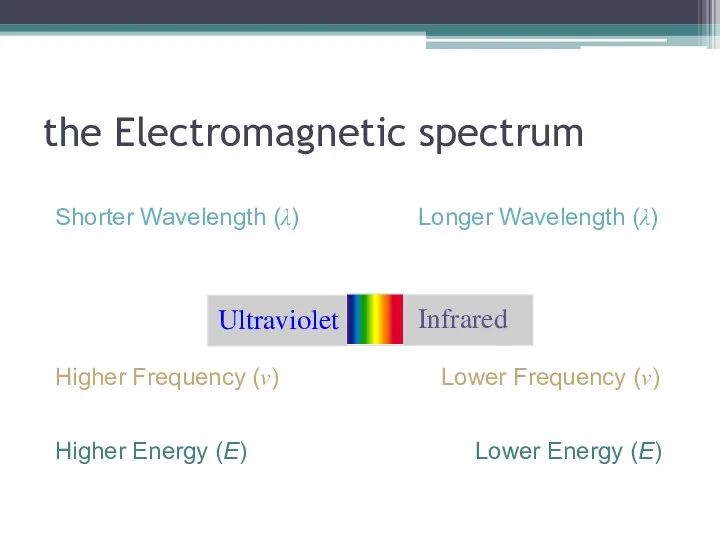
- 4. the Electromagnetic spectrum Longer Wavelength (λ) Shorter Wavelength (λ) Higher Frequency (ν) Lower Frequency (ν) Higher
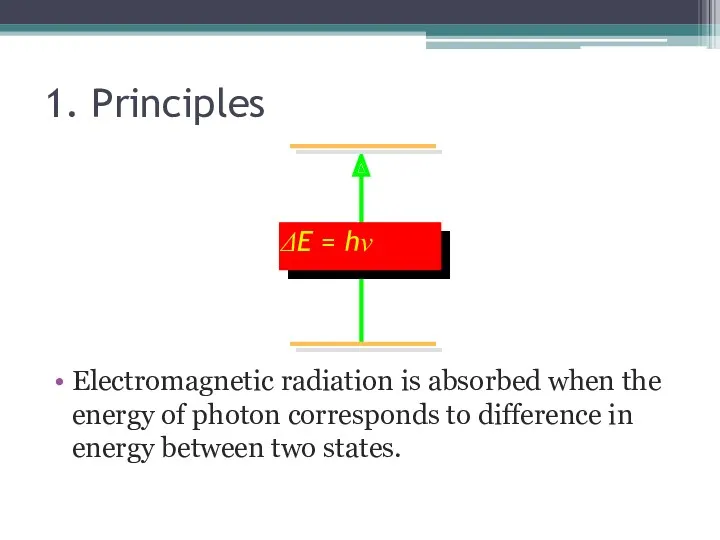
- 5. 1. Principles Electromagnetic radiation is absorbed when the energy of photon corresponds to difference in energy
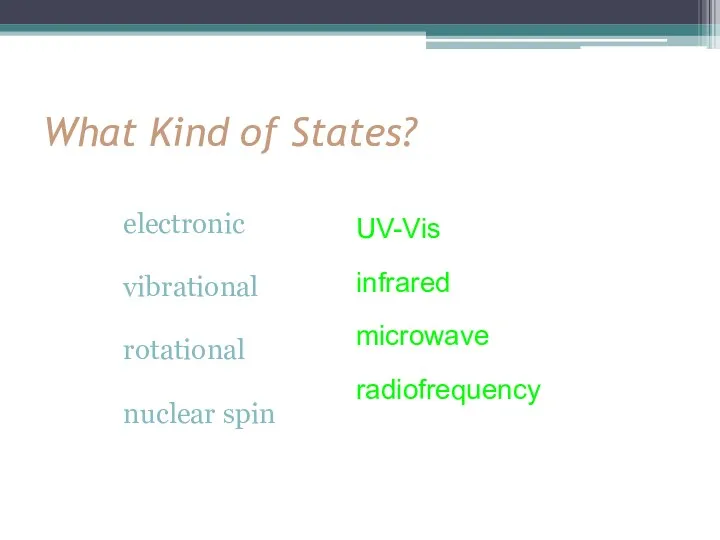
- 6. What Kind of States? electronic vibrational rotational nuclear spin UV-Vis infrared microwave radiofrequency
- 7. The nuclei that are most useful to organic chemists are: 1H and 13C both have spin
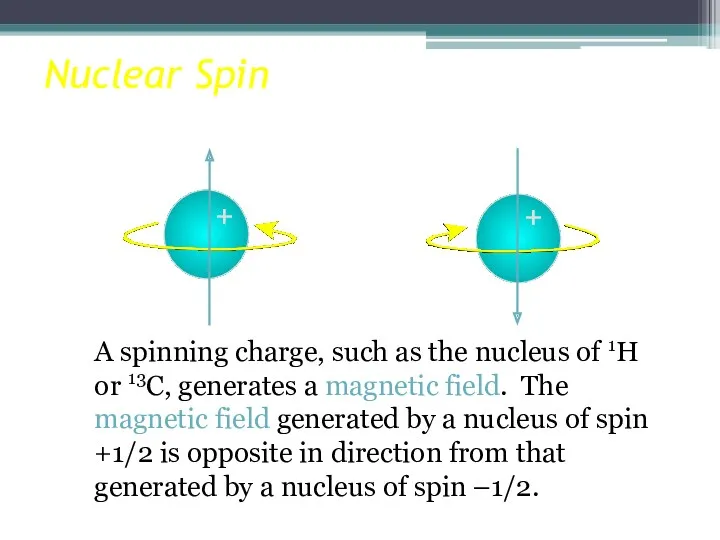
- 8. Nuclear Spin A spinning charge, such as the nucleus of 1H or 13C, generates a magnetic
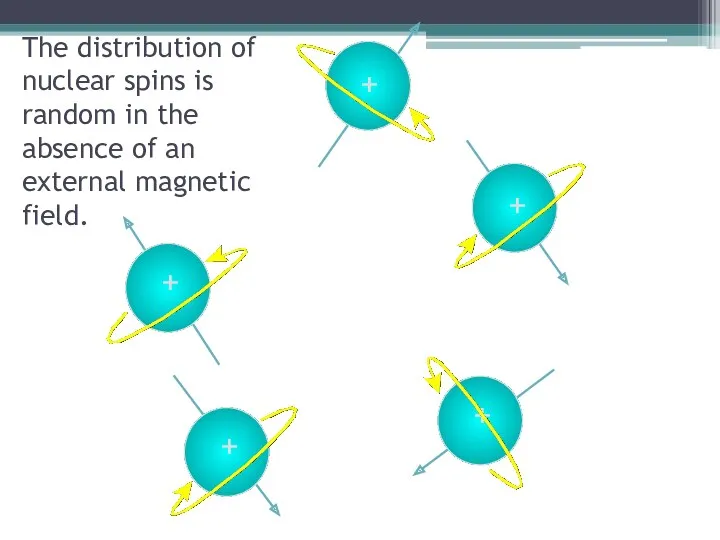
- 9. + The distribution of nuclear spins is random in the absence of an external magnetic field.
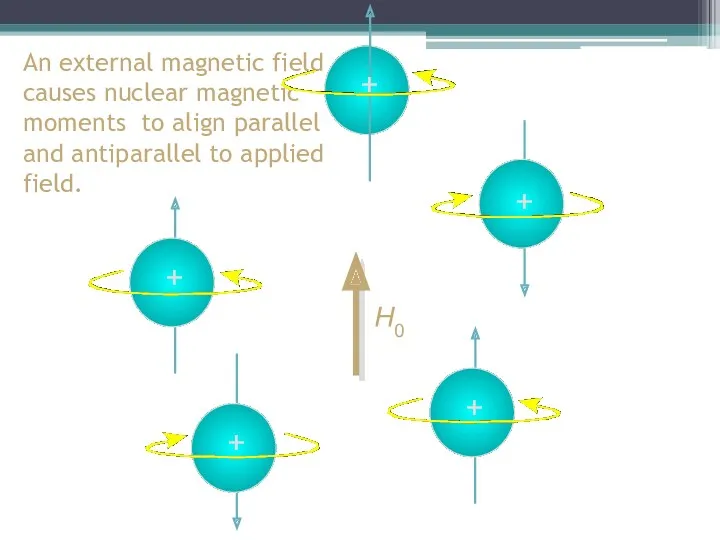
- 10. + An external magnetic field causes nuclear magnetic moments to align parallel and antiparallel to applied
- 11. Some important relationships in NMR The frequency of absorbed electromagnetic radiation is proportional to the energy
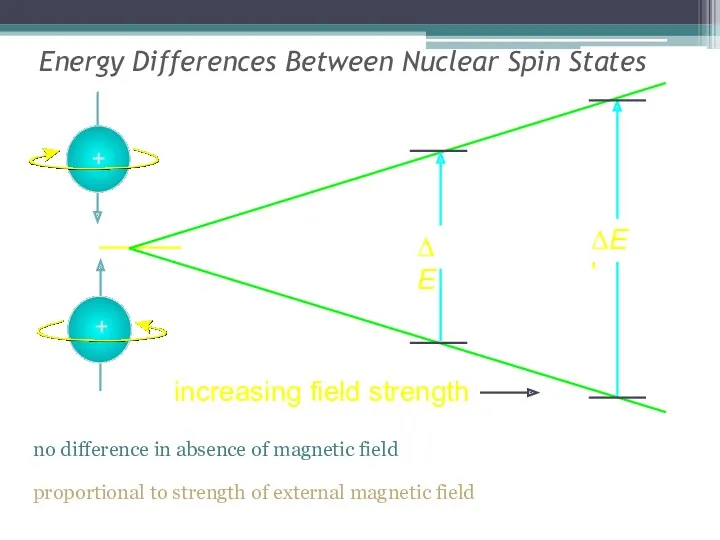
- 12. Energy Differences Between Nuclear Spin States no difference in absence of magnetic field proportional to strength
- 13. The frequency of absorbed electromagnetic radiation for a particular nucleus (such as 1H) depends on its
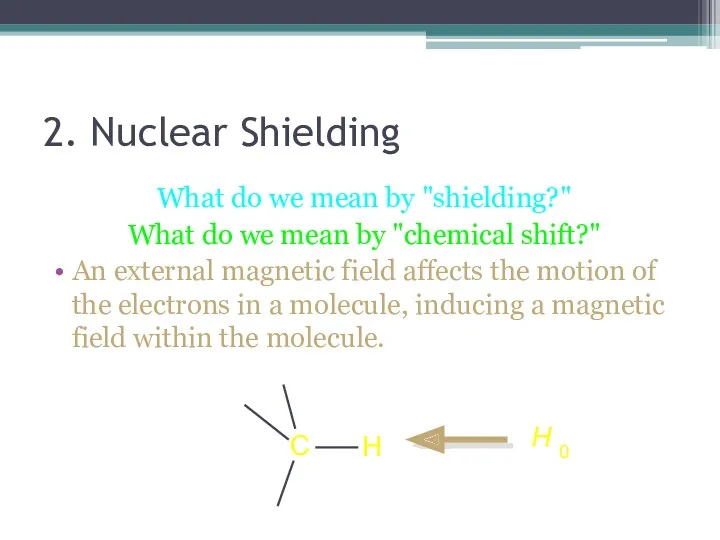
- 14. 2. Nuclear Shielding What do we mean by "shielding?" What do we mean by "chemical shift?"
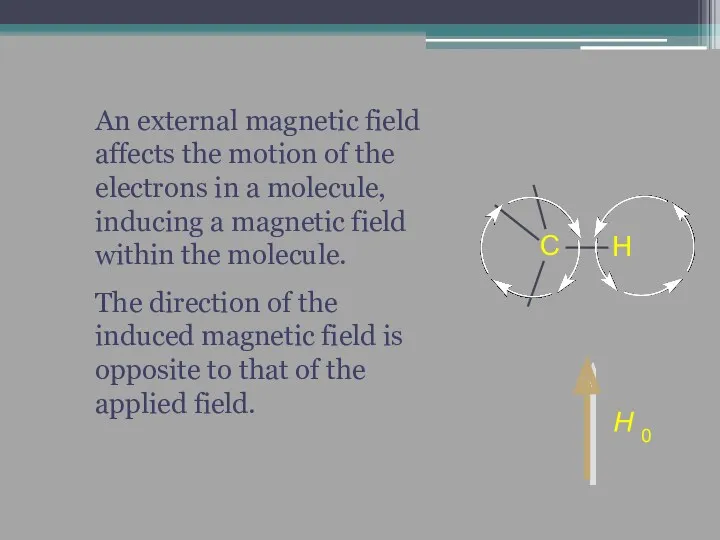
- 15. An external magnetic field affects the motion of the electrons in a molecule, inducing a magnetic
- 16. The induced field shields the nuclei (in this case, C and H) from the applied field.
- 17. Chemical shift (δ, ppm) measured relative to TMS Upfield Increased shielding Downfield Decreased shielding (CH3)4Si (TMS)
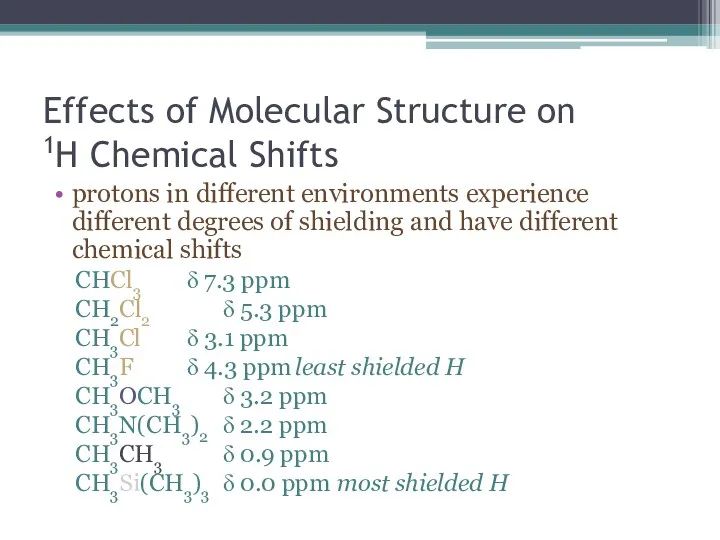
- 18. Effects of Molecular Structure on 1H Chemical Shifts protons in different environments experience different degrees of
- 19. Conclusion A spinning charge can make us understand the structure of matter An external magnetic field
- 21. Скачать презентацию








 Открытый урок по физике в 7 кл: Выталкивающая сила с использованием ЦОР и ИД
Открытый урок по физике в 7 кл: Выталкивающая сила с использованием ЦОР и ИД Диэлектрические потери
Диэлектрические потери Механические свойства материалов. Диаграммы растяжения и сжатия. (Лекция 4)
Механические свойства материалов. Диаграммы растяжения и сжатия. (Лекция 4) Физика и познание мира
Физика и познание мира Урок физики в 10-м классе по теме Сила трения
Урок физики в 10-м классе по теме Сила трения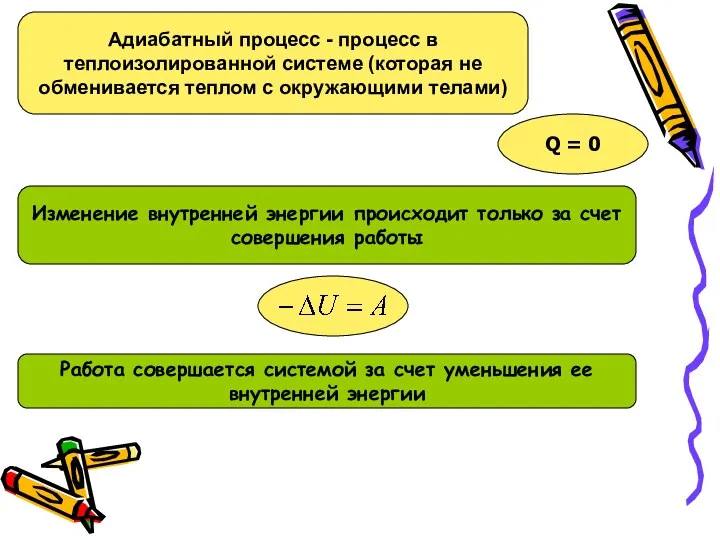 Адиабатный процесс
Адиабатный процесс Фотоэлектрические преобразователи (фотовольтаика)
Фотоэлектрические преобразователи (фотовольтаика) Некоторые средства развития познавательного интереса на уроках физики 7-8 классов.
Некоторые средства развития познавательного интереса на уроках физики 7-8 классов. Курс лекций по сопротивлению материалов (11- 18)
Курс лекций по сопротивлению материалов (11- 18) Фонтан Герона
Фонтан Герона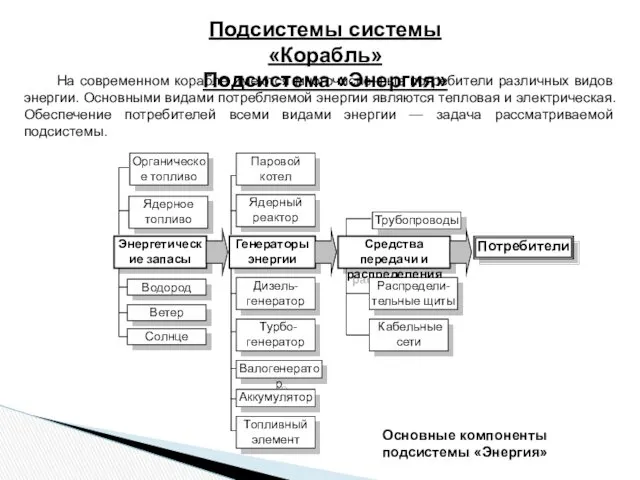 Подсистемы системы Корабль. Подсистема Энергия
Подсистемы системы Корабль. Подсистема Энергия Сферические зеркала, построение изображения в сферическом зеркале
Сферические зеркала, построение изображения в сферическом зеркале Sensors and actuators
Sensors and actuators Қозғалыс материяның ажырамас қасиеті. Материалдық нүкте. Санақ жүйесі. Салыстырмалы механикалық қозғалыс
Қозғалыс материяның ажырамас қасиеті. Материалдық нүкте. Санақ жүйесі. Салыстырмалы механикалық қозғалыс Электротехника. Электрическое поле. Электрические и магнитные цепи. Анализ и расчет электрических цепей
Электротехника. Электрическое поле. Электрические и магнитные цепи. Анализ и расчет электрических цепей Слайды. Полупроводниковые материалы. (Лекция 6)
Слайды. Полупроводниковые материалы. (Лекция 6) Урок физики в 8 классе по теме Плотность
Урок физики в 8 классе по теме Плотность Давление твёрдых тел, жидкостей и газов (решение задач). Физика, 7 класс
Давление твёрдых тел, жидкостей и газов (решение задач). Физика, 7 класс Домашняя лабораторная работа. Определение плотности куска хозяйственного мыла
Домашняя лабораторная работа. Определение плотности куска хозяйственного мыла Ремонт тормозных механизмов автомобиля ЗИЛ
Ремонт тормозных механизмов автомобиля ЗИЛ Ультразвук и инфразвук
Ультразвук и инфразвук Урок по физике в 8 классе на тему Влажность воздуха
Урок по физике в 8 классе на тему Влажность воздуха Генератор
Генератор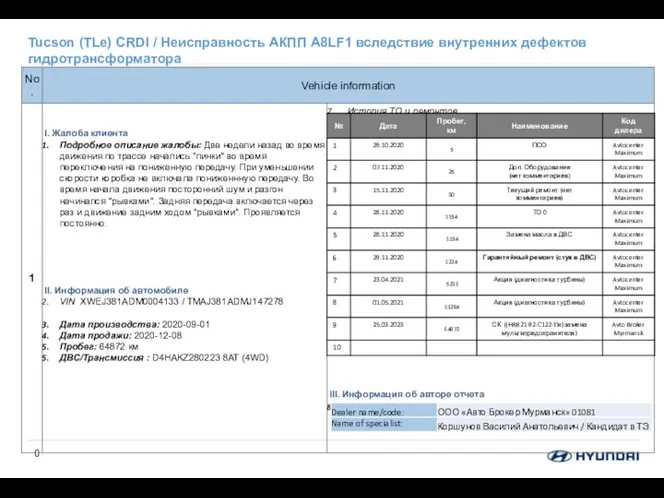 Неисправность АКПП A8LF1 вследствие внутренних дефектов гидротрансформатора
Неисправность АКПП A8LF1 вследствие внутренних дефектов гидротрансформатора Дисперсия. Дифракция. Интерференция. Физический диктант
Дисперсия. Дифракция. Интерференция. Физический диктант Дипломный проект: Технологический процесс технического обслуживания и ремонта сцепления автомобиля
Дипломный проект: Технологический процесс технического обслуживания и ремонта сцепления автомобиля Электротехника и электроника. Трехфазные цепи
Электротехника и электроника. Трехфазные цепи Модальный метод синтеза непрерывных астатических систем управления
Модальный метод синтеза непрерывных астатических систем управления