Содержание
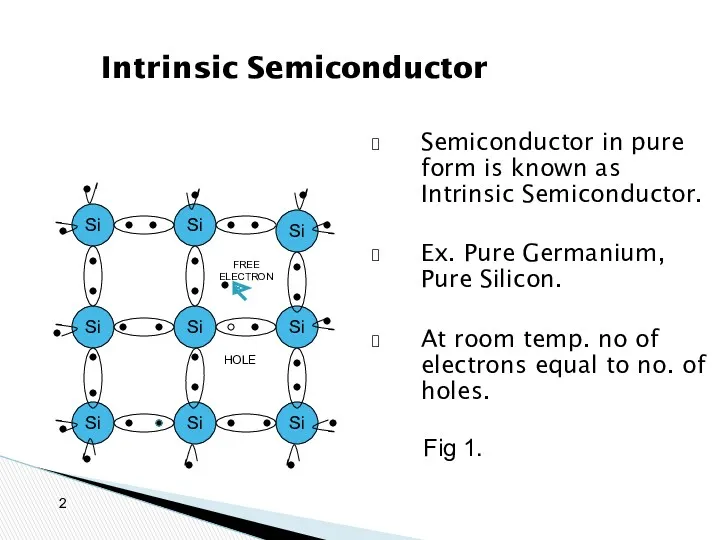
- 2. Intrinsic Semiconductor Semiconductor in pure form is known as Intrinsic Semiconductor. Ex. Pure Germanium, Pure Silicon.
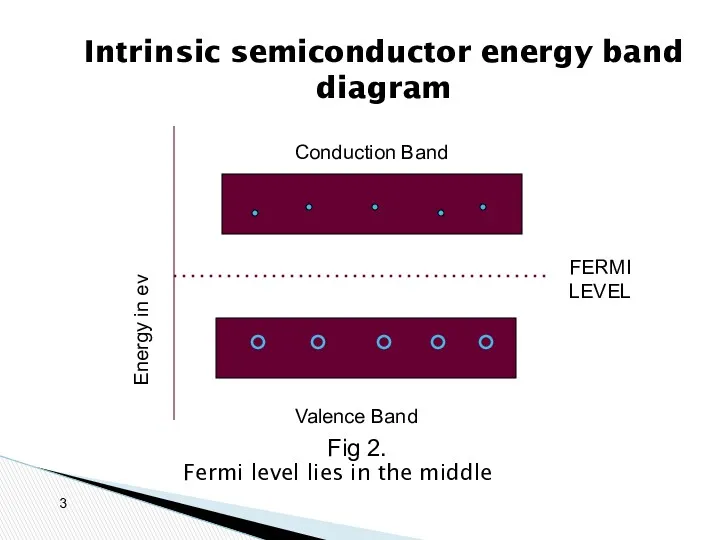
- 3. Intrinsic semiconductor energy band diagram Fermi level lies in the middle Conduction Band Valence Band Energy
- 4. When we add an impurity to pure semiconductor to increase the charge carriers then it becomes
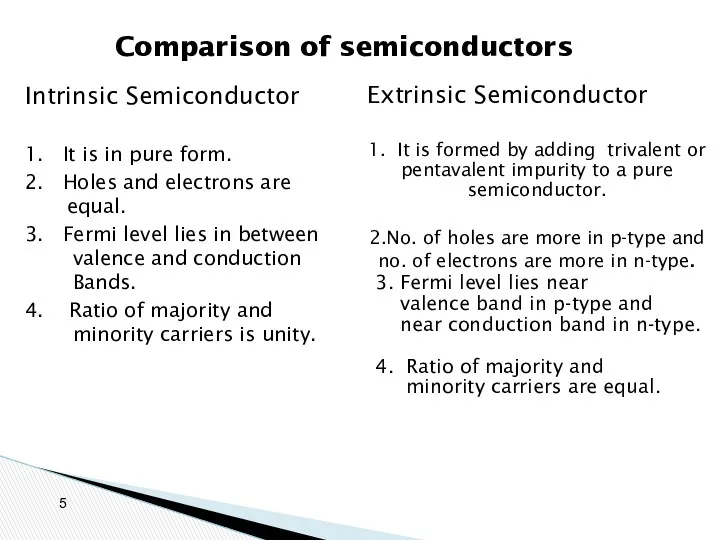
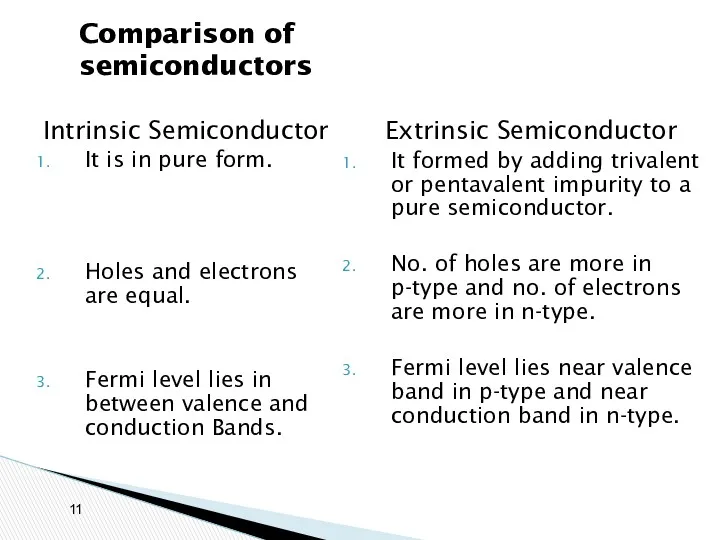
- 5. Comparison of semiconductors Intrinsic Semiconductor 1. It is in pure form. 2. Holes and electrons are
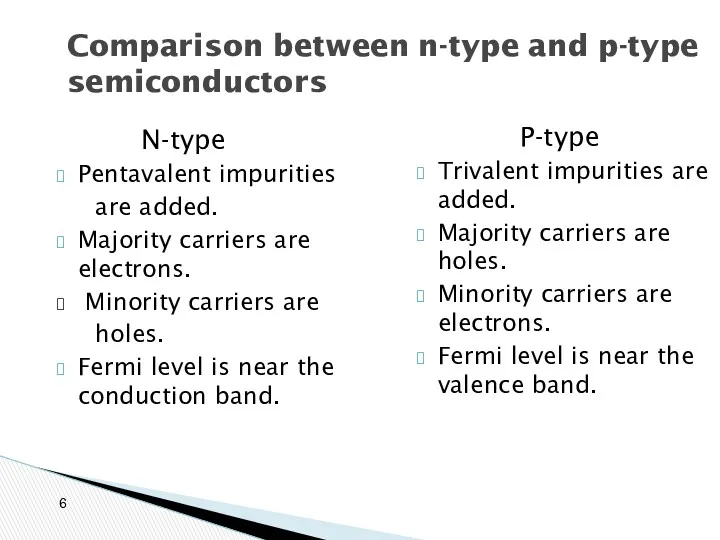
- 6. Comparison between n-type and p-type semiconductors N-type Pentavalent impurities are added. Majority carriers are electrons. Minority
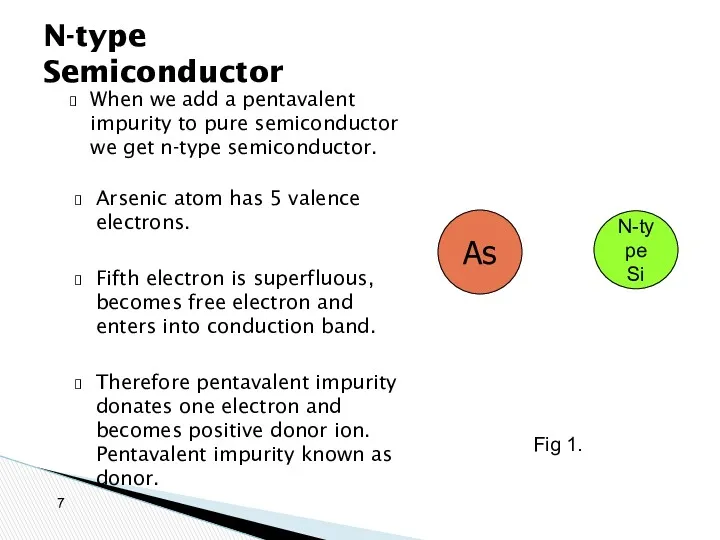
- 7. When we add a pentavalent impurity to pure semiconductor we get n-type semiconductor. N-type Semiconductor As
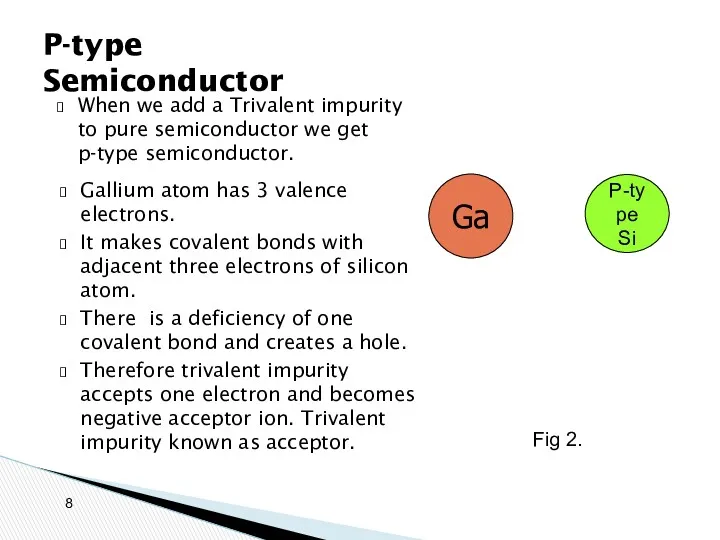
- 8. When we add a Trivalent impurity to pure semiconductor we get p-type semiconductor. P-type Semiconductor Ga
- 9. In addition to this, some of the covalent bonds break due temperature and electron hole pairs
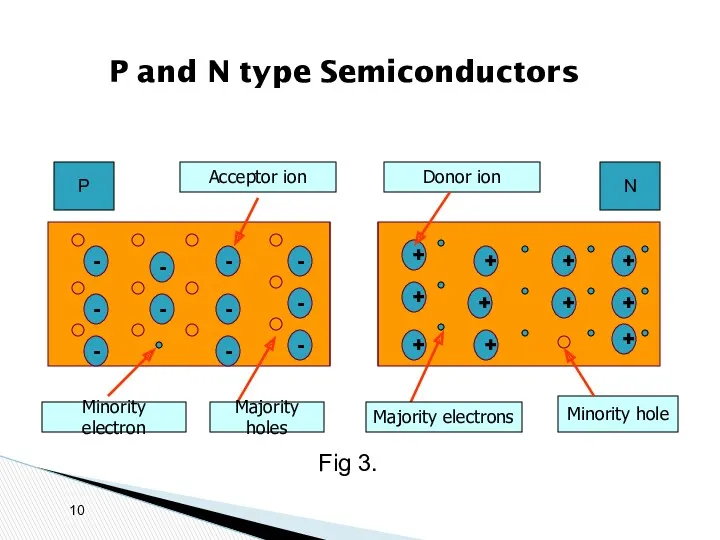
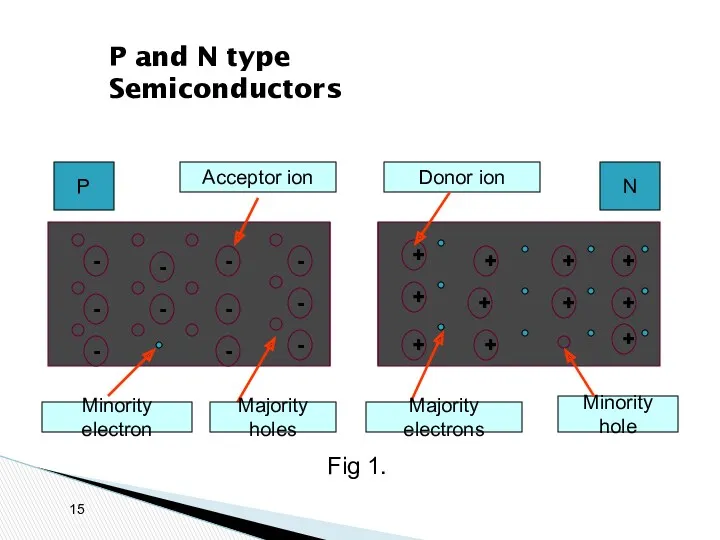
- 10. P and N type Semiconductors + + + + + + + + + + +
- 11. Comparison of semiconductors Intrinsic Semiconductor It is in pure form. Holes and electrons are equal. Fermi
- 12. Conduction is carried out by means of 1. Drift Process. 2. Diffusion Process. Conduction in Semiconductors
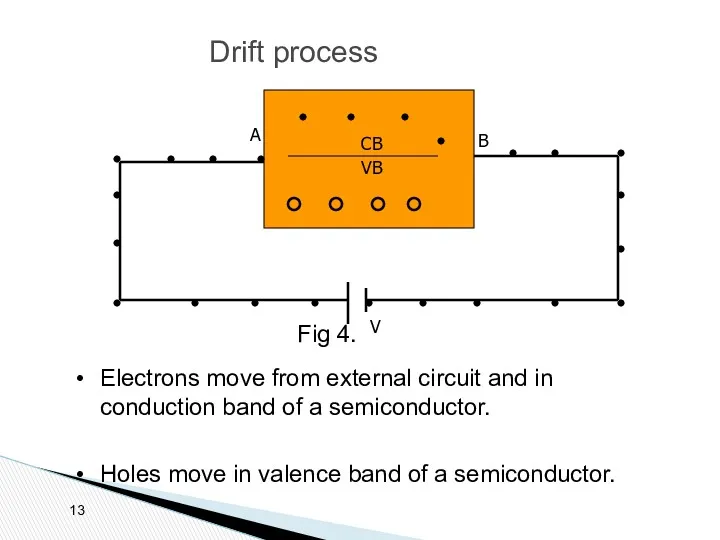
- 13. Drift process CB VB Electrons move from external circuit and in conduction band of a semiconductor.
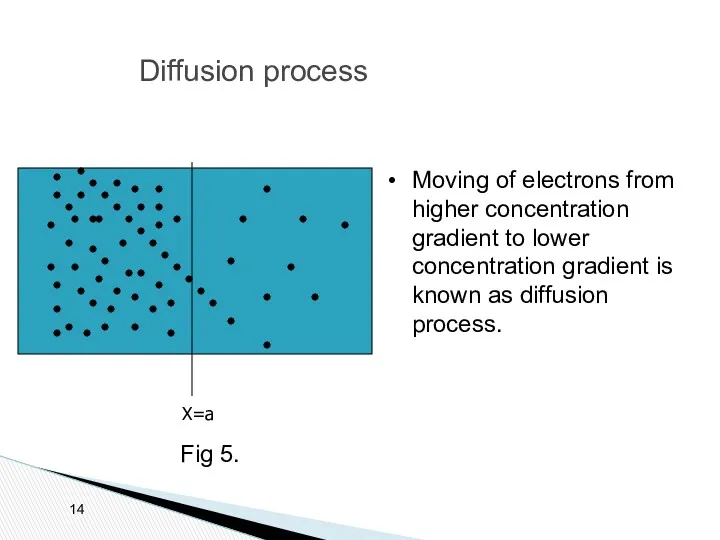
- 14. Diffusion process X=a Moving of electrons from higher concentration gradient to lower concentration gradient is known
- 15. P and N type Semiconductors + + + + + + + + + + +
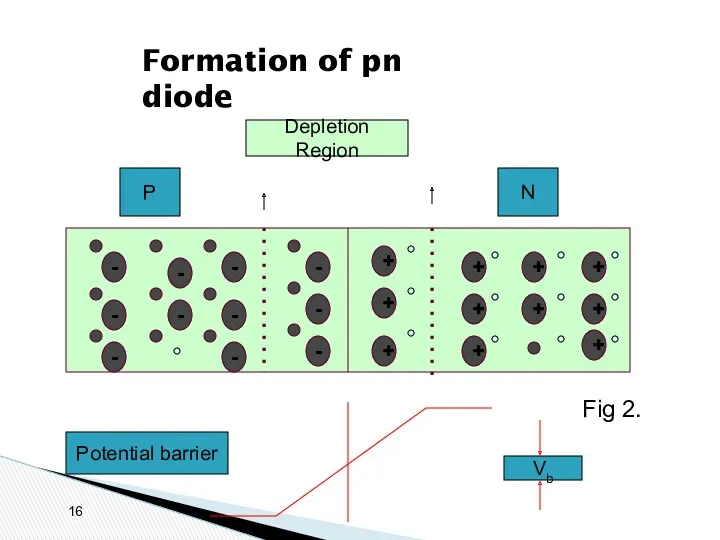
- 16. Formation of pn diode - - - - - - - - - - - +
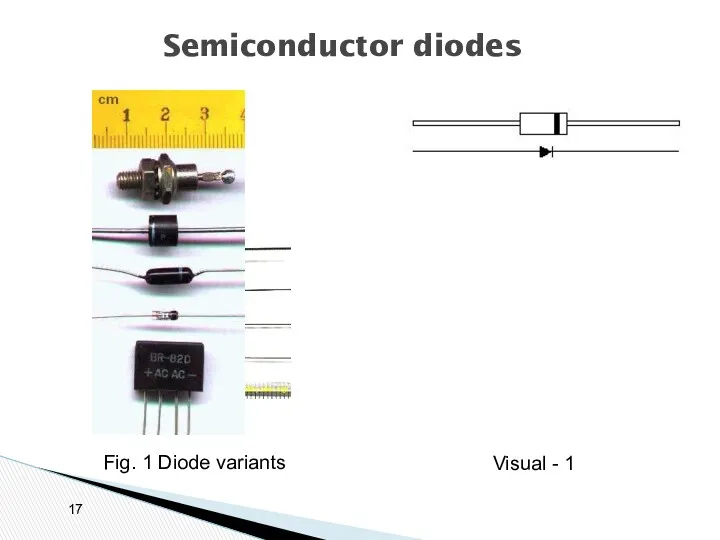
- 17. Semiconductor diodes Fig. 1 Diode variants Visual - 1
- 19. Скачать презентацию

 Взаимодействие заряженных тел. Закон Кулона. Закон сохранения электрического заряда. Электрическое поле
Взаимодействие заряженных тел. Закон Кулона. Закон сохранения электрического заряда. Электрическое поле Физические основы механики. Элементы кинематики
Физические основы механики. Элементы кинематики Роль испарения и конденсации в природе, в жизни человека и животных
Роль испарения и конденсации в природе, в жизни человека и животных Свободные затухающие колебания. Дифференциальное уравнение затухающих колебаний
Свободные затухающие колебания. Дифференциальное уравнение затухающих колебаний урок по физике Магнитное поле
урок по физике Магнитное поле Бесступенчатая коробка передач
Бесступенчатая коробка передач Архимед (287 - 212 до н.э.)
Архимед (287 - 212 до н.э.) Тербелістер мен толқындар
Тербелістер мен толқындар презентация физика 8
презентация физика 8 Виды теплопередачи теплопроводность, конвекция, излучение
Виды теплопередачи теплопроводность, конвекция, излучение Урок Обобщение материала по теме Силы в природе. 7 класс.
Урок Обобщение материала по теме Силы в природе. 7 класс. Электрические явления. Расчет электроэнергии, потребляемой бытовыми приборами. (8 класс)
Электрические явления. Расчет электроэнергии, потребляемой бытовыми приборами. (8 класс) Закон Ома для участка цепи
Закон Ома для участка цепи Фізичні та хімічні явища. (7 клас)
Фізичні та хімічні явища. (7 клас) Улаштування та ТО рульового керування
Улаштування та ТО рульового керування Физика в спорте
Физика в спорте Экспериментальные газовые законы. Абсолютная температура
Экспериментальные газовые законы. Абсолютная температура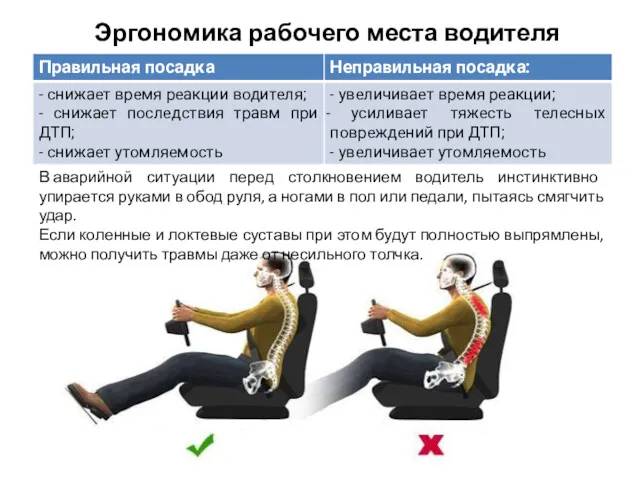 Рабочее место водителя
Рабочее место водителя Взаимодействие света с веществом. Дисперсия света. Нормальная и аномальная дисперсия. Классическая теория дисперсии
Взаимодействие света с веществом. Дисперсия света. Нормальная и аномальная дисперсия. Классическая теория дисперсии Тест по теме Элементарные частицы 11 класс
Тест по теме Элементарные частицы 11 класс Динамика твердого тела. Уравнения движения твердого тела
Динамика твердого тела. Уравнения движения твердого тела презентация к уроку Диффузия вещества. Золото этрусков.
презентация к уроку Диффузия вещества. Золото этрусков. Законы и формулы молекулярной физики
Законы и формулы молекулярной физики Модель урока по теме Тела и их взаимодействие. Инерциальное движение.
Модель урока по теме Тела и их взаимодействие. Инерциальное движение. Расчёт пути и времени движения (физика,7 класс)
Расчёт пути и времени движения (физика,7 класс) Сопротивление материалов. Введение. Основные понятия
Сопротивление материалов. Введение. Основные понятия Проектирование и конструирование. Механические передачи
Проектирование и конструирование. Механические передачи Электромагнитная совместимость
Электромагнитная совместимость