Содержание
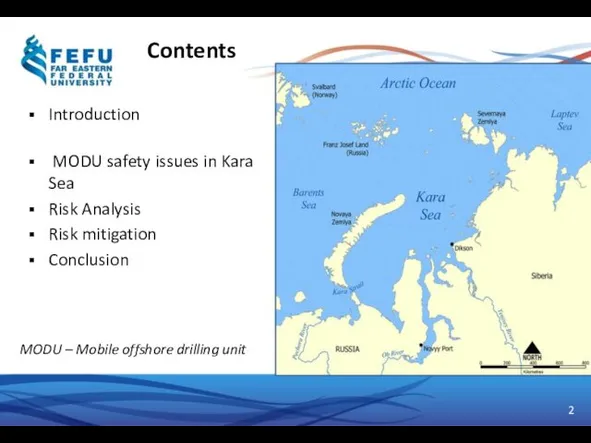
- 2. Contents Introduction MODU safety issues in Kara Sea Risk Analysis Risk mitigation Conclusion MODU – Mobile
- 3. Timeliness of the topic Oil and gas projects of exploration drilling in the Kara Sea are
- 4. State of knowledge Foreign methods for risk assessment are more diverse and approved for the exploitation
- 5. Goal: Introduction Improvement the of operation risk assessment of MODU in ice conditions Tasks: 1. Conduct
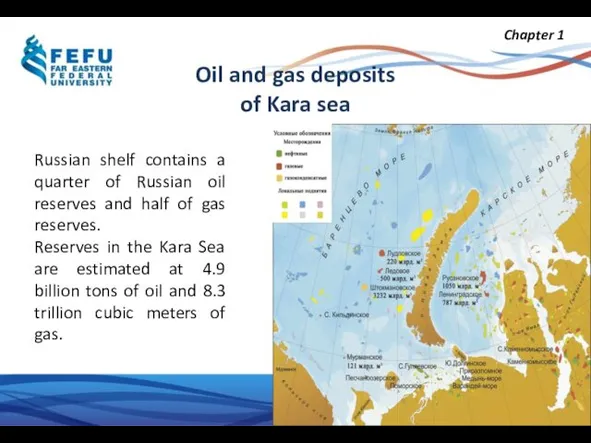
- 6. Russian shelf contains a quarter of Russian oil reserves and half of gas reserves. Reserves in
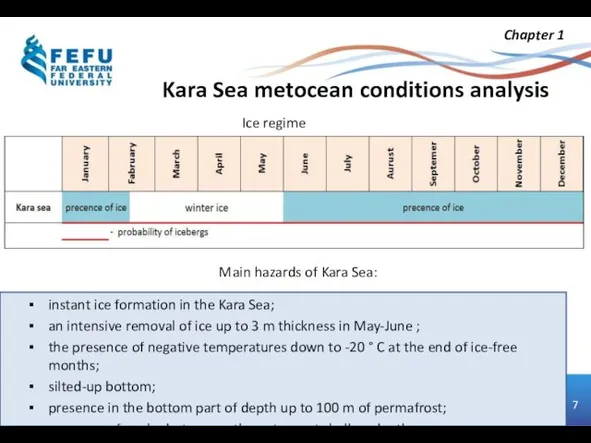
- 7. Kara Sea metocean conditions analysis Ice regime instant ice formation in the Kara Sea; an intensive
- 8. Configurations of MODUs for ice conditions Main factors for choosing the configuration: Depth of water External
- 9. Possible MODUs configurations for ice conditions Types of drilling units for ice conditions: a - egg-shaped;
- 10. The main problems of safety in the operation of MODU Construction safety of MODU is achieved
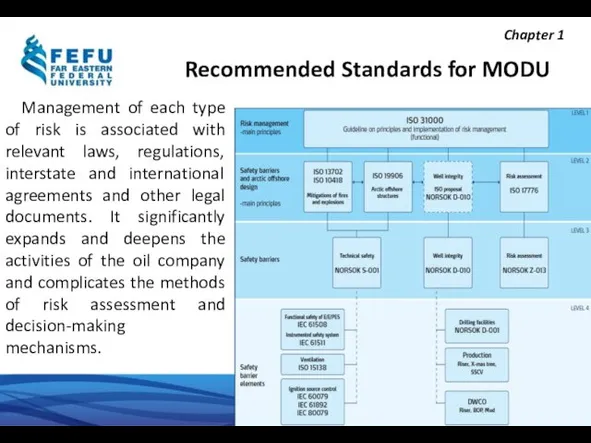
- 11. Recommended Standards for MODU Management of each type of risk is associated with relevant laws, regulations,
- 12. Methods of Risk Analysis Risk analysis methodologies: Checklist “What If” Analysis Hazard and Operability (HAZOP) Failure
- 13. Identification of hazards for MODU The hazards associated with offshore structures: Equipment-related Hazards Process-related Hazards Well-related
- 14. Identification of hazards for MODU Basic ice hazards: the passage of ice under the MODUs; impact
- 15. Initial data for risk assessment Chapter 2 1)Meteorology 2) Hydrology 3) Characterization of sites and structures
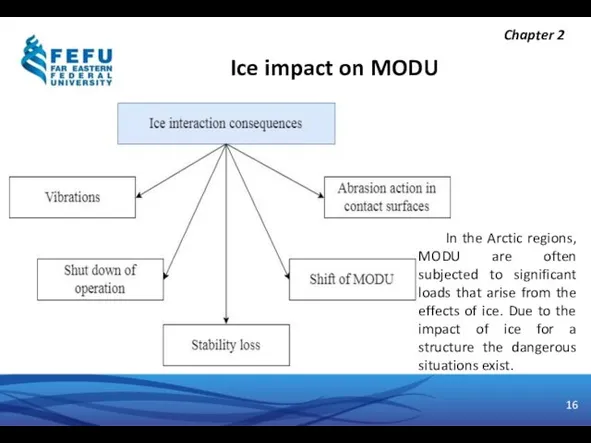
- 16. Ice impact on MODU Chapter 2 In the Arctic regions, MODU are often subjected to significant
- 17. Managed ice Chapter 2
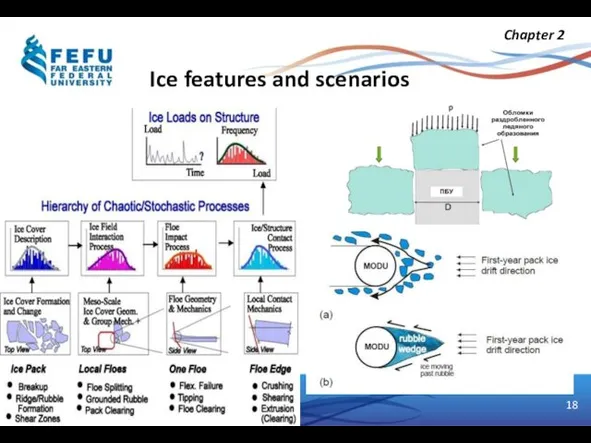
- 18. Ice features and scenarios Chapter 2
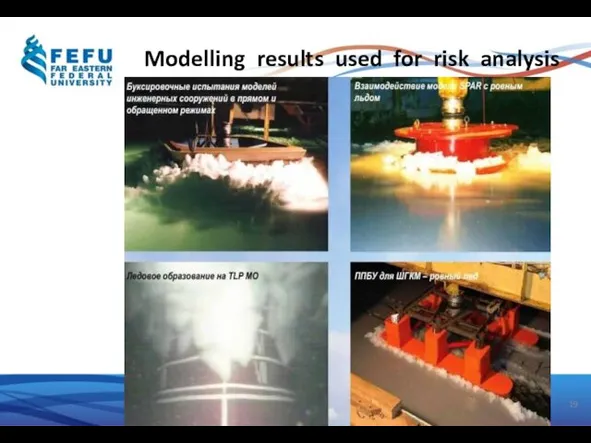
- 19. Modelling results used for risk analysis
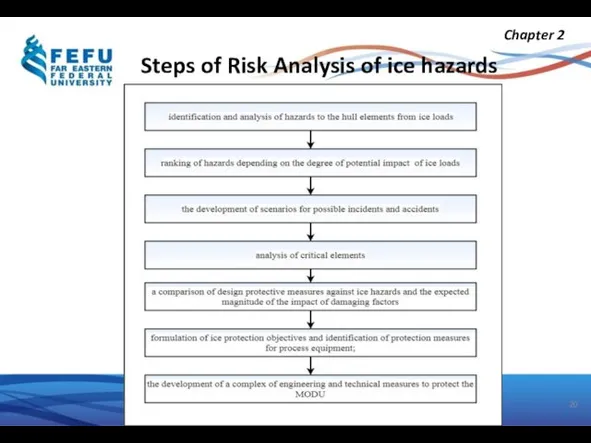
- 20. Steps of Risk Analysis of ice hazards Chapter 2
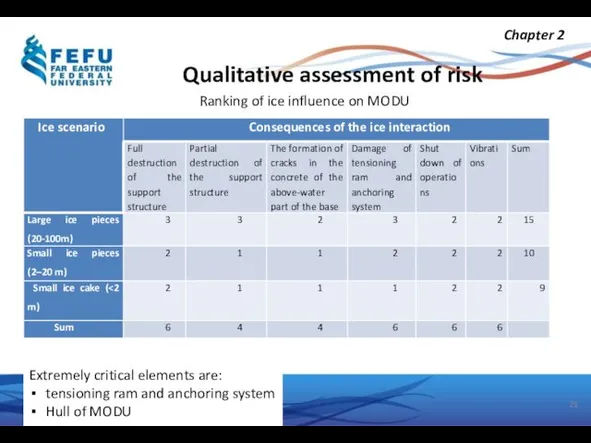
- 21. Qualitative assessment of risk Chapter 2 Ranking of ice influence on MODU Extremely critical elements are:
- 22. Chapter 2 Matrix of qualitative expert ranking of accidents, possible on MODU Qualitative assessment of risk
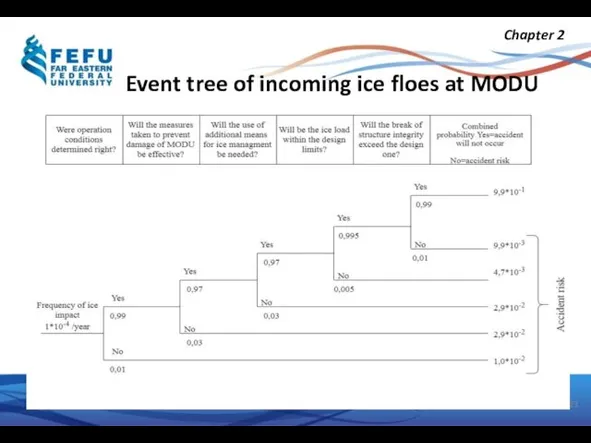
- 23. Event tree of incoming ice floes at MODU Chapter 2
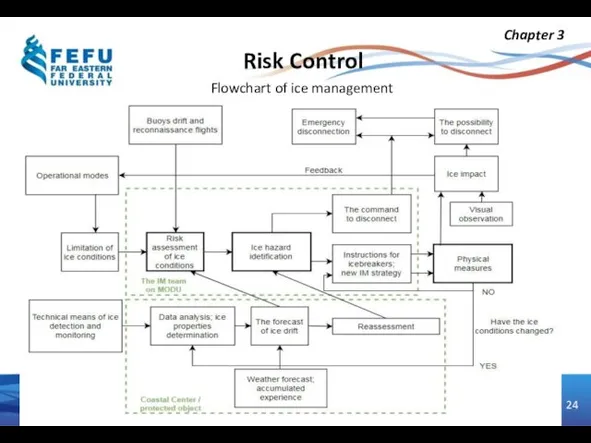
- 24. Risk Control Chapter 3 Flowchart of ice management
- 25. The recommendations on ice risks mitigation Chapter 3
- 26. The recommendations on ice risks mitigation To ensure safe operation of MODUs, it is necessary to
- 27. Conclusions Risk assessment for the operation of the MODU in ice conditions depends on defining how
- 29. Скачать презентацию














 Уго́рська Респу́бліка
Уго́рська Респу́бліка Каспий теңізі
Каспий теңізі Сообщества водных объектов. Определить название растения/животного
Сообщества водных объектов. Определить название растения/животного Моря, омывающие берега России
Моря, омывающие берега России Геотехника. Начало…
Геотехника. Начало… The Travel Bug
The Travel Bug Північна Дакота
Північна Дакота На севере Европы
На севере Европы Численность населения, его динамика и структура занятости
Численность населения, его динамика и структура занятости English-speaking countries
English-speaking countries Аналитическое счисление. Аналитический учет течения. Сущность аналитического счисления и вывод основных формул
Аналитическое счисление. Аналитический учет течения. Сущность аналитического счисления и вывод основных формул Хозяйство Восточной Сибири. 9 класс
Хозяйство Восточной Сибири. 9 класс География/ Лекция 1. Обзор курса. Введение. Различные виды карт
География/ Лекция 1. Обзор курса. Введение. Различные виды карт Золотое Кольцо. Кострома
Золотое Кольцо. Кострома Рельеф. Рельефообразующие процессы
Рельеф. Рельефообразующие процессы Горы Южной Сибири
Горы Южной Сибири Мировое хозяйство
Мировое хозяйство Почвенные исследования
Почвенные исследования Бразилия
Бразилия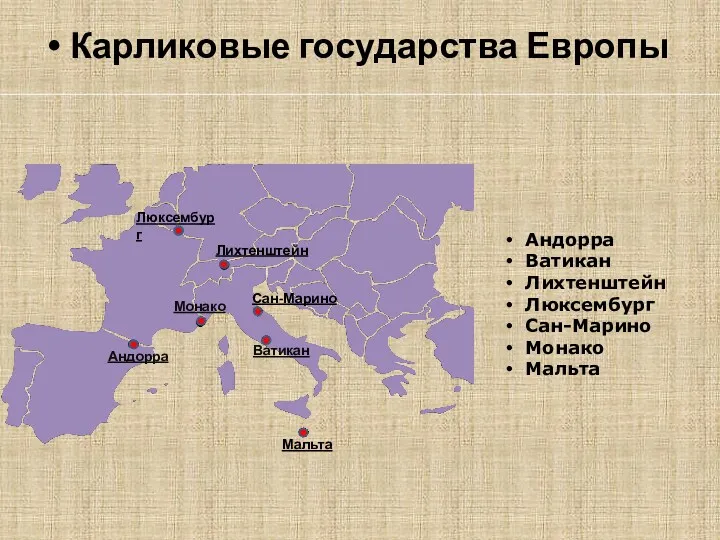 Карликовые государства Европы
Карликовые государства Европы Геометриялық нивелирлеудің мәні
Геометриялық нивелирлеудің мәні Тесты. ТЭК, металлургический комплекс
Тесты. ТЭК, металлургический комплекс Факторы, влияющие на климат России
Факторы, влияющие на климат России Готовимся к Всероссийской контрольной работе по географии 6 класс
Готовимся к Всероссийской контрольной работе по географии 6 класс Природные условия и ресурсы Дальнего Востока
Природные условия и ресурсы Дальнего Востока Атмосферное давление. Ветер
Атмосферное давление. Ветер Круговорот воды в природе
Круговорот воды в природе Hungarian soft powers
Hungarian soft powers