Содержание
- 2. Session 10 Part II
- 3. The North Atlantic Treaty Organization The International Atomic Energy Agency The World Bank and the International
- 4. established in 1949 to provide the assured concerted defence of each of its member states NATO
- 5. Yugoslavia 1999 - NATO undertook its largest military operation since its creation in 1949: Operation Allied
- 6. Since the “global war on terrorism” began in September 2001, NATO has sought to maintain its
- 7. 1997- the first wave of new members, including Poland, Hungary, and the Czech Republic, were admitted
- 8. During most of the 1990s (as well as these days), Russia oppose NATO enlargement, alarm at
- 9. UN-based agency established in 1957 to disseminate knowledge about nuclear energy and promote its peaceful uses,
- 10. Inspectors for the IAEA visited Iraqi sites after the 1991 Gulf War and North Korean sites
- 11. The end of the Cold War and the dismemberment of the Soviet Union have resulted in
- 12. In 2003 - North Korea publicly admitted that it was engaged in a nuclearweapons program and
- 13. In 2008, North Korea’s leader, Kim Jong-11, threatened to resume weapons development because the promised aid
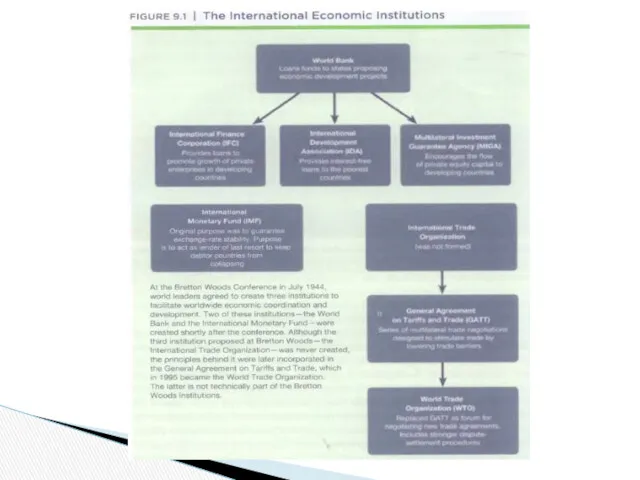
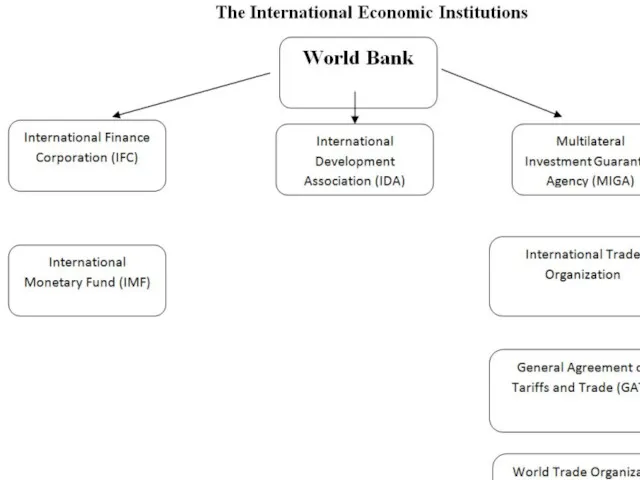
- 16. Support of trade liberalization, because trade is the engine for growth and economic development Nondiscrimination in
- 17. 1950s and 1960s - the bank adopted a strategy for development that emphasized the critical role
- 18. International Finance - the World Bank 1990s- sustainable development, an approach to economic development that incorporates
- 20. Karen A. Mingst, Ivan M. Arreguin-Toft. Essentials of International Relations. 5th Ed. 2010: New York: W.W.
- 22. Скачать презентацию

















 Победа Дональда Трампа
Победа Дональда Трампа Роль государства в обеспечении национальной безопасности Российской Федерации
Роль государства в обеспечении национальной безопасности Российской Федерации Особенности президентской системы в США
Особенности президентской системы в США Россия и СНГ (Содружество Независимых Государств)
Россия и СНГ (Содружество Независимых Государств) Идеология в структуре политического сознания
Идеология в структуре политического сознания Политические партии, политическое участие, гражданское общество
Политические партии, политическое участие, гражданское общество Традиции, парадигмы и споры в теории международных отношений. (Лекция 3)
Традиции, парадигмы и споры в теории международных отношений. (Лекция 3) Политика и власть
Политика и власть Україна - це ми!
Україна - це ми! Политическая реклама, как политический текст
Политическая реклама, как политический текст Elections in USA
Elections in USA Глобальный этнический кризис
Глобальный этнический кризис Introduction to comparative politics. Women’s movements
Introduction to comparative politics. Women’s movements Политика. Политическая сфера. Формы политической деятельности. Типы власти
Политика. Политическая сфера. Формы политической деятельности. Типы власти Демократия. Формы демократии
Демократия. Формы демократии Президент В.В.Путин
Президент В.В.Путин Ліберально-демократична партія України
Ліберально-демократична партія України Институциализация внешнеполитических органов Европейского союза
Институциализация внешнеполитических органов Европейского союза Политическое развитие и модернизация
Политическое развитие и модернизация Қазақстан Республикасының қазіргі таңдағы қоғамдық-саяси партиясы
Қазақстан Республикасының қазіргі таңдағы қоғамдық-саяси партиясы Государственная структура Китайской Народной республики (КНР)
Государственная структура Китайской Народной республики (КНР) Introduction to Comparative Politics
Introduction to Comparative Politics Понятие власти
Понятие власти Брежнев Леонид Ильич
Брежнев Леонид Ильич Critical Guide on Political Studies
Critical Guide on Political Studies Внешняя политика России
Внешняя политика России Актуальные проблемы в кадровой работе и их решение
Актуальные проблемы в кадровой работе и их решение Дипломатия как институт и инструмент внешней политики государства
Дипломатия как институт и инструмент внешней политики государства