Слайд 2

Social movements: focus on women
The feminist movement refers to a set
of political movements, cultural and economic factors that aimed at equal rights of women to men.
Слайд 3

Organizing women
- Gender Frames/repertoires
Maternal : women have biological differences and
distinct social roles. Engagement will focus on maternal, educational issues.
Equality: sameness with men, call for the same rights.
Feminine-expressive: women called into action by self-parodying feminine stereotypes. Ex: Femen?
Слайд 4

Organizing women 2
Gendered groups addressed non-gender specific issues: gun violence and
Iraq.
Hybrid gender org: an org where 2 different types of gender identities are combined: maternity and egalitarianism.
Hybridity makes it more difficult for opponents to discredit the movement.
Слайд 5

Three waves: the history of feminist movements
The first wave refers to the
feminist movement (18th- early 20th centuries), which fights by the women votes.
Ex: votes, right to property and education.
Momentum/opportunities: Industrialization, First and Second world wars.
Слайд 6

Suffragettes in the UK
1867: MP John Stuart Mill supports equality for
women in the Second Reform Act, but is defeated.
1903: The Women's Social and Political party, later referred to as the suffragettes, holds its first meeting.
1918: Representation of the People's Act allows women over 30 to vote.
1928: Women over 21 get the vote.
Слайд 7

The Suffragettes knew Jiu jitsu
Слайд 8

Слайд 9
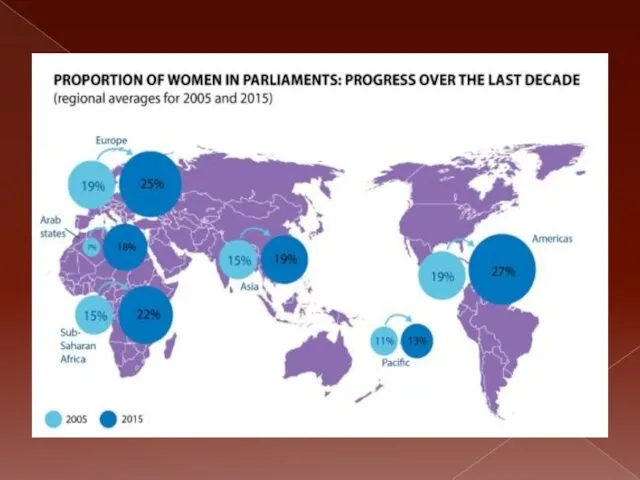
Слайд 10

Second-wave feminism
The second wave (1960s-1980s) is battle for social, cultural and
gender equality. Also called Woman's Liberation Movement.
Ex: domestic violence, cultural representation, contraception/abortion rights.
Momentum/opportunities: Women’s full employment, Vietnam war.
Слайд 11

Слайд 12











 Саяси режимдер
Саяси режимдер Қазіргі шешендіктің түрлері. Елбасы Н. Назарбаевтың “Тәуелсіздік толғауы” эссесі. Саяси - әлеуметтік мәні
Қазіргі шешендіктің түрлері. Елбасы Н. Назарбаевтың “Тәуелсіздік толғауы” эссесі. Саяси - әлеуметтік мәні Коммуникационные процессы в политической системе
Коммуникационные процессы в политической системе Гельмут Коль (Федеральный канцлер ФРГ 1982-1998 гг)
Гельмут Коль (Федеральный канцлер ФРГ 1982-1998 гг) Кадровая политика
Кадровая политика Rada Bezpieczenstwa ONZ
Rada Bezpieczenstwa ONZ Демократические выборы и политические партии. 10 класс
Демократические выборы и политические партии. 10 класс Политические партии и партийные системы
Политические партии и партийные системы Демократия, её основные ценности и признаки
Демократия, её основные ценности и признаки Саяси қақтығыс
Саяси қақтығыс Евромайдан. Революция от начала и до конца
Евромайдан. Революция от начала и до конца Democracy by mistake
Democracy by mistake Политика и власть
Политика и власть Соціальна та молодіжна політика в Португалії
Соціальна та молодіжна політика в Португалії Система управления в Древней Греции
Система управления в Древней Греции Послание Главы Казахстана Касым - Жомарт Токаева к народу Казахстана
Послание Главы Казахстана Касым - Жомарт Токаева к народу Казахстана L’actualité en France. Club de discussion
L’actualité en France. Club de discussion Политическая культура и политическое сознание
Политическая культура и политическое сознание Политическая сфера. Политика и власть
Политическая сфера. Политика и власть Демократия, её основные признаки и ценности
Демократия, её основные признаки и ценности Политика и власть
Политика и власть Государство, как политический институт
Государство, как политический институт Политические изменения
Политические изменения Політичні вибори
Політичні вибори Структура системы международных отношений. Тема 7
Структура системы международных отношений. Тема 7 Политические отношения и политический процесс
Политические отношения и политический процесс США в Африке после 1945 года
США в Африке после 1945 года Діни экстремизм.Терроризм
Діни экстремизм.Терроризм