Содержание
- 2. Agenda Basic Information How to include JS Code into HTML Comments Variables Data Types Type Casting
- 3. Basic Information about JavaScript
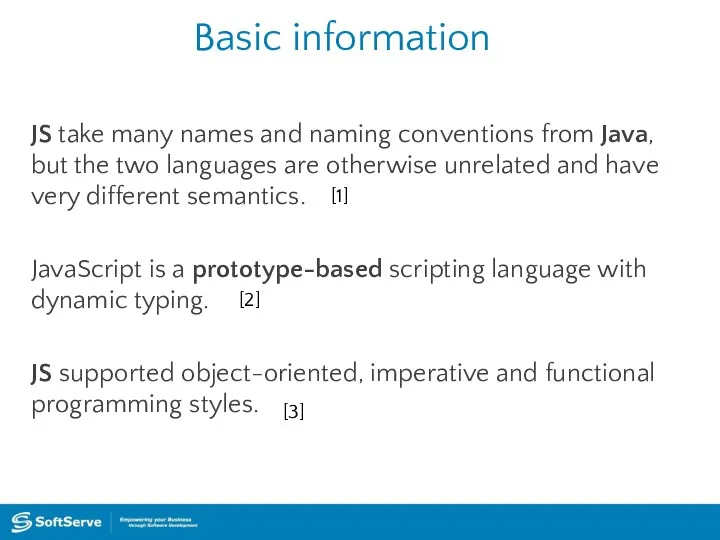
- 4. Basic information JavaScript - dynamic computer programming language. It is most commonly used as part of
- 5. Basic information JS take many names and naming conventions from Java, but the two languages are
- 6. How to include JS Code into HTML
- 7. Including of JavaScript Exist three ways to include script into HTML page: Inline in HTML Inside
- 8. Inline including …. Unfortunately, this is the worst solution. Holistic code will be broken into smaller
- 9. Inside tag f() ; Sometimes it makes sense. But in the general case, page size will
- 10. In separate file This is the best way. Code is holistic. It’s easy to test and
- 11. Comments
- 12. Comments Comments - part of the program text which will be ignored by language interpreter The
- 13. Variables
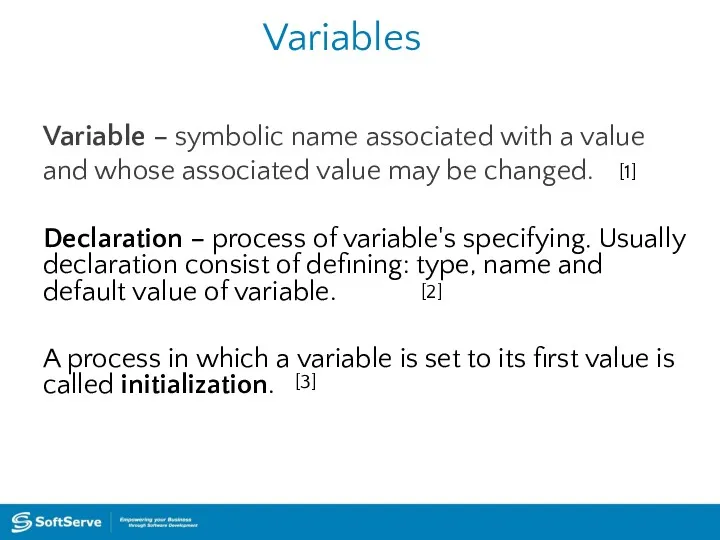
- 14. Variables Variable – symbolic name associated with a value and whose associated value may be changed.
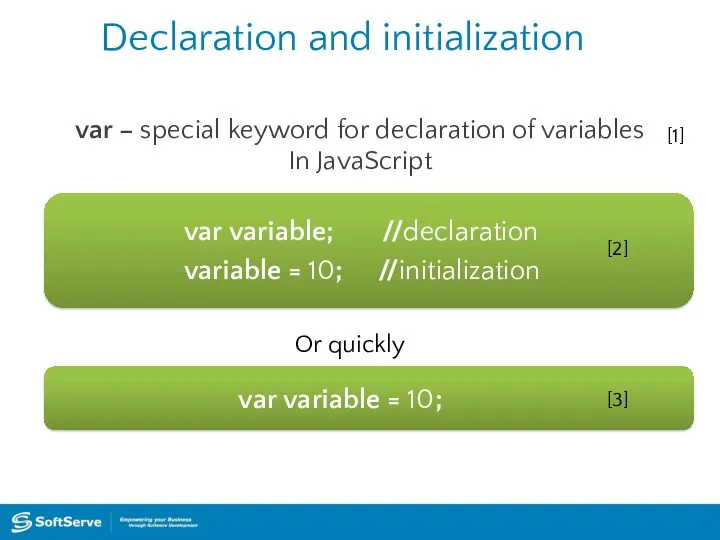
- 15. Declaration and initialization var – special keyword for declaration of variables In JavaScript var variable; //declaration
- 16. Global and local JavaScript has two types of variables: global - exist in memory and is
- 17. Data Types
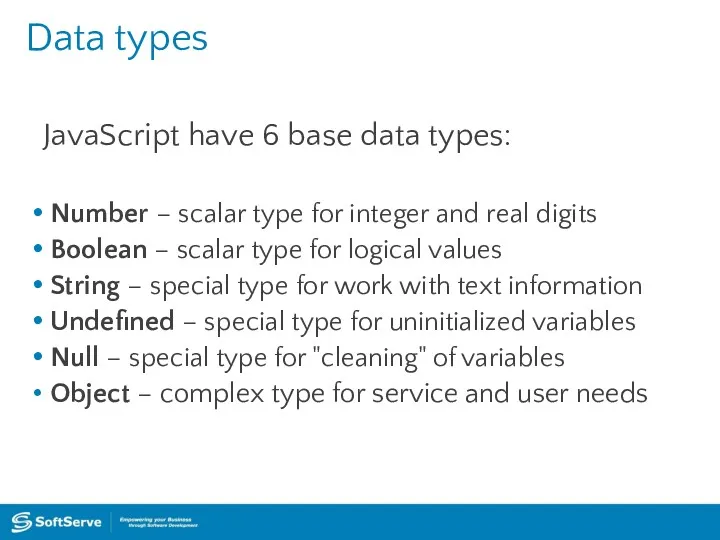
- 18. Data types JavaScript have 6 base data types: Number – scalar type for integer and real
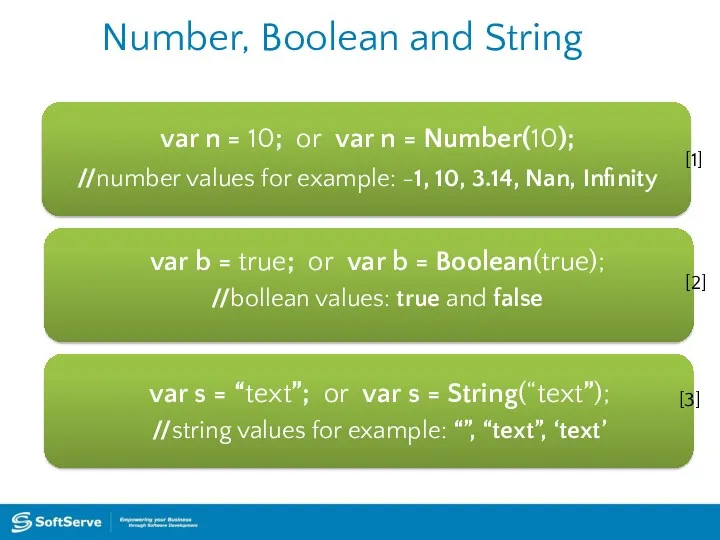
- 19. Number, Boolean and String var n = 10; or var n = Number(10); //number values for
- 20. Null and Undefined var n = null; //null variables can have only null value var u;
- 21. Type Casting
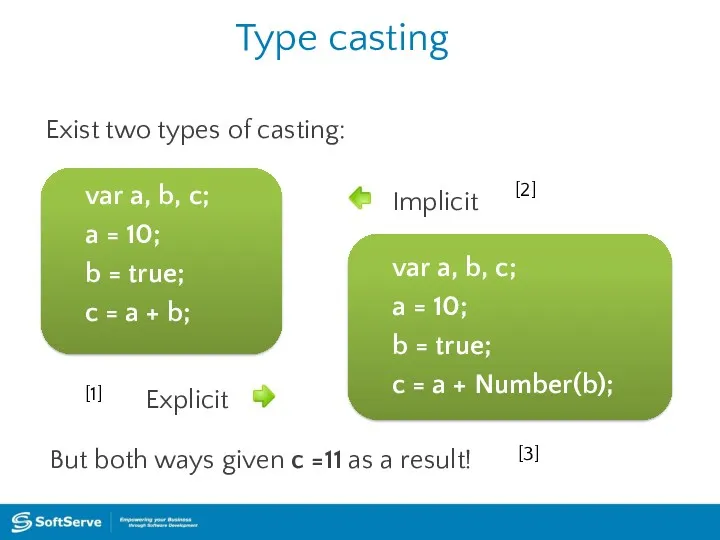
- 22. Type casting var a, b, c; a = 10; b = true; c = a +
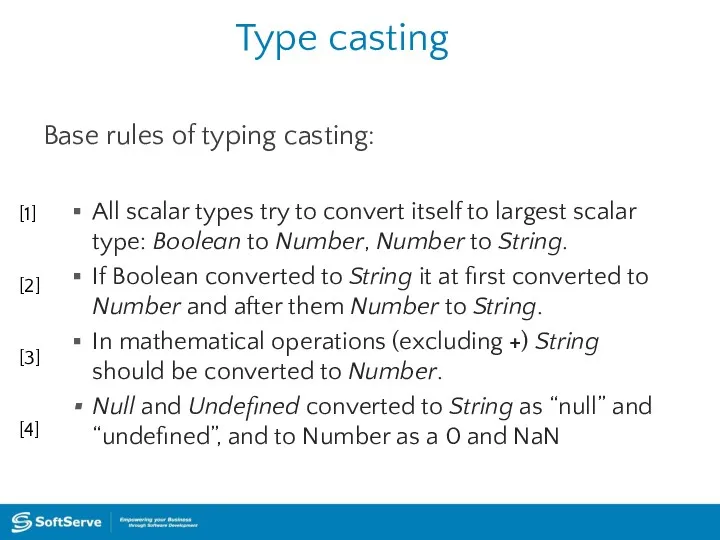
- 23. Type casting Base rules of typing casting: All scalar types try to convert itself to largest
- 24. Functions in JS
- 25. Basic Information In mathematics: In classical programming [3] Function is a relation between a set of
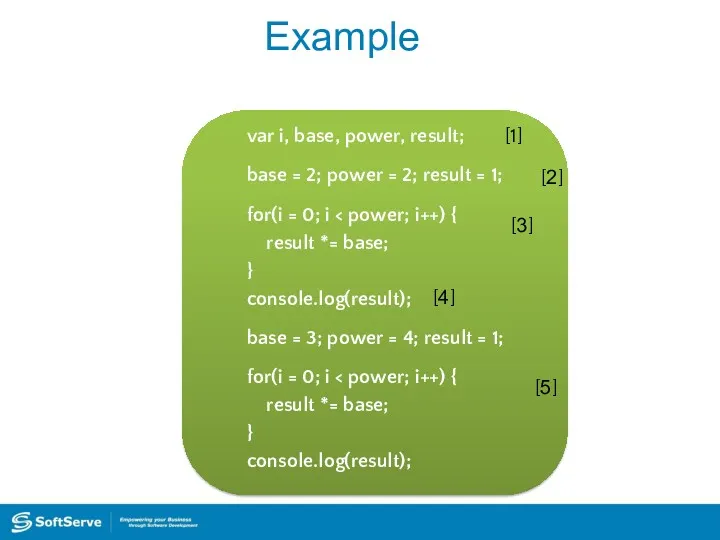
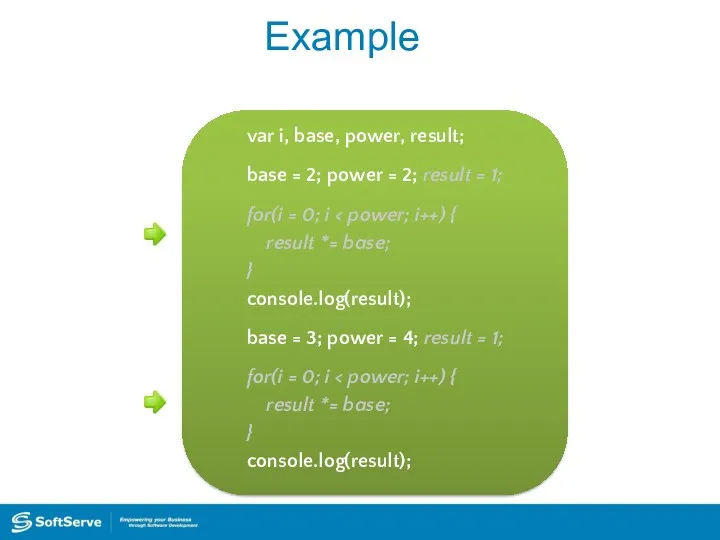
- 26. Example var i, base, power, result; base = 2; power = 2; result = 1; for(i
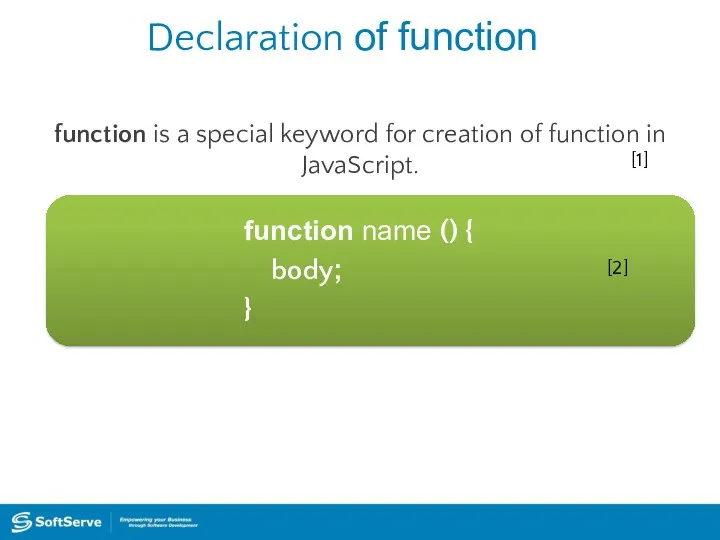
- 27. Declaration of function function is a special keyword for creation of function in JavaScript. function name
- 28. Example var i, base, power, result; base = 2; power = 2; result = 1; for(i
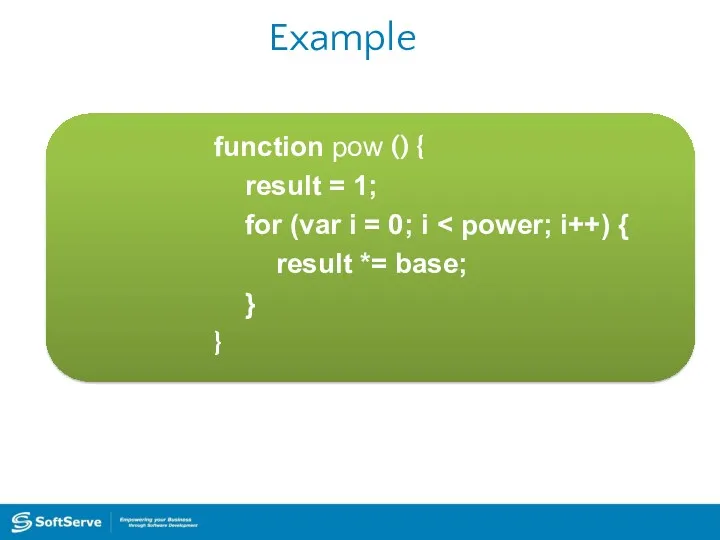
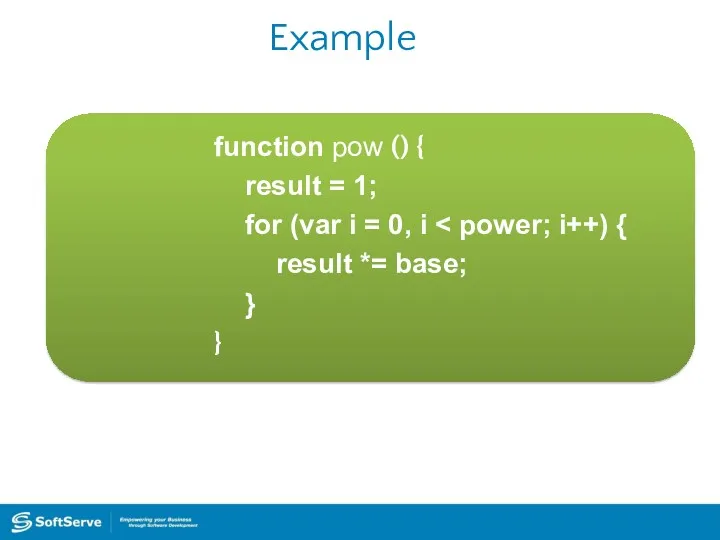
- 29. Example function pow () { result = 1; for (var i = 0; i result *=
- 30. Function call Call - operation for execution of function. ( ) – operator for this action.
- 31. Example var base, power, result; base = 2; power = 2; pow(); console.log(result); base = 3;
- 32. Input and Output
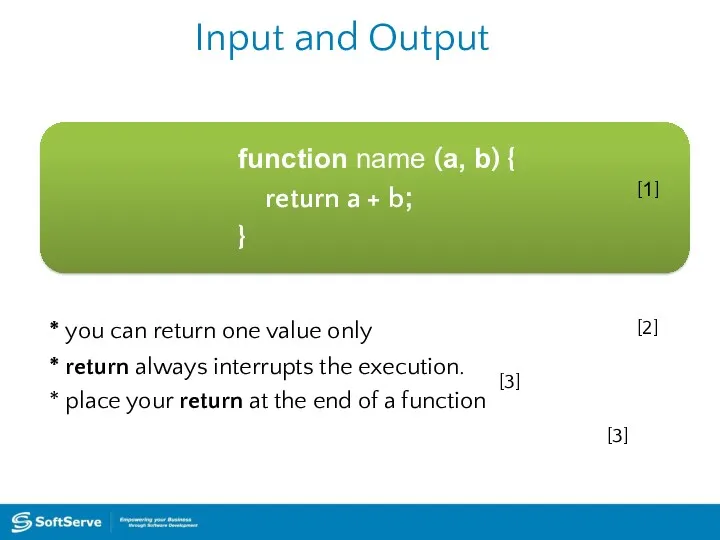
- 33. Input and Output function name (a, b) { return a + b; } [1] * you
- 34. Example function pow () { result = 1; for (var i = 0, i result *=
- 35. Example function pow (base, power) { var result = 1; for (var i = 0, i
- 36. Example var out; out = pow(2, 2); console.log(out); out = pow(3, 4); console.log(out); function pow (base,
- 37. JS Code Processing
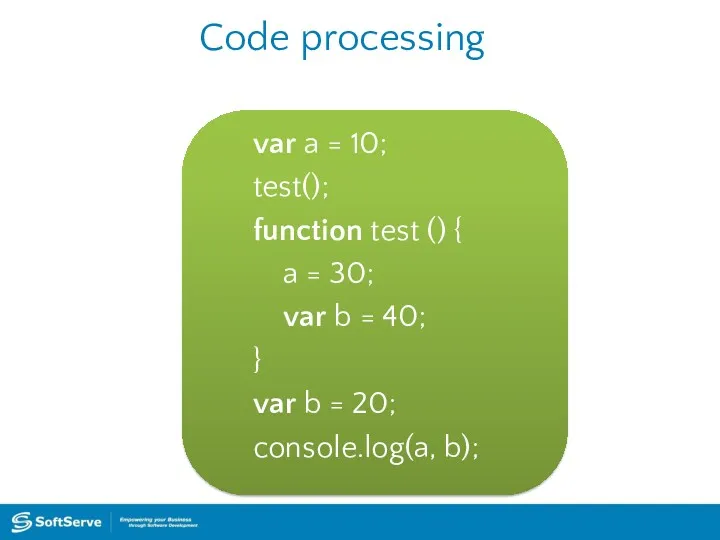
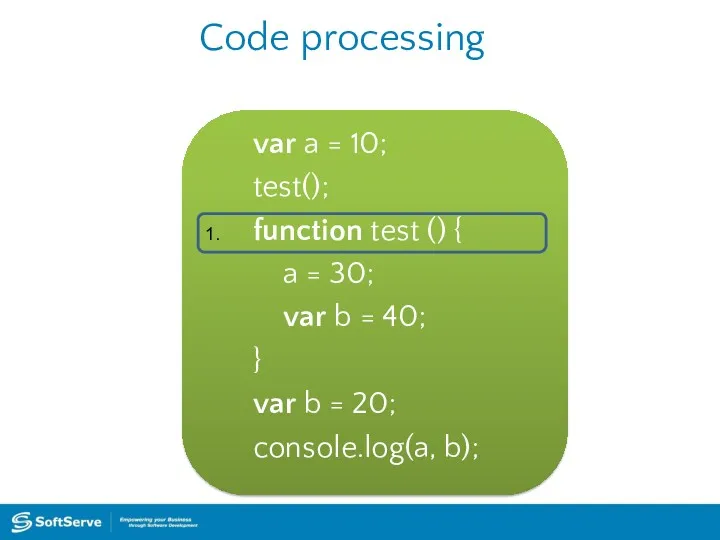
- 38. Code processing var a = 10; test(); function test () { a = 30; var b
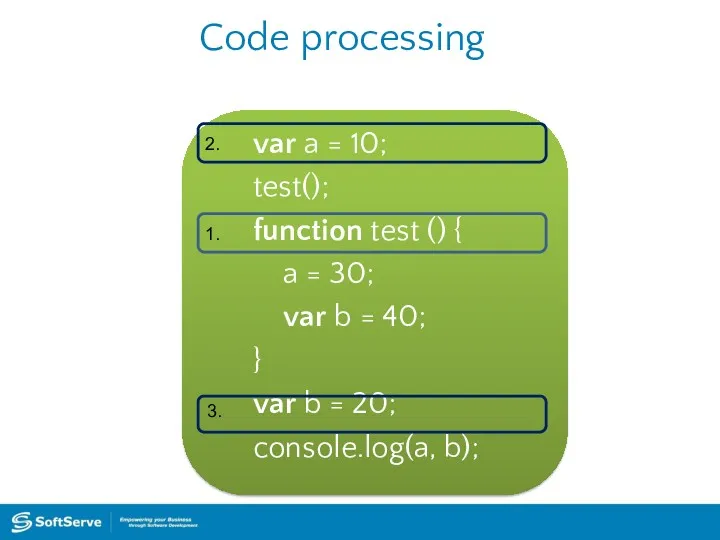
- 39. Code processing var a = 10; test(); function test () { a = 30; var b
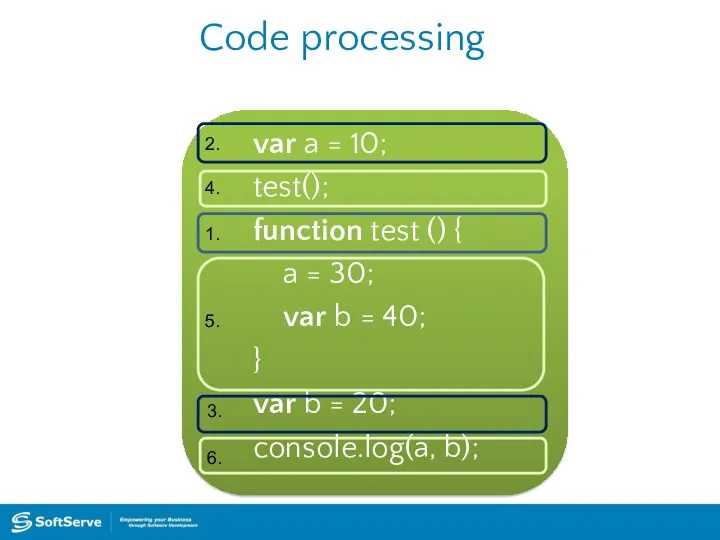
- 40. Code processing var a = 10; test(); function test () { a = 30; var b
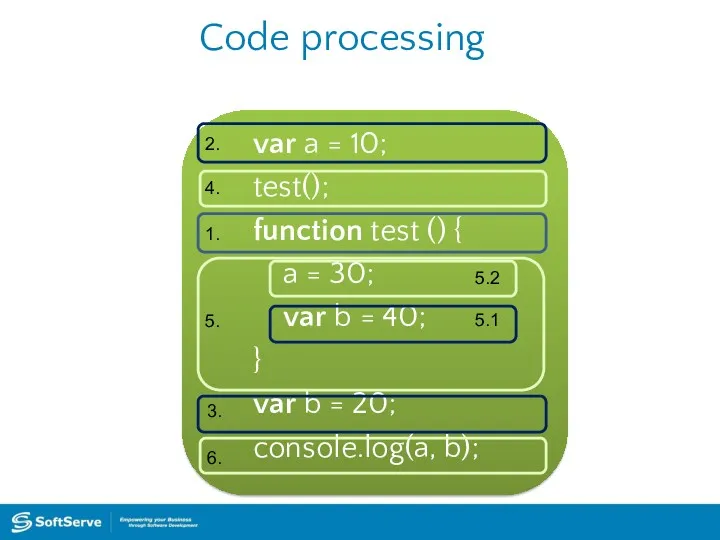
- 41. Code processing var a = 10; test(); function test () { a = 30; var b
- 42. Code processing var a = 10; test(); function test () { a = 30; var b
- 43. Declaration and Expression
- 44. Declaration and Expression function name () { body; } [1] var name = function () {
- 45. Additional Facts About Functions Functions in JavaScript are Objects. As a result, functions are accessible by
- 46. Practice Task
- 48. Скачать презентацию














![Basic Information In mathematics: In classical programming [3] Function is](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/205834/slide-24.jpg)





![Declaration and Expression function name () { body; } [1]](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/205834/slide-43.jpg)


 Построение запросов в СУБД Access
Построение запросов в СУБД Access Компьютерные энциклопедии и справочники
Компьютерные энциклопедии и справочники Создание 3D эффектов для фотоизображений
Создание 3D эффектов для фотоизображений 11 класс подготовка к ЕГЭ по информатике. Задание С1
11 класс подготовка к ЕГЭ по информатике. Задание С1 OOP with C#. Introduction C#. Data Types. Variables, expressions, statements. C# decision and iteration constructs
OOP with C#. Introduction C#. Data Types. Variables, expressions, statements. C# decision and iteration constructs 328818
328818 Имитация объема в Photoshop
Имитация объема в Photoshop Средства программирования для компьютеров с распределённой памятью
Средства программирования для компьютеров с распределённой памятью Файлы в С++
Файлы в С++ Обработка текстовой информации
Обработка текстовой информации Основы работы в Outlook 2013
Основы работы в Outlook 2013 Метод координат
Метод координат Методы и средства проектирования ПО. Введение
Методы и средства проектирования ПО. Введение ВКР: Разработка информационной системы управления заявками клиентов в магазине бытовой техники и электроники
ВКР: Разработка информационной системы управления заявками клиентов в магазине бытовой техники и электроники Призначення клавіш
Призначення клавіш Работа со звуком
Работа со звуком Программирование на языке Python (10 класс)
Программирование на языке Python (10 класс) Алгоритмы с повторением
Алгоритмы с повторением Игра Безопасный Интернет
Игра Безопасный Интернет Управление репутацией в социальных сетях и СМИ
Управление репутацией в социальных сетях и СМИ Конфигурация персонального компьютера. Лекция № 2
Конфигурация персонального компьютера. Лекция № 2 Разработка информационной системы учета предоставляемых услуг Центра научно-технической информации
Разработка информационной системы учета предоставляемых услуг Центра научно-технической информации Истинность и ложность высказываний
Истинность и ложность высказываний Моделирование в проектировании многофункциональных инфокоммуникационных систем и систем связи
Моделирование в проектировании многофункциональных инфокоммуникационных систем и систем связи Внешние сортировки
Внешние сортировки С#. Тема 2. Структурированные типы данных. Двумерные массивы
С#. Тема 2. Структурированные типы данных. Двумерные массивы Фасад. Патерни проектування
Фасад. Патерни проектування Готовим инфографику
Готовим инфографику