Содержание
- 2. Agenda Arrays While For Break, continue Search item in the array Sorting Practical tasks
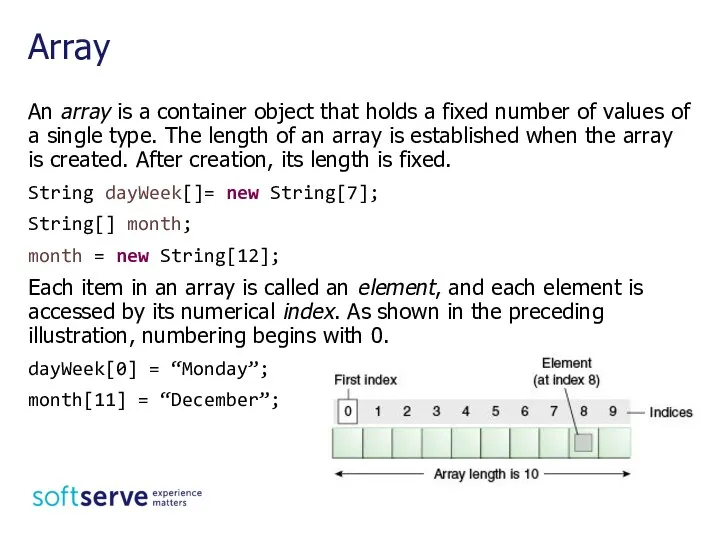
- 3. An array is a container object that holds a fixed number of values of a single
- 4. int month_days[ ] = {31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31}
- 5. char twod1[ ][ ]= new char[3][4]; char[ ][ ] twod2= new char[3][4]; double m[ ][ ]=
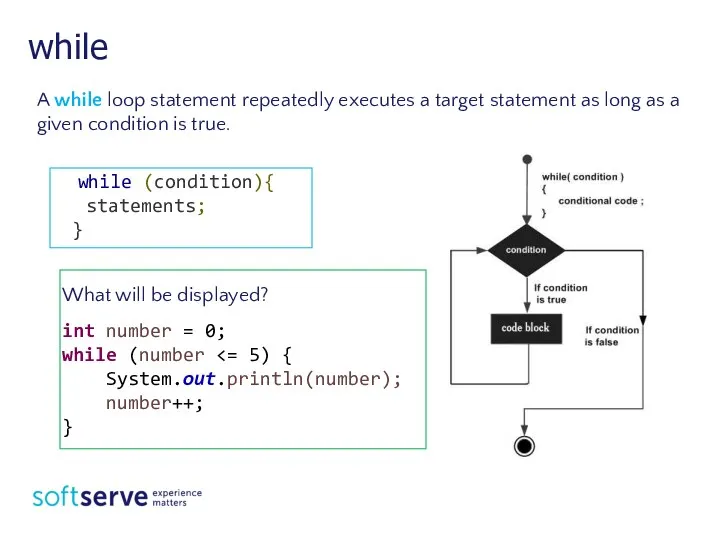
- 6. while A while loop statement repeatedly executes a target statement as long as a given condition
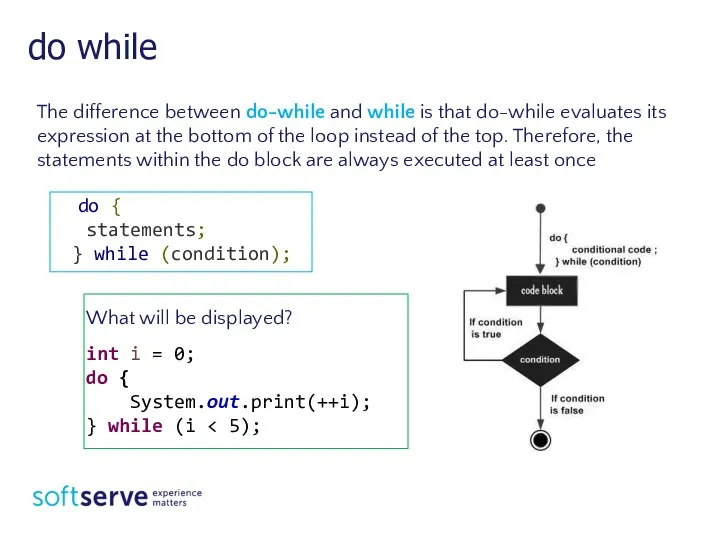
- 7. do while The difference between do-while and while is that do-while evaluates its expression at the
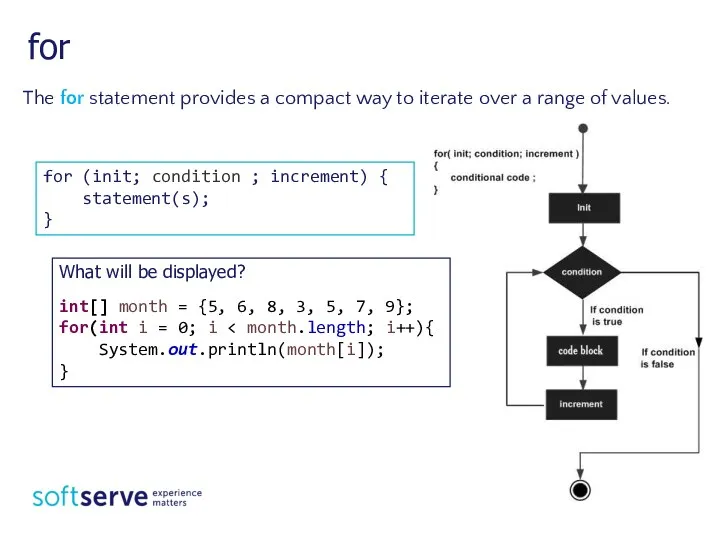
- 8. The for statement provides a compact way to iterate over a range of values. for What
- 9. for for (type variable : collection) { statement(s); } int[] workHours = { 8, 6, 8,
- 10. break The break statement terminates the for, while and do-while loop. What will be displayed? Scanner
- 11. continue The continue statement skips the current iteration the for, while and do-while loop. What will
- 12. There’s an array int[] arr = {2, -5, 7, -4, 8}; What will results after running
- 13. Minimum, maximum ... There’s an array int[] arr = {2, -5, 7, -4, 8}; What will
- 14. Sorting There’s an array int[] arr = {2, -5, 7, -4, 8}; What will results after
- 15. Create an array of ten integers. Display the biggest of these numbers; the sum of positive
- 16. HomeWork (online course) UDEMY course "Java Tutorial for Complete Beginners": https://www.udemy.com/java-tutorial/ Complete lessons 8, 9, 12,
- 17. Ask user to enter the number of month. Read the value and write the amount of
- 19. Скачать презентацию

![int month_days[ ] = {31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30,](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/398755/slide-3.jpg)
![char twod1[ ][ ]= new char[3][4]; char[ ][ ] twod2=](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/398755/slide-4.jpg)
![for for (type variable : collection) { statement(s); } int[]](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/398755/slide-8.jpg)


![There’s an array int[] arr = {2, -5, 7, -4,](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/398755/slide-11.jpg)
![Minimum, maximum ... There’s an array int[] arr = {2,](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/398755/slide-12.jpg)
![Sorting There’s an array int[] arr = {2, -5, 7,](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/398755/slide-13.jpg)



 Data types and databases
Data types and databases Формы мышления. Логика
Формы мышления. Логика Основные принципы построения компьютеров
Основные принципы построения компьютеров Дерево игры. Поиск выигрышной стратегии
Дерево игры. Поиск выигрышной стратегии Голосовой помощник Маруся. Кто такая Маруся и что она умеет?
Голосовой помощник Маруся. Кто такая Маруся и что она умеет? Типы компьютеров
Типы компьютеров Функции АСУ ТП
Функции АСУ ТП Интерактивная образовательная платформа
Интерактивная образовательная платформа Отчеты в MS ACCESS
Отчеты в MS ACCESS Звіт з практики. Видавництво Мамине сонечко
Звіт з практики. Видавництво Мамине сонечко Информация измерение
Информация измерение ГОСТ Р ИСО/МЭК 12207. Лекция №3
ГОСТ Р ИСО/МЭК 12207. Лекция №3 Платформы для дистанционного обучения
Платформы для дистанционного обучения Интернет-сервис Антиплагиат. Ру
Интернет-сервис Антиплагиат. Ру ПрезентацияУрок - игра по теме Закрепление пройденного. 11 класс
ПрезентацияУрок - игра по теме Закрепление пройденного. 11 класс Вложенные циклы. Решение задач
Вложенные циклы. Решение задач Машинно-зависимые языки и основы компиляции
Машинно-зависимые языки и основы компиляции Программно-технические системы реализации информационных процессов
Программно-технические системы реализации информационных процессов Особенности разработки требований к ПО. (Лекция 1)
Особенности разработки требований к ПО. (Лекция 1) ИКТ – компетентность участников образовательного процесса
ИКТ – компетентность участников образовательного процесса Устройство персонального компьютера
Устройство персонального компьютера Редактор презентаций Power Point. (Часть 1)
Редактор презентаций Power Point. (Часть 1) Компетентнісна задача з інформатики
Компетентнісна задача з інформатики 1. Introduction to Java Language. 2. Java SDK & IDE
1. Introduction to Java Language. 2. Java SDK & IDE Формализациялау жөніндетүсінік, инфармацияны формализациялаудың негізгі тұрлері: формула, мәтін, кесте граф, алгоритм
Формализациялау жөніндетүсінік, инфармацияны формализациялаудың негізгі тұрлері: формула, мәтін, кесте граф, алгоритм Презентация к уроку
Презентация к уроку Атрибуты deftemplate
Атрибуты deftemplate Основные понятия операционной системы
Основные понятия операционной системы