Содержание
- 2. Agenda Array System.Collections Hashtables Stack, Queue SortedList Collection Interfaces System.Collections.Generic List
- 3. Array is a data structure that contains several variables of the same type. type [ ]
- 4. int[] a = new int[5]; int [,] myMatrix=new int [6,8]; a[0] = 17; a[1] = 32;
- 5. Multidimensional arrays: string [ , ] names = new string[5,4]; Array-of-arrays (jagged): byte [ ][ ]
- 6. Array. Benefits. Limitations Benefits of Arrays: Easy to use: arrays are used in almost every programming
- 7. System.Collections. ArrayList System.Collections namespace ArrayList, HashTable, SortedList, Queue, Stack: A collection can contain an unspecified number
- 8. ArrayList is a special array that provides us with some functionality over and above that of
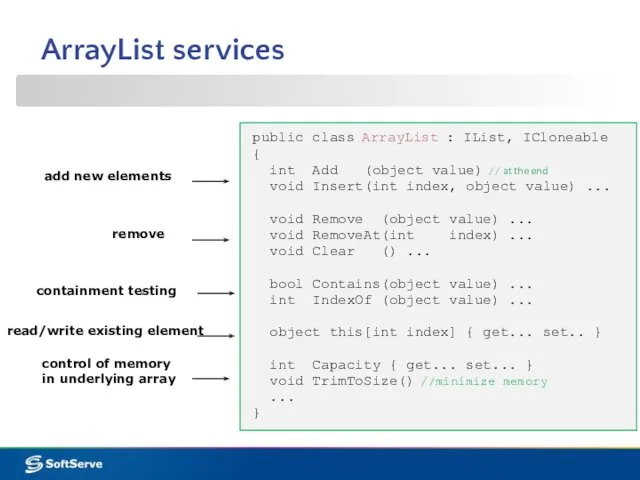
- 9. ArrayList services public class ArrayList : IList, ICloneable { int Add (object value) // at the
- 10. ArrayList. Benefits and Limitation Benefits of ArrayList: Supports automatic resizing. Inserts elements: An ArrayList starts with
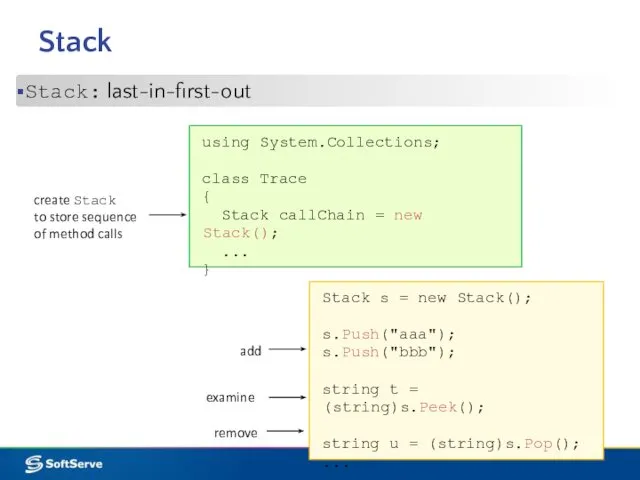
- 11. Stack Stack: last-in-first-out
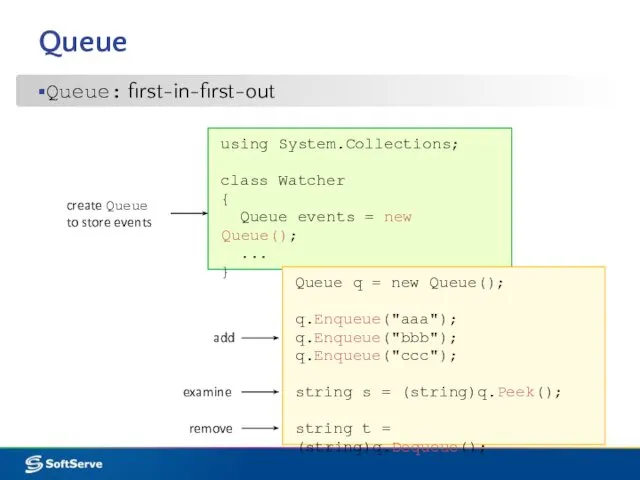
- 12. Queue Queue: first-in-first-out using System.Collections; class Watcher { Queue events = new Queue(); ... } create
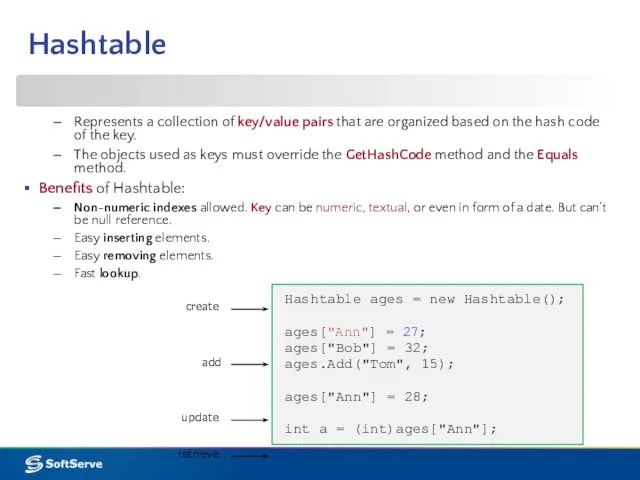
- 13. Hashtable Represents a collection of key/value pairs that are organized based on the hash code of
- 14. Hashtable Limitations of Hashtable: Performance and speed: Hashtable objects are slower to update but faster to
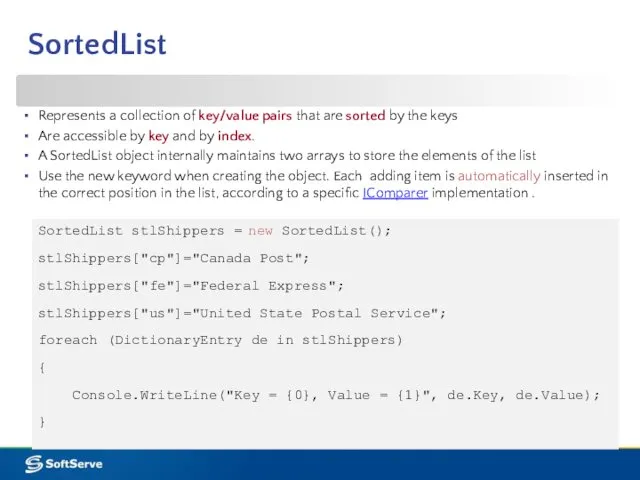
- 15. SortedList Represents a collection of key/value pairs that are sorted by the keys Are accessible by
- 16. [SerializableAttribute] [ComVisibleAttribute(true)] public class SortedList : IDictionary, ICollection, IEnumerable, ICloneable {…} SortedList
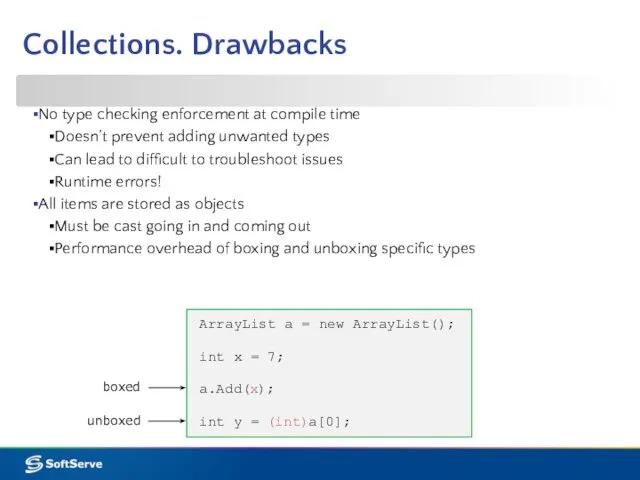
- 17. Collections. Drawbacks No type checking enforcement at compile time Doesn’t prevent adding unwanted types Can lead
- 18. System.Collections.Generic Open constructed types Classes defined without a specific type Type is specified when instantiated Provides
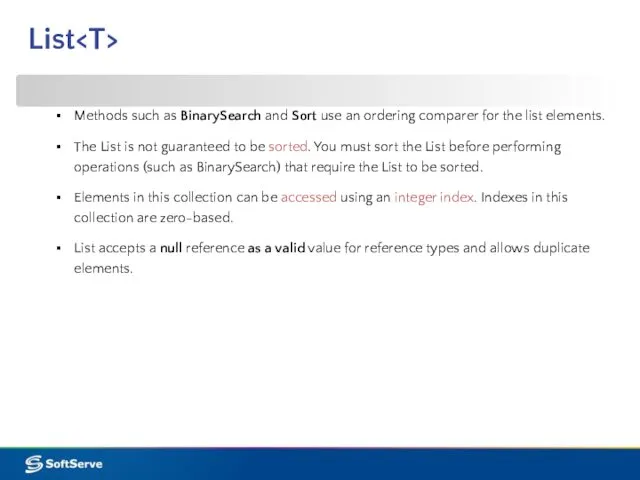
- 19. List List generic class: [SerializableAttribute] public class List : IList , ICollection , IEnumerable , IList,
- 20. Methods such as BinarySearch and Sort use an ordering comparer for the list elements. The List
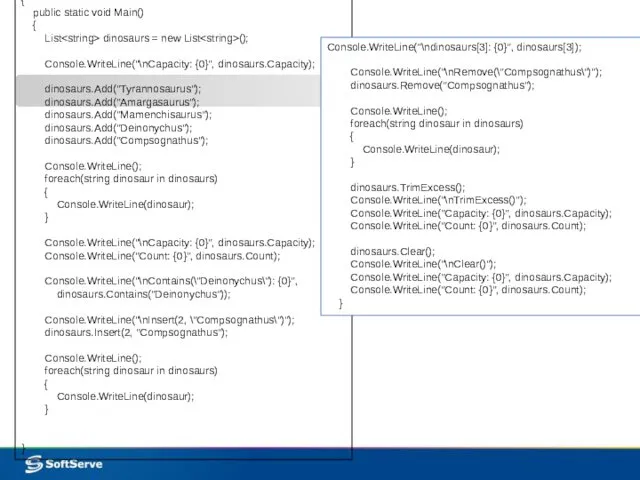
- 21. using System; using System.Collections.Generic; public class Example { public static void Main() { List dinosaurs =
- 23. Скачать презентацию


![int[] a = new int[5]; int [,] myMatrix=new int [6,8];](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/2562/slide-3.jpg)
![Multidimensional arrays: string [ , ] names = new string[5,4];](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/2562/slide-4.jpg)





![[SerializableAttribute] [ComVisibleAttribute(true)] public class SortedList : IDictionary, ICollection, IEnumerable, ICloneable {…} SortedList](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/2562/slide-15.jpg)

![List List generic class: [SerializableAttribute] public class List : IList](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/2562/slide-18.jpg)
 История информатики
История информатики Настройка сети Windows 7
Настройка сети Windows 7 ELC PBA September 2018
ELC PBA September 2018 Windows Movie Maker
Windows Movie Maker Область видимости и время жизни программы. (Лекция 8)
Область видимости и время жизни программы. (Лекция 8) Архитектура Web-баз данных. Лекция 3.19
Архитектура Web-баз данных. Лекция 3.19 INSTAGRAM – магазин нижнего белья
INSTAGRAM – магазин нижнего белья Операции и стандартные функции Turbo Pascal 7.0
Операции и стандартные функции Turbo Pascal 7.0 Cистема управления версиями Git
Cистема управления версиями Git Эти люди изменили мир
Эти люди изменили мир ГИС Панорама. Разработка программного обеспечения и архитектура геоинформационных систем
ГИС Панорама. Разработка программного обеспечения и архитектура геоинформационных систем Сравнительный анализ дизайна сайтов
Сравнительный анализ дизайна сайтов Самообразование – одна из форм повышения профессионального мастерства педагога
Самообразование – одна из форм повышения профессионального мастерства педагога Отчет по учебной практике ПМ08. Разработка дизайна веб-приложений
Отчет по учебной практике ПМ08. Разработка дизайна веб-приложений Аналіз складних об’єктів і систем. Аналітичні дослідження
Аналіз складних об’єктів і систем. Аналітичні дослідження Multithreading IO Streams Java Core
Multithreading IO Streams Java Core Урок информатики по учебнику Плаксина М.А. темаКак работать с компьютером 3 класс
Урок информатики по учебнику Плаксина М.А. темаКак работать с компьютером 3 класс Возможности программы КОМПАС 3D
Возможности программы КОМПАС 3D Основы боевой подготовки. Лекция №10
Основы боевой подготовки. Лекция №10 Школа подготовки технических администраторов. Домены, хостинги, сайты. (Занятие 11)
Школа подготовки технических администраторов. Домены, хостинги, сайты. (Занятие 11) Presentation template
Presentation template Programming Logic and Design, Seventh Edition
Programming Logic and Design, Seventh Edition Основные понятия объектно-ориентированного языка программирования
Основные понятия объектно-ориентированного языка программирования Первый канал
Первый канал Язык Python в школьном курсе информатики
Язык Python в школьном курсе информатики Решение расчётной задачи в среде электронной таблицы EXCEL
Решение расчётной задачи в среде электронной таблицы EXCEL Маркировка. Поддержка в 1С. Практика автоматизации с пользой для бизнеса
Маркировка. Поддержка в 1С. Практика автоматизации с пользой для бизнеса Моделирование 9 класс
Моделирование 9 класс