Содержание
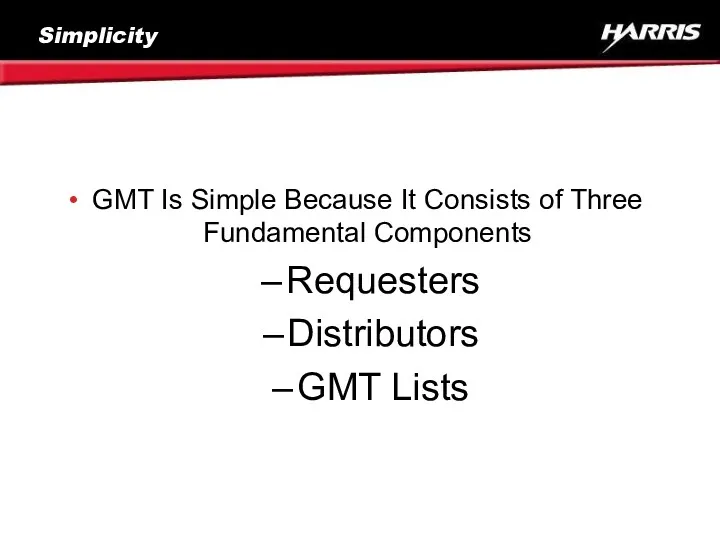
- 2. Simplicity GMT Is Simple Because It Consists of Three Fundamental Components
- 3. Simplicity GMT Is Simple Because It Consists of Three Fundamental Components Requesters
- 4. Simplicity GMT Is Simple Because It Consists of Three Fundamental Components Requesters Distributors
- 5. Simplicity GMT Is Simple Because It Consists of Three Fundamental Components Requesters Distributors GMT Lists
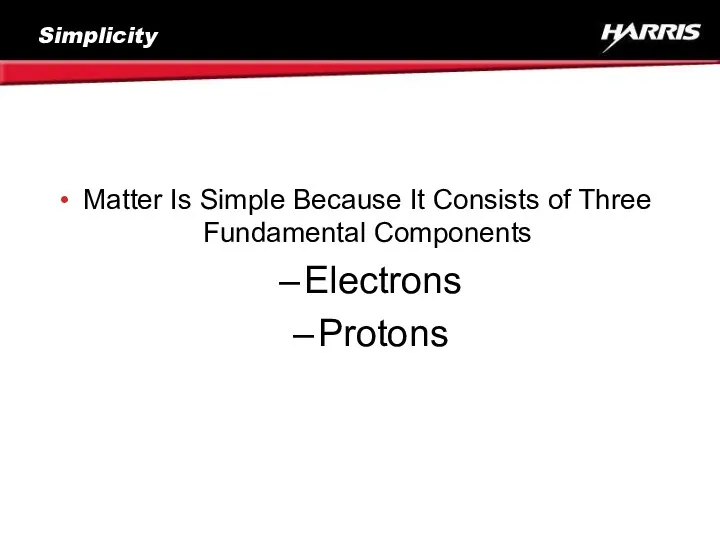
- 6. Simplicity Matter Is Simple Because It Consists of Three Fundamental Components
- 7. Simplicity Matter Is Simple Because It Consists of Three Fundamental Components Electrons
- 8. Simplicity Matter Is Simple Because It Consists of Three Fundamental Components Electrons Protons
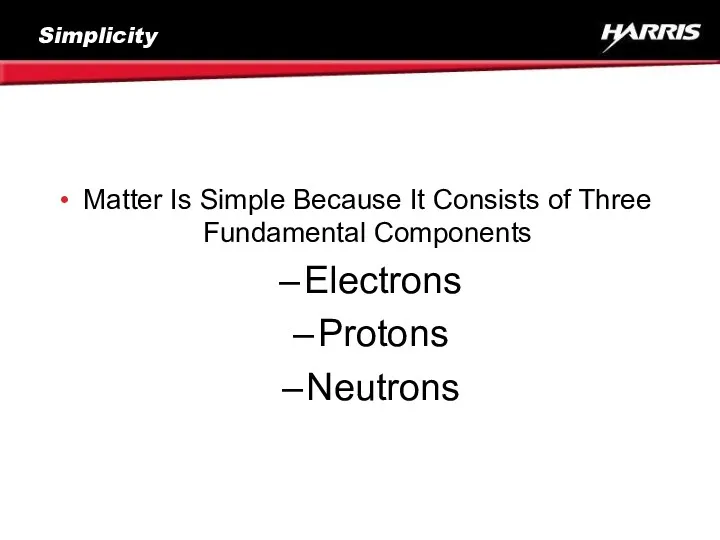
- 9. Simplicity Matter Is Simple Because It Consists of Three Fundamental Components Electrons Protons Neutrons
- 10. Simplicity Therefore Understanding GMT Is Simple In the Same Way That Understanding Sub-Atomic Particle Physics Is
- 11. So… Let’s Look at These Little Buggers
- 12. Requesters Are Assigned to a Transmission List Should Be Higher Channel Than Other Devices Can Be
- 13. Requesters Filter Requests Same Parameters As Disk’s Record Qualifiers SOM Filtering for Baseband Filtering is Available
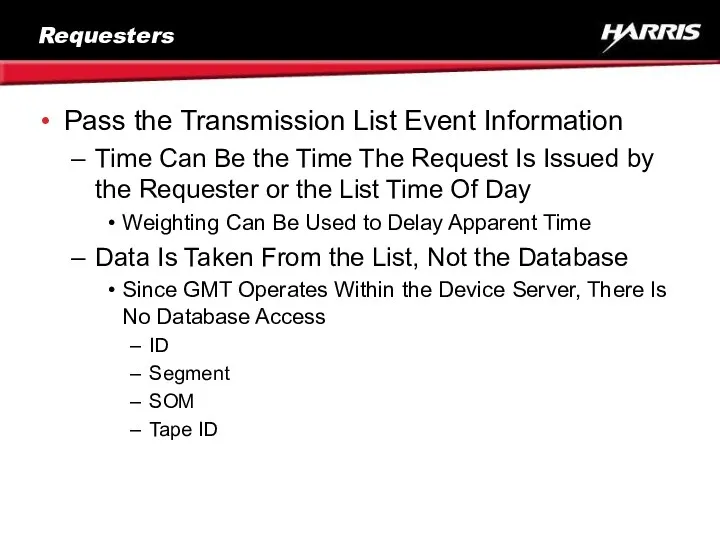
- 14. Requesters Pass the Transmission List Event Information Time Can Be the Time The Request Is Issued
- 15. Requesters Maintain Collection of Pending Requests Collection Size Displayed in ID Field of Device Status Window
- 16. Requesters Define Destination for Transfers Encoder Port of Disk Fibre Handle of Disk Archive Transfer Destinations
- 17. Requesters Point to a Specific Distributor Can Make Requests for Multiple Transfer Modes Baseband Fibre Archive
- 18. Distributors Are Assigned to a GMT List Support Only One Transfer Mode Baseband Fibre Archive The
- 19. Distributors Build Collection of Unprocessed Requests There Is No Available View of Distributor Collections There Is
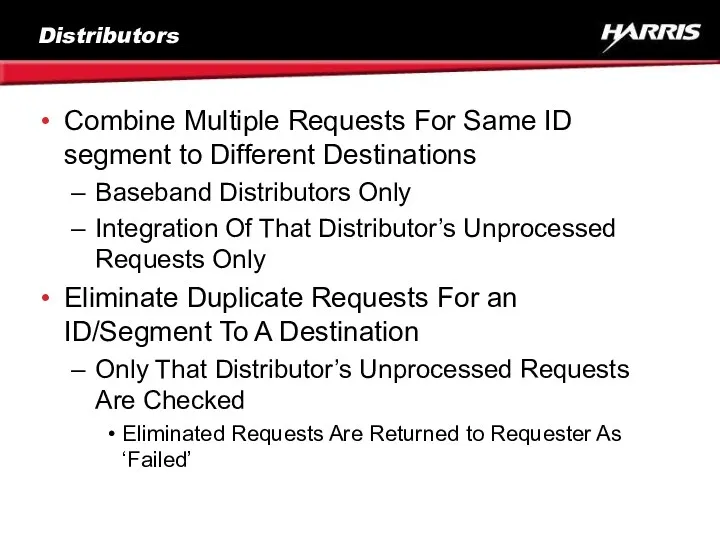
- 20. Distributors Combine Multiple Requests For Same ID segment to Different Destinations Baseband Distributors Only Integration Of
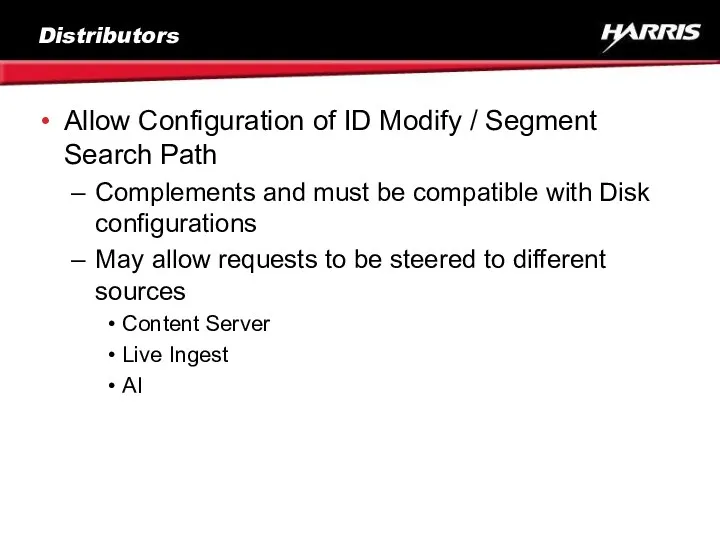
- 21. Distributors Allow Configuration of ID Modify / Segment Search Path Complements and must be compatible with
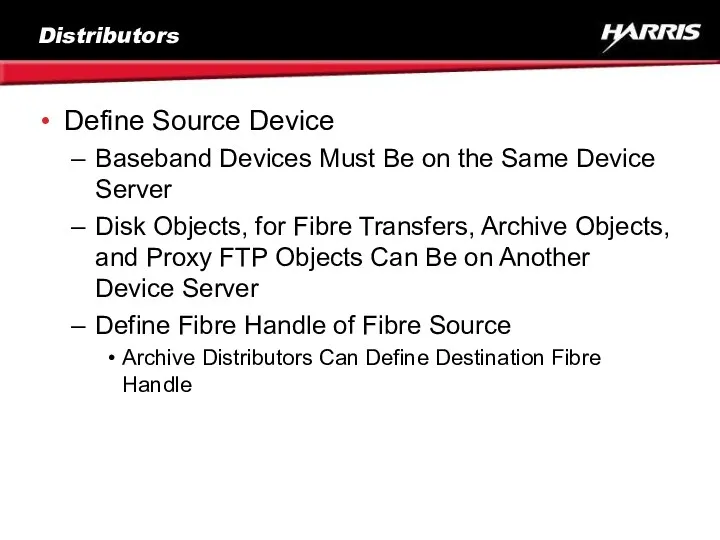
- 22. Distributors Define Source Device Baseband Devices Must Be on the Same Device Server Disk Objects, for
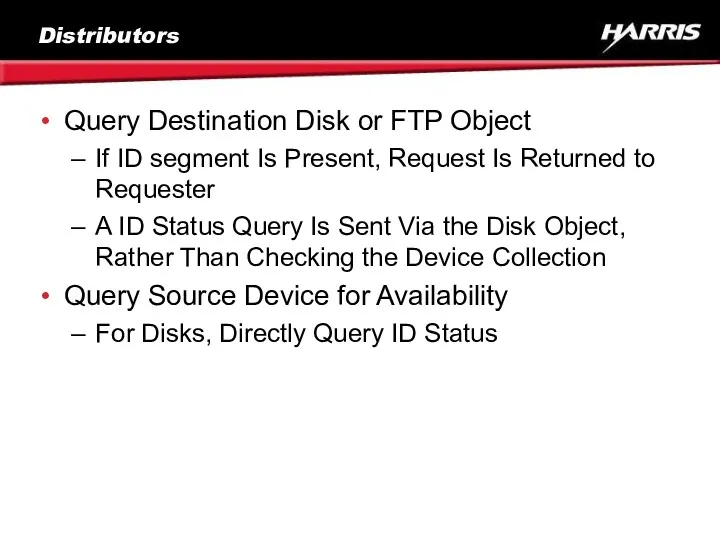
- 23. Distributors Query Destination Disk or FTP Object If ID segment Is Present, Request Is Returned to
- 24. Distributors If ID Segment Is Not Available If ‘Wait for Missing Media’ Is Enabled, Event Is
- 25. Distributors Build Events on GMT List Fibre, Archive, and FTP Events Are Single Events Containing a
- 26. Distributors Build Events on GMT List Baseband Transfers Consist of a Primary Event to Play Back
- 27. Distributors Build Events on GMT List Baseband Playback Events Are Built Unregistered Baseband Record Events Are
- 28. Distributors Build Events on GMT List Duration of Fibre and Archive Events Is Non-Deterministic For Requests
- 29. Distributors Build Events on GMT List All Other Information From The Transmission List Event Is Copied
- 30. Distributors Once A Request Is Processed, It Is Deleted From the Distributor’s Collection This Takes Place
- 31. Distributors Once A Request Is Processed, It Is Deleted From the Distributor’s Collection This Takes Place
- 32. Distributors Once A Request Is Processed, It Is Not Deleted From the Distributor’s Collection If ‘Wait
- 33. Distributors Once A Request Is Processed, It Is Not Deleted From the Distributor’s Collection If ‘Wait
- 34. Distributors When an Event Runs on the GMT List, It Is Again Added to the Distributor’s
- 35. GMT Lists Are Non-Sequential, Non-timed Lists List Automatically Threads and Runs Events Can Run Out of
- 36. GMT Lists Are Non-Sequential, Non-timed Lists Event Time and Thus Ordering May Be Time of Request
- 37. GMT Lists Certain Devices Are Assigned These Devices Must Be on the Same Device Server As
- 38. GMT Lists Certain Devices Are Not Assigned and May Be on a Different Device Server Than
- 39. GMT Lists Events Register and Run Depending on Their Type Fibre Events Utilize a Distributor If
- 40. GMT Lists Events Register and Run Depending on Their Type Transfer Command Is Issued to Disk
- 41. GMT Lists Events Register and Run Depending on Their Type The Destination Disk Is Queried If
- 42. GMT Lists Events Register and Run Depending on Their Type There Is No Method for Determining
- 43. GMT Lists Events Register and Run Depending on Their Type When the Disk Indicates a Transfer
- 44. GMT Lists Events Register and Run Depending on Their Type Archive Events Utilize a Distributor As
- 45. GMT Lists Events Register and Run Depending on Their Type Transfer Command Is Issued to the
- 46. GMT Lists Events Register and Run Depending on Their Type The Archive Will Return a Failure
- 47. GMT Lists Events Register and Run Depending on Their Type When the Archive Indicates Transfer Is
- 48. GMT Lists Events Register and Run Depending on Their Type Baseband Events Are Registered and Run
- 49. GMT Lists Events Register and Run Depending on Their Type Baseband Events Are Registered and Run
- 50. GMT Lists Events Register and Run Depending on Their Type Encoders Are Cued on the Lowest
- 51. GMT Lists A Single GMT List Can Support Multiple Simultaneous Processes Multiple GMT Lists May Be
- 52. Simplicity See, Wasn’t That Simple!
- 53. GMT’s Function GMT Is Demand Driven It Operates Solely to Fulfill Requests Success Is Measured by
- 54. Requester Output A Requester Will Normally Generate Requests As Fast As Events Enter the Lookahead of
- 55. Requester Output A Requester Will Normally Generate Requests As Fast As Events Enter the Lookahead of
- 56. Requester Output When a Playlist Is Loaded or Appended, Multiple Requests Can Be Generated at Once
- 57. Requester Output Inserting, Pasting, or Dropping Multiple Events Into the Lookahead Can Cause Multiple Requests to
- 58. Multi-Requester Output Multi-Requesters Have All of the Behaviors of a Requesters Multiple Requests Are Made for
- 59. Air / Protect Requests A Distributor Fed by Requesters Associated With a Transmission List’s Air and
- 60. Distributor Throughput Regardless of the Rate at Which They Receive Requests, Distributors Always Process and Pass
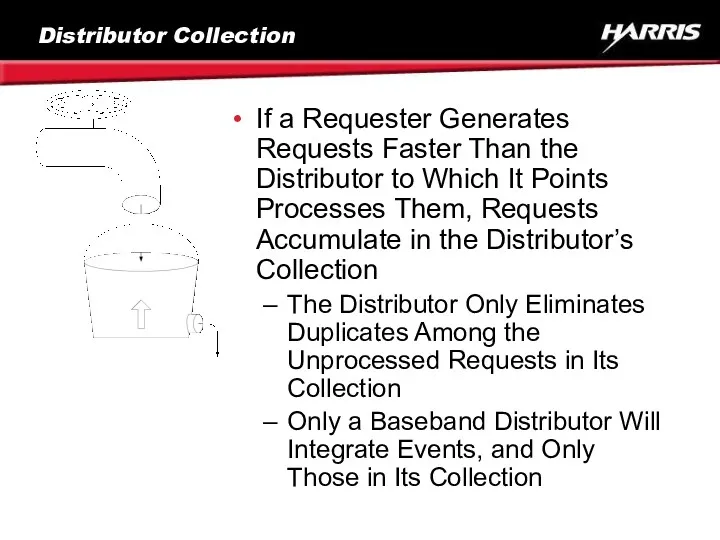
- 61. Distributor Collection If a Requester Generates Requests Faster Than the Distributor to Which It Points Processes
- 62. Distributor Collection If Excessive Requests Accumulate in a Distributor’s Collection, an Overflow Occurs Each Distributor Maintains
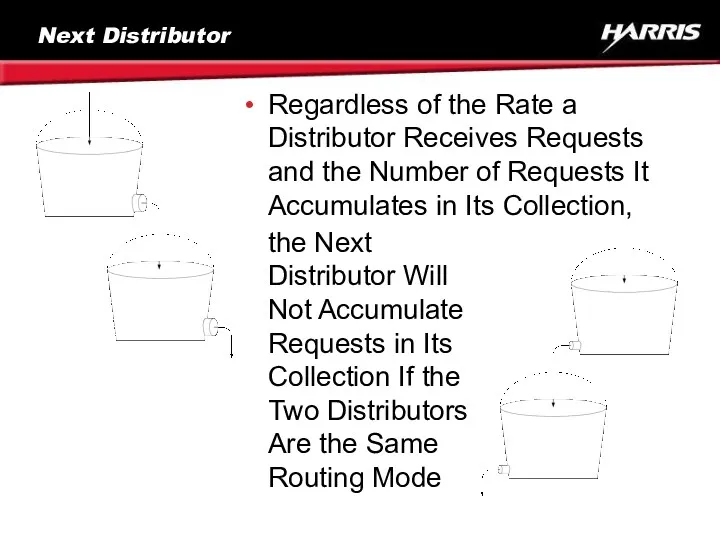
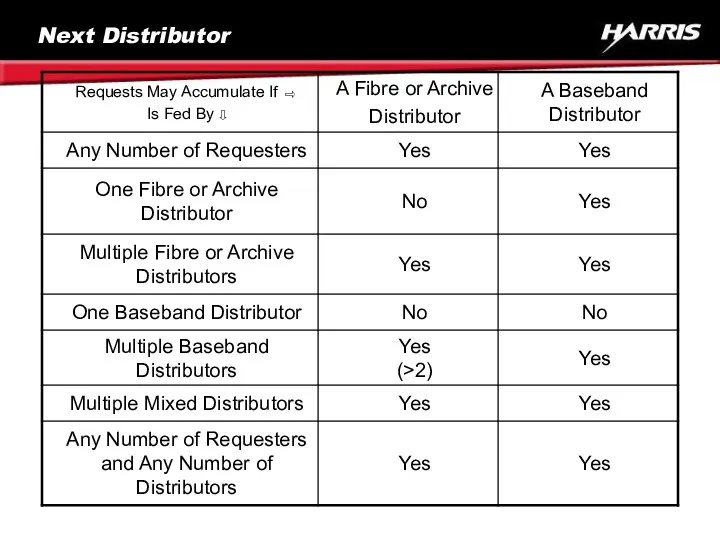
- 63. Next Distributor Regardless of the Rate a Distributor Receives Requests and the Number of Requests It
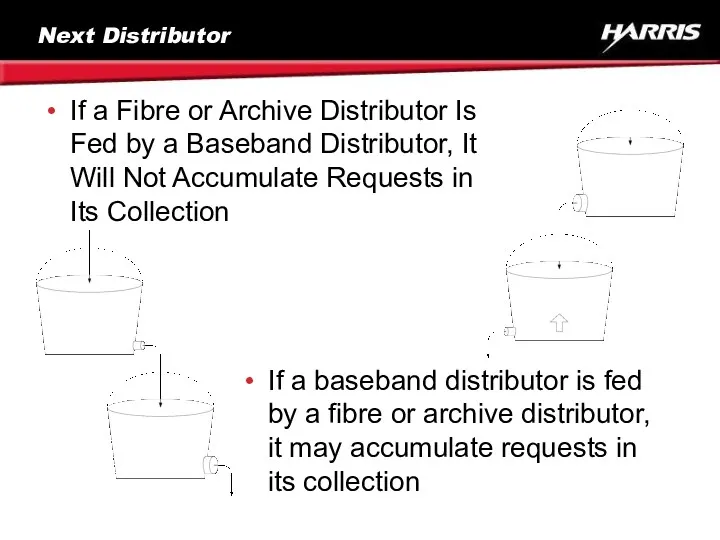
- 64. Next Distributor If a Fibre or Archive Distributor Is Fed by a Baseband Distributor, It Will
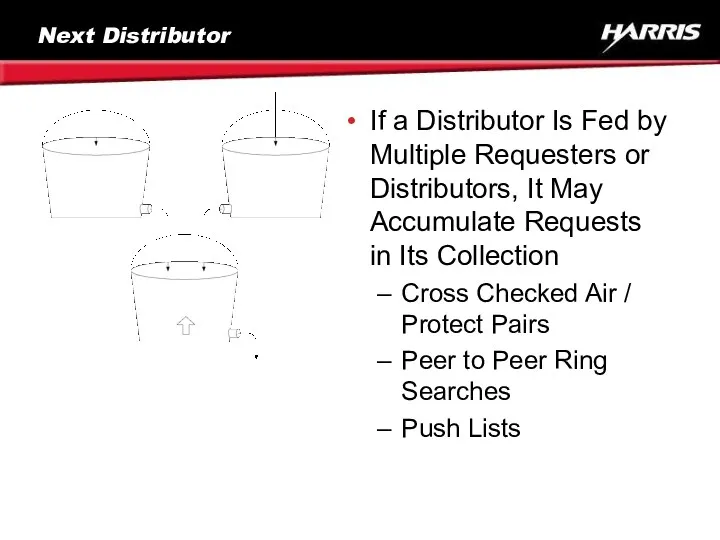
- 65. Next Distributor If a Distributor Is Fed by Multiple Requesters or Distributors, It May Accumulate Requests
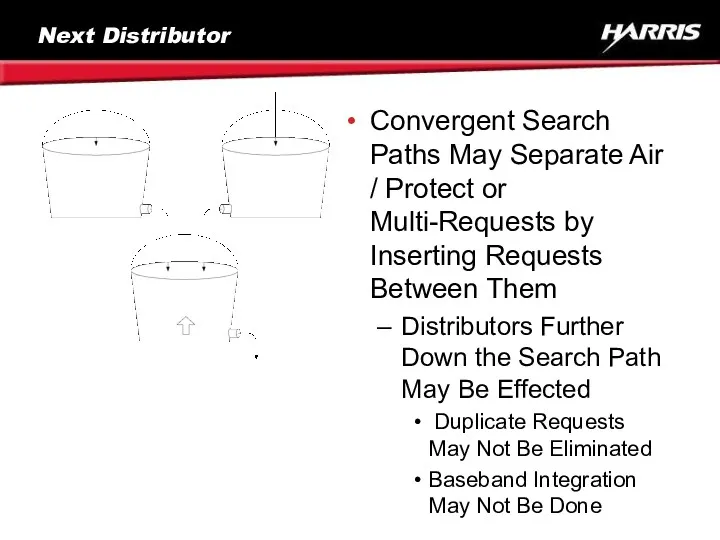
- 66. Next Distributor Convergent Search Paths May Separate Air / Protect or Multi-Requests by Inserting Requests Between
- 67. Next Distributor
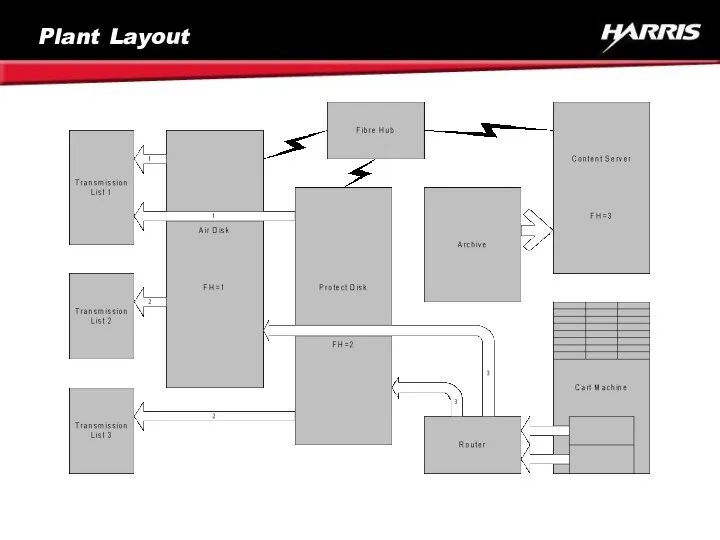
- 68. Plant Description The System Consists of Three Video File Servers, an Archive and a Cart Machine
- 69. Plant Description There Are Three Transmission Lists List 1 Plays Out Air/protect From Servers 1 and
- 70. Plant Layout
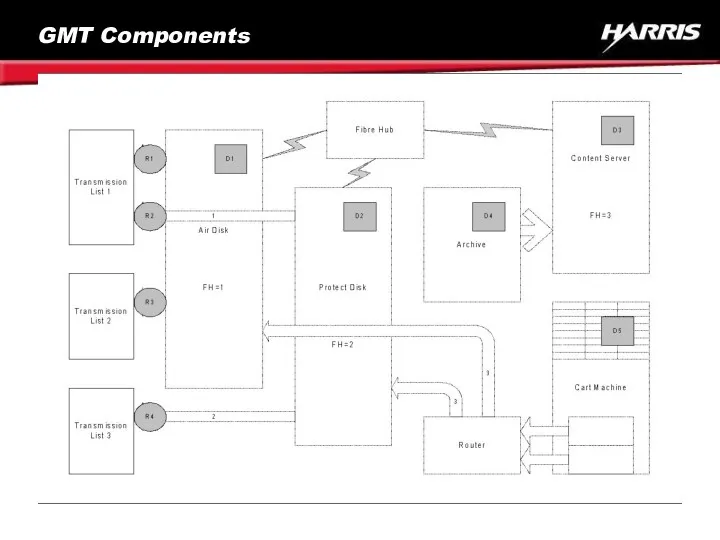
- 71. GMT Components
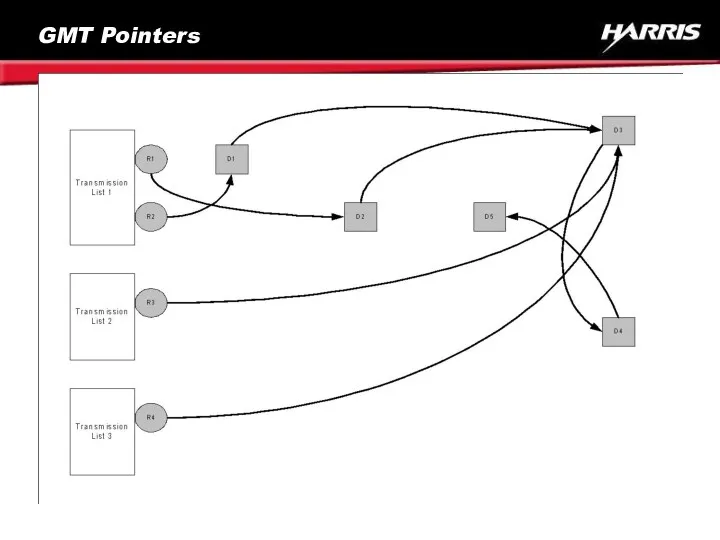
- 72. GMT Pointers
- 74. Скачать презентацию















































 Медицинская ERP-система регионального уровня
Медицинская ERP-система регионального уровня Кодирование графифической информации
Кодирование графифической информации Интернет как глобальная информационная система
Интернет как глобальная информационная система Programare in retea
Programare in retea Встроенные функции в электронных таблицах Excel
Встроенные функции в электронных таблицах Excel Сотовые телефоны: за и против
Сотовые телефоны: за и против Требования к разработке ПО
Требования к разработке ПО Поняття алгоритму та програми
Поняття алгоритму та програми Управление процессами
Управление процессами Решение задач с использованием символьных величин и строк символов. Практическая работа №13
Решение задач с использованием символьных величин и строк символов. Практическая работа №13 Презентация к уроку по информатике Компьютерное лото
Презентация к уроку по информатике Компьютерное лото Проектирование на основе WEB-технологии современной образовательной среды
Проектирование на основе WEB-технологии современной образовательной среды Презентация по теме: Цикл
Презентация по теме: Цикл Серверные операционные системы
Серверные операционные системы Разработка урока информатики по теме Редактирование и форматирование текста. Создание газеты
Разработка урока информатики по теме Редактирование и форматирование текста. Создание газеты Аппаратное и программное обеспечение ЭВМ и сетей
Аппаратное и программное обеспечение ЭВМ и сетей Информационные технологии. Счет в древнем мире
Информационные технологии. Счет в древнем мире Немой монолог
Немой монолог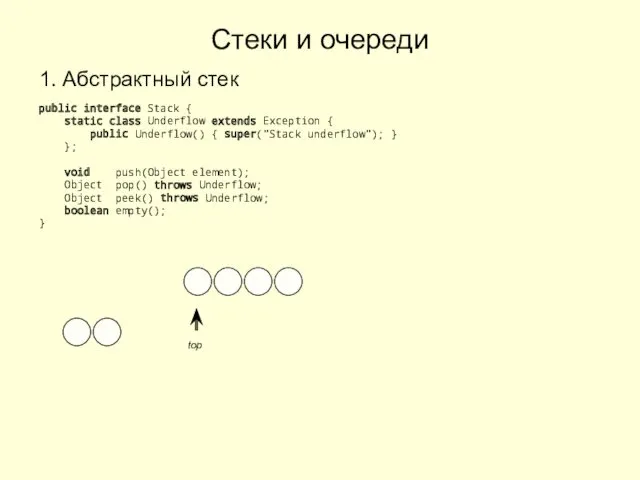 Стеки и очереди
Стеки и очереди Основные компоненты компьютера и их функции
Основные компоненты компьютера и их функции Важные формулы. Задание 9
Важные формулы. Задание 9 Методичка по созданию сайта на Google платформе
Методичка по созданию сайта на Google платформе Обработка событий
Обработка событий Мультимедиа технологии
Мультимедиа технологии Паскаль – язык структурного программирования
Паскаль – язык структурного программирования Step by step instructions: Creating a username and Password screen in C#
Step by step instructions: Creating a username and Password screen in C# Измерение информации. Алфавитный подход
Измерение информации. Алфавитный подход Agenda Software Testing Jira
Agenda Software Testing Jira