Содержание
- 2. Agenda Software Testing JIRA introduction
- 3. SOFTWARE TESTING
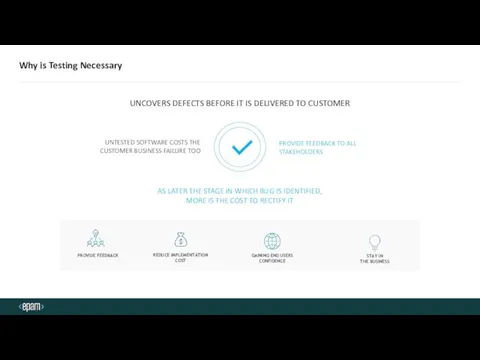
- 4. Why is Testing Necessary UNCOVERS DEFECTS BEFORE IT IS DELIVERED TO CUSTOMER UNTESTED SOFTWARE COSTS THE
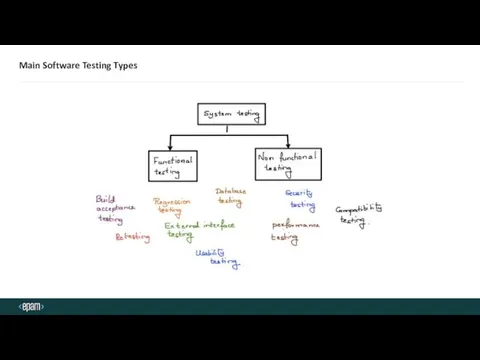
- 5. Main Software Testing Types
- 6. Functional Testing The functions are “what” the system should do. Functional tests tend to answer the
- 7. Non-Functional testing Non-functional tests tend to answer the question of “how well” the system behaves.
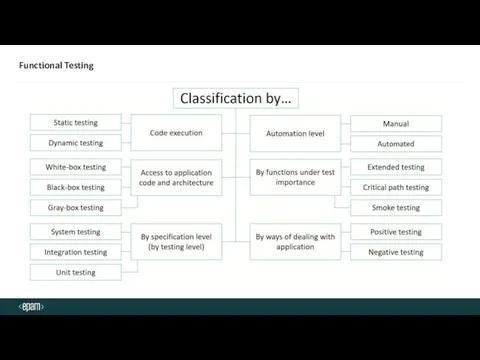
- 8. Functional Testing
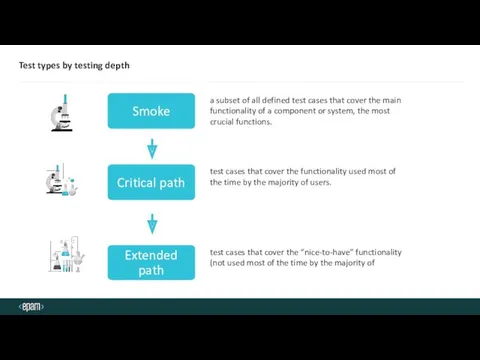
- 9. Test types by testing depth test cases that cover the “nice-to-have” functionality (not used most of
- 10. Software Testing Levels focuses on components that are separately testable focuses on interactions between components to
- 11. Software Testing Levels UNIT ACCEPTANCE Who: DEV, QA When: Component is developed Why: To validate that
- 12. JIRA INTRODUCTION
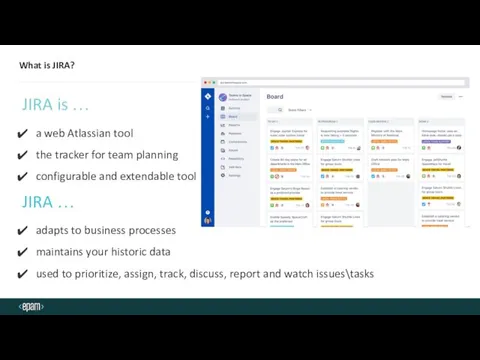
- 13. What is JIRA? JIRA is … a web Atlassian tool the tracker for team planning configurable
- 14. JIRA advantages and disadvantages
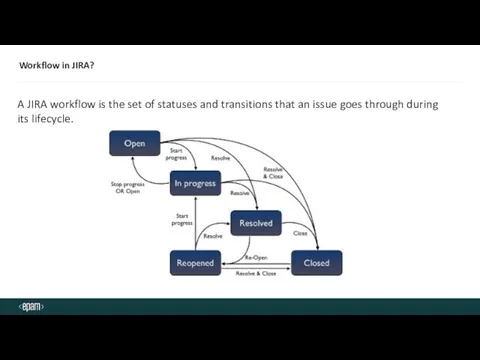
- 15. Workflow in JIRA? A JIRA workflow is the set of statuses and transitions that an issue
- 16. What is an issue? Issue – any task that requires an action from a person. Issue
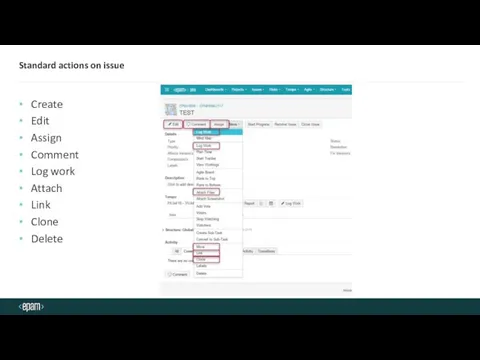
- 17. Standard actions on issue Create Edit Assign Comment Log work Attach Link Clone Delete
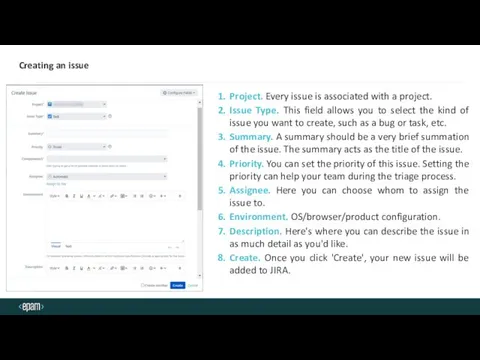
- 18. Creating an issue Project. Every issue is associated with a project. Issue Type. This field allows
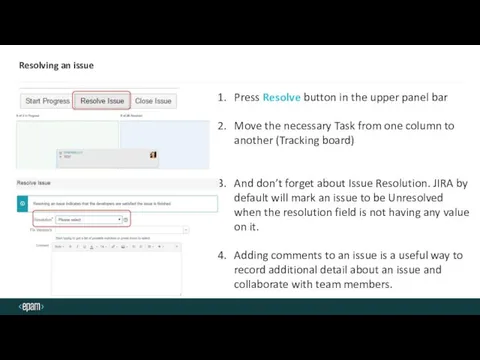
- 19. Resolving an issue Press Resolve button in the upper panel bar Move the necessary Task from
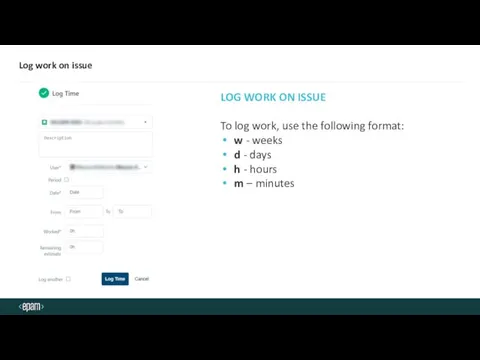
- 20. Log work on issue LOG WORK ON ISSUE To log work, use the following format: w
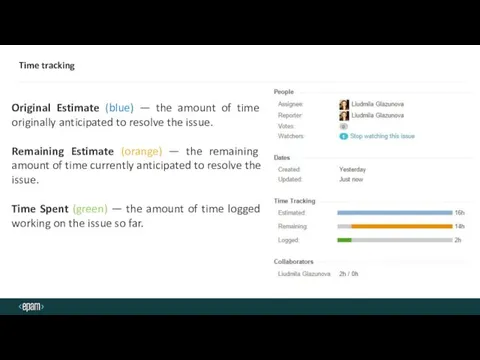
- 21. Time tracking Original Estimate (blue) — the amount of time originally anticipated to resolve the issue.
- 22. KANBAN board Kanban is a catalyst for change through small, incremental improvements to your existing process
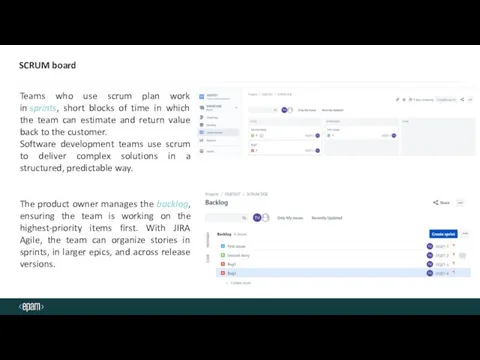
- 23. SCRUM board Teams who use scrum plan work in sprints, short blocks of time in which
- 25. Скачать презентацию









 Урок информатики Компьютерная помощница- мышь
Урок информатики Компьютерная помощница- мышь Подготовка к ЕГЭ Динамическое программирование. Исполнитель Калькулятор
Подготовка к ЕГЭ Динамическое программирование. Исполнитель Калькулятор Приложения с базами данных
Приложения с базами данных Шаблон кейса
Шаблон кейса Adobe Photoshop – многофункциональный редактор для работы с фото и видеофайлами
Adobe Photoshop – многофункциональный редактор для работы с фото и видеофайлами Основы информационной безопасности. Угрозы АС. (Тема 1.2)
Основы информационной безопасности. Угрозы АС. (Тема 1.2) Лекция 5. Модели жизненного цикла программного обеспечения
Лекция 5. Модели жизненного цикла программного обеспечения CDEK Cross border offer eng — for web site
CDEK Cross border offer eng — for web site Урок информатики в 5 классе с применением ИКТ Компьютер инструмент искусства.
Урок информатики в 5 классе с применением ИКТ Компьютер инструмент искусства. Американская транснациональная публичная корпорация Google
Американская транснациональная публичная корпорация Google Мы в современном медиапространстве: уважение, безопасность, достоверность
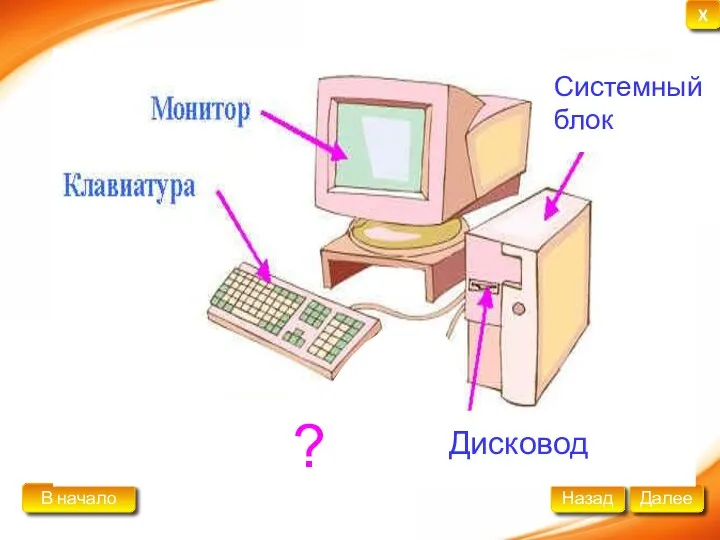
Мы в современном медиапространстве: уважение, безопасность, достоверность Принцип построения компьютера
Принцип построения компьютера Национальный цифровой ресурс на базе технологии Контекстум
Национальный цифровой ресурс на базе технологии Контекстум Шифр Плейфера. Полибианский квадрат
Шифр Плейфера. Полибианский квадрат Новая социальная сеть M-club
Новая социальная сеть M-club Программирование линейных алгоритмов
Программирование линейных алгоритмов Режим возвращения в ноль. Панель HAAS
Режим возвращения в ноль. Панель HAAS Формирование решений средствами таблиц MS Excel
Формирование решений средствами таблиц MS Excel Лекция 2. Моделирование технологических процессов. Аналитические аппроксимации распределения ионов
Лекция 2. Моделирование технологических процессов. Аналитические аппроксимации распределения ионов Презентация к элективному занятию Решение прикладных задач в Excel
Презентация к элективному занятию Решение прикладных задач в Excel Основы языка VB Урок 1: Данные
Основы языка VB Урок 1: Данные Базовая станция МегаФон
Базовая станция МегаФон Информационные системы
Информационные системы Основы построения телекоммуникационных сетей
Основы построения телекоммуникационных сетей Издательство Росмэн
Издательство Росмэн Современные возможности ES-2015
Современные возможности ES-2015 Информатиканы оқытуда мұғалімнің рөлі
Информатиканы оқытуда мұғалімнің рөлі Характеристики величин. Числові типи даних (8 клас)
Характеристики величин. Числові типи даних (8 клас)