Содержание
- 2. Agenda What is the computing model? Batch processing Remote Job Entry and autonomous agents Host &
- 3. What is the computing model? A complex picture of: Application storage Data origin, data input Application
- 4. Computing models Depend on: Hardware and software capabilities Networks availability and connection User and manufacturer preferences
- 5. Batch processing Computer processing of information that has been assembled into batches of transactions prior to
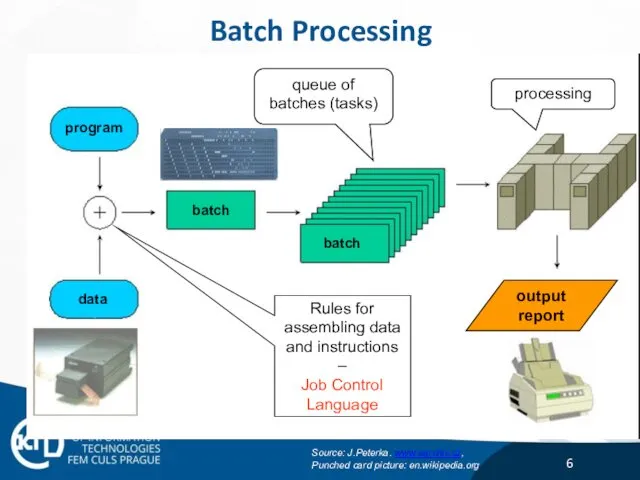
- 6. Batch Processing program data batch batch output report Rules for assembling data and instructions – Job
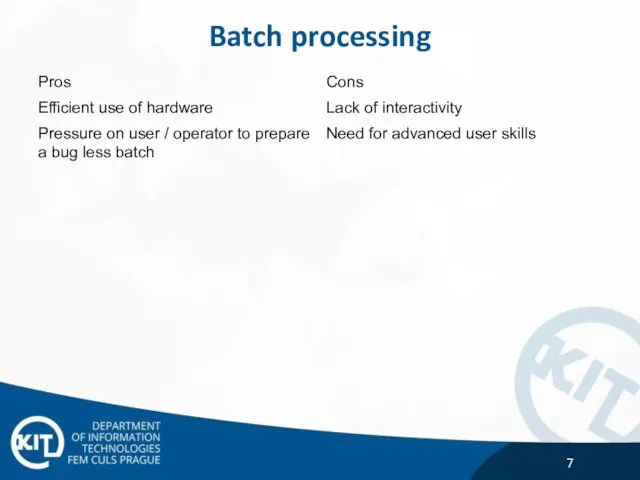
- 7. Batch processing
- 8. Remote Job Entry & agents Remote Job Entry (RJE) Newer form of batch processing The batch
- 9. Decomposition of a complex task 2*(23-7)+((14/2)+(8+12)*(9-8))-(8*9)+((7*2)*(6-2))-(((2*3)+(4-7))-(9-7))=? The task is too time-difficult and space-consuming for one computational
- 10. Gathering of the computational power Voluntary BOINC Payed Cryptocurrency Stolen Botnets
- 11. Interactive processing Mainframe terminals/workstations Each user action causes a response Exchange of information between a user
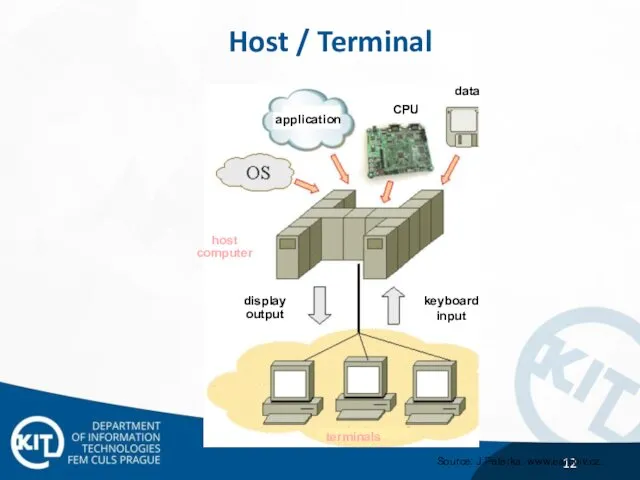
- 12. application terminals host computer display output keyboard input data CPU Source: J.Peterka. www.earchiv.cz. Host / Terminal
- 13. Host / Terminal - example
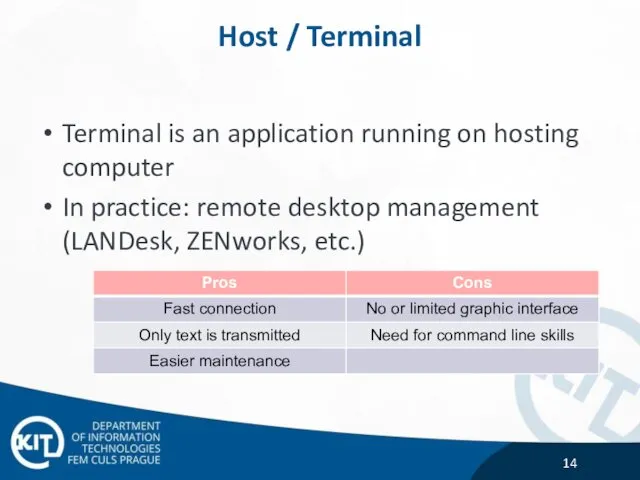
- 14. Host / Terminal Terminal is an application running on hosting computer In practice: remote desktop management
- 15. Desktop PC Since 1980s Connected with hardware advancements and price decrease Major platform: Windows, alternative: Mac
- 16. Desktop PC A computer intended for stand-alone use by an individual Higher productivity of work Inexpensive
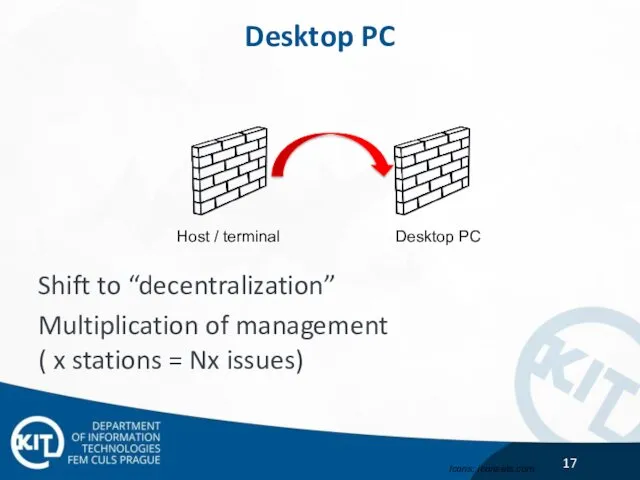
- 17. Desktop PC Shift to “decentralization” Multiplication of management ( x stations = Nx issues) Host /
- 18. Seek for compromise Sharing vs. owning
- 19. Need for sharing – inception of LANs LAN = Local Area Networks Fast network connection (100
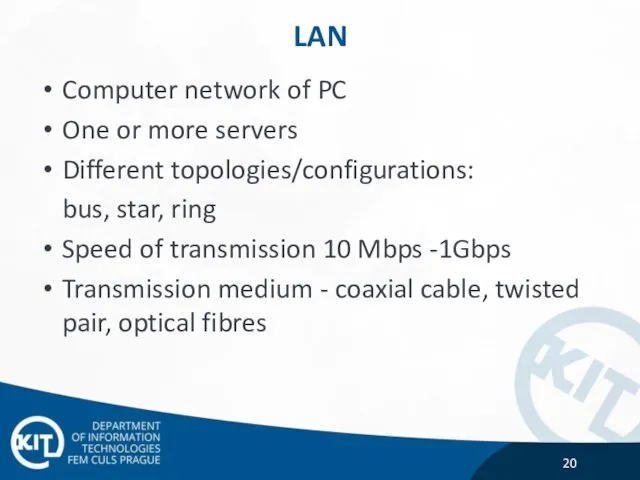
- 20. LAN Computer network of PC One or more servers Different topologies/configurations: bus, star, ring Speed of
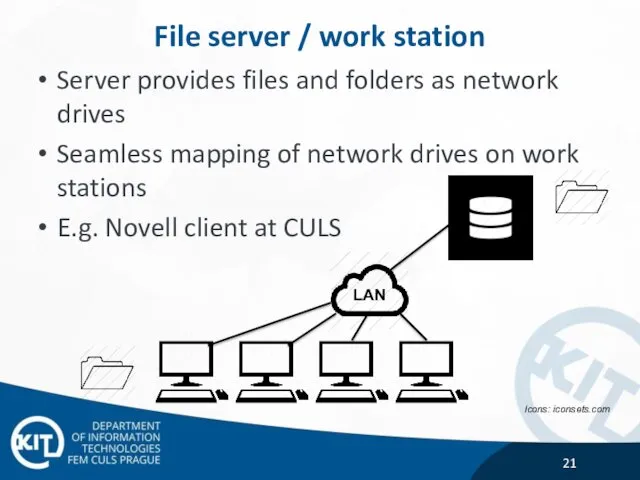
- 21. File server / work station Server provides files and folders as network drives Seamless mapping of
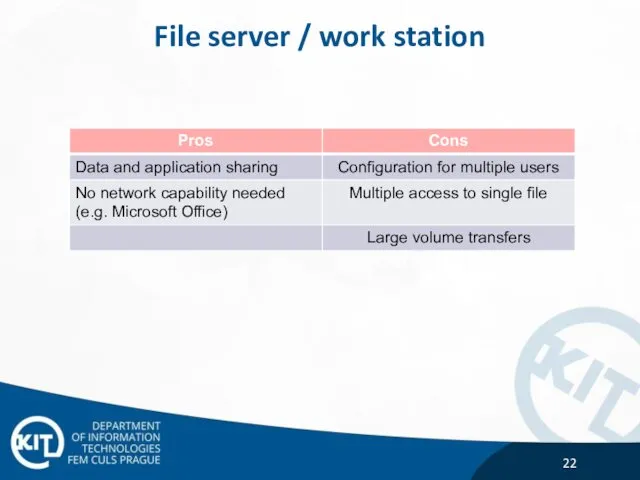
- 22. File server / work station
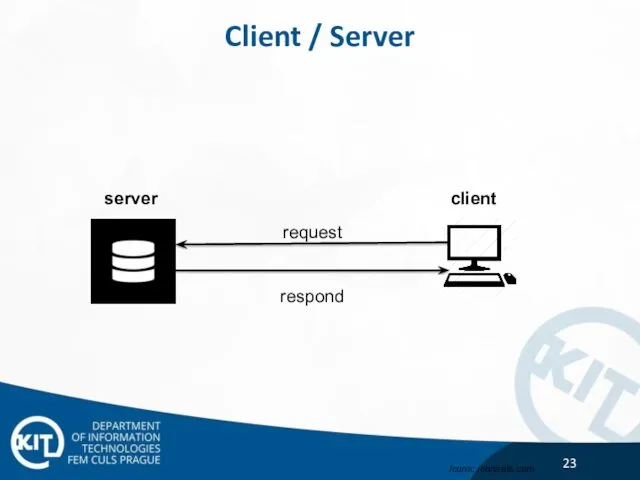
- 23. Client / Server client server request respond Icons: iconsets.com
- 24. Client / Server Architecture More general concept - middleware clients - PC servers - database, print,
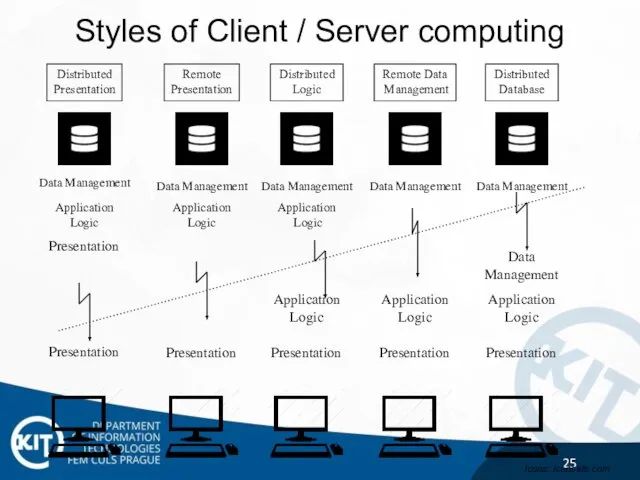
- 25. Distributed Presentation Remote Presentation Distributed Logic Remote Data Management Distributed Database Presentation Presentation Presentation Presentation Presentation
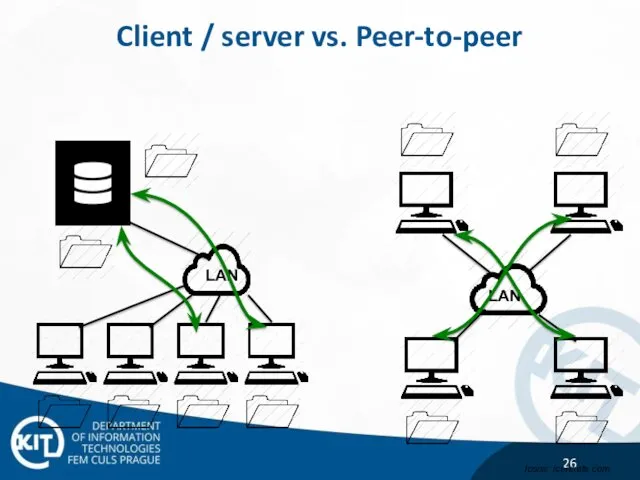
- 26. Client / server vs. Peer-to-peer LAN Icons: iconsets.com
- 27. Three-layer C/S model In traditional C/S model – for each client platform … new client application.
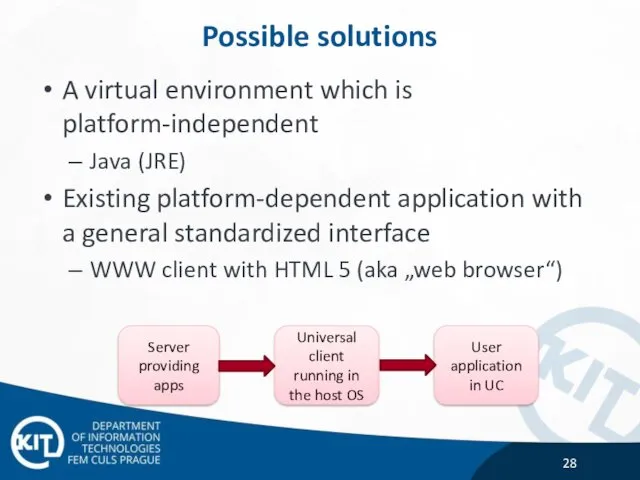
- 28. Possible solutions A virtual environment which is platform-independent Java (JRE) Existing platform-dependent application with a general
- 30. Скачать презентацию










 Текстовая информация
Текстовая информация Установка и настройка Apache и PHP
Установка и настройка Apache и PHP Презентация Состав объектов, 7 класс
Презентация Состав объектов, 7 класс Фактологические жанры PR-текстов
Фактологические жанры PR-текстов Алгоритмы. Свойства и формы представления
Алгоритмы. Свойства и формы представления Инструкция по запуску дистанционных курсов
Инструкция по запуску дистанционных курсов Эффективное использование инструментов разработки веб-страниц
Эффективное использование инструментов разработки веб-страниц Основные понятия и определения информатики
Основные понятия и определения информатики Перезапуск официального сайта: этапы и предложения
Перезапуск официального сайта: этапы и предложения Пользователи Instagram
Пользователи Instagram Ғаламтор, әлеуметтік желілердің жасөспірімдердің қылмысына қатысы
Ғаламтор, әлеуметтік желілердің жасөспірімдердің қылмысына қатысы Прототип мобильного приложения для обучения правильной технике свинга при помощи AI
Прототип мобильного приложения для обучения правильной технике свинга при помощи AI Работа с графическими объектами в текстовом реакторе
Работа с графическими объектами в текстовом реакторе C# decision and iteration constructs
C# decision and iteration constructs Публичная кадастровая карта
Публичная кадастровая карта Рекламные пакеты Турбопромо
Рекламные пакеты Турбопромо Информационные системы управления персоналом. Лекция 1
Информационные системы управления персоналом. Лекция 1 Б-Безопасность ACL, NAT, VPN
Б-Безопасность ACL, NAT, VPN Курс Базы данных. Программирование на языке PL/SQL. Часть 2
Курс Базы данных. Программирование на языке PL/SQL. Часть 2 Проектування у графічному редакторі Sweet Нome 3D
Проектування у графічному редакторі Sweet Нome 3D Программирование на языке Си. Простейшие программы
Программирование на языке Си. Простейшие программы Представление числовой информации с помощью систем счисления (1). 8 класс
Представление числовой информации с помощью систем счисления (1). 8 класс Сервис Отвечает аудитор
Сервис Отвечает аудитор Основные инструменты графического редактора
Основные инструменты графического редактора Числа в памяти компютера
Числа в памяти компютера Программирование ветвлений на Паскаль. Повторение
Программирование ветвлений на Паскаль. Повторение Табличная форма представления информации
Табличная форма представления информации Оценка максимально достижимого параллелизма и масштабируемости параллельных вычислений
Оценка максимально достижимого параллелизма и масштабируемости параллельных вычислений