Содержание
- 2. HYBRID FIBER-COAXIAL NETWORK (HFC) Lecture 6
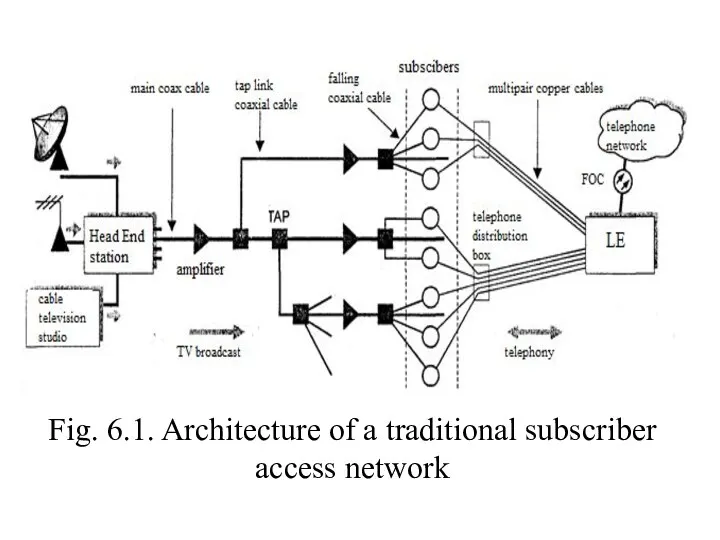
- 3. Traditional access by CATV and telephone networks Fig. 6.1 shows the general scheme of the traditional
- 4. Fig. 6.1. Architecture of a traditional subscriber access network
- 5. From the main cable to the branch nodes - taps (tap) - can be separated by
- 6. Thus, firstly, the network subscribers are provided for receiving television channels. Secondly, subscribers are provided with
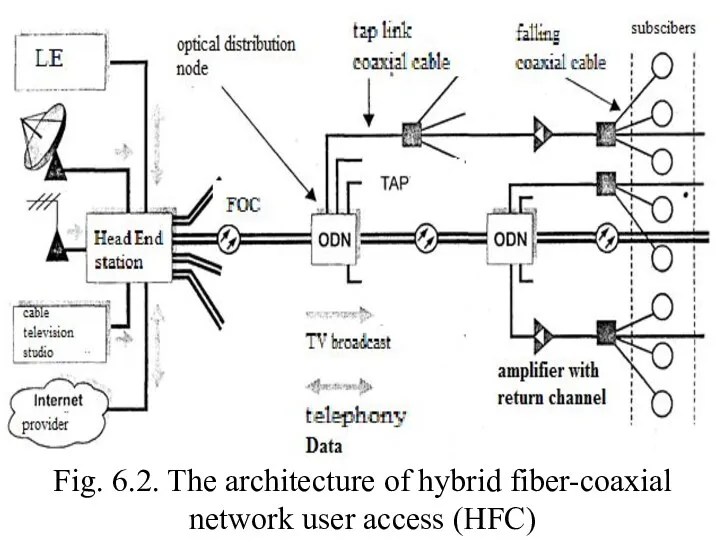
- 7. HFC network The hybrid fiber-coaxial network HFC (hybrid fiber/coax) is based on the coaxial and fiber
- 8. Fig. 6.2. The architecture of hybrid fiber-coaxial network user access (HFC)
- 9. Appointment of fiber in HFC networks much the same as in telephone networks which, based on
- 10. The optical signal coming in ODN, again converted into an electrical\followed by coaxial branches of the
- 11. HFC network involves the installation of equipment at a mutually agreed main node (HC, main node
- 12. Many companies specializing in the production of telecommunications network equipment supplying a large inventory of HFC
- 13. 802.14 physical layer specifications support asymmetric bidirectional transmission of signals on network HFC. HFC network allows
- 14. Upstream transmission devices formed on the subscriber side of the ISU and reach the National Assembly
- 15. These services have several different attributes, in particular the allowable delay "explosive" nature of traffic. Some
- 16. Frequency distribution of streams General diagram of the frequency distribution of streams is shown in Fig.
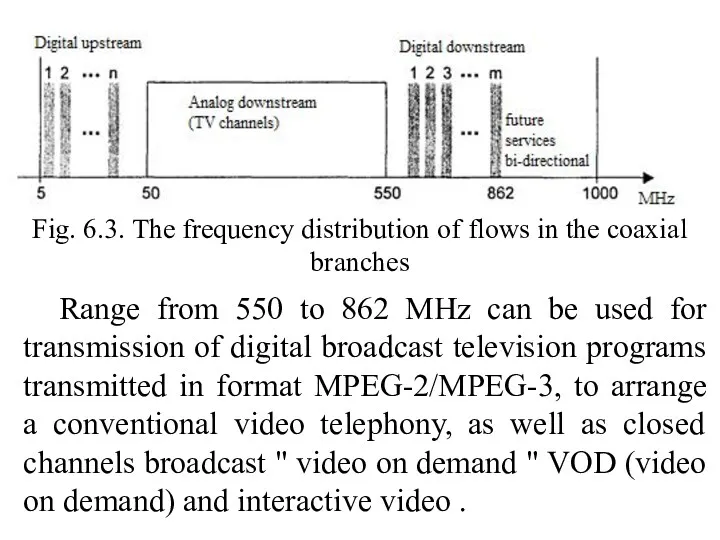
- 17. Fig. 6.3. The frequency distribution of flows in the coaxial branches Range from 550 to 862
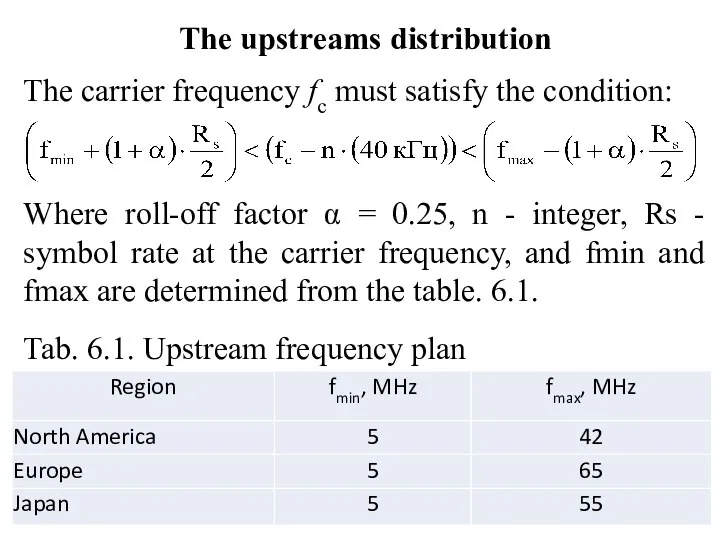
- 18. The upstreams distribution The carrier frequency fc must satisfy the condition: Where roll-off factor α =
- 19. In practice the choice of the frequency allocation of channels depends on factors (such as to
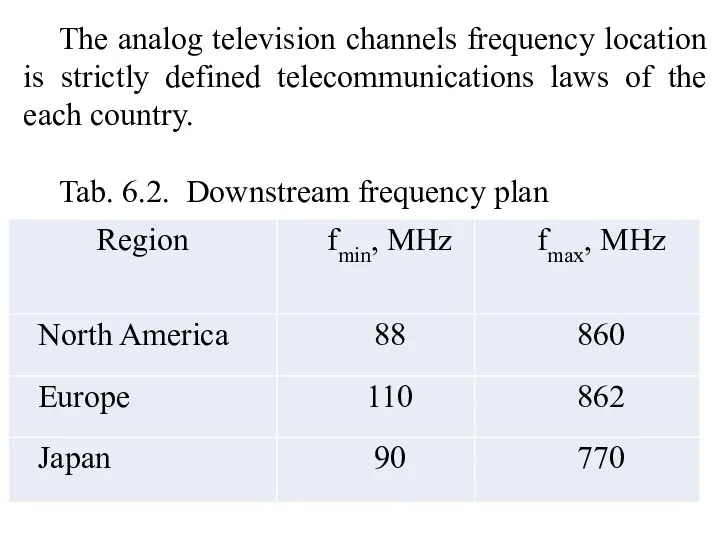
- 20. The analog television channels frequency location is strictly defined telecommunications laws of the each country. Tab.
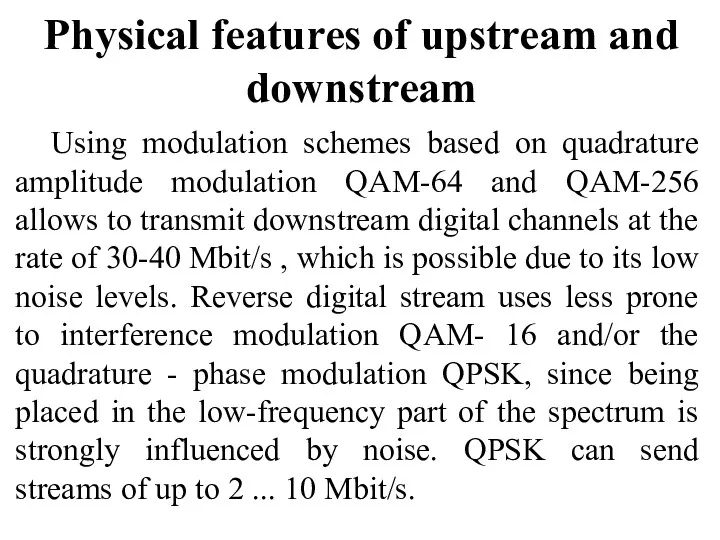
- 21. Physical features of upstream and downstream Using modulation schemes based on quadrature amplitude modulation QAM-64 and
- 22. Why does upstream locate in the lower part of the spectrum (5 ... 45 MHz )?
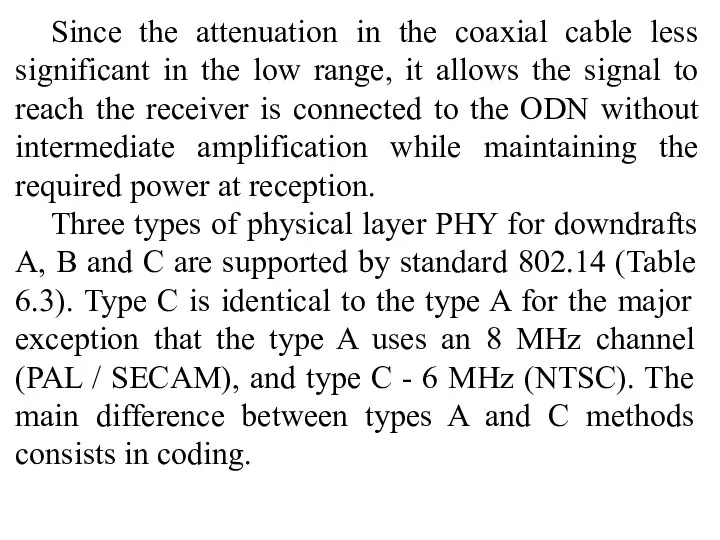
- 23. Since the attenuation in the coaxial cable less significant in the low range, it allows the
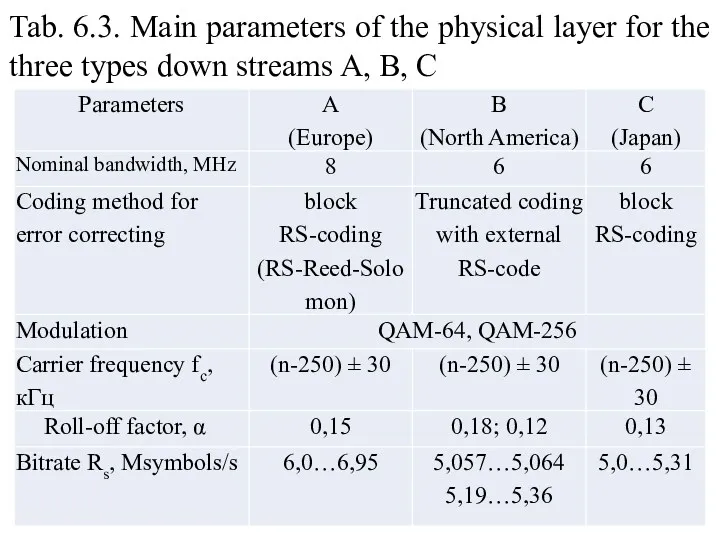
- 24. Tab. 6.3. Main parameters of the physical layer for the three types down streams A, B,
- 25. Conclusions We formulate the basic principles on which the HFC network , and trends in their
- 26. - Hybrid transmission of information: analog and digital. Allowed a gradual transition to digital transmission only.
- 28. Скачать презентацию







 Структурное программирование. Тема 03
Структурное программирование. Тема 03 Антивирустар. Компьютерлік вирус
Антивирустар. Компьютерлік вирус Относительные, абсолютные и смешанные ссылки. 9 класс
Относительные, абсолютные и смешанные ссылки. 9 класс Функции в электронных таблицах
Функции в электронных таблицах Применение простых чисел в криптографии с открытым ключом
Применение простых чисел в криптографии с открытым ключом Інтернет-магазин комп’ютерної техніки
Інтернет-магазин комп’ютерної техніки Массив вида N*N
Массив вида N*N Алгоритм решения задач средствами алгебры логики
Алгоритм решения задач средствами алгебры логики Создание Telegram-бота
Создание Telegram-бота Теория систем счисления
Теория систем счисления Языки и методы программирования
Языки и методы программирования Школа::Кода Основы программирования на языке Python. 14 занятие
Школа::Кода Основы программирования на языке Python. 14 занятие Пользовательский интерфейс
Пользовательский интерфейс Теорія графів
Теорія графів Доставка для интернет-магазинов
Доставка для интернет-магазинов SQLite. Способы доступа СУБД к БД
SQLite. Способы доступа СУБД к БД Информатика лидері
Информатика лидері Текстовые редакторы. Урок 10
Текстовые редакторы. Урок 10 Кодирование графической и мультимедийной информации
Кодирование графической и мультимедийной информации Алгоритм. Способы записи алгоритмов
Алгоритм. Способы записи алгоритмов Universal. Многофункциональный микрокомпьютерный комплекс
Universal. Многофункциональный микрокомпьютерный комплекс Об'єктно-орієнтоване проектування з використанням UML 2.0 Діаграми варіантів використання
Об'єктно-орієнтоване проектування з використанням UML 2.0 Діаграми варіантів використання Основы программирования и баз данных. Модуль 1. Базовые понятия и определения
Основы программирования и баз данных. Модуль 1. Базовые понятия и определения Юные мыслители
Юные мыслители Основы программирования
Основы программирования С++. Базовый уровень Классы и объекты. Принципы ООП
С++. Базовый уровень Классы и объекты. Принципы ООП Видеоигра Devil May Cry
Видеоигра Devil May Cry HTML-документы, которые содержат фреймы
HTML-документы, которые содержат фреймы