Содержание
- 2. Week plan 1. What is Cassandra? 2. Install Apache Cassandra on Ubuntu 3. Work with Cassandra
- 3. Tutorial
- 4. What is Cassandra? Apache Cassandra is a top level Apache project born at Facebook and built
- 5. What is Cassandra? Cassandra’s architecture is responsible for its ability to scale, perform, and offer continuous
- 6. What is Cassandra? In Cassandra, all nodes are equal, which means no master node, no master-slave
- 7. Elastic scalability - add more nodes to accommodate more clients for data easily. Always on architecture
- 8. With all its shiny parts, Cassandra still has some let downs: A range scan implementation is
- 9. Data Replication in Cassandra In Cassandra, replicas for a given piece of data are distributed on
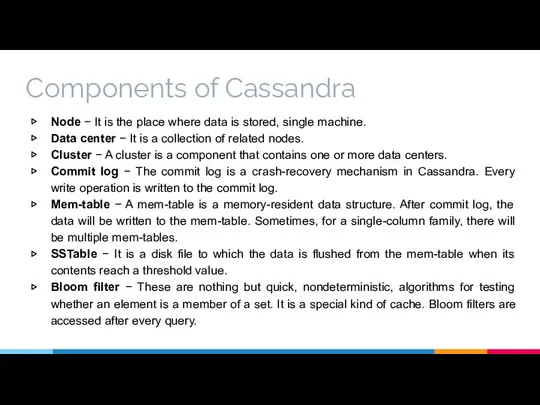
- 10. Components of Cassandra Node − It is the place where data is stored, single machine. Data
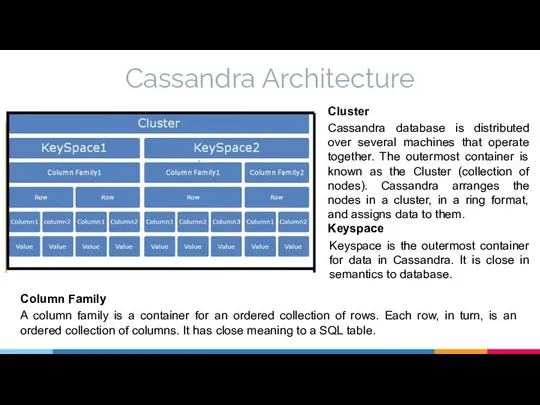
- 11. Cassandra Architecture Cluster Cassandra database is distributed over several machines that operate together. The outermost container
- 12. Cassandra Query Language The Cassandra Query Language (CQL) is the primary language for communicating with the
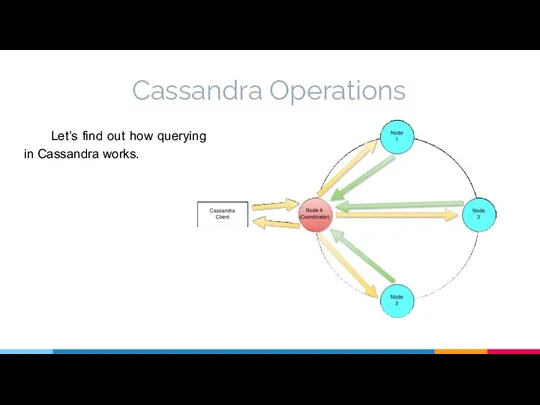
- 13. Cassandra Operations Let’s find out how querying in Cassandra works.
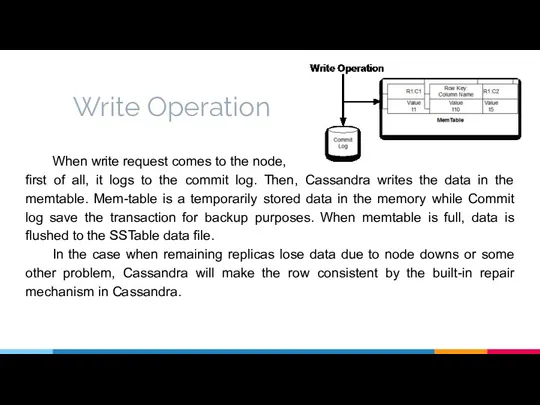
- 14. Write Operation When write request comes to the node, first of all, it logs to the
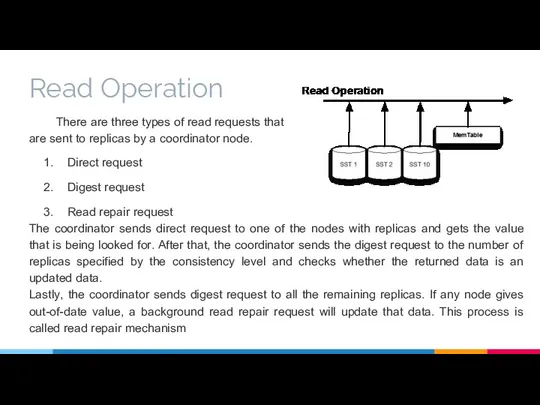
- 15. Read Operation There are three types of read requests that are sent to replicas by a
- 16. Install Java on Ubuntu Before installing Cassandra, make sure that Java is already installed on your
- 17. Install Java on Ubuntu Then, install the Oracle JRE. Installing this particular package not only installs
- 18. Install Apache Cassandra on Ubuntu We will use DataStax Community repository with a few simple steps
- 19. Install Apache Cassandra on Ubuntu 2. Add the DataStax repository key to your aptitude trusted keys
- 20. Install Apache Cassandra on Ubuntu Because the Ubuntu packages start the Cassandra service automatically, you must
- 21. Cassandra and Python For managing Cassandra via Python you have to install cassandra-driver package from PyPI
- 22. Create a Keyspace and Table First, you need to connect to the Cluster. And check your
- 23. Create a Keyspace and Table Let's create a table, it will be called "users_". >>> session.execute(
- 24. Insert and Select Records We are going to add data to our table in three different
- 25. Insert and Select Records Let's select all the records to make sure that we have done
- 26. Update and Delete Records Let's change country for record with id = 3, and then check
- 27. Update and Delete Records Let's delete one of the records, such as having id = 2.
- 28. Alter Table Modify the column metadata of a table. Adding a column To add a column
- 29. Exercises
- 30. Task #1 Add a new record to the users_ table with the following values: id =
- 31. Task #2 Add new column into your table, let it be called "login", it should contain
- 32. Task #3 Change country to "Ukraine" for user having id = 4 and display count of
- 34. Скачать презентацию
























 Виды Баз Данных
Виды Баз Данных Модель OSI и стек TCP/IP
Модель OSI и стек TCP/IP Готовимся в проектной работе
Готовимся в проектной работе Корпоративные системы электронного документооборота. Классификация систем электронного документооборота
Корпоративные системы электронного документооборота. Классификация систем электронного документооборота Положення та принципи організації комп’ютерної технології на підприємстві
Положення та принципи організації комп’ютерної технології на підприємстві Влияние цифровизации на здравоохранение
Влияние цифровизации на здравоохранение Определение и проблемы языков программирования
Определение и проблемы языков программирования Помехоустойчивое кодирование. Линейные коды
Помехоустойчивое кодирование. Линейные коды Вредоносное программное обеспечение. Описание. Классификация
Вредоносное программное обеспечение. Описание. Классификация Сравнительный анализ дизайна интернет-сайтов
Сравнительный анализ дизайна интернет-сайтов Інформаційні технології та системи в економіці: визначення, еволюція та сучасна класифікація
Інформаційні технології та системи в економіці: визначення, еволюція та сучасна класифікація Jizzax viloyat xalq ta’limi xodimlarini qayta tayyorlash va ularning malakasini oshirish hududiy markazi tomonidan tayyorlangan
Jizzax viloyat xalq ta’limi xodimlarini qayta tayyorlash va ularning malakasini oshirish hududiy markazi tomonidan tayyorlangan Програмне забезпечення комп’ютера за новою програмою
Програмне забезпечення комп’ютера за новою програмою Создание веб-сайтов
Создание веб-сайтов Миниатюра аватара
Миниатюра аватара Открытость деятельности органов власти
Открытость деятельности органов власти Моделирование равноускоренного движения в электронных таблицах
Моделирование равноускоренного движения в электронных таблицах Автоматизированное тестирование
Автоматизированное тестирование Понятие информации и измерение информации
Понятие информации и измерение информации Создание однотабличной и многотабличной базы данных
Создание однотабличной и многотабличной базы данных Дизайн приложения и функций. Приложения “Родитель ” или “Ребенок ”
Дизайн приложения и функций. Приложения “Родитель ” или “Ребенок ” Программа для программирования Scratch
Программа для программирования Scratch Методология и этапы проектирования баз данных
Методология и этапы проектирования баз данных Покадрова анімація. Анімація на основі фотоколажу. Експортування анімації
Покадрова анімація. Анімація на основі фотоколажу. Експортування анімації Язык программирования Go
Язык программирования Go История развития глобальных сетей
История развития глобальных сетей Информационная система персональных данных
Информационная система персональных данных Программирование на языке Python 8 класс
Программирование на языке Python 8 класс