Infographic Style
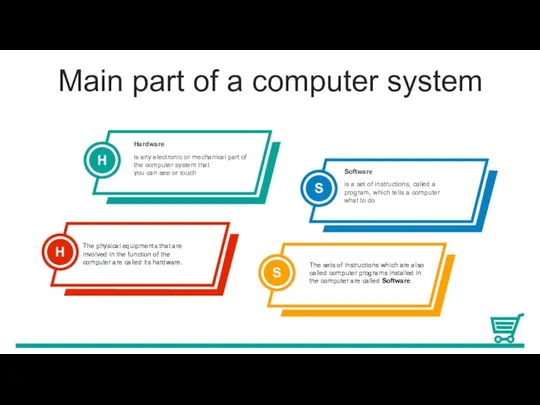
Storage refers to the media on which data, instructions, and
information are kept, as well as the devices that record and retrieve these items.
The collection of unorganized facts that can include words, numbers, pictures, sounds, and videos is called data
A series of instructions that tells a computer how to perform the tasks is called program
An instruction given to a computer program is called command
A character is stored in the computer as a group of 0s and 1s, called a Byte.
The Random Access Memory (RAM) is a volatile form of a computer memory.
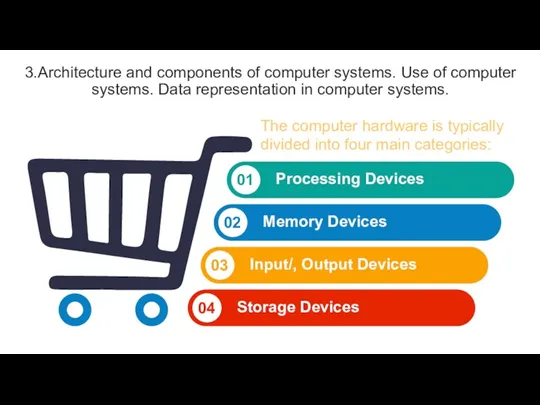
Processing Devices
The first technical characteristics of a CPU is a speed.
Two major components of a Central Processing Unit are Control Unit (CU) and the Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU), which work together to perform the processing operations.
The Control Unit (CU). As you know, a computer program or set of instructions must be stored in memory for a computer to process data. The CPU uses its CU to execute these instructions.
The Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU). ALU performs the arithmetic, comparison, and logical operations.
Memory Devices
I/O Devices
Storage Devices









 Миниатюра аватара
Миниатюра аватара Жизненный цикл информационных систем
Жизненный цикл информационных систем Ұғымдардың атауы: программа, программалаудың деңгейлері және дәрежелері (бағыттары), программаларды өңдеу және аспаптары
Ұғымдардың атауы: программа, программалаудың деңгейлері және дәрежелері (бағыттары), программаларды өңдеу және аспаптары создание тура в программе Мастер-Тур
создание тура в программе Мастер-Тур Вычислительные системы, сети и телекоммуникации. Введение
Вычислительные системы, сети и телекоммуникации. Введение Разработка Web-сайта 2019 год – год театра
Разработка Web-сайта 2019 год – год театра Кейсы окупаемости Focus для ТЦ
Кейсы окупаемости Focus для ТЦ Решение задач в Excel
Решение задач в Excel Как устроен интернет
Как устроен интернет Комп’ютерна верстка
Комп’ютерна верстка урок информатики по учебнику Плаксина М.А. тема Как управлять компьютером с помощью клавиатуры
урок информатики по учебнику Плаксина М.А. тема Как управлять компьютером с помощью клавиатуры Разработка ТЗ
Разработка ТЗ GitHub - найбільший веб-сервіс для хостингу IT-проектів і їх спільної розробки
GitHub - найбільший веб-сервіс для хостингу IT-проектів і їх спільної розробки Презентация к интегрированному уроку Пословицы и поговорки
Презентация к интегрированному уроку Пословицы и поговорки Язык программирования Python. Процедуры и функции в языке Python
Язык программирования Python. Процедуры и функции в языке Python Анализ еженедельного вечернего выпуска новостей телеканала НТВ
Анализ еженедельного вечернего выпуска новостей телеканала НТВ Архитектура компьютера открытый урок
Архитектура компьютера открытый урок Информатика лидері
Информатика лидері Компьютерные презентации. Разработка и создание презентации
Компьютерные презентации. Разработка и создание презентации IV поколение ЭВМ
IV поколение ЭВМ Безпека інформаційних технологій. Інформація та інформаційні відносини. Урок 1. Інформатика. 10(11) клас
Безпека інформаційних технологій. Інформація та інформаційні відносини. Урок 1. Інформатика. 10(11) клас Влияние социальных сетей на личность подростка
Влияние социальных сетей на личность подростка Анализ бизнес-процессов средствами BPwin
Анализ бизнес-процессов средствами BPwin 3D принтеры
3D принтеры Установка Microsoft Office
Установка Microsoft Office Физминутка
Физминутка The app is a notification and alert app with a basic points and reward database, and an analysis section to record app data
The app is a notification and alert app with a basic points and reward database, and an analysis section to record app data Кодирование и декодирование информации
Кодирование и декодирование информации