Содержание
- 2. Introduction to Database Systems G51DBS Textbook Recommended textbooks: ‘Database Systems: A practical approach to design, implementation
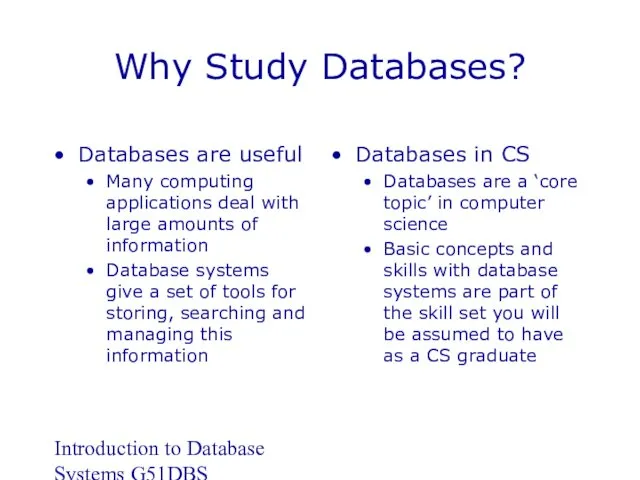
- 3. Introduction to Database Systems G51DBS Why Study Databases? Databases are useful Many computing applications deal with
- 4. Introduction to Database Systems G51DBS What is a Database? “A set of information held in a
- 5. Introduction to Database Systems G51DBS Databases Web indexes Library catalogues Medical records Bank accounts Stock control
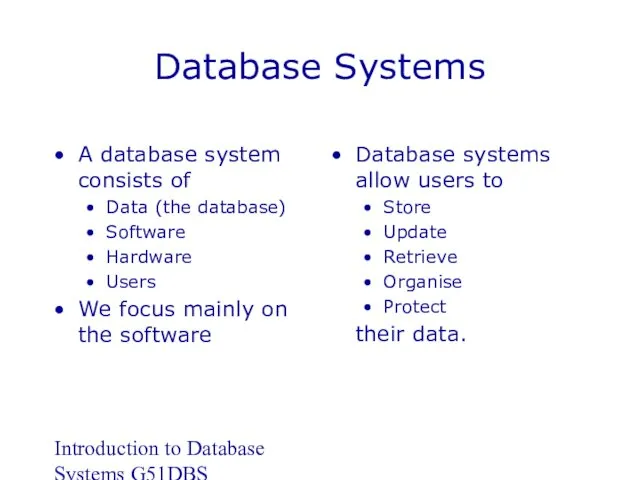
- 6. Introduction to Database Systems G51DBS Database Systems A database system consists of Data (the database) Software
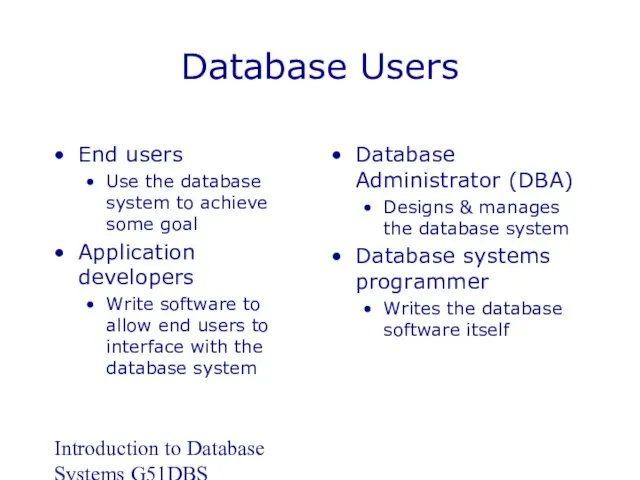
- 7. Introduction to Database Systems G51DBS Database Users End users Use the database system to achieve some
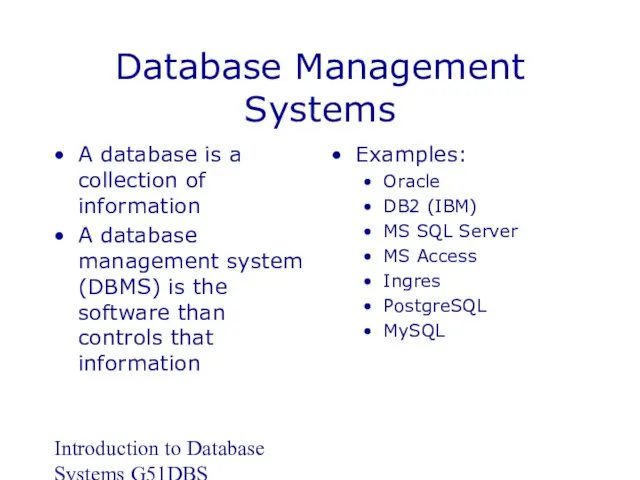
- 8. Introduction to Database Systems G51DBS Database Management Systems A database is a collection of information A
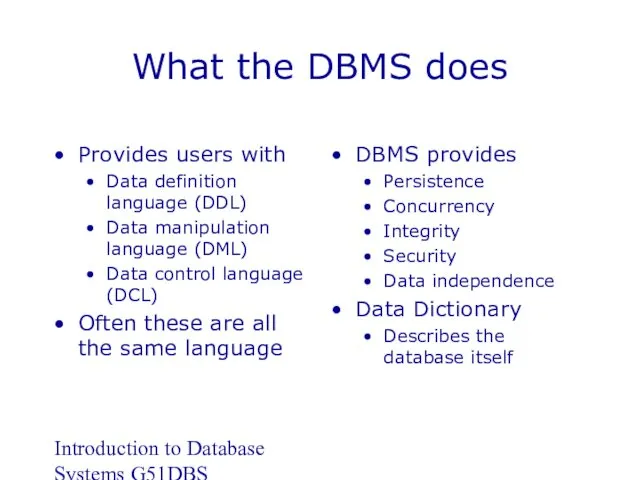
- 9. Introduction to Database Systems G51DBS What the DBMS does Provides users with Data definition language (DDL)
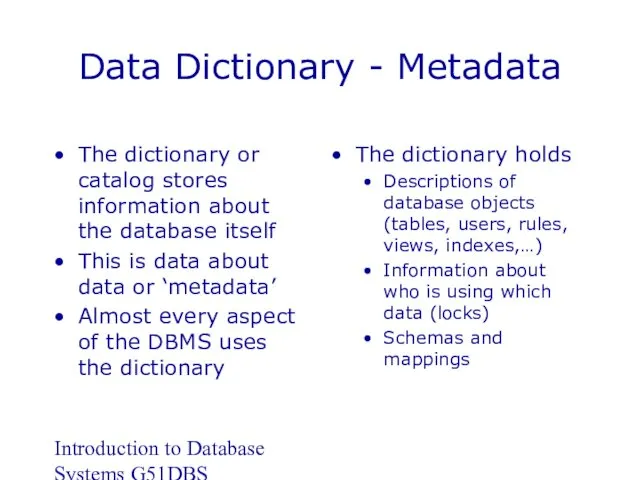
- 10. Introduction to Database Systems G51DBS Data Dictionary - Metadata The dictionary or catalog stores information about
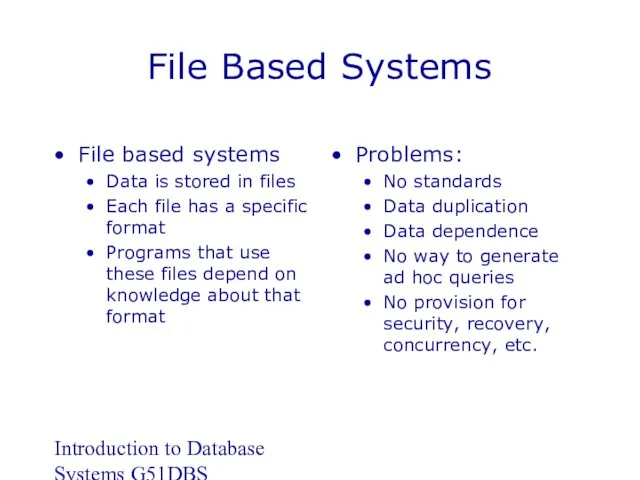
- 11. Introduction to Database Systems G51DBS File Based Systems File based systems Data is stored in files
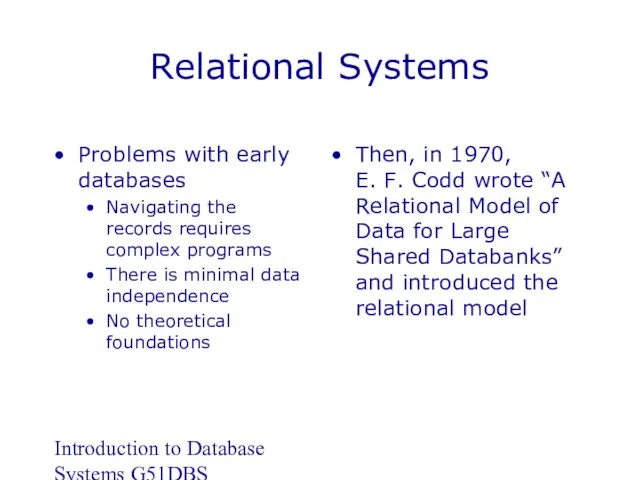
- 12. Introduction to Database Systems G51DBS Relational Systems Problems with early databases Navigating the records requires complex
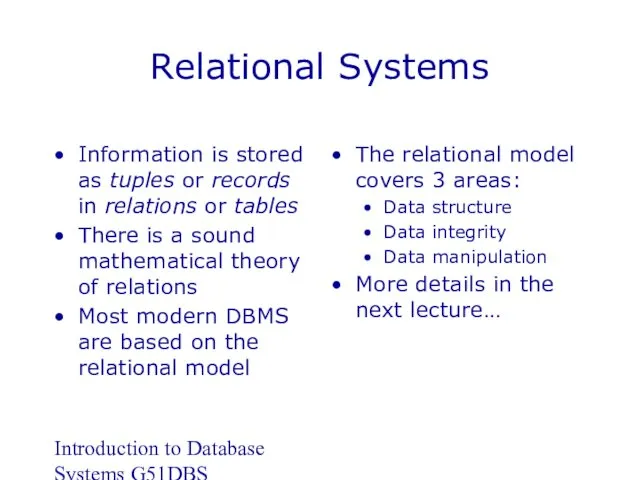
- 13. Introduction to Database Systems G51DBS Relational Systems Information is stored as tuples or records in relations
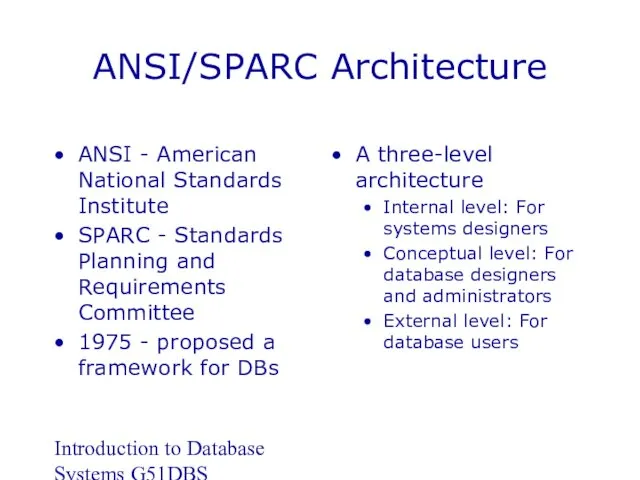
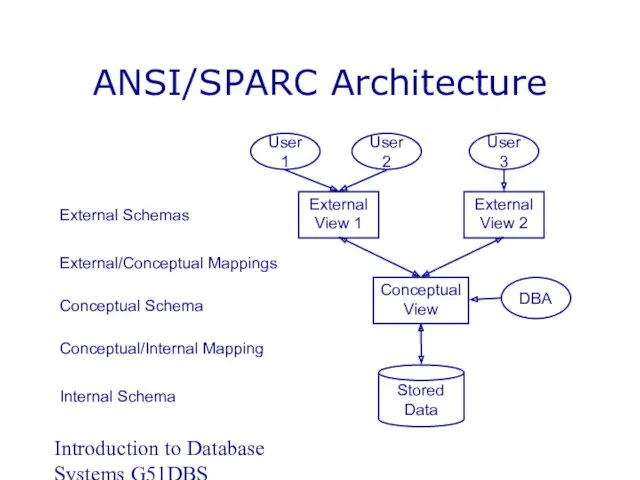
- 14. Introduction to Database Systems G51DBS ANSI/SPARC Architecture ANSI - American National Standards Institute SPARC - Standards
- 15. Introduction to Database Systems G51DBS Internal Level Deals with physical storage of data Structure of records
- 16. Introduction to Database Systems G51DBS Conceptual Level Deals with the organisation of the data as a
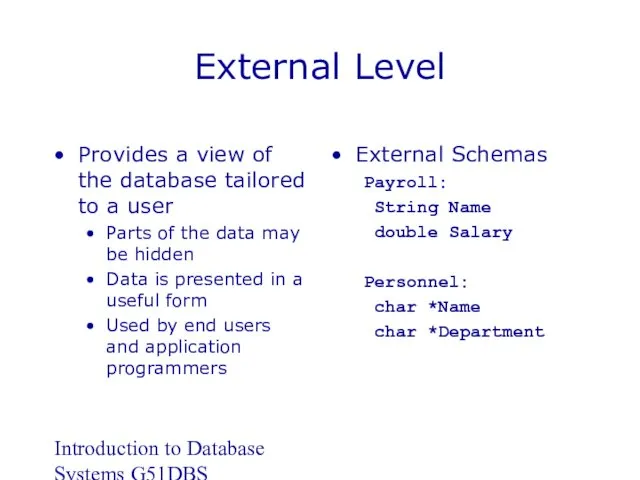
- 17. Introduction to Database Systems G51DBS External Level Provides a view of the database tailored to a
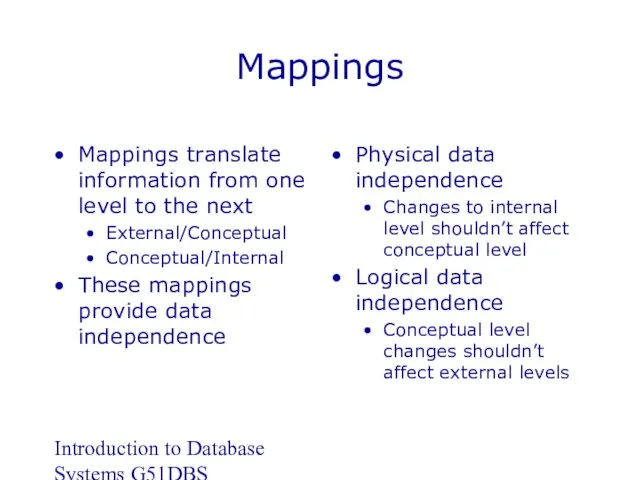
- 18. Introduction to Database Systems G51DBS Mappings Mappings translate information from one level to the next External/Conceptual
- 19. Introduction to Database Systems G51DBS ANSI/SPARC Architecture External Schemas External/Conceptual Mappings Conceptual Schema Internal Schema Conceptual/Internal
- 20. Introduction to Database Systems G51DBS This Lecture in Exams Describe the three levels of the ANSI/SPARC
- 22. Скачать презентацию






 Словарные методы сжатия. Лекция 3
Словарные методы сжатия. Лекция 3 Измерение информации
Измерение информации Обработка персональных данных
Обработка персональных данных Обеспечение безопасности веб-приложения
Обеспечение безопасности веб-приложения Информация
Информация Автоматизация системы управления технологическими процессами в компании ООО Скиф-Аналит
Автоматизация системы управления технологическими процессами в компании ООО Скиф-Аналит Информационные технологии в библиотеке
Информационные технологии в библиотеке Організація баз даних та знань. Моделі даних. Ієрархічна та мережна модель даних
Організація баз даних та знань. Моделі даних. Ієрархічна та мережна модель даних Развитие компьютерной техники
Развитие компьютерной техники Сравнительный анализ программных продуктов по электронной отчетности
Сравнительный анализ программных продуктов по электронной отчетности Инженерно-техническая защита информации на предприятии
Инженерно-техническая защита информации на предприятии Архивация данных
Архивация данных Презентация по теме Системы счисления. Арифметические операции в позиционных системах счисления для 9, 10 кл.
Презентация по теме Системы счисления. Арифметические операции в позиционных системах счисления для 9, 10 кл. Структуры данных в R. импорт и экспорт данных в R
Структуры данных в R. импорт и экспорт данных в R Системы счисления. Представление информации в компьютере
Системы счисления. Представление информации в компьютере Безопасность в сети Интернет
Безопасность в сети Интернет Школьная медиатека. Перспективы развития библиотек в школах России
Школьная медиатека. Перспективы развития библиотек в школах России Локальные компьютерные сети
Локальные компьютерные сети Стандарты и протоколы передачи данных в IoT
Стандарты и протоколы передачи данных в IoT Разработка урока Построение диаграмм и графиков в электронных таблицах
Разработка урока Построение диаграмм и графиков в электронных таблицах Основы программирования
Основы программирования Линейные программы
Линейные программы Поиск информации в интернете
Поиск информации в интернете Криптография: история развития и базовые знания
Криптография: история развития и базовые знания Білімдерін тексеру
Білімдерін тексеру Управление ИТ-инфраструктурой предприятия
Управление ИТ-инфраструктурой предприятия Компьютерная графика
Компьютерная графика Электронное портфолио
Электронное портфолио