Содержание
- 2. Teaching Lectures – by Me (15 lectures on a weekly basis) Labs and Practical sessions –
- 3. Some information to help you to take this module
- 4. Course Objectives 15 lectures – one per week Provide overview of Security Principles Encryption, Network Security,
- 5. What you can get from this course Why protect? What protect? How protect? Sorts of threats
- 6. Syllabus at a glance Basic terminology. Classical Encryption. Early cryptography. Rotor machines: Enigma and its relatives.
- 7. How to take this course: reading Basic literature (Required Reading!): Cryptography and Network Security by William
- 8. How to take this course: schedule Attend all lectures Submit assignments on time Do not leave
- 9. Assessment Overall mark: 30% - 1st term 30% - 2nd term 40% - Final Examination The
- 10. Questions?
- 11. Basic Concepts and Terminology Vulnerability Threat Attack Security concepts: Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability Security Service
- 12. Vulnerability Some state of the system of being open to attacks or injuries. Example in house
- 13. Threat A statement of an intention to injure, damage or any other enemy action. A potential
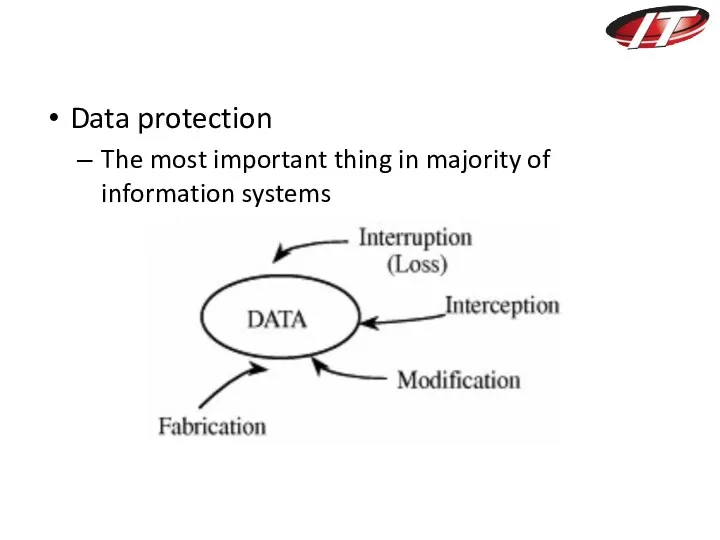
- 14. 4 kind of threats: Interception Interruption Modification Fabrication
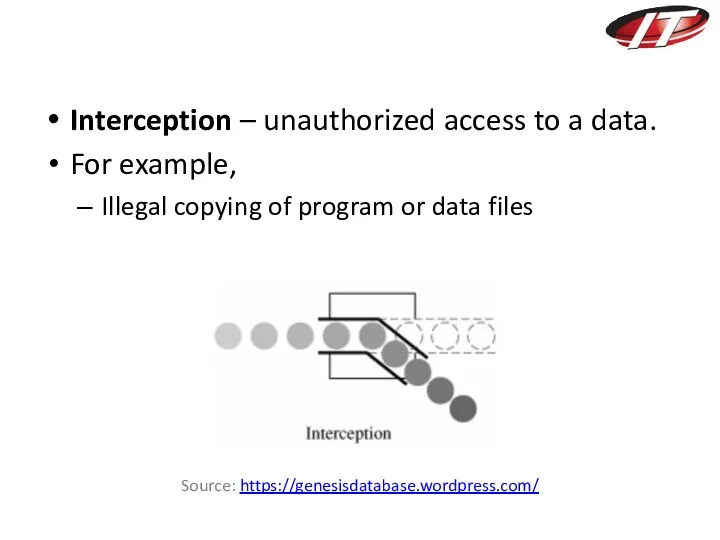
- 15. Interception – unauthorized access to a data. For example, Illegal copying of program or data files
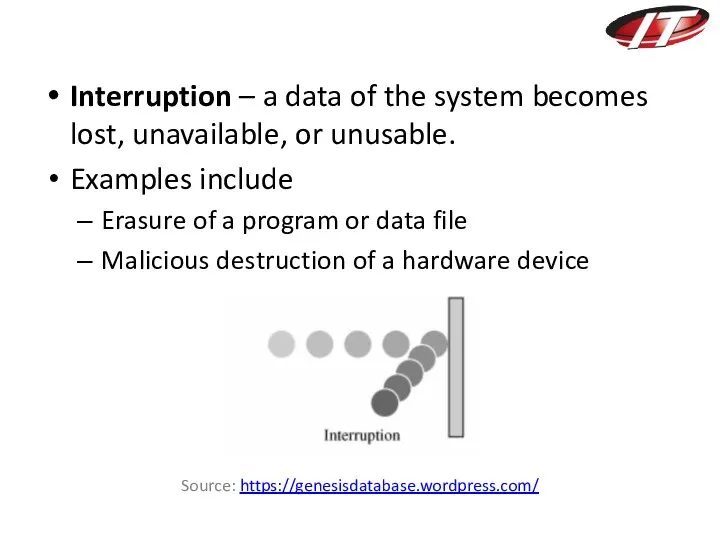
- 16. Interruption – a data of the system becomes lost, unavailable, or unusable. Examples include Erasure of
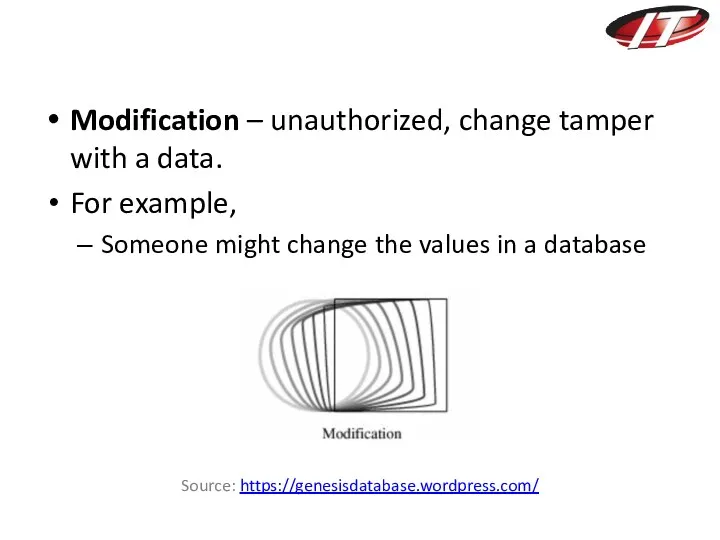
- 17. Modification – unauthorized, change tamper with a data. For example, Someone might change the values in
- 18. Fabrication – E.g. Unauthorized insertion to a existing database. Source: https://genesisdatabase.wordpress.com/
- 19. Attack An assault on system security A deliberate attempt to evade security services Kind of attacks:
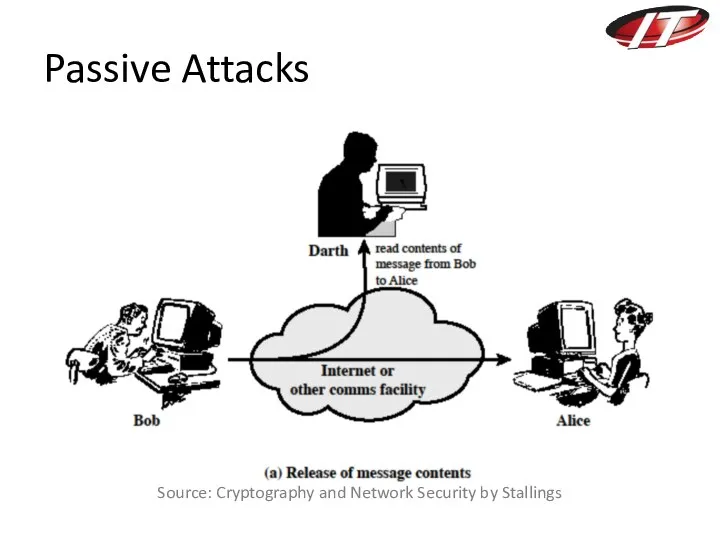
- 20. Passive Attacks Source: Cryptography and Network Security by Stallings
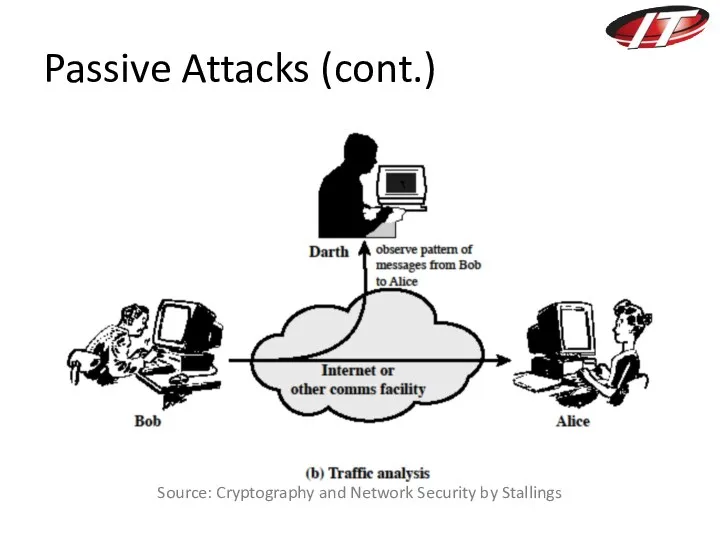
- 21. Passive Attacks (cont.) Source: Cryptography and Network Security by Stallings
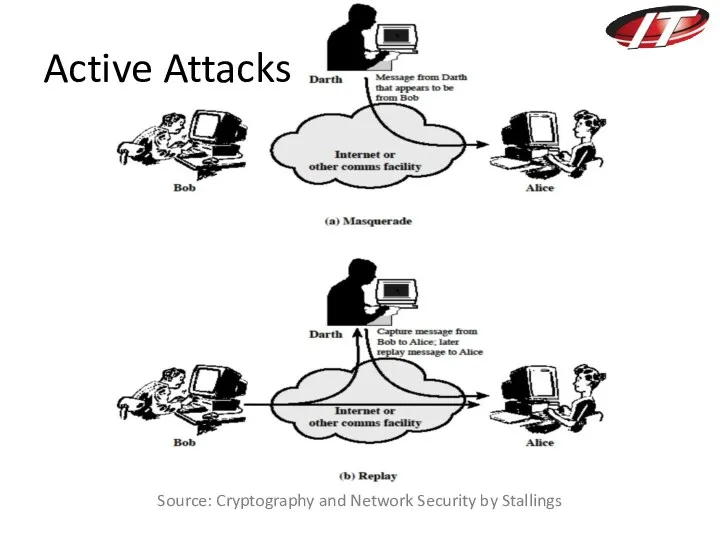
- 22. Source: Cryptography and Network Security by Stallings Active Attacks
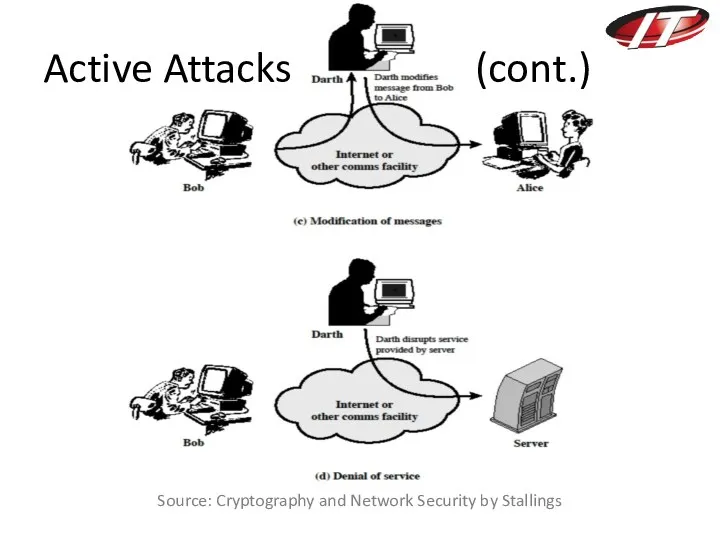
- 23. Source: Cryptography and Network Security by Stallings Active Attacks (cont.)
- 24. Why to attack? (MOM) Method: skills, knowledge, tools, etc. Opportunity: time and access Motive: fame, money,
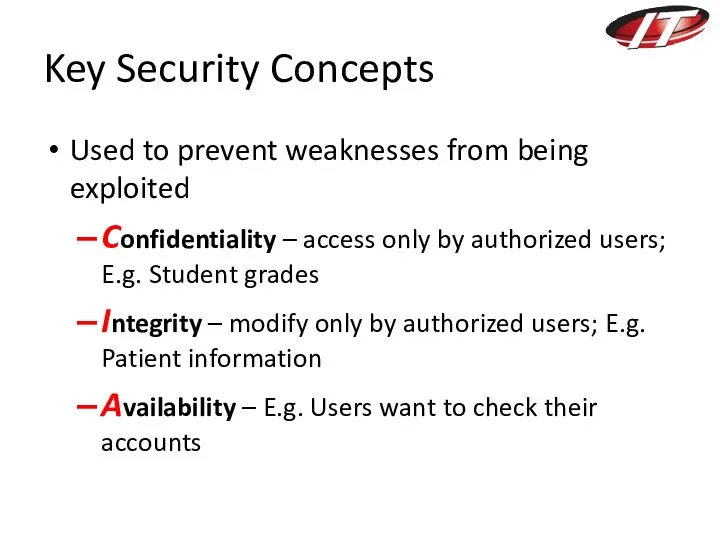
- 25. Key Security Concepts Used to prevent weaknesses from being exploited Confidentiality – access only by authorized
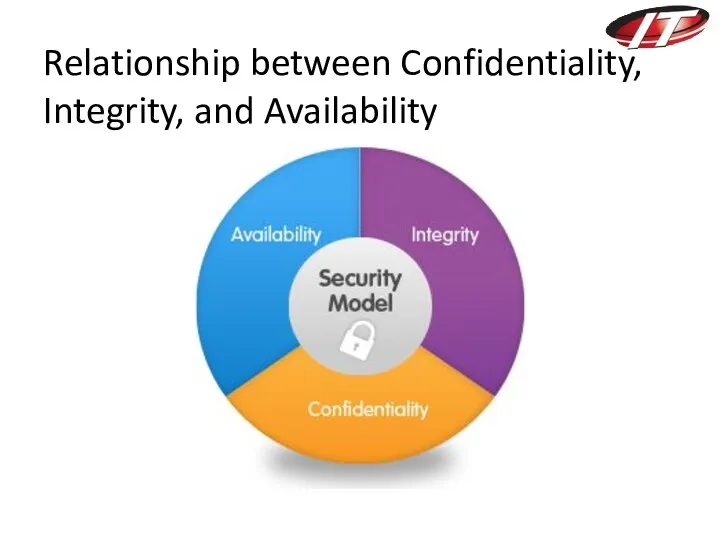
- 26. Relationship between Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability
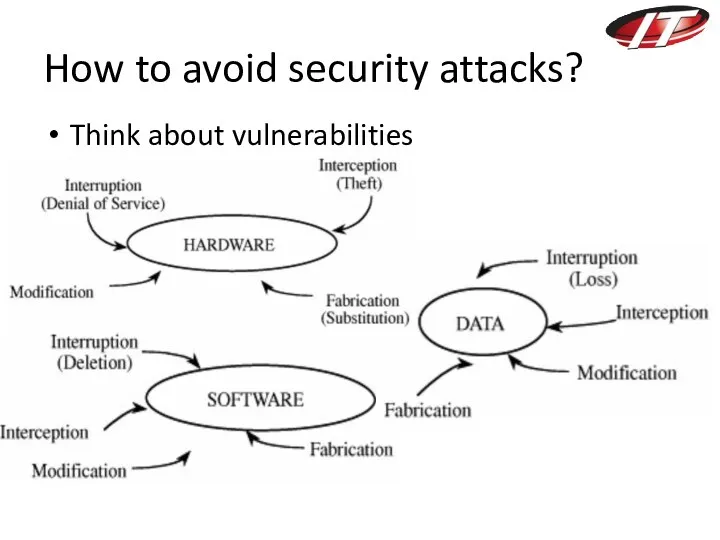
- 27. How to avoid security attacks? Think about vulnerabilities
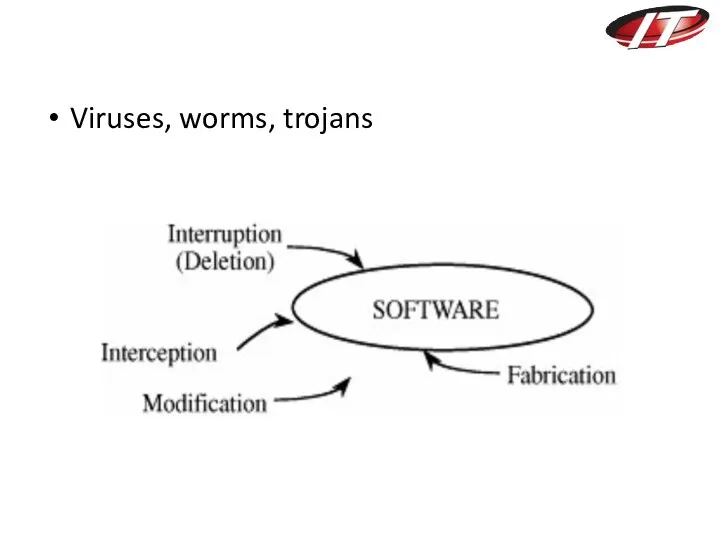
- 28. Viruses, worms, trojans
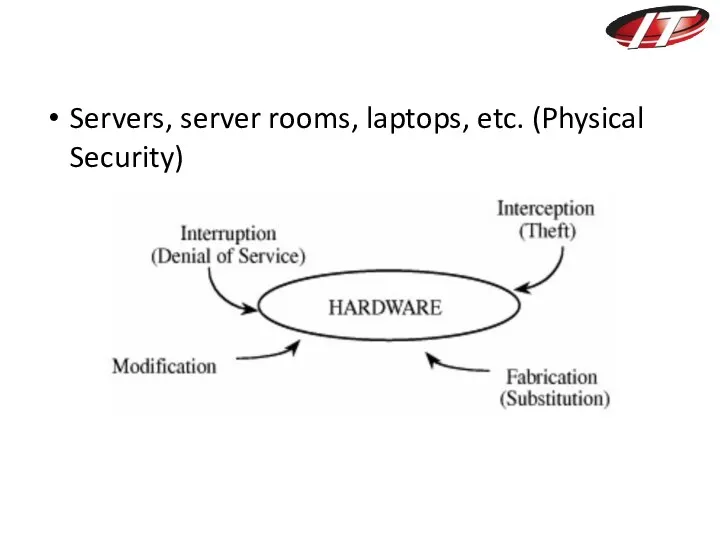
- 29. Servers, server rooms, laptops, etc. (Physical Security)
- 30. Data protection The most important thing in majority of information systems
- 31. How to protect? 3Ds of Security Defense – reducing risks and saving costs of incidents (E.g.
- 32. How to protect? Security Service Enhance security of data processing systems and information transfers of an
- 33. Security Services X.800: “a service provided by a protocol layer of communicating open systems, which ensures
- 34. Security Services (X.800) Authentication – assure that communication entity is the one claimed Access Control –
- 35. Security Mechanisms (X.800) Features designed to protect, prevent, or recover from a security attack No single
- 36. Summary Basic Information Security Terminology Key Security Concepts Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability Subject of attacks? Hardware, Software
- 37. Reading Cryptography and Network Security by Stallings Chapter 1: Sections 1.1, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5, 1.8
- 39. Скачать презентацию























 Интернет технологии Язык HTML и основы Web - страниц
Интернет технологии Язык HTML и основы Web - страниц Отладка простейшей программы в Microsoft Visual Studio 2008
Отладка простейшей программы в Microsoft Visual Studio 2008 Обучение оформления заказов через онлайн-сервис
Обучение оформления заказов через онлайн-сервис Система счисления. Перевод чисел в десятичную систему счисления
Система счисления. Перевод чисел в десятичную систему счисления Работа со слоями эффектов. (Лекция 2)
Работа со слоями эффектов. (Лекция 2) Компанія Apple
Компанія Apple Мастер-классы по ремонту и дизайну. Краткий обзор
Мастер-классы по ремонту и дизайну. Краткий обзор Прикладное программное обеспечение
Прикладное программное обеспечение Язык программирования Object Pascal. Общий обзор
Язык программирования Object Pascal. Общий обзор Обеспечивающие информационные системы
Обеспечивающие информационные системы Creation of a simple network configuration
Creation of a simple network configuration Автоматизированные информационные технологии
Автоматизированные информационные технологии Динамическое программирование
Динамическое программирование Задачи графика
Задачи графика Центральная библиотека имени Н.А. Некрасова, Николаевский район. Продвижение в социальных сетях
Центральная библиотека имени Н.А. Некрасова, Николаевский район. Продвижение в социальных сетях Сетевые устройства
Сетевые устройства Архитектура и система команд процесоров Intel. (Тема 1)
Архитектура и система команд процесоров Intel. (Тема 1) Электронная библиотечная система Лань
Электронная библиотечная система Лань Эстафета
Эстафета Принцип построения компьютера
Принцип построения компьютера Introduction to computer systems. Architecture of computer systems
Introduction to computer systems. Architecture of computer systems Алгоритм, 4 класс
Алгоритм, 4 класс Влияние СМИ на формирование общественного мнения
Влияние СМИ на формирование общественного мнения Современные угрозы информационной безопасности в России
Современные угрозы информационной безопасности в России Урок по теме Табличные информационные модели
Урок по теме Табличные информационные модели Электронные таблицы. (7 класс)
Электронные таблицы. (7 класс) Исполнитель Робот. Цикл N раз
Исполнитель Робот. Цикл N раз Клан JAS - мой дом
Клан JAS - мой дом