Programming Logic and Design Seventh Edition. Chapter 1. An Overview of Computers and Programming презентация
Содержание
- 2. Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Computer systems Simple program logic The steps involved
- 3. Understanding Computer Systems Computer system Combination of all the components required to process and store data
- 4. Understanding Computer Systems (continued) Application software such as word processing, spreadsheets, payroll and inventory, even games
- 5. Understanding Computer Systems (continued) Output Resulting information that is sent to a printer, a monitor, or
- 6. Understanding Computer Systems (continued) Computer memory Computer’s temporary, internal storage – random access memory (RAM) Volatile
- 7. Understanding Simple Program Logic Program executes or runs Input will be accepted, some processing will occur,
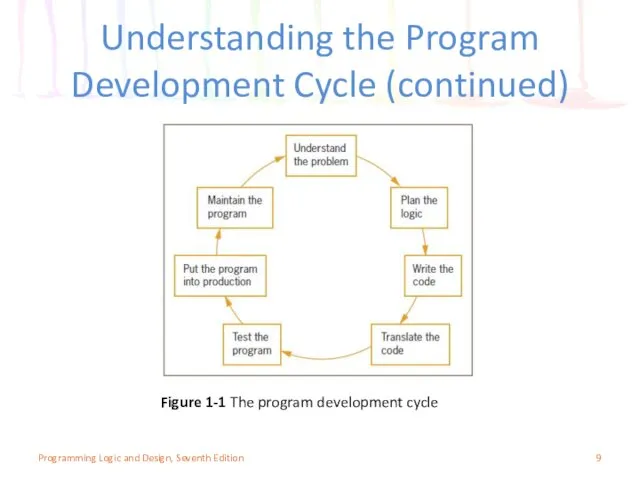
- 8. Understanding the Program Development Cycle Program development cycle Understand the problem Plan the logic Code the
- 9. Understanding the Program Development Cycle (continued) Figure 1-1 The program development cycle Programming Logic and Design,
- 10. Understanding the Problem One of the most difficult aspects of programming Users or end users People
- 11. Planning the Logic Heart of the programming process Most common planning tools Flowcharts Pseudocode IPO charts
- 12. Coding the Program Hundreds of programming languages available Choose based on features Similar in their basic
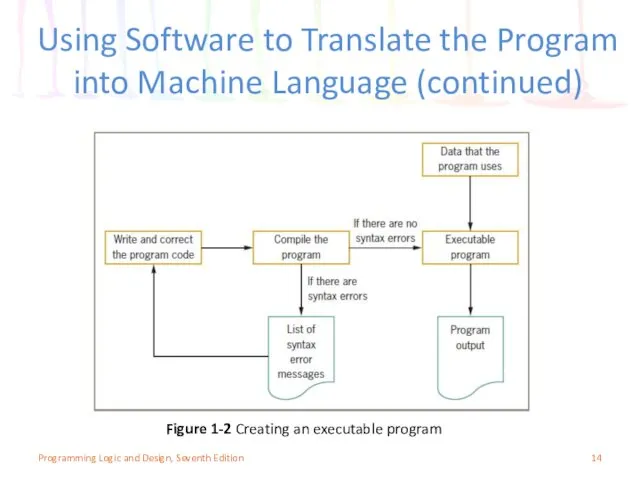
- 13. Using Software to Translate the Program into Machine Language Translator program Compiler or interpreter Changes the
- 14. Using Software to Translate the Program into Machine Language (continued) Figure 1-2 Creating an executable program
- 15. Testing the Program Logical error Results when a syntactically correct statement, but the wrong one for
- 16. Putting the Program into Production Process depends on program’s purpose May take several months Conversion The
- 17. Maintaining the Program Maintenance Making changes after the program is put into production Common first programming
- 18. Using Pseudocode Statements and Flowchart Symbols Pseudocode English-like representation of the logical steps it takes to
- 19. Writing Pseudocode Pseudocode representation of a number-doubling problem start input myNumber set myAnswer = myNumber *
- 20. Writing Pseudocode (continued) Programmers preface their pseudocode with a beginning statement like start and end it
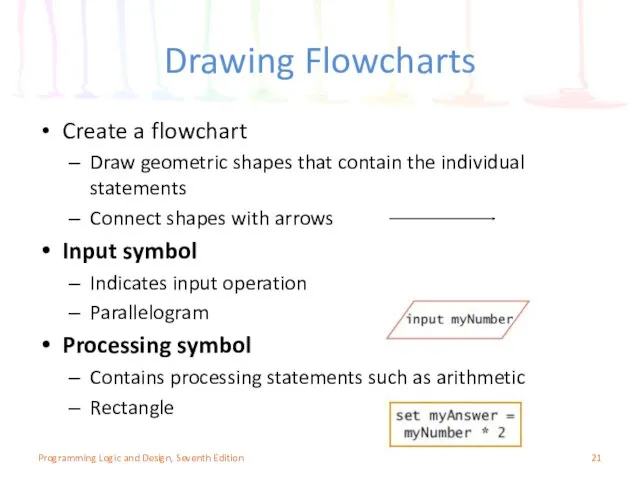
- 21. Drawing Flowcharts Create a flowchart Draw geometric shapes that contain the individual statements Connect shapes with
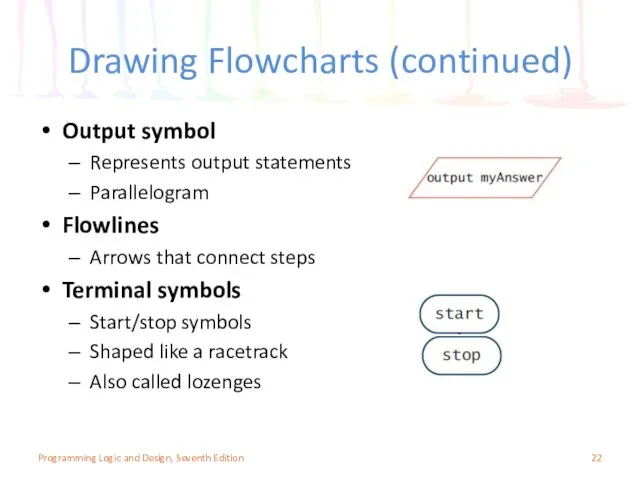
- 22. Drawing Flowcharts (continued) Output symbol Represents output statements Parallelogram Flowlines Arrows that connect steps Terminal symbols
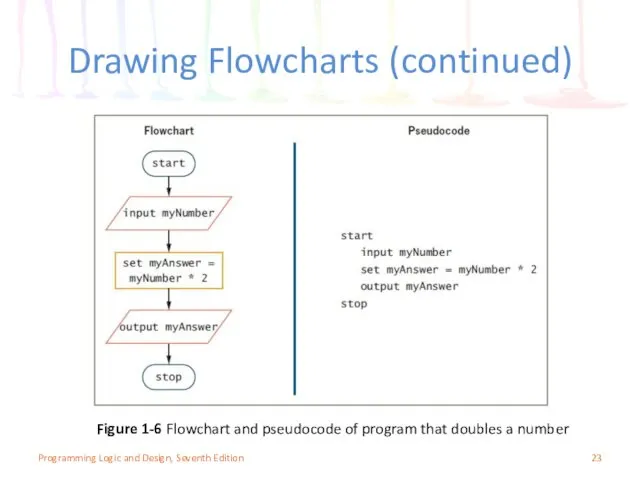
- 23. Drawing Flowcharts (continued) Figure 1-6 Flowchart and pseudocode of program that doubles a number Programming Logic
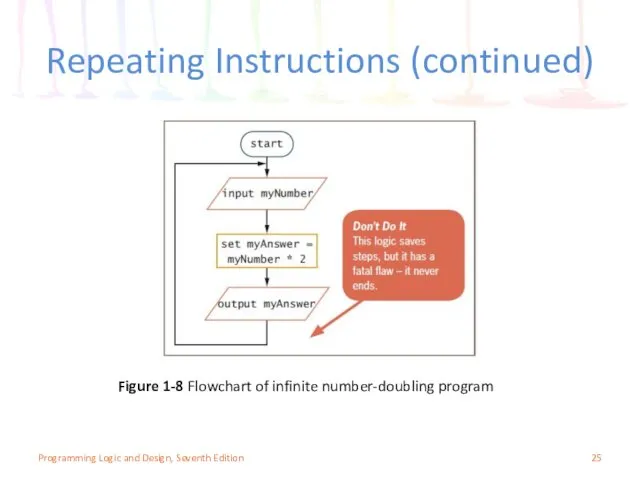
- 24. Repeating Instructions Program in Figure 1-6 only works for one number Not feasible to run the
- 25. Repeating Instructions (continued) Figure 1-8 Flowchart of infinite number-doubling program Programming Logic and Design, Seventh Edition
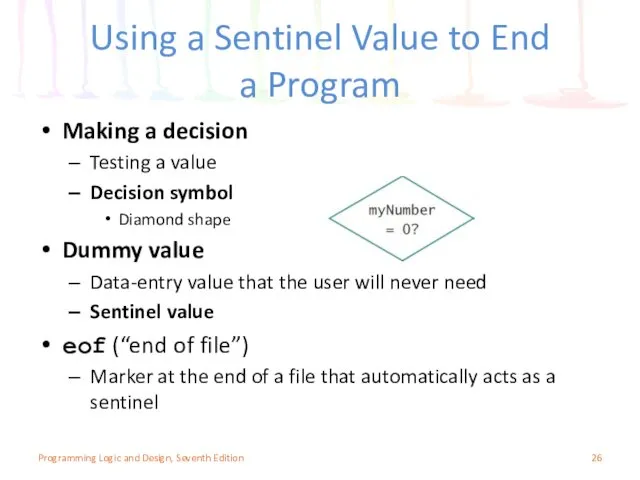
- 26. Using a Sentinel Value to End a Program Making a decision Testing a value Decision symbol
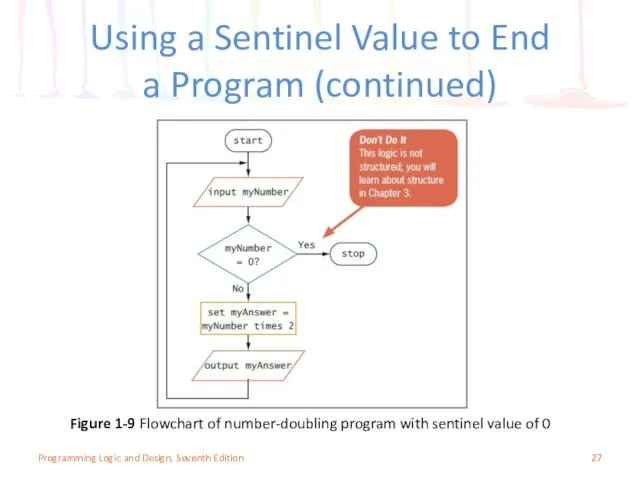
- 27. Using a Sentinel Value to End a Program (continued) Figure 1-9 Flowchart of number-doubling program with
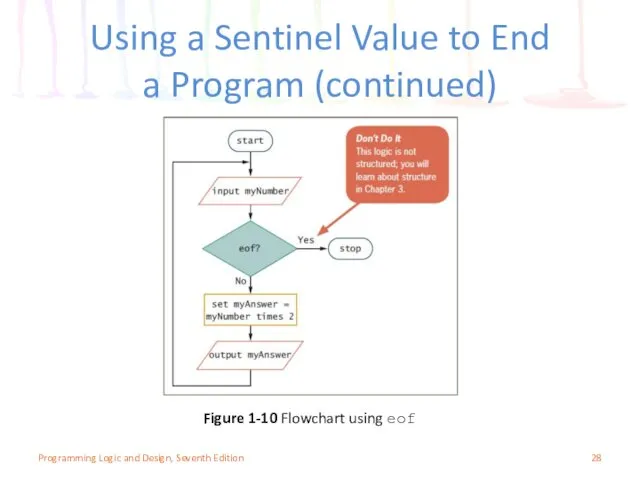
- 28. Using a Sentinel Value to End a Program (continued) Figure 1-10 Flowchart using eof Programming Logic
- 29. Understanding Programming and User Environments Many options for programming and user environments Planning Flowchart Pseudocode Coding
- 30. Understanding Programming Environments Use a keyboard to type program statements into an editor Plain text editor
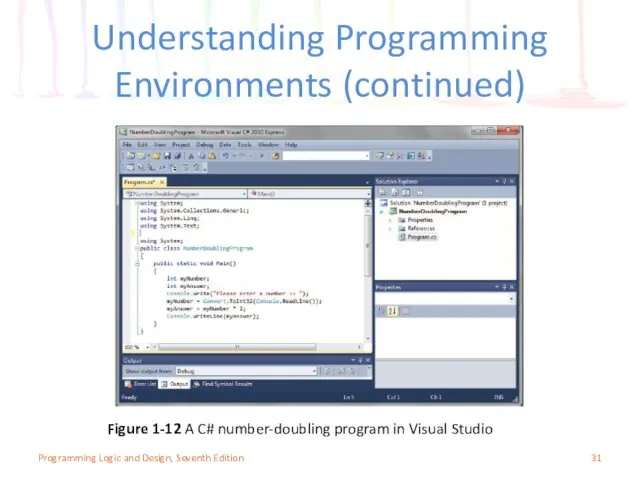
- 31. Understanding Programming Environments (continued) Figure 1-12 A C# number-doubling program in Visual Studio Programming Logic and
- 32. Understanding User Environments Command line Location on your computer screen where you type text entries to
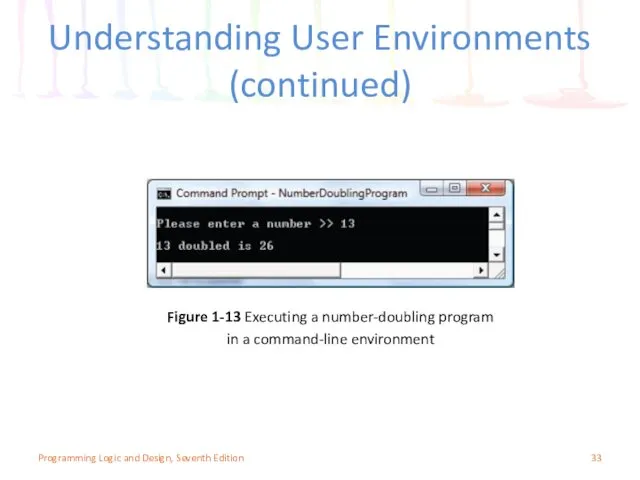
- 33. Understanding User Environments (continued) Figure 1-13 Executing a number-doubling program in a command-line environment Programming Logic
- 34. Understanding User Environments (continued) Figure 1-14 Executing a number-doubling program in a GUI environment Programming Logic
- 35. Understanding the Evolution of Programming Models People have been writing modern computer programs since the 1940s
- 36. Understanding the Evolution of Programming Models (continued) Major models or paradigms used by programmers Procedural programming
- 38. Скачать презентацию



















 Приложение Delphi , его интерфейс, задачи визуального объектно-ориентированного программирования
Приложение Delphi , его интерфейс, задачи визуального объектно-ориентированного программирования Структурная схема компьютера
Структурная схема компьютера Remote Method Invocation. Порядок разработки и запуска RMI-приложений. Нововведения в Java 5
Remote Method Invocation. Порядок разработки и запуска RMI-приложений. Нововведения в Java 5 Трекинг и кеинг. Работа в After Effects c 3D объектами. Взаимодействие с другими графическими и 3D редакторами
Трекинг и кеинг. Работа в After Effects c 3D объектами. Взаимодействие с другими графическими и 3D редакторами Кодирование текстовой информации
Кодирование текстовой информации Яка небезпека очікує дітей в інтернеті
Яка небезпека очікує дітей в інтернеті Система и окружающая среда
Система и окружающая среда Програмне забезпечення для комп'ютерної поліграфії
Програмне забезпечення для комп'ютерної поліграфії Программа Access. Оболочка, меню, настройка панелей
Программа Access. Оболочка, меню, настройка панелей Арбитраж. 9 поток
Арбитраж. 9 поток Классификация и возможности технических разведок
Классификация и возможности технических разведок Информатика. 10 класс (углублённый уровень)
Информатика. 10 класс (углублённый уровень) Облачные вычисления
Облачные вычисления Использование интернет-технологий на уроках иностранного языка
Использование интернет-технологий на уроках иностранного языка Модернизация ИТ-инфраструктуры с помощью Windows Server 2016 (совместно с Veeam Software)
Модернизация ИТ-инфраструктуры с помощью Windows Server 2016 (совместно с Veeam Software) Жизненный цикл информационных систем
Жизненный цикл информационных систем Информационная безопасность. Правовое обеспечение защиты информации
Информационная безопасность. Правовое обеспечение защиты информации Технологии программирования (методы программирования)
Технологии программирования (методы программирования) Бот для магазина цветов в Telegram
Бот для магазина цветов в Telegram Элективный курсМатематика и компьютер. Mathcad: помощь в вычислениях
Элективный курсМатематика и компьютер. Mathcad: помощь в вычислениях Կոմերցիոն առաջարկ
Կոմերցիոն առաջարկ GYMNASIUM 47. Зачем изучать программирование
GYMNASIUM 47. Зачем изучать программирование Исследование степени сжатия информации различными архиваторами
Исследование степени сжатия информации различными архиваторами Технические аспекты работы пользователей с сайтом Корпоративного университета РДШ
Технические аспекты работы пользователей с сайтом Корпоративного университета РДШ Базы знаний. Модели представления знаний. Лекция 9
Базы знаний. Модели представления знаний. Лекция 9 Измерение количества информации. 7 класс
Измерение количества информации. 7 класс Инструкция по работе студента в системе дистанционного обучения
Инструкция по работе студента в системе дистанционного обучения Информационная модель. Этапы построения
Информационная модель. Этапы построения