Содержание
- 2. Objectives After completing this training you should be able to: Install the Remy-MF1/P1 in the field.
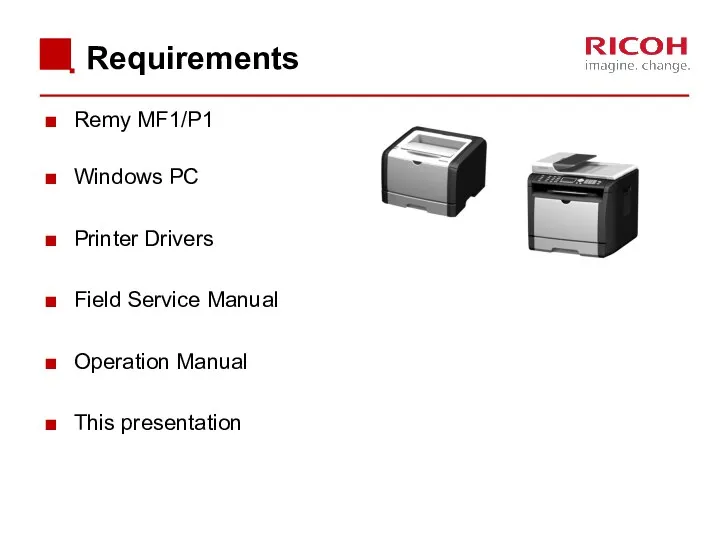
- 3. Requirements Remy MF1/P1 Windows PC Printer Drivers Field Service Manual Operation Manual This presentation
- 4. Pre-requisites and exam Before starting this training you must already have followed the My-Ricoh training for:
- 5. Module overview Introduction Maintenance Detailed Section Descriptions Troubleshooting
- 6. 1. Introduction
- 7. Remy models Remy-MF1a M156: SP 311SFN Remy-MF1aw M157: SP 311SFNw Remy-P1a M154: SP 311DN Remy-P1aw M155:
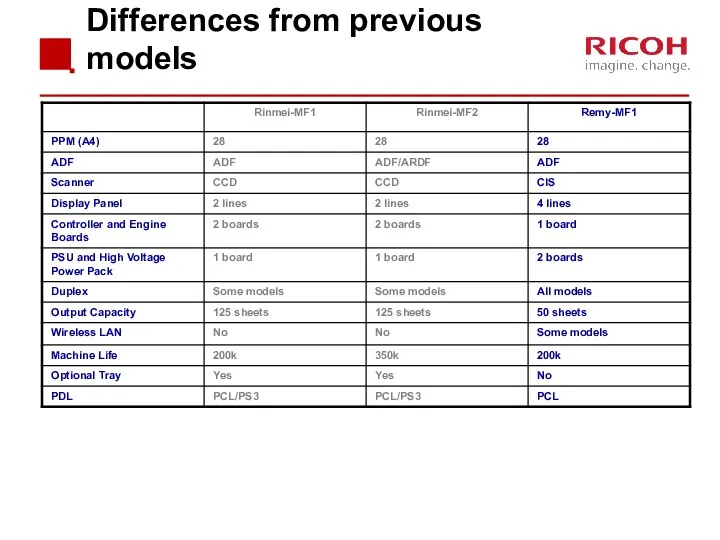
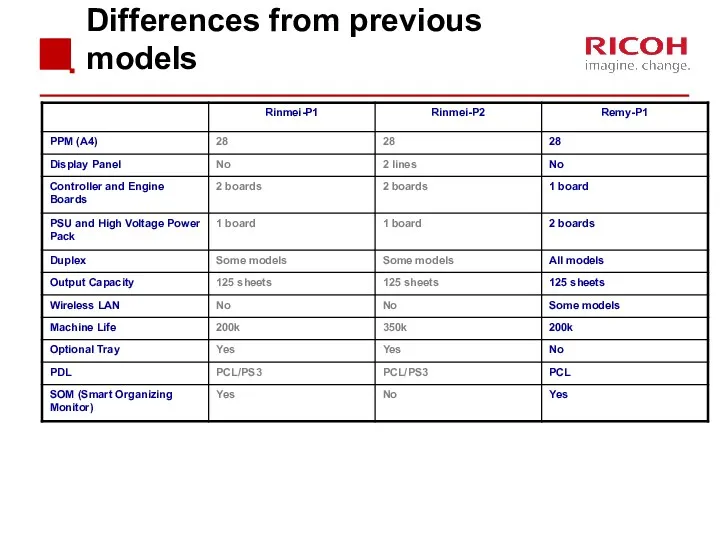
- 8. Differences from previous models
- 9. Differences from previous models
- 10. Other Points Remy-MF1/P1 do not have a USB host or the scan to USB feature. There
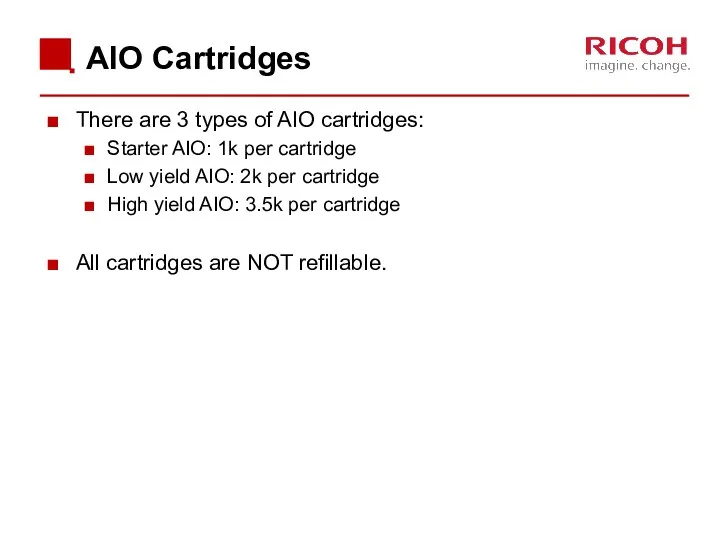
- 11. AIO Cartridges There are 3 types of AIO cartridges: Starter AIO: 1k per cartridge Low yield
- 12. Targets Monthly Print Volume Average: 0.7K Maximum: 5.8K Estimated Unit Life: 5 years or 200K prints
- 13. 2. Maintenance
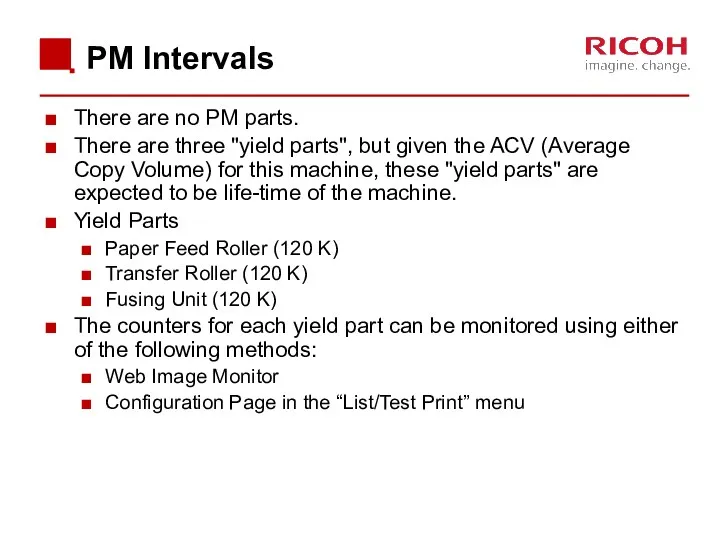
- 14. PM Intervals There are no PM parts. There are three "yield parts", but given the ACV
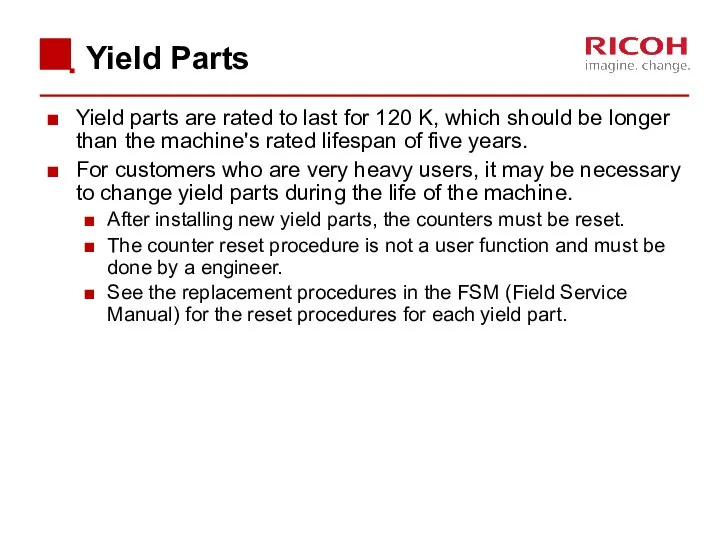
- 15. Yield Parts Yield parts are rated to last for 120 K, which should be longer than
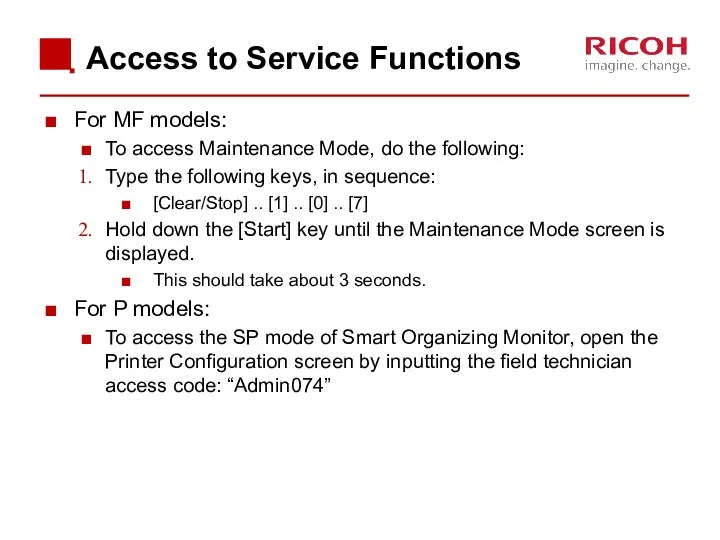
- 16. Access to Service Functions For MF models: To access Maintenance Mode, do the following: Type the
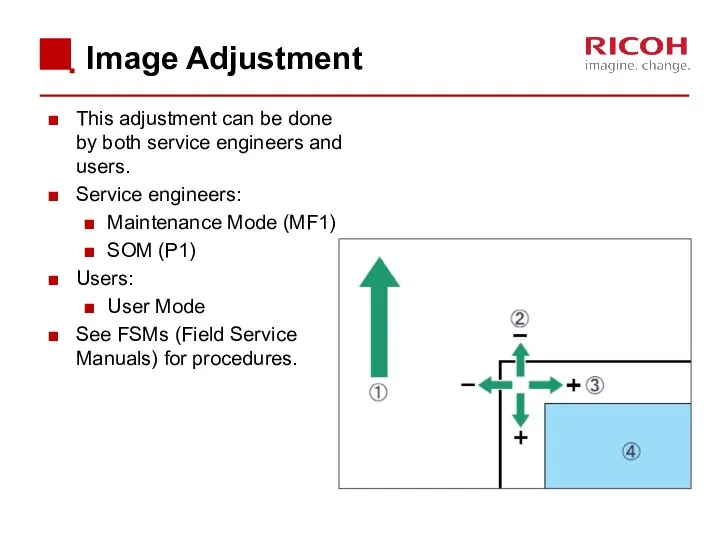
- 17. Image Adjustment This adjustment can be done by both service engineers and users. Service engineers: Maintenance
- 18. Firmware Updating You need a PC to do the firmware update. See the service manual for
- 19. 3. Detailed Section Descriptions
- 20. 3.1 Machine Overview
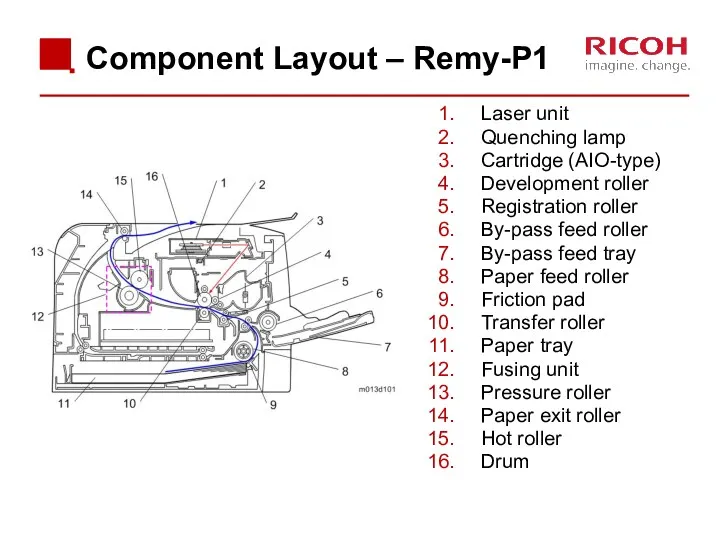
- 21. Component Layout – Remy-P1 Laser unit Quenching lamp Cartridge (AIO-type) Development roller Registration roller By-pass feed
- 22. Paper Path – Remy-P1 [A]: Duplex section [B]: Paper tray
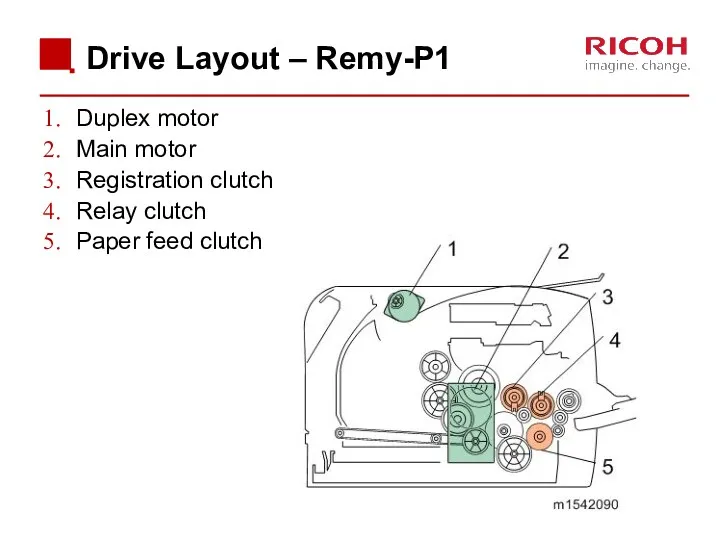
- 23. Drive Layout – Remy-P1 Duplex motor Main motor Registration clutch Relay clutch Paper feed clutch
- 24. 3.2 Cover Removal & Part Replacement
- 25. General Precautions Before you start to work on the machine: If there are printer jobs in
- 26. General Precautions Many of the parts are held in place with plastic latches which can break
- 27. Removing Covers The covers have a lot of hooks and tabs. Disconnect these carefully, as explained
- 28. Re-installing the Top Cover When re-installing the top cover, always verify that the two paperweights [A]
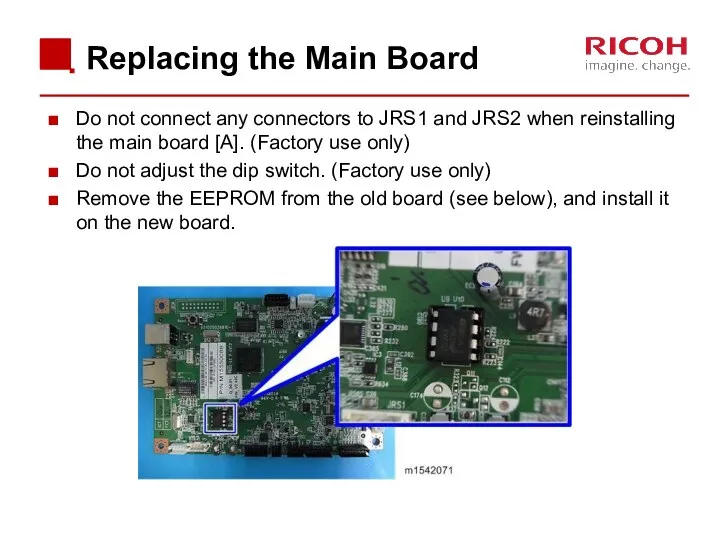
- 29. Replacing the Main Board Do not connect any connectors to JRS1 and JRS2 when reinstalling the
- 30. Install a New EEPROM Do the following settings after installing a new EEPROM. Input the PnP
- 31. 3.3 ADF
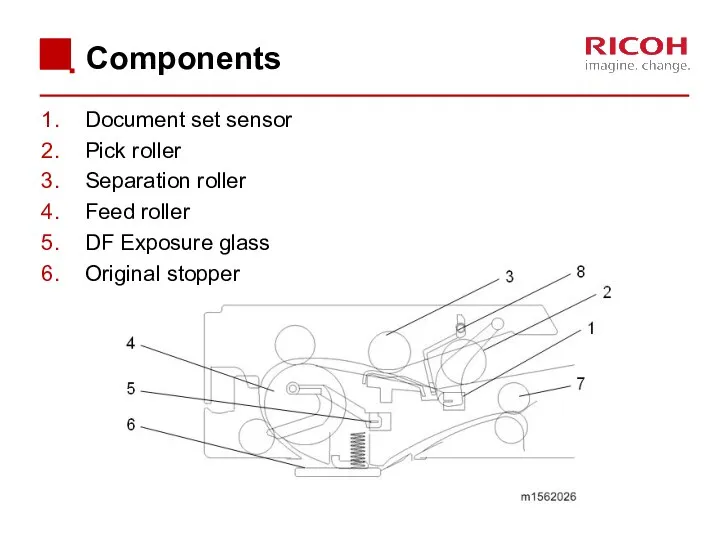
- 32. Components Document set sensor Pick roller Separation roller Feed roller DF Exposure glass Original stopper
- 33. Paper Path When the document set sensor [1] detects an original, the ADF motor rotates to
- 34. 3.4 Scanner
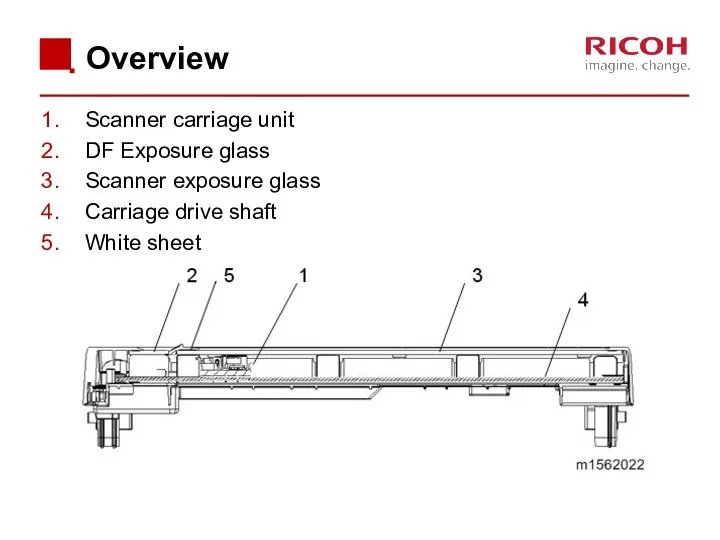
- 35. Overview Scanner carriage unit DF Exposure glass Scanner exposure glass Carriage drive shaft White sheet
- 36. Drive Scanner motor [A]: Drives the scanner carriage unit [B] through gears and a timing belt
- 37. 3.5 Laser Exposure
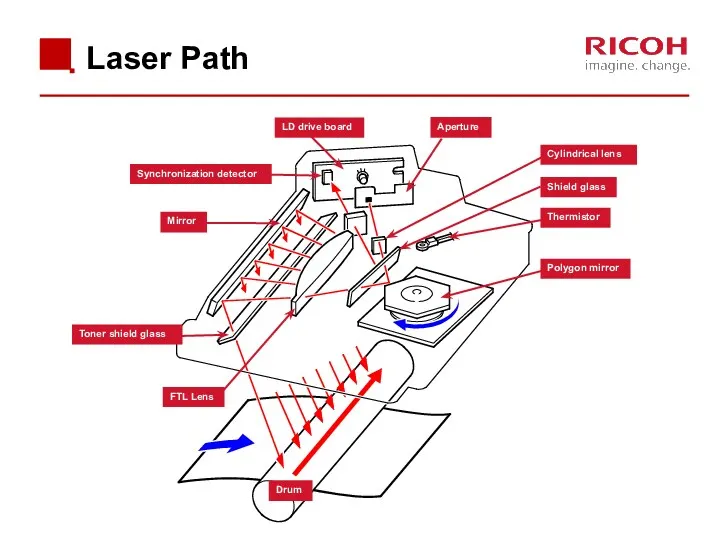
- 38. Laser Path Polygon mirror LD drive board Synchronization detector Aperture Cylindrical lens Shield glass Thermistor Drum
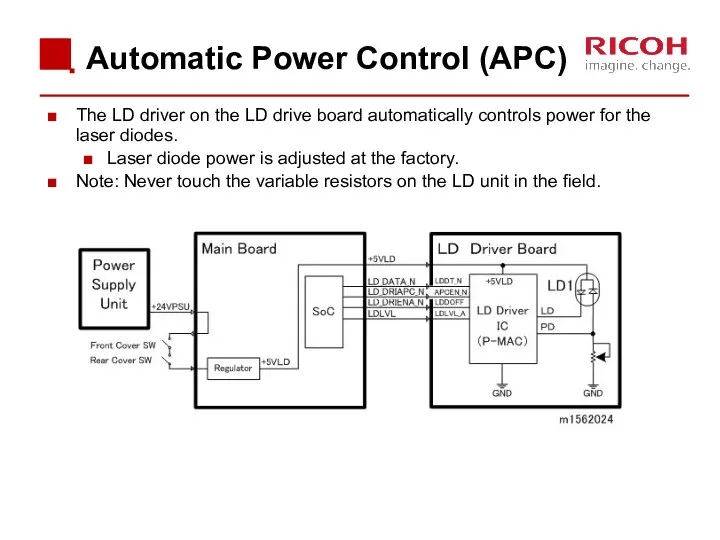
- 39. Automatic Power Control (APC) The LD driver on the LD drive board automatically controls power for
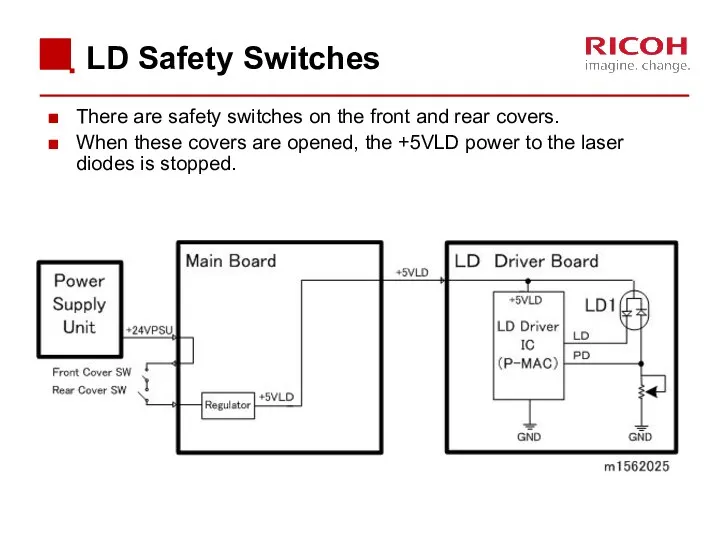
- 40. LD Safety Switches There are safety switches on the front and rear covers. When these covers
- 41. 3.6 AIO
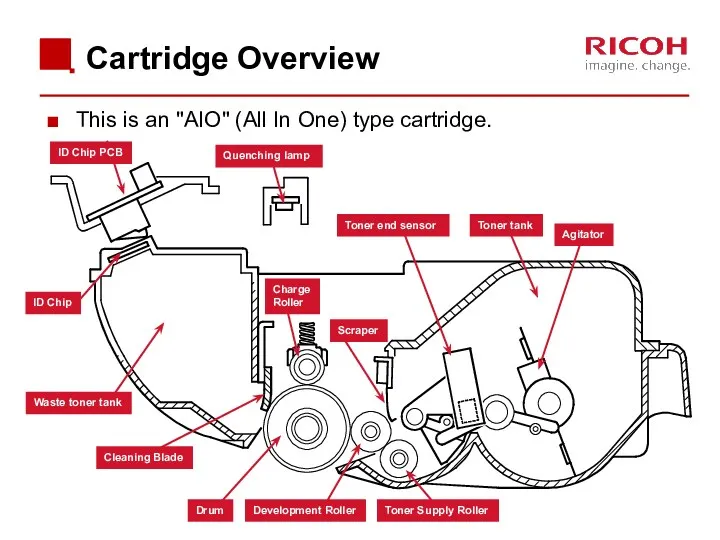
- 42. Cartridge Overview This is an "AIO" (All In One) type cartridge. Quenching lamp Waste toner tank
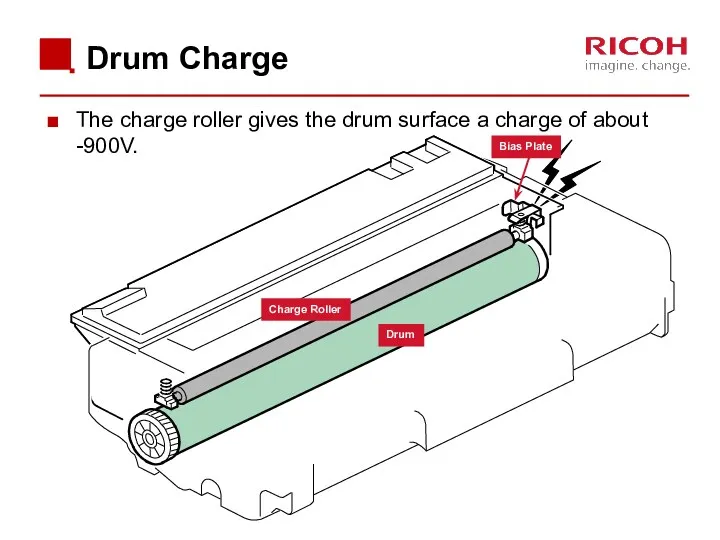
- 43. Drum Charge The charge roller gives the drum surface a charge of about -900V. Bias Plate
- 44. 3.7 Toner Supply and Development
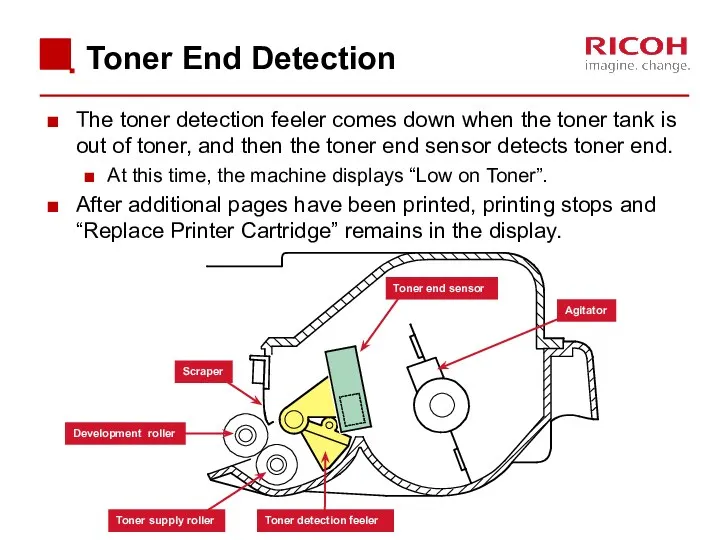
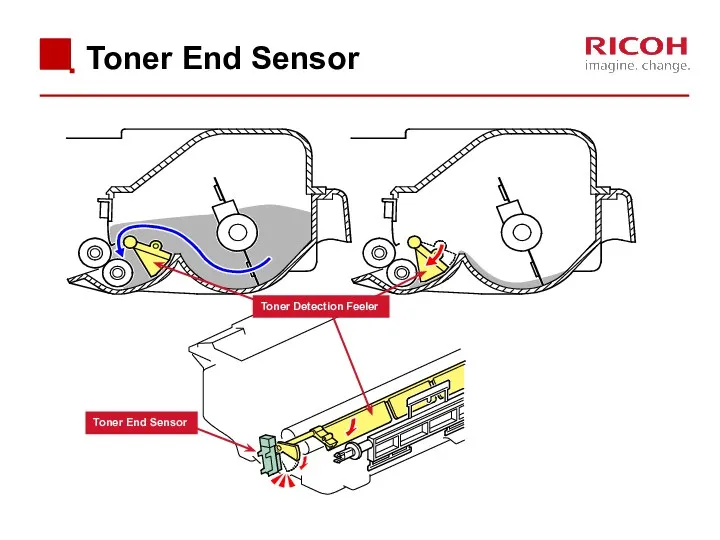
- 45. Toner End Detection The toner detection feeler comes down when the toner tank is out of
- 46. Toner End Sensor Toner End Sensor Toner Detection Feeler
- 47. Toner Overflow Prevention 1/2 Main Motor Rotation Count Time to replace the AIO cartridge can also
- 48. Toner Overflow Prevention 2/2 Why do we need this feature? Normally, the AIO is replaced by
- 49. AIO Replacement The new AIO is detected by the machine with the ID chip when it
- 50. 3.8 Transfer & Separation
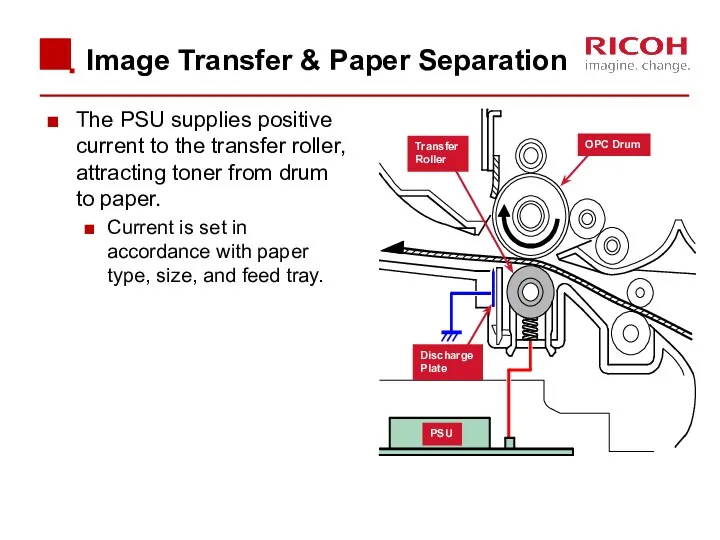
- 51. Image Transfer & Paper Separation The PSU supplies positive current to the transfer roller, attracting toner
- 52. Image Transfer Current Timing There are two transfer current levels: low and high. Low level: Before
- 53. Transfer Roller Cleaning In case of a paper jam or printing on smaller paper than the
- 54. 3.9 Paper Feed
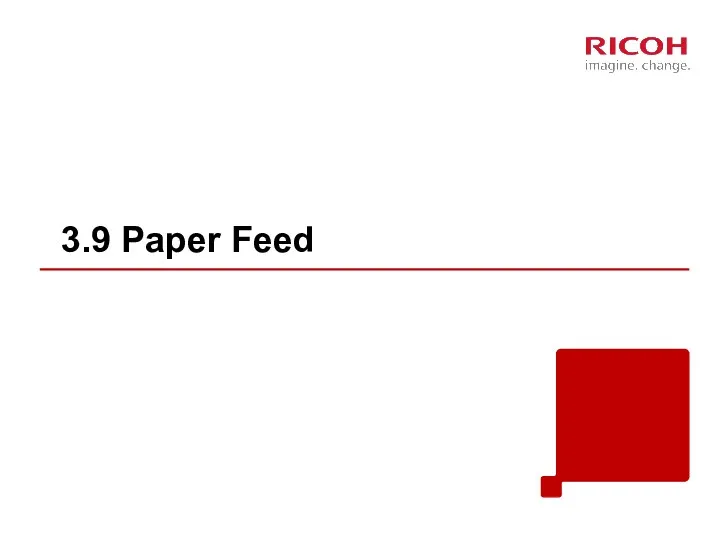
- 55. Paper Tray The tray capacity is 250 sheets. Feed roller Friction pad Bottom plate
- 56. Paper Path [A]: Duplex section [B]: Paper tray
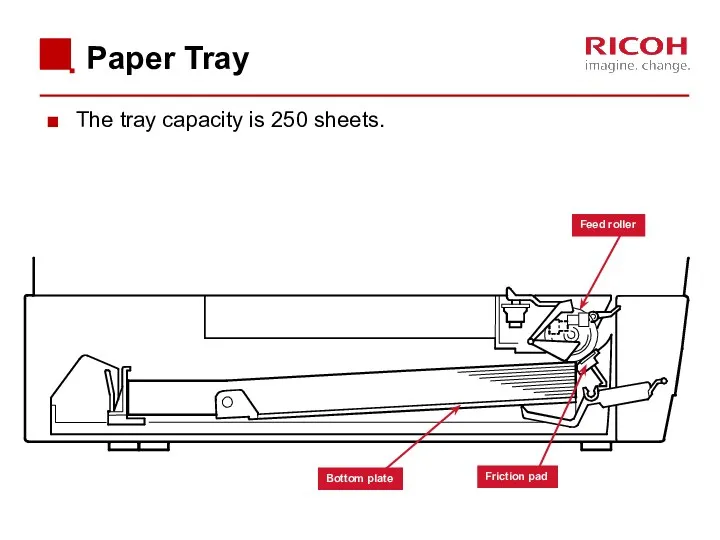
- 57. Paper Tray Extension Locks The user can extend the tray manually to hold paper longer than
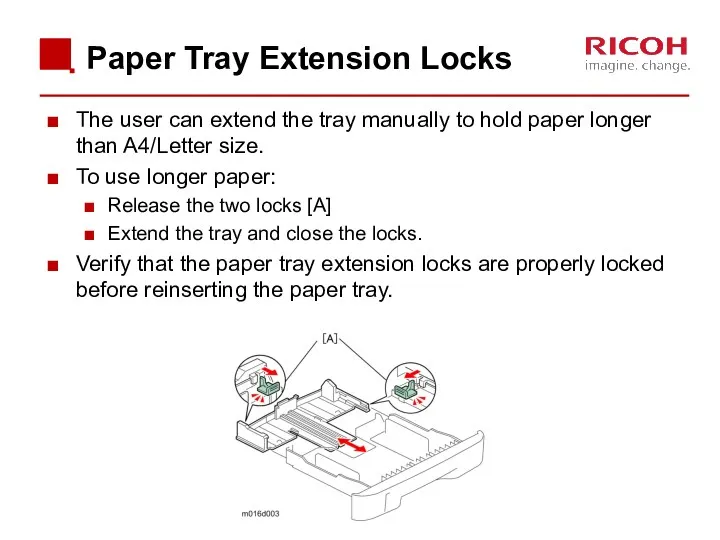
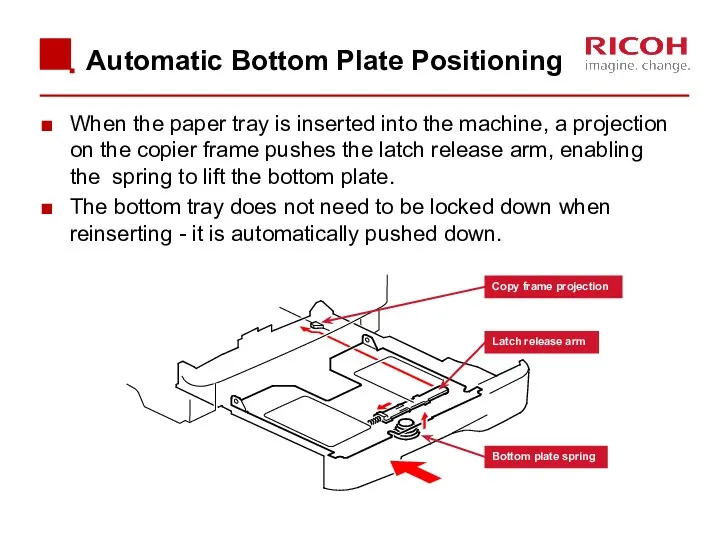
- 58. When the paper tray is inserted into the machine, a projection on the copier frame pushes
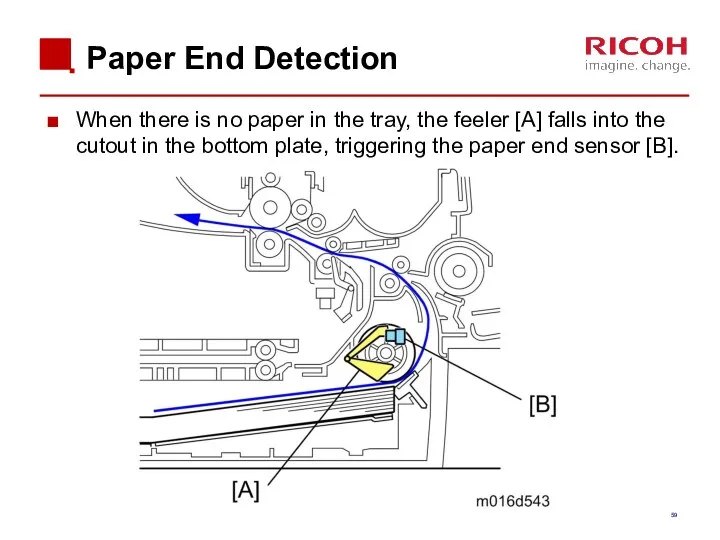
- 59. Paper End Detection When there is no paper in the tray, the feeler [A] falls into
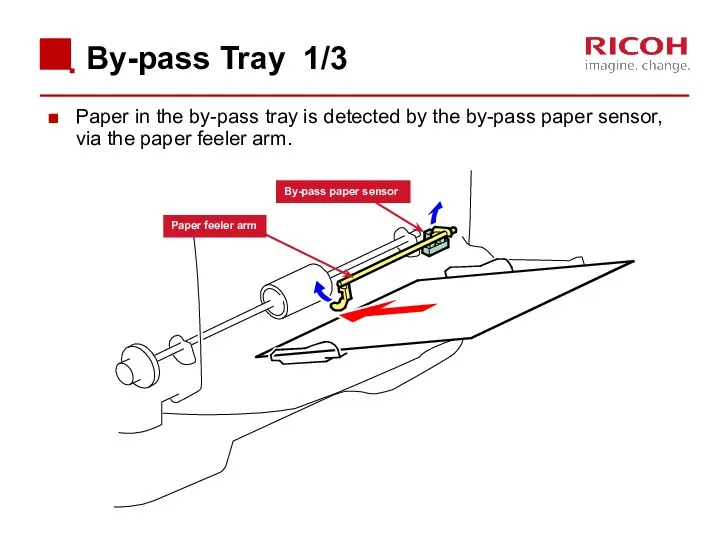
- 60. By-pass Tray 1/3 Paper in the by-pass tray is detected by the by-pass paper sensor, via
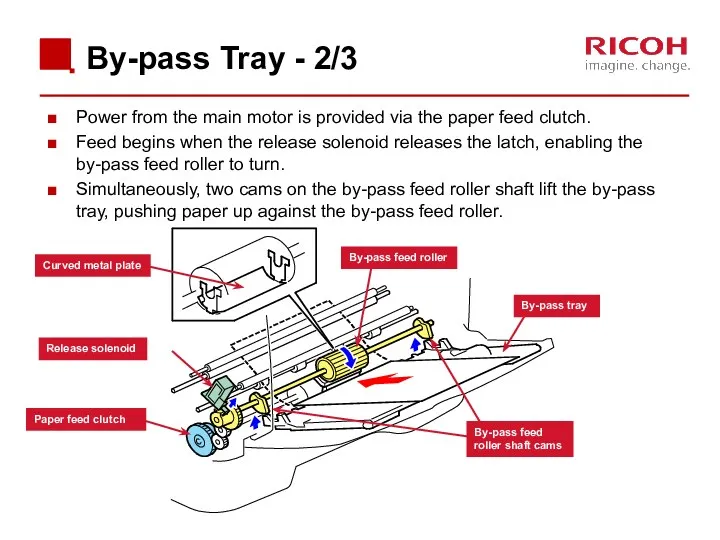
- 61. By-pass Tray - 2/3 Power from the main motor is provided via the paper feed clutch.
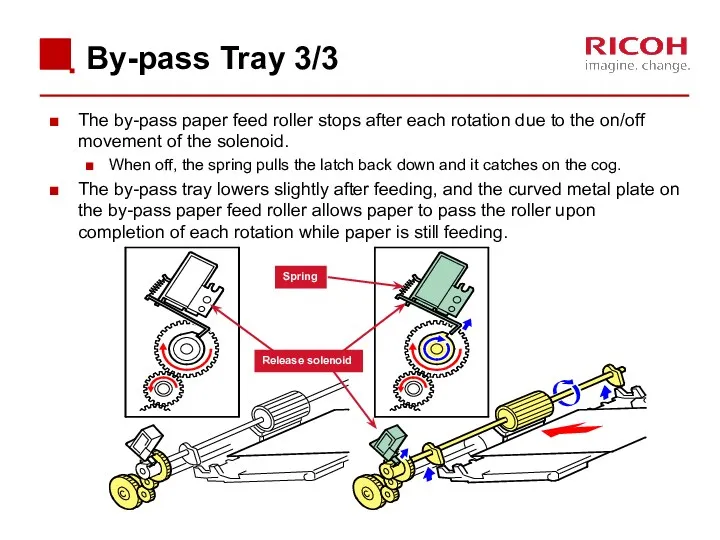
- 62. By-pass Tray 3/3 The by-pass paper feed roller stops after each rotation due to the on/off
- 63. 3.10 Fusing & Paper Exit
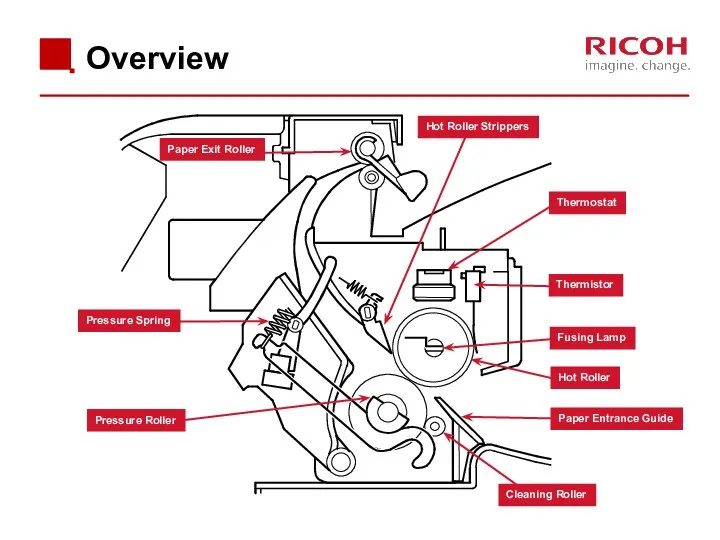
- 64. Overview Paper Exit Roller Hot Roller Strippers Thermostat Thermistor Fusing Lamp Hot Roller Paper Entrance Guide
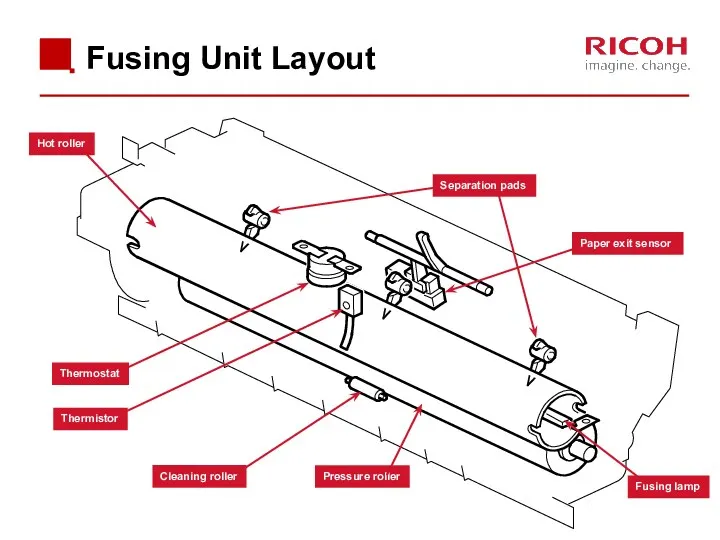
- 65. Fusing Unit Layout Separation pads Paper exit sensor Hot roller Pressure roller Fusing lamp Cleaning roller
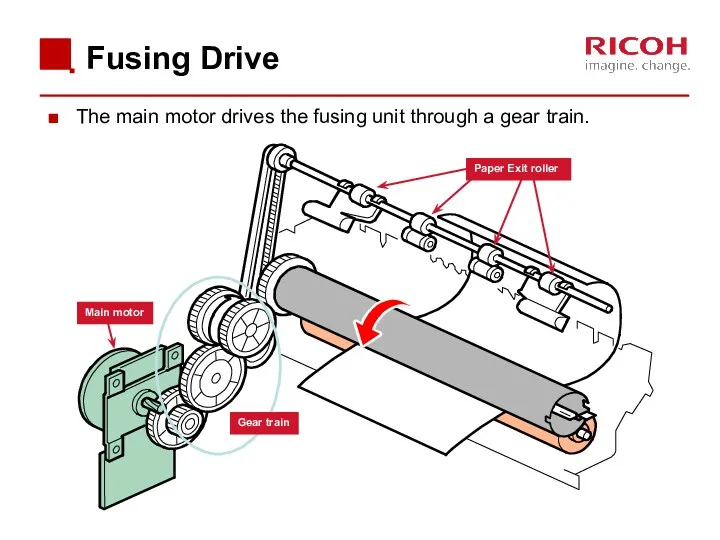
- 66. Fusing Drive The main motor drives the fusing unit through a gear train. Main motor Paper
- 67. Envelope Levers Envelope levers are provided on the right and left sides of the fusing unit.
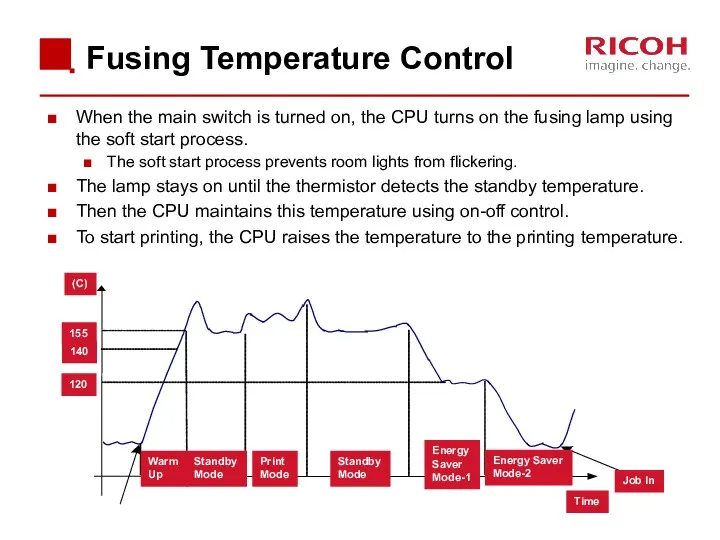
- 68. Fusing Temperature Control When the main switch is turned on, the CPU turns on the fusing
- 69. Overheat Protection When hot roller temperature becomes greater than 225°C, the CPU cuts off power to
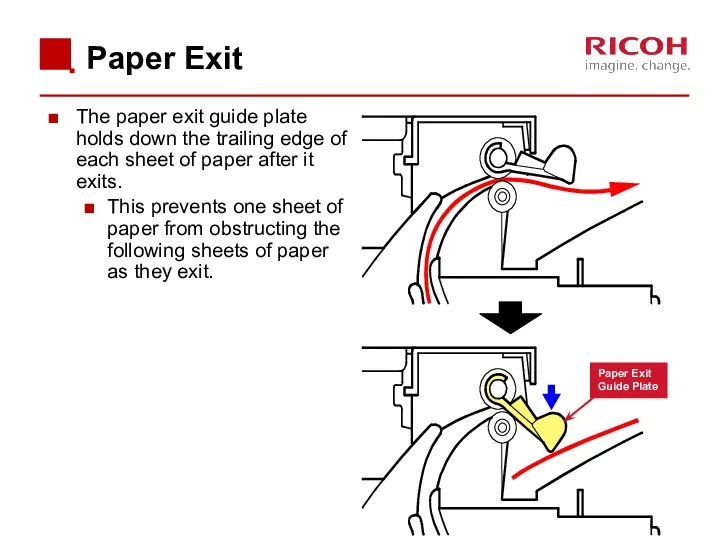
- 70. Paper Exit The paper exit guide plate holds down the trailing edge of each sheet of
- 71. 3.11 Duplex
- 72. Paper Path [A]: Duplex section [B]: Paper tray
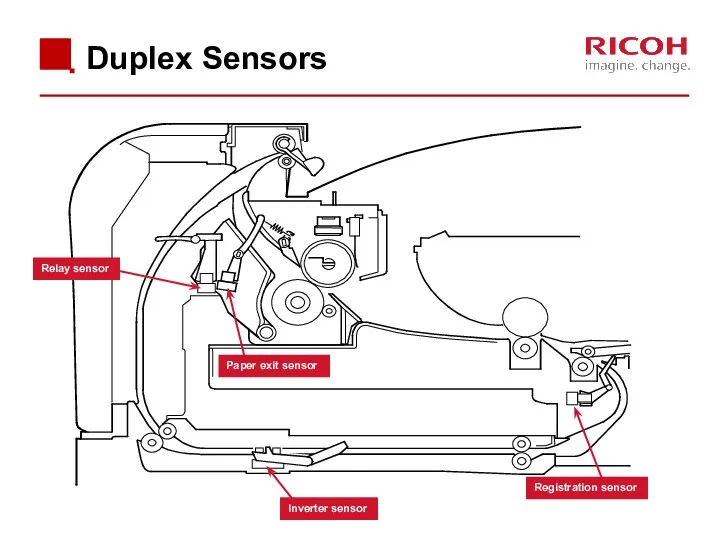
- 73. Duplex Sensors Relay sensor Paper exit sensor Inverter sensor Registration sensor
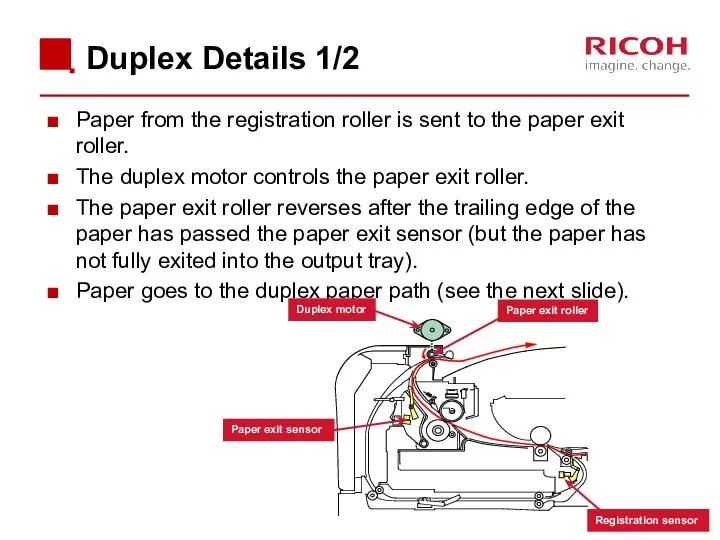
- 74. Paper from the registration roller is sent to the paper exit roller. The duplex motor controls
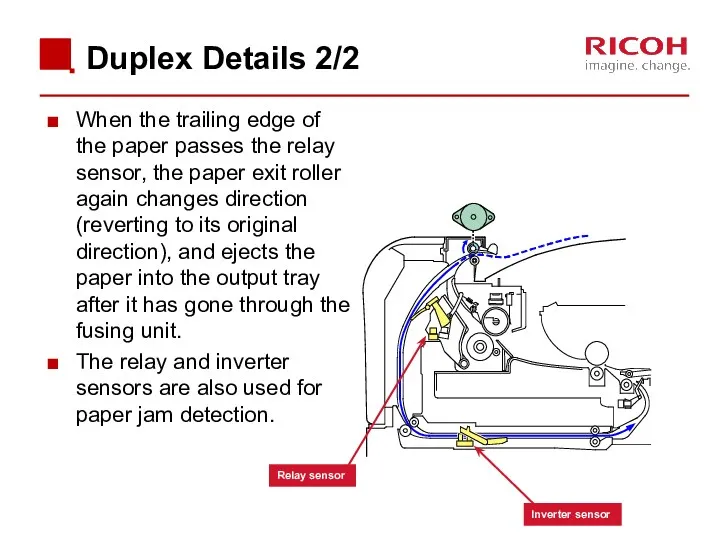
- 75. Duplex Details 2/2 When the trailing edge of the paper passes the relay sensor, the paper
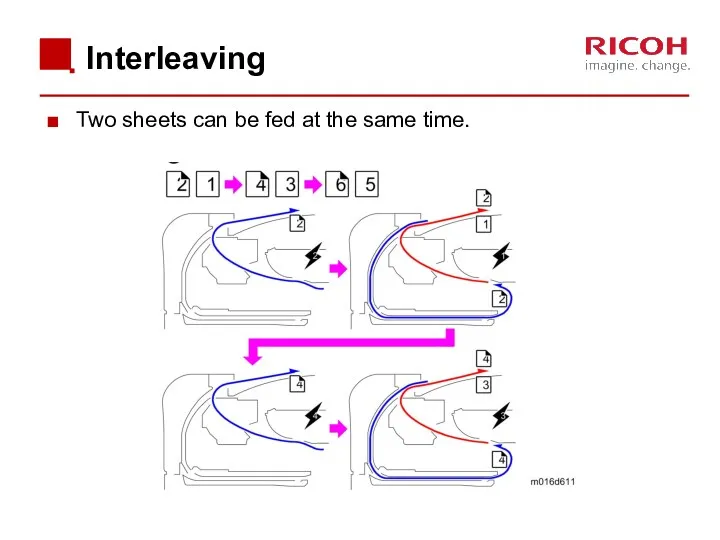
- 76. Interleaving Two sheets can be fed at the same time.
- 77. 4. Troubleshooting
- 78. Paper Jams Various types of paper jams and their causes are detailed in the service manual.
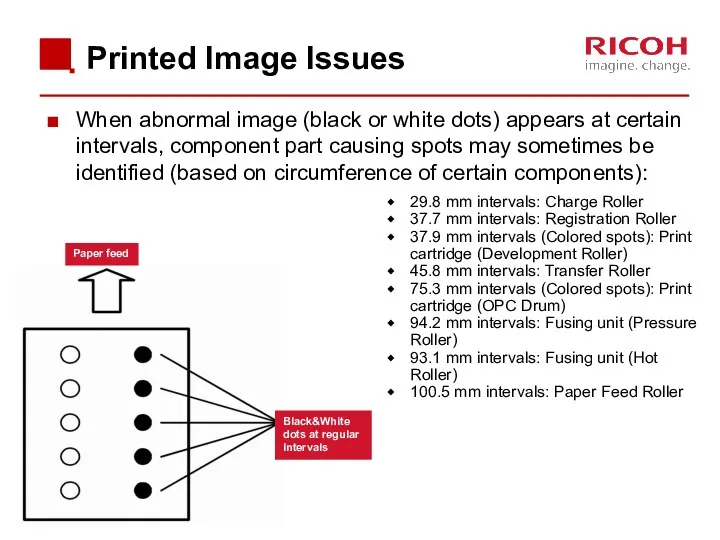
- 79. Printed Image Issues When abnormal image (black or white dots) appears at certain intervals, component part
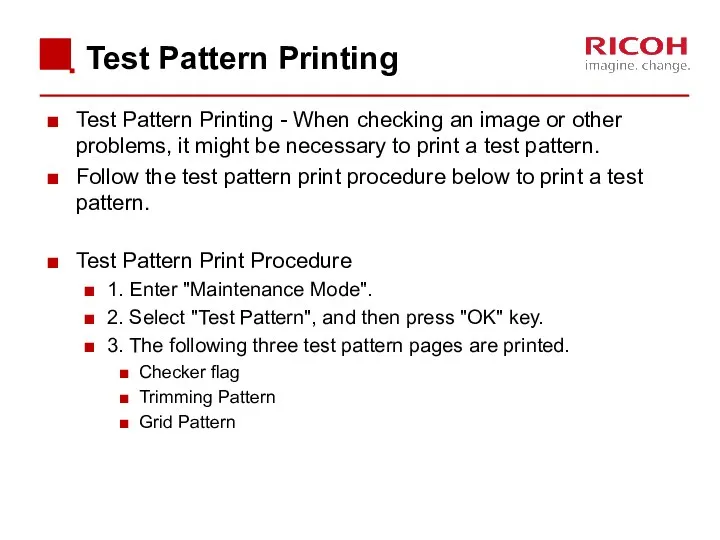
- 80. Test Pattern Printing Test Pattern Printing - When checking an image or other problems, it might
- 82. Скачать презентацию







![Paper Path – Remy-P1 [A]: Duplex section [B]: Paper tray](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/16015/slide-21.jpg)







![Paper Path When the document set sensor [1] detects an](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/16015/slide-32.jpg)

![Drive Scanner motor [A]: Drives the scanner carriage unit [B]](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/16015/slide-35.jpg)






![Paper Path [A]: Duplex section [B]: Paper tray](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/16015/slide-55.jpg)



![Paper Path [A]: Duplex section [B]: Paper tray](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/16015/slide-71.jpg)


 Эмпирические методы исследования
Эмпирические методы исследования Ракурсы. Классификация
Ракурсы. Классификация Компьютерная сеть та модель – OSI
Компьютерная сеть та модель – OSI Компьютерная графика
Компьютерная графика Belcome. Новый туризм
Belcome. Новый туризм Использование функций в табличном процессоре MS EXCEL
Использование функций в табличном процессоре MS EXCEL Разработка сайта для фигуристов-любителей
Разработка сайта для фигуристов-любителей Одномерные массивы.
Одномерные массивы. Кодирование графической информации
Кодирование графической информации Алгоритмизация и программирование. Понятие алгоритма и его свойства
Алгоритмизация и программирование. Понятие алгоритма и его свойства Презентация - Коммуникационные технологии
Презентация - Коммуникационные технологии Дешифрирование космических снимков с использованием ПО ERDAS Imagine
Дешифрирование космических снимков с использованием ПО ERDAS Imagine Управление внедрением информационных систем. Управление содержанием
Управление внедрением информационных систем. Управление содержанием Мультимедийная презентация по дисциплине Информатика и ИКТ Диск
Мультимедийная презентация по дисциплине Информатика и ИКТ Диск Скрипты предложения продукта ШПД и работа с возражениями
Скрипты предложения продукта ШПД и работа с возражениями Уровни тестирования программного обеспечения
Уровни тестирования программного обеспечения Отличия языка С++ от языка С
Отличия языка С++ от языка С Инструкция по работе с модулем карт в Sales Works
Инструкция по работе с модулем карт в Sales Works Прямая аренда от собственника!
Прямая аренда от собственника! Функции СМИ и система
Функции СМИ и система Редакторский анализ концепции научно-популярного журнала Квант
Редакторский анализ концепции научно-популярного журнала Квант Учебный 2022 год с Марусей
Учебный 2022 год с Марусей Тема: Измерение информации. Алфавитный и содержательный подход.
Тема: Измерение информации. Алфавитный и содержательный подход. Технологии поиска информации в интернете
Технологии поиска информации в интернете Опрацювання одновимірних масивів. (Лекція 5, 6)
Опрацювання одновимірних масивів. (Лекція 5, 6) Графики и диаграммы
Графики и диаграммы Программирование на языке Си. Графика (тема 10)
Программирование на языке Си. Графика (тема 10) Процедурное программирование на языке C++
Процедурное программирование на языке C++