Содержание
- 2. Agenda Self-study, home work discussion. Questions. SDLC. Processes. What is Agile? Scrum, Waterfall, XP… Practice.
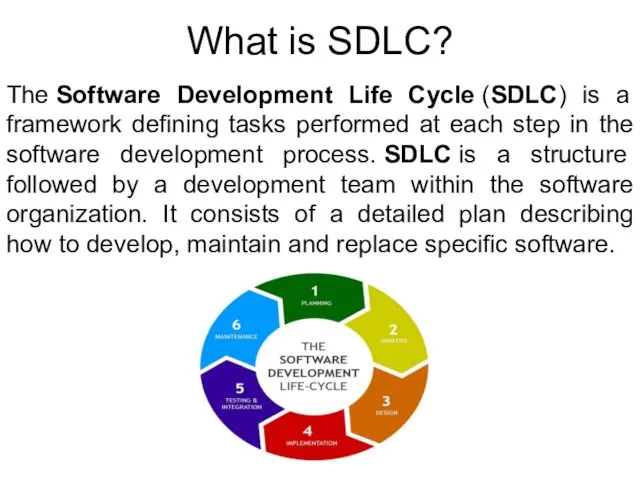
- 3. What is SDLC? The Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a framework defining tasks performed at
- 4. Processes. Why do we care about it?
- 5. For any company Customer satisfaction critical Project should end successfully all the time Project: complex NEW
- 6. SDLC gone wrong
- 7. Software Development Methodologies Waterfall Iterative RUP Agile XP …
- 8. Traditional Approach
- 9. What is Agility? “Values, principles and practices that foster team communication and feedbacks to regularly deliver
- 10. Agile Manifesto Individuals and interactions over processes and tools Working software over comprehensive documentation Customer collaboration
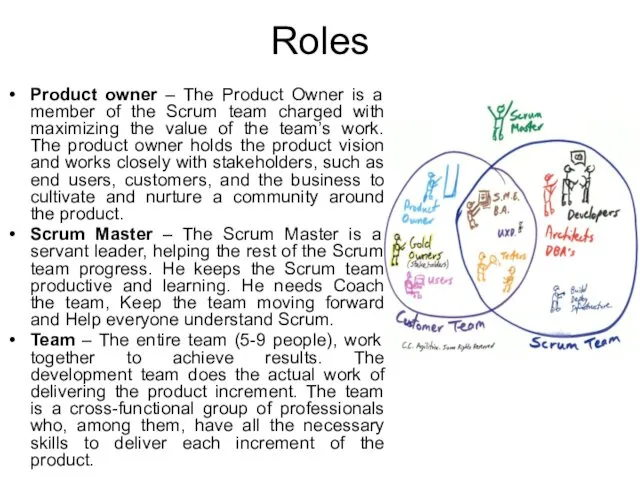
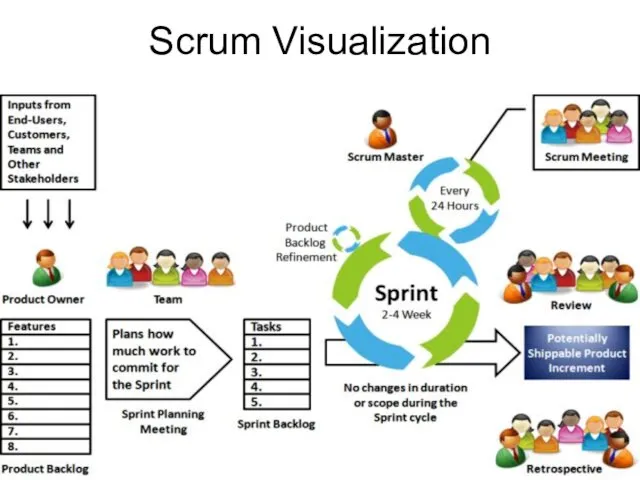
- 11. Roles Product owner – The Product Owner is a member of the Scrum team charged with
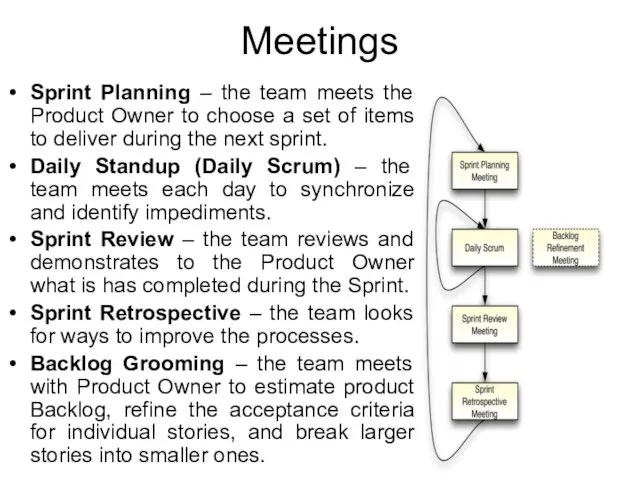
- 12. Meetings Sprint Planning – the team meets the Product Owner to choose a set of items
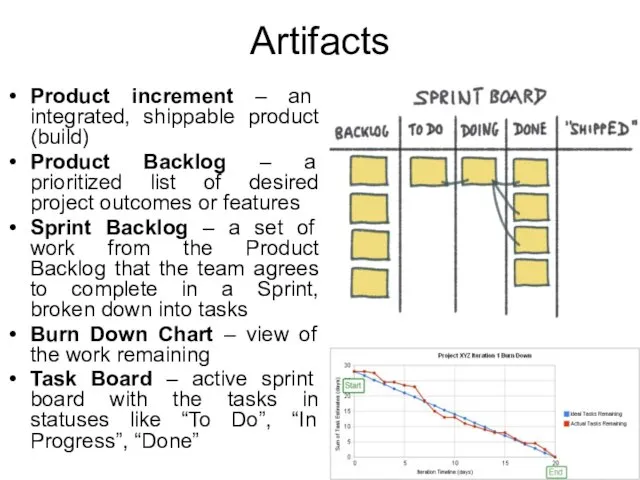
- 13. Artifacts Product increment – an integrated, shippable product (build) Product Backlog – a prioritized list of
- 14. Scrum Visualization
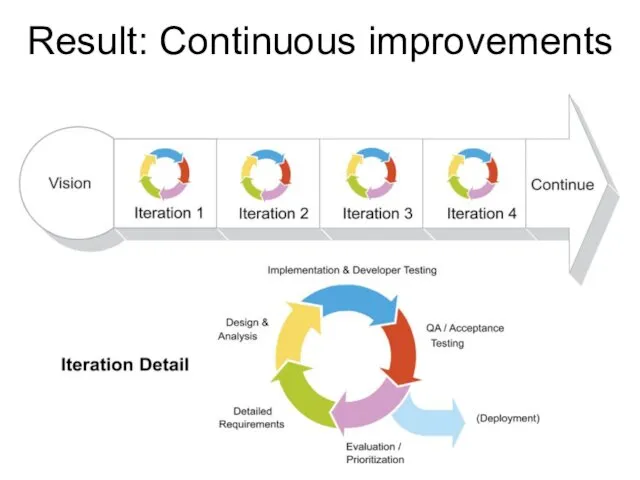
- 15. Result: Continuous improvements
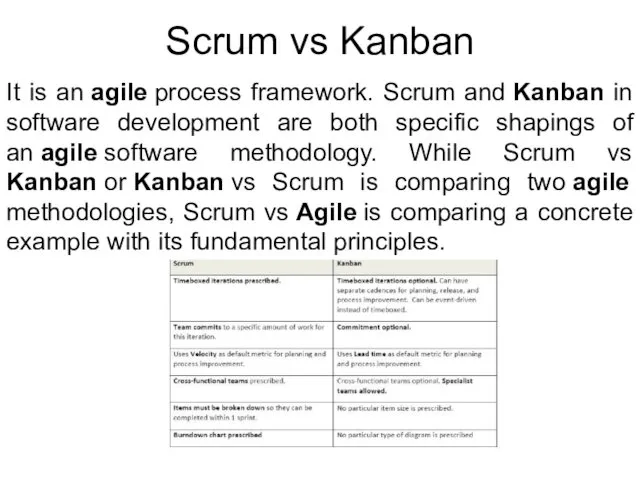
- 16. Scrum vs Kanban It is an agile process framework. Scrum and Kanban in software development are
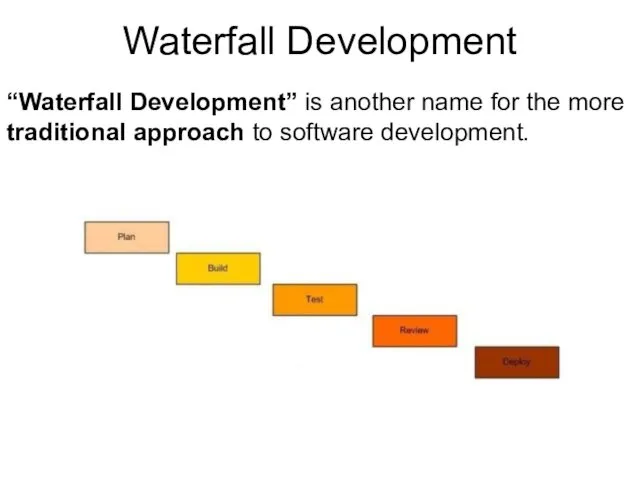
- 17. Waterfall Development “Waterfall Development” is another name for the more traditional approach to software development.
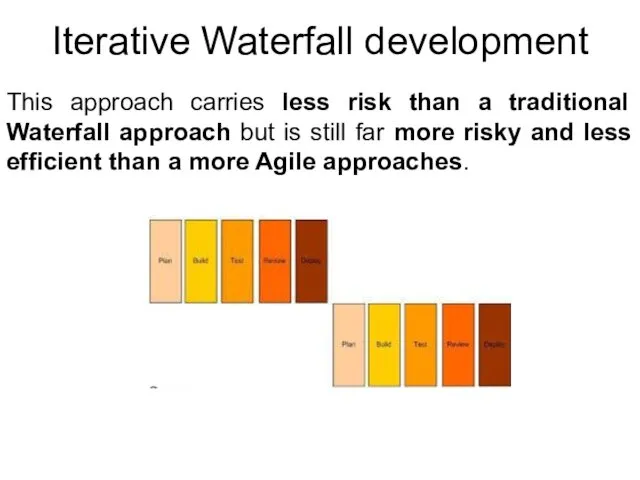
- 18. Iterative Waterfall development This approach carries less risk than a traditional Waterfall approach but is still
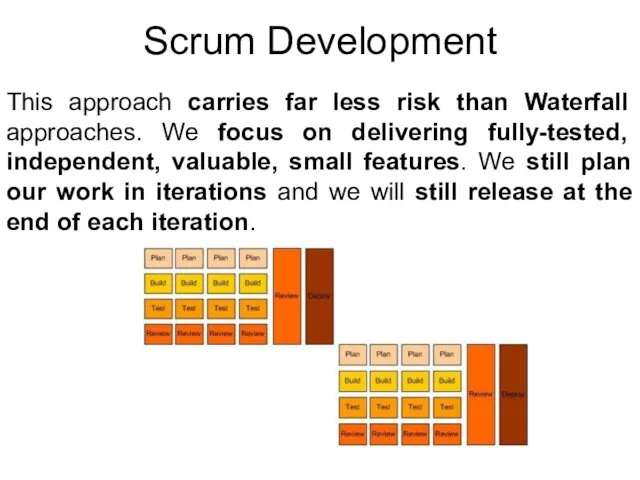
- 19. Scrum Development This approach carries far less risk than Waterfall approaches. We focus on delivering fully-tested,
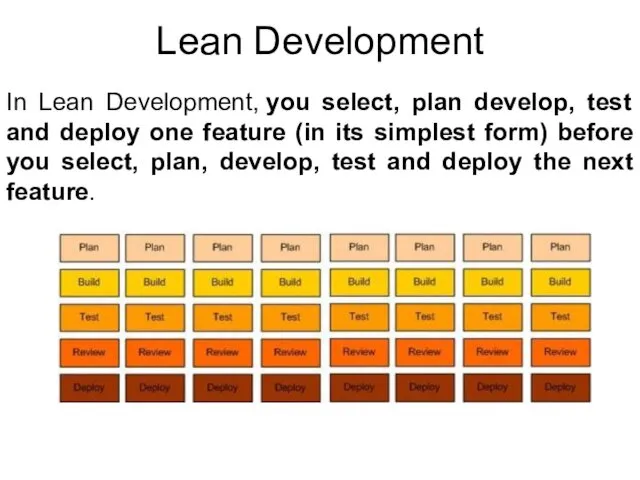
- 20. Lean Development In Lean Development, you select, plan develop, test and deploy one feature (in its
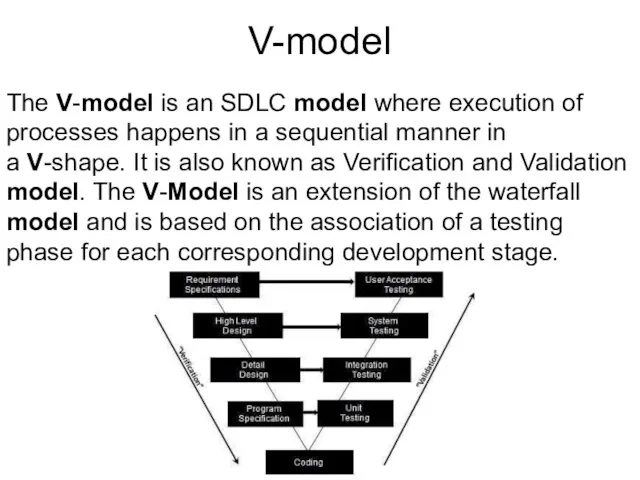
- 21. V-model The V-model is an SDLC model where execution of processes happens in a sequential manner
- 22. Scrum vs Waterfall in reality Scrum takes its cue from RUGBY SRCUM where a team is
- 23. Practice: Scrum Penny Game
- 24. Why Agile works? Less functional on iteration, less risks and wrong estimates. Fast rump-up (no need
- 26. Скачать презентацию











 Data types and databases
Data types and databases Формы мышления. Логика
Формы мышления. Логика Основные принципы построения компьютеров
Основные принципы построения компьютеров Дерево игры. Поиск выигрышной стратегии
Дерево игры. Поиск выигрышной стратегии Голосовой помощник Маруся. Кто такая Маруся и что она умеет?
Голосовой помощник Маруся. Кто такая Маруся и что она умеет? Типы компьютеров
Типы компьютеров Функции АСУ ТП
Функции АСУ ТП Интерактивная образовательная платформа
Интерактивная образовательная платформа Отчеты в MS ACCESS
Отчеты в MS ACCESS Звіт з практики. Видавництво Мамине сонечко
Звіт з практики. Видавництво Мамине сонечко Информация измерение
Информация измерение ГОСТ Р ИСО/МЭК 12207. Лекция №3
ГОСТ Р ИСО/МЭК 12207. Лекция №3 Платформы для дистанционного обучения
Платформы для дистанционного обучения Интернет-сервис Антиплагиат. Ру
Интернет-сервис Антиплагиат. Ру ПрезентацияУрок - игра по теме Закрепление пройденного. 11 класс
ПрезентацияУрок - игра по теме Закрепление пройденного. 11 класс Вложенные циклы. Решение задач
Вложенные циклы. Решение задач Машинно-зависимые языки и основы компиляции
Машинно-зависимые языки и основы компиляции Программно-технические системы реализации информационных процессов
Программно-технические системы реализации информационных процессов Особенности разработки требований к ПО. (Лекция 1)
Особенности разработки требований к ПО. (Лекция 1) ИКТ – компетентность участников образовательного процесса
ИКТ – компетентность участников образовательного процесса Устройство персонального компьютера
Устройство персонального компьютера Редактор презентаций Power Point. (Часть 1)
Редактор презентаций Power Point. (Часть 1) Компетентнісна задача з інформатики
Компетентнісна задача з інформатики 1. Introduction to Java Language. 2. Java SDK & IDE
1. Introduction to Java Language. 2. Java SDK & IDE Формализациялау жөніндетүсінік, инфармацияны формализациялаудың негізгі тұрлері: формула, мәтін, кесте граф, алгоритм
Формализациялау жөніндетүсінік, инфармацияны формализациялаудың негізгі тұрлері: формула, мәтін, кесте граф, алгоритм Презентация к уроку
Презентация к уроку Атрибуты deftemplate
Атрибуты deftemplate Основные понятия операционной системы
Основные понятия операционной системы