Содержание
- 2. Purpose to present the Standard Software system and its functionality to end users (operators, technologists, automation
- 3. Automation system Concept The automation control system is based on physical, procedural and recipe model of
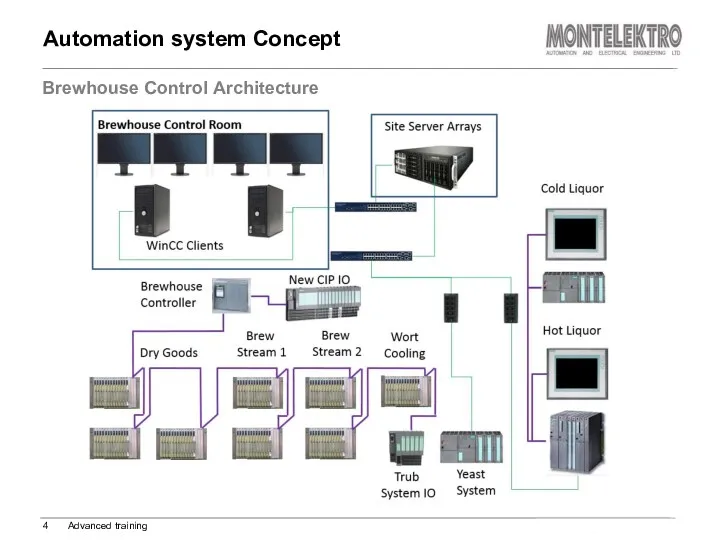
- 4. Automation system Concept Brewhouse Control Architecture Advanced training
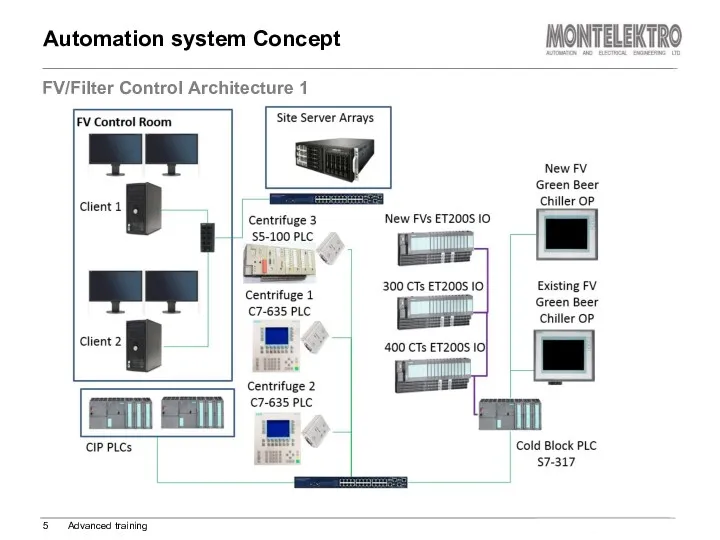
- 5. Automation system Concept FV/Filter Control Architecture 1 Advanced training
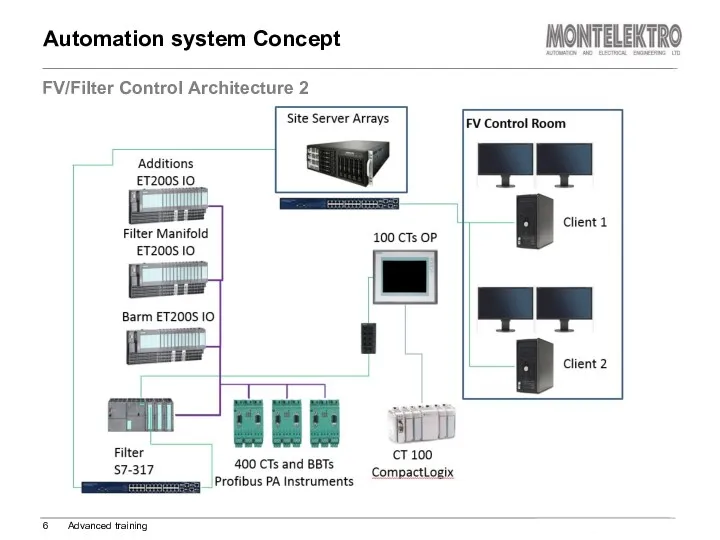
- 6. Automation system Concept FV/Filter Control Architecture 2 Advanced training
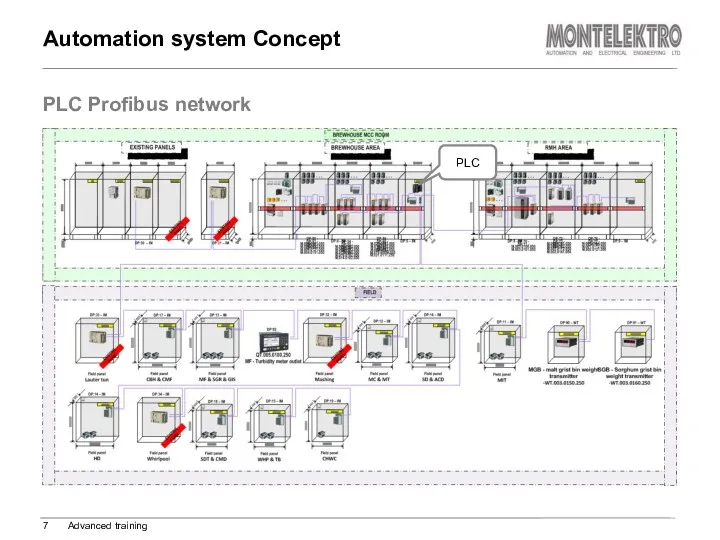
- 7. PLC Profibus network Automation system Concept Advanced training PLC
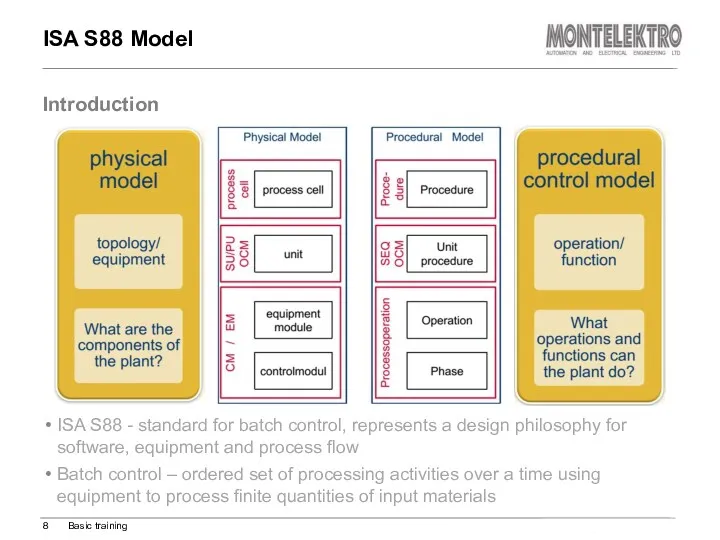
- 8. ISA S88 Model ISA S88 - standard for batch control, represents a design philosophy for software,
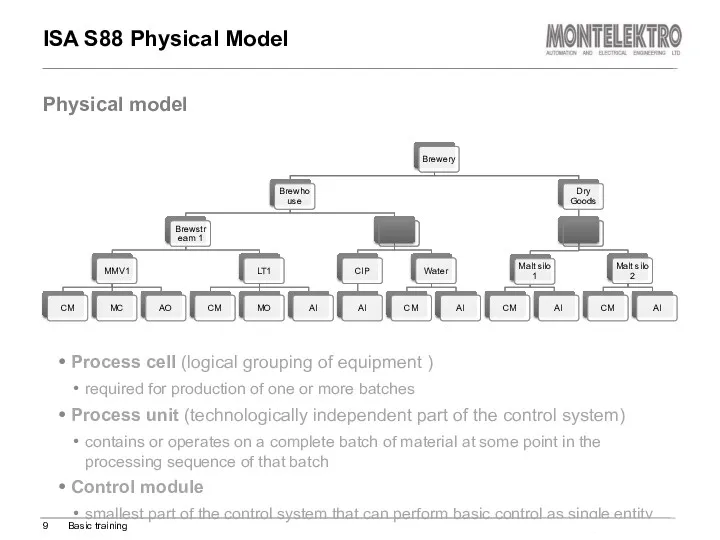
- 9. ISA S88 Physical Model Process cell (logical grouping of equipment ) required for production of one
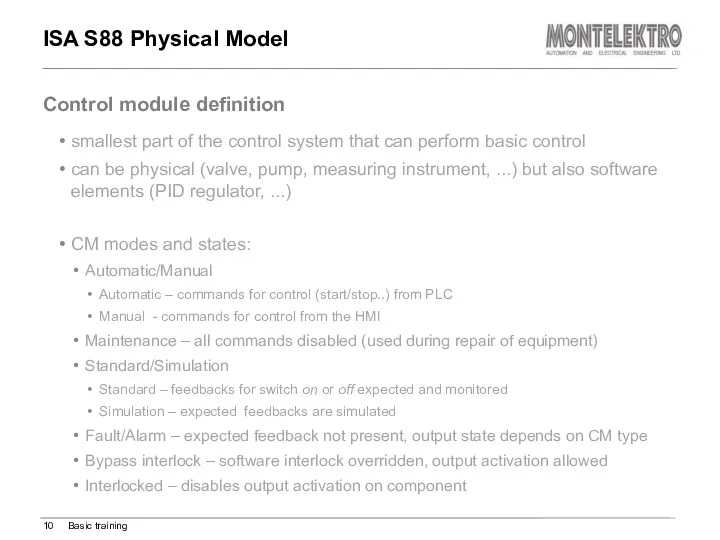
- 10. smallest part of the control system that can perform basic control can be physical (valve, pump,
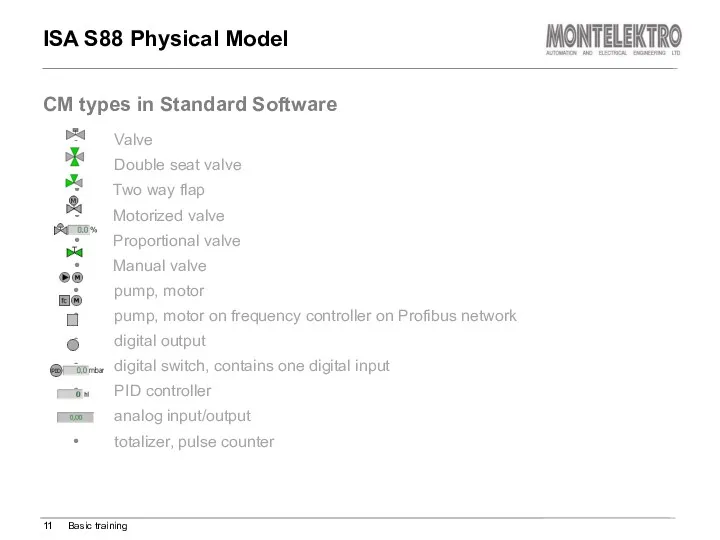
- 11. Valve Double seat valve Two way flap Motorized valve Proportional valve Manual valve pump, motor pump,
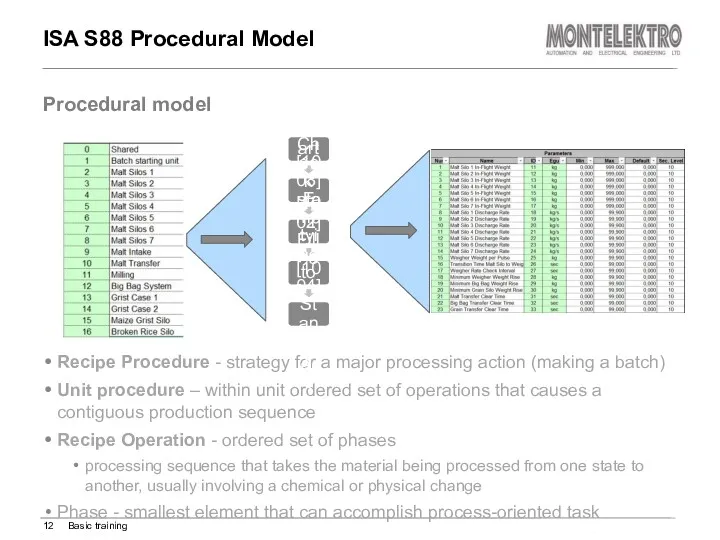
- 12. ISA S88 Procedural Model Recipe Procedure - strategy for a major processing action (making a batch)
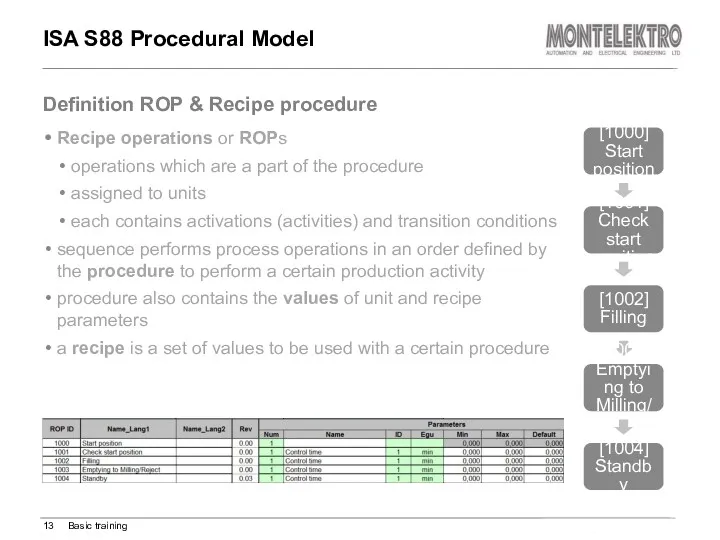
- 13. ISA S88 Procedural Model Recipe operations or ROPs operations which are a part of the procedure
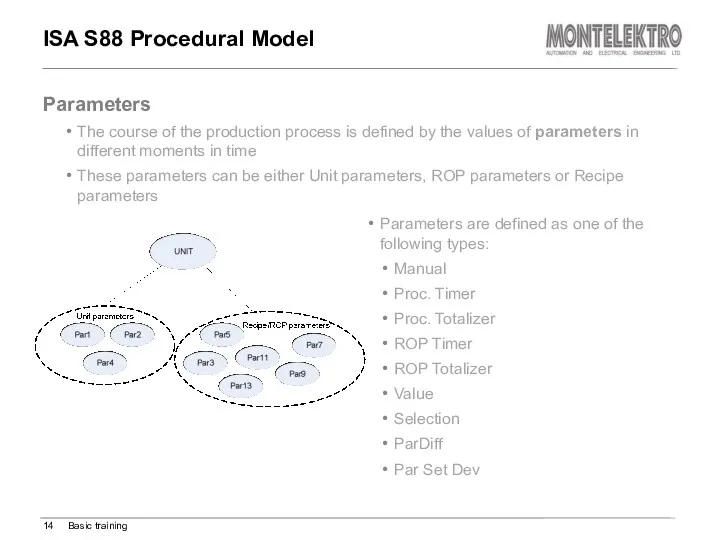
- 14. ISA S88 Procedural Model Parameters are defined as one of the following types: Manual Proc. Timer
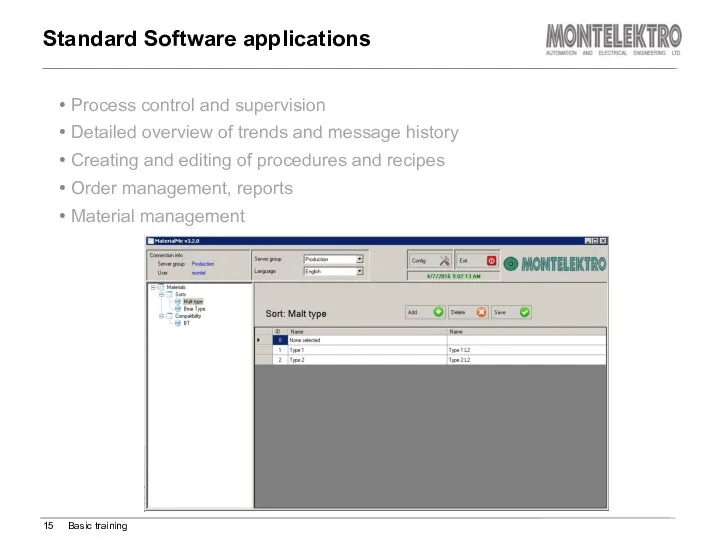
- 15. Process control and supervision Detailed overview of trends and message history Creating and editing of procedures
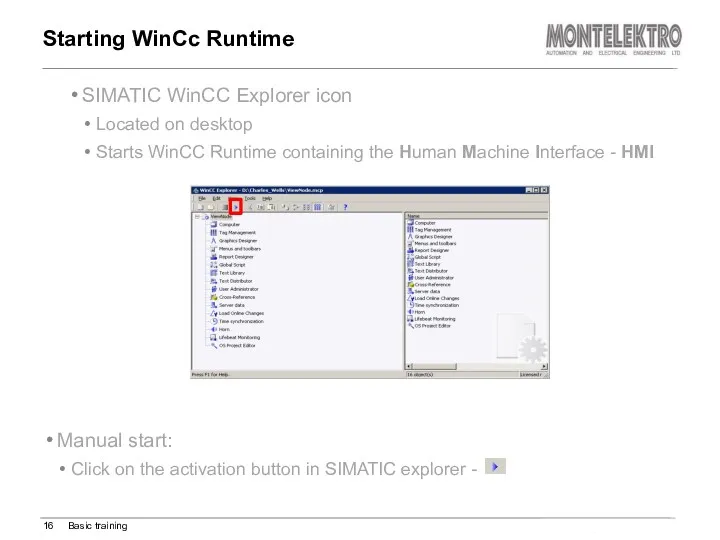
- 16. SIMATIC WinCC Explorer icon Located on desktop Starts WinCC Runtime containing the Human Machine Interface -
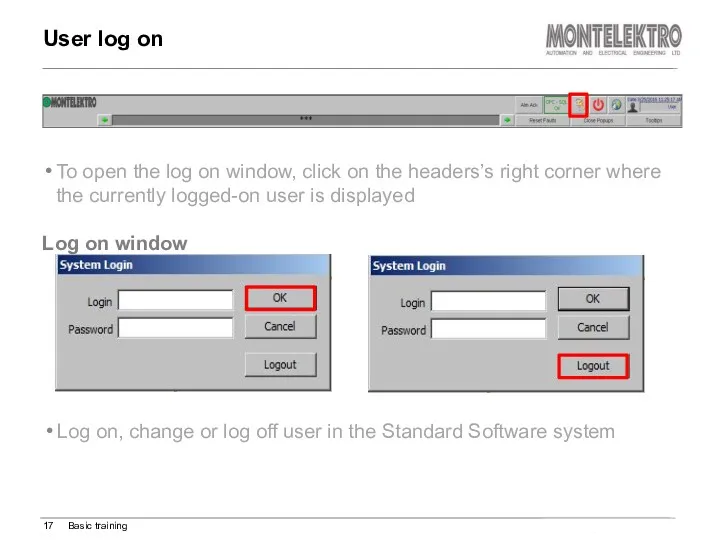
- 17. Log on, change or log off user in the Standard Software system Log on window User
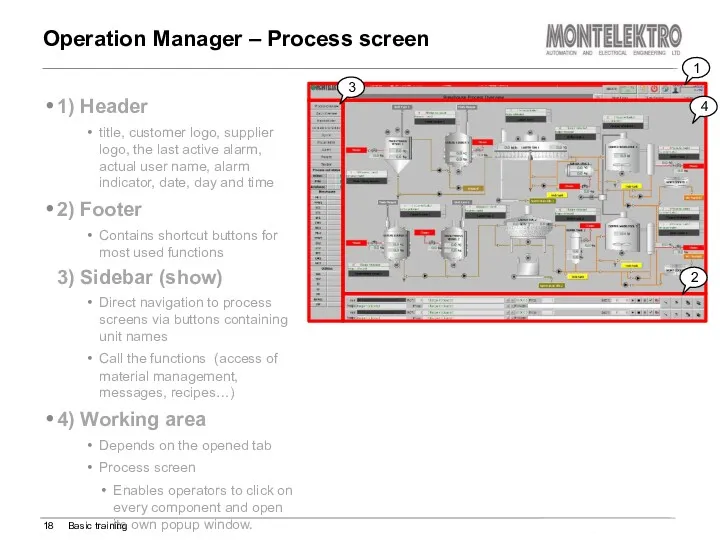
- 18. 1) Header title, customer logo, supplier logo, the last active alarm, actual user name, alarm indicator,
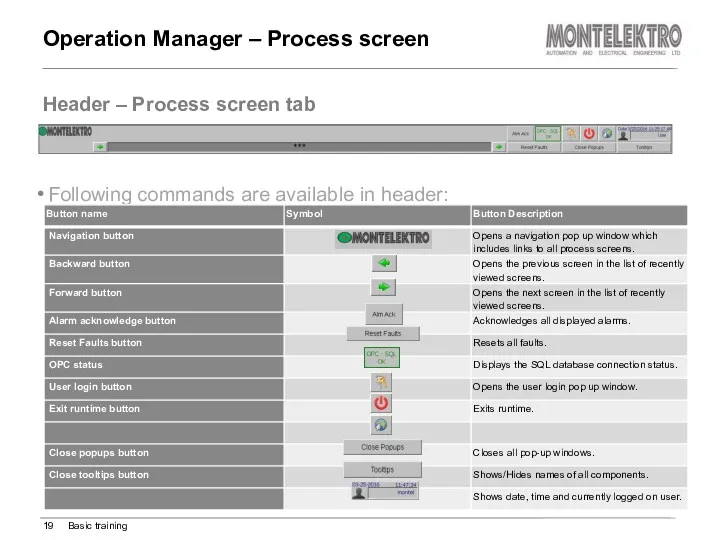
- 19. Header – Process screen tab Operation Manager – Process screen Basic training Following commands are available
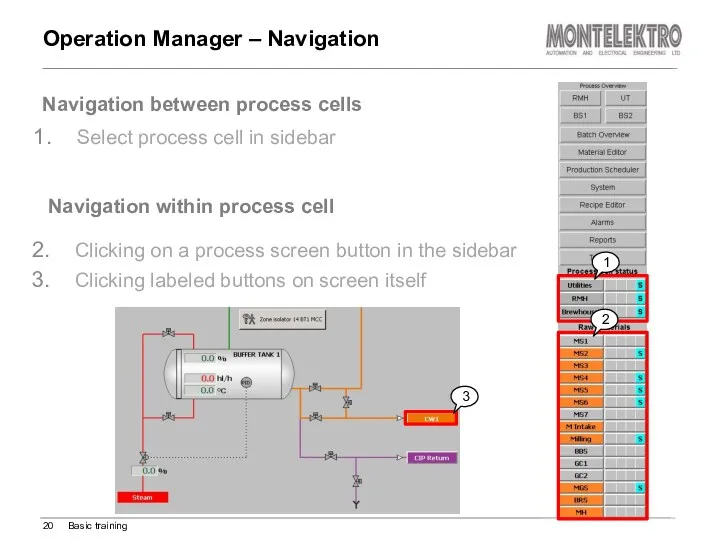
- 20. Select process cell in sidebar Navigation within process cell Operation Manager – Navigation Basic training Navigation
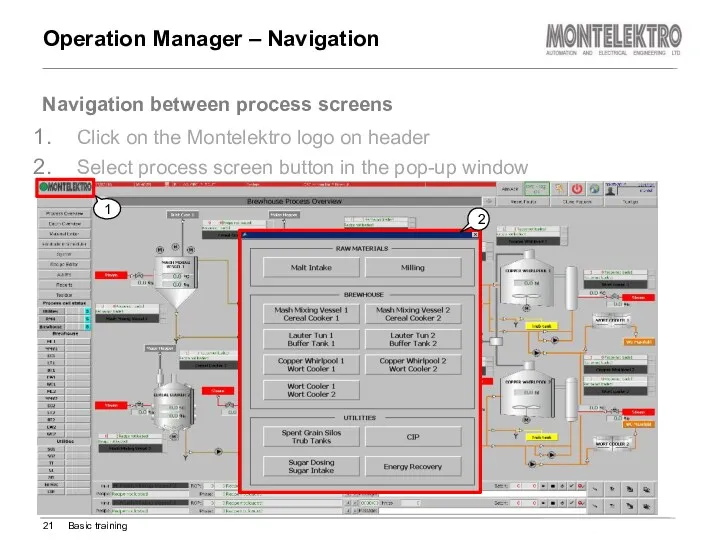
- 21. Click on the Montelektro logo on header Select process screen button in the pop-up window Operation
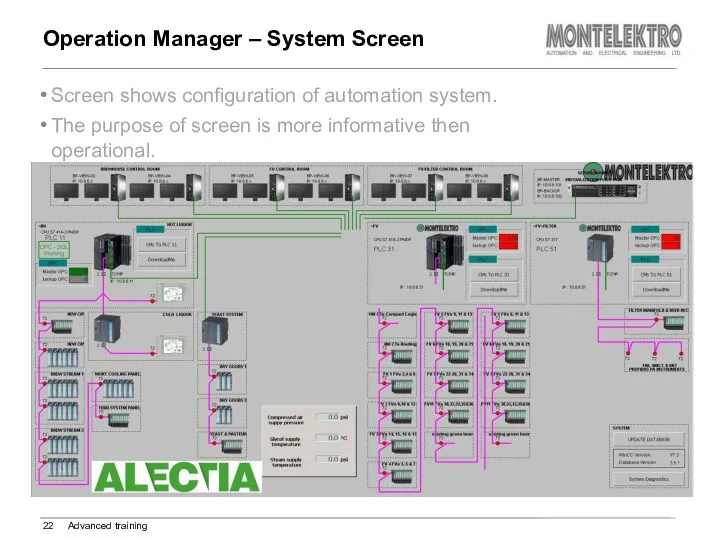
- 22. Screen shows configuration of automation system. The purpose of screen is more informative then operational. Operation
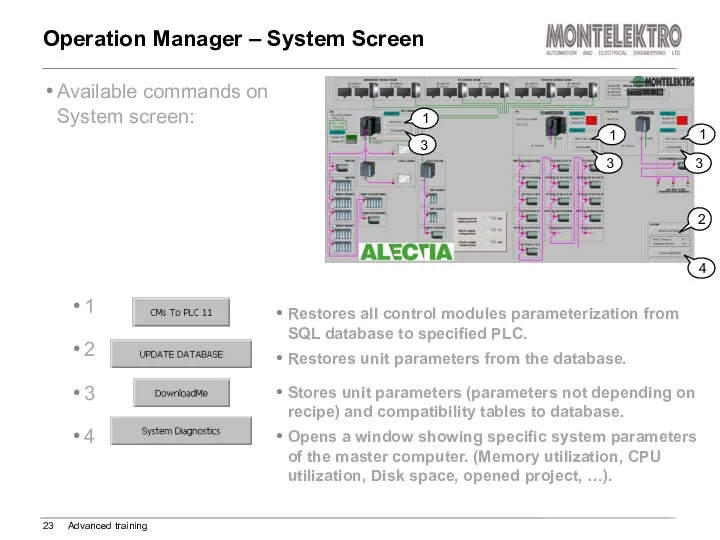
- 23. Available commands on System screen: Operation Manager – System Screen Advanced training 2 1 1 1
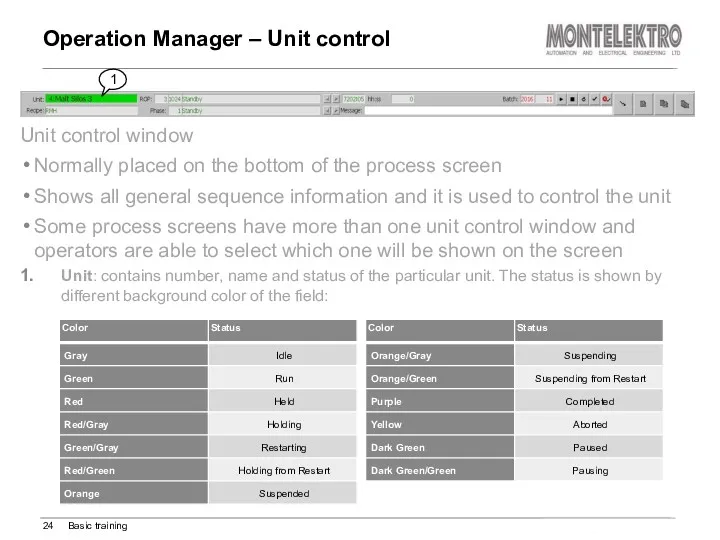
- 24. Unit control window Normally placed on the bottom of the process screen Shows all general sequence
- 25. Operation Manager – Unit control Basic training Recipe: The field shows the actual active recipe for
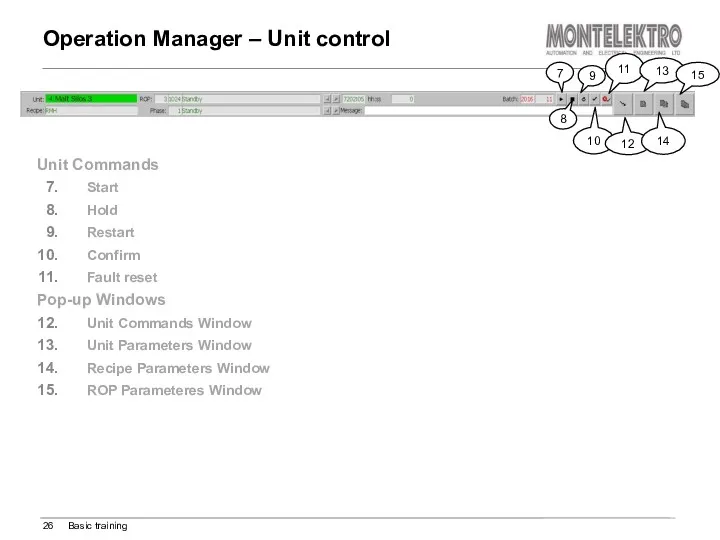
- 26. Operation Manager – Unit control Basic training Unit Commands Start Hold Restart Confirm Fault reset Pop-up
- 27. Operation Manager – Unit commands Window Basic training Contains the whole set of operator commands to
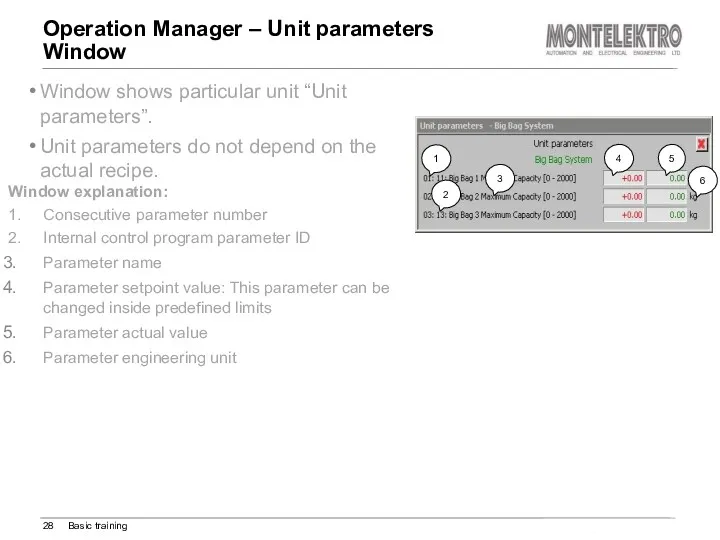
- 28. Operation Manager – Unit parameters Window Basic training Window shows particular unit “Unit parameters”. Unit parameters
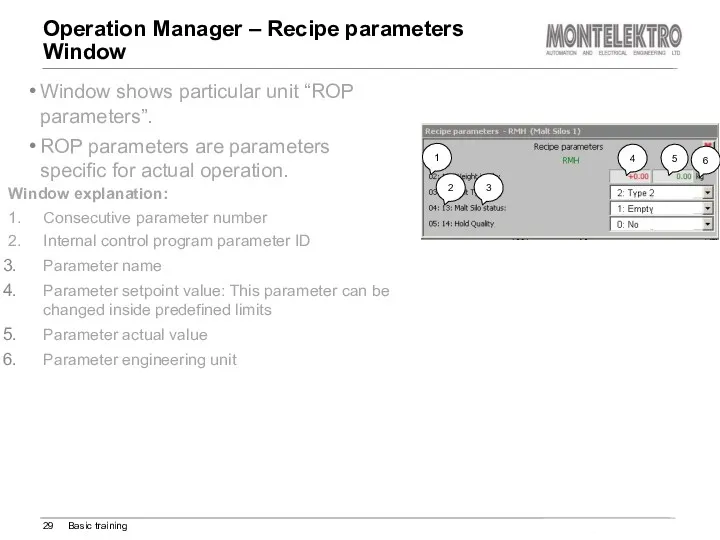
- 29. Operation Manager – Recipe parameters Window Basic training Window shows particular unit “ROP parameters”. ROP parameters
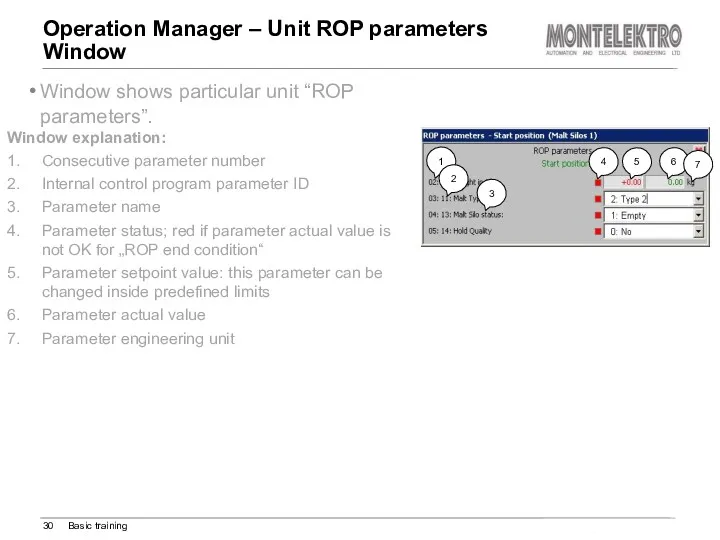
- 30. Operation Manager – Unit ROP parameters Window Basic training Window shows particular unit “ROP parameters”. Window
- 31. Smallest part of the control system that can perform basic control Can be physical but also
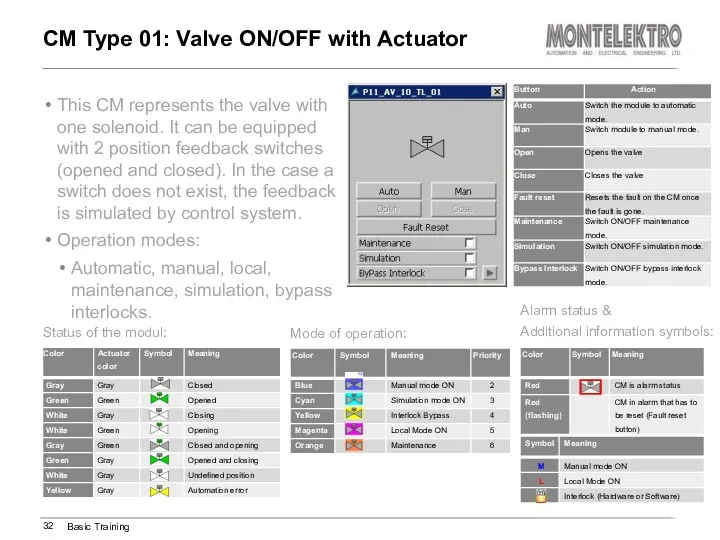
- 32. This CM represents the valve with one solenoid. It can be equipped with 2 position feedback
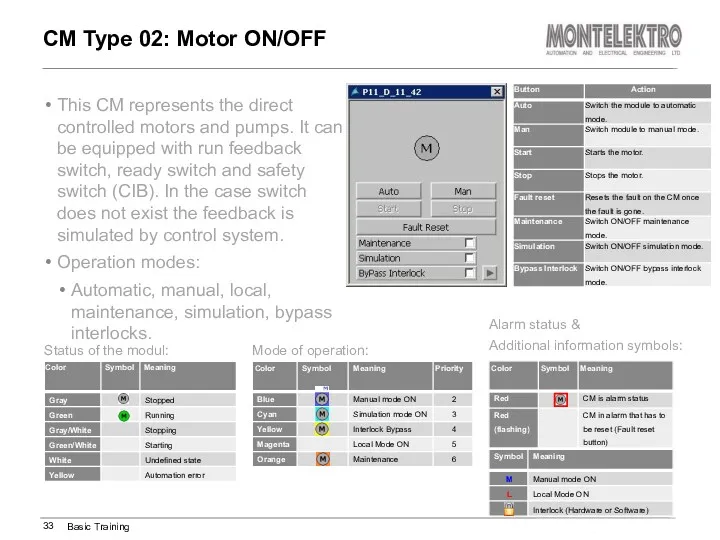
- 33. This CM represents the direct controlled motors and pumps. It can be equipped with run feedback
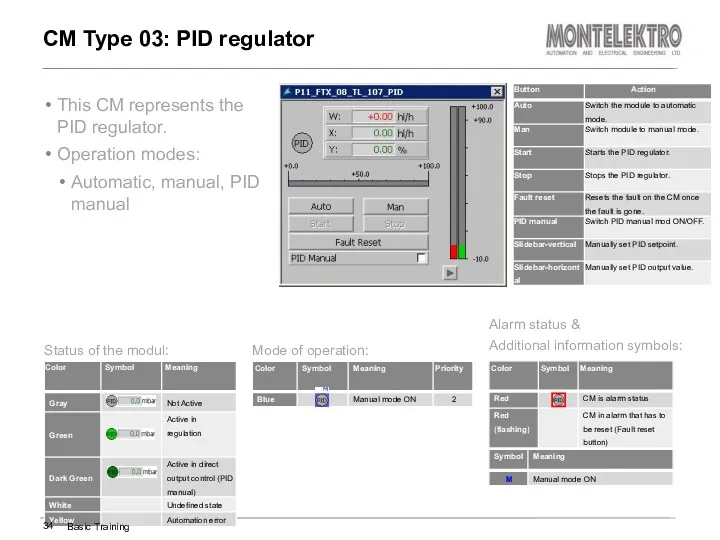
- 34. This CM represents the PID regulator. Operation modes: Automatic, manual, PID manual CM Type 03: PID
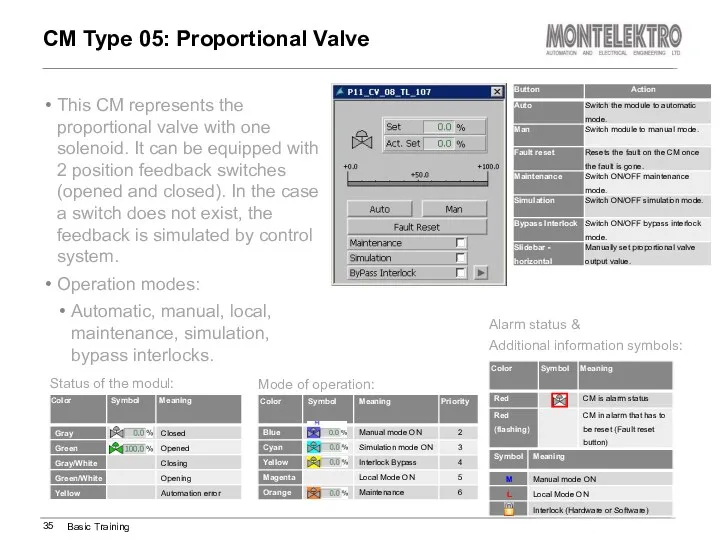
- 35. This CM represents the proportional valve with one solenoid. It can be equipped with 2 position
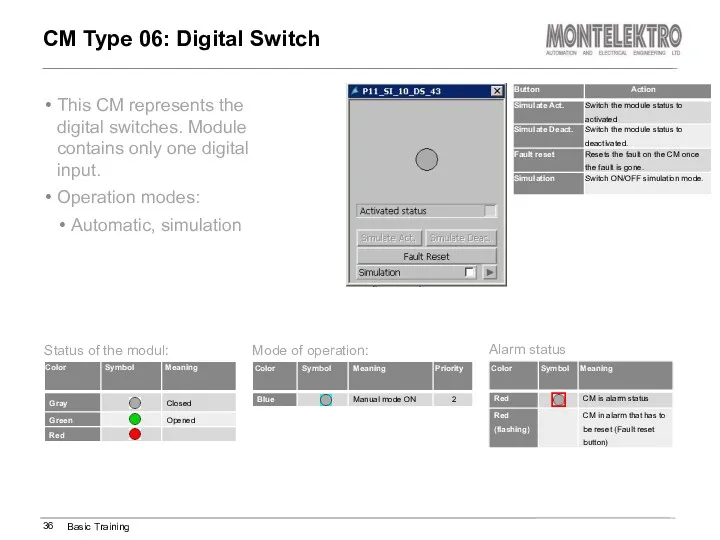
- 36. This CM represents the digital switches. Module contains only one digital input. Operation modes: Automatic, simulation
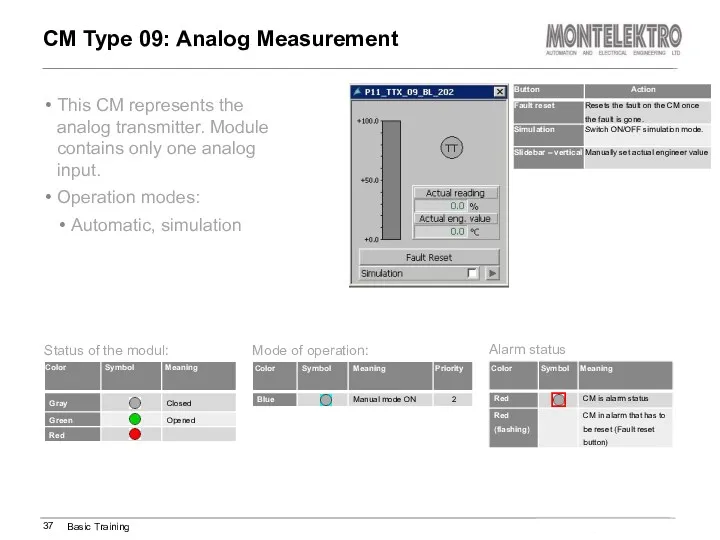
- 37. This CM represents the analog transmitter. Module contains only one analog input. Operation modes: Automatic, simulation
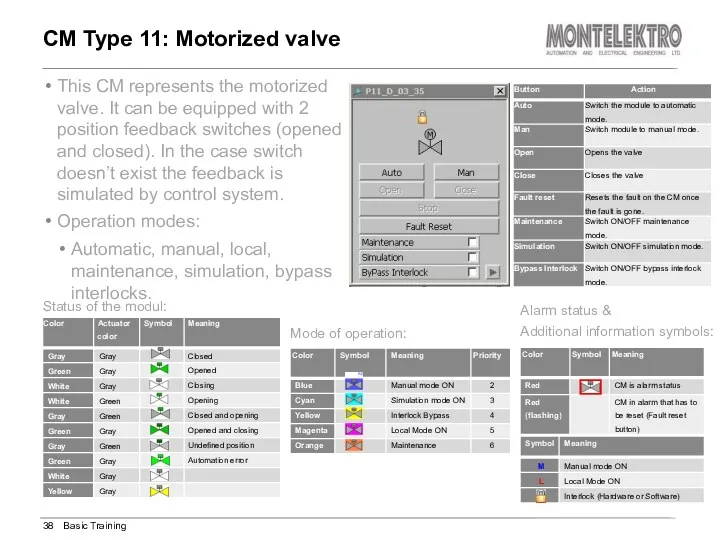
- 38. This CM represents the motorized valve. It can be equipped with 2 position feedback switches (opened
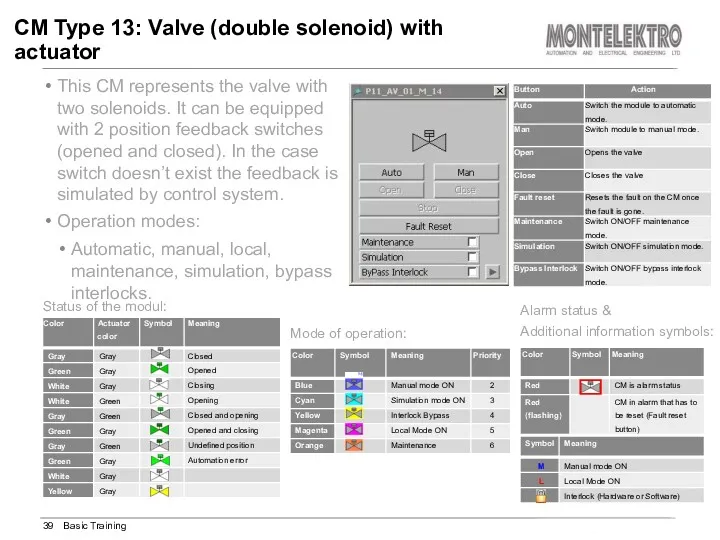
- 39. This CM represents the valve with two solenoids. It can be equipped with 2 position feedback
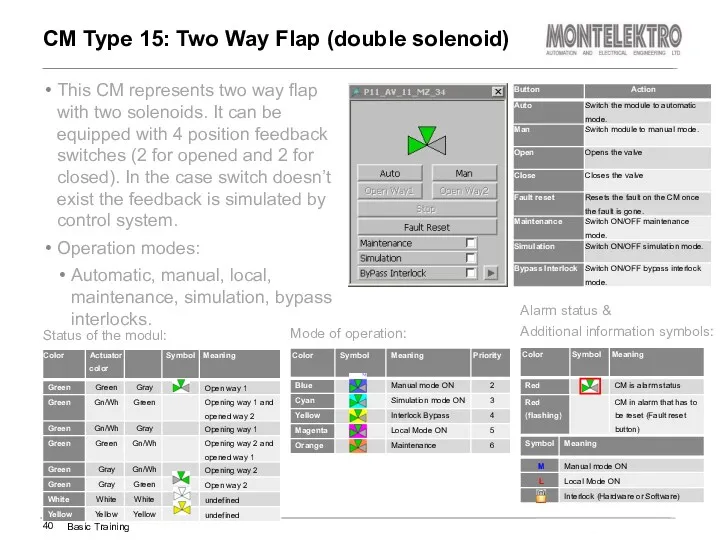
- 40. This CM represents two way flap with two solenoids. It can be equipped with 4 position
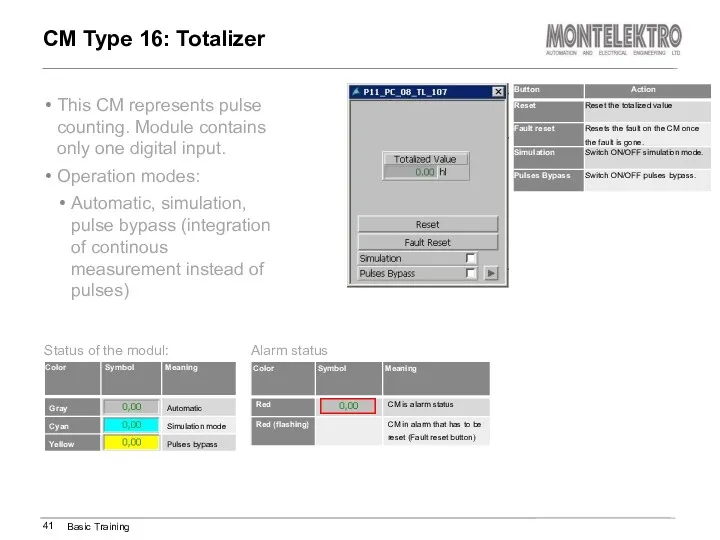
- 41. This CM represents pulse counting. Module contains only one digital input. Operation modes: Automatic, simulation, pulse
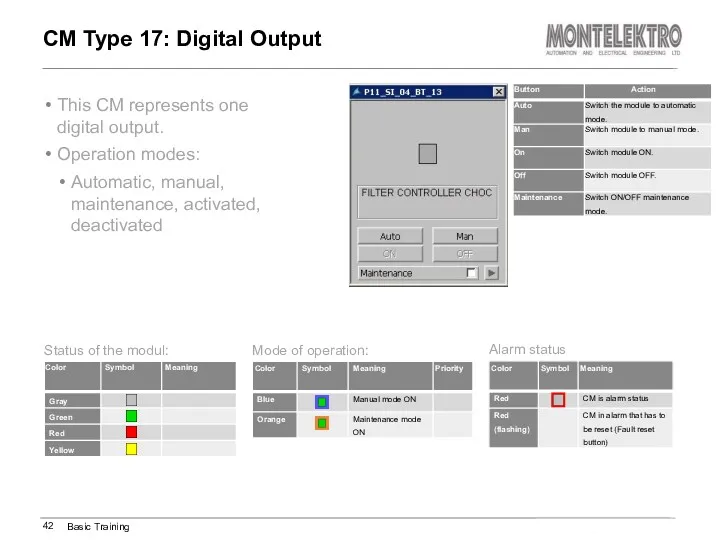
- 42. This CM represents one digital output. Operation modes: Automatic, manual, maintenance, activated, deactivated CM Type 17:
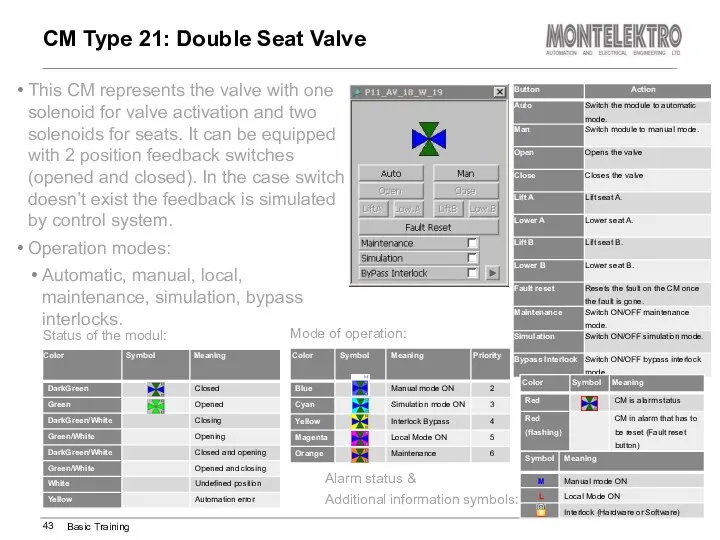
- 43. This CM represents the valve with one solenoid for valve activation and two solenoids for seats.
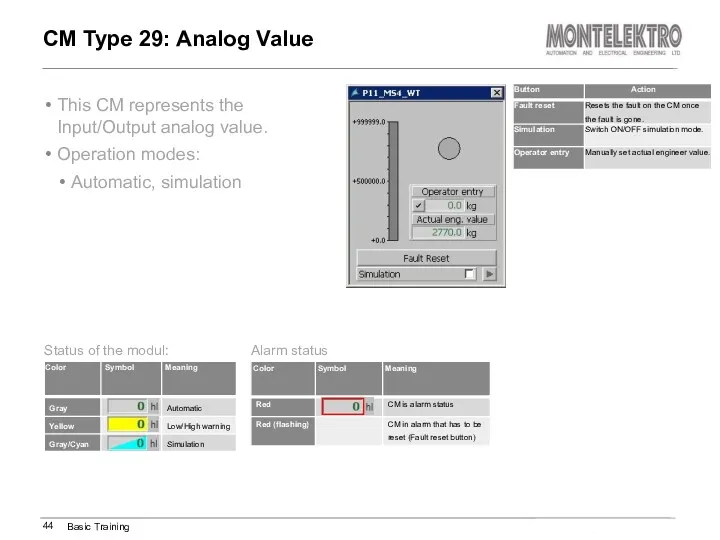
- 44. This CM represents the Input/Output analog value. Operation modes: Automatic, simulation CM Type 29: Analog Value
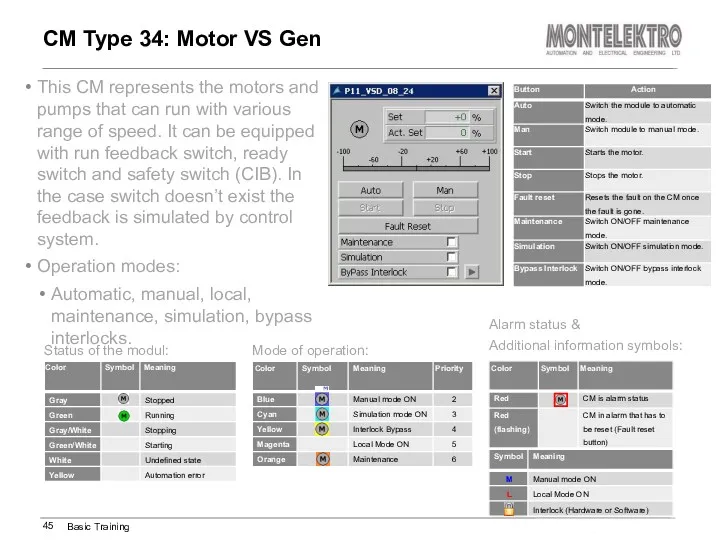
- 45. This CM represents the motors and pumps that can run with various range of speed. It
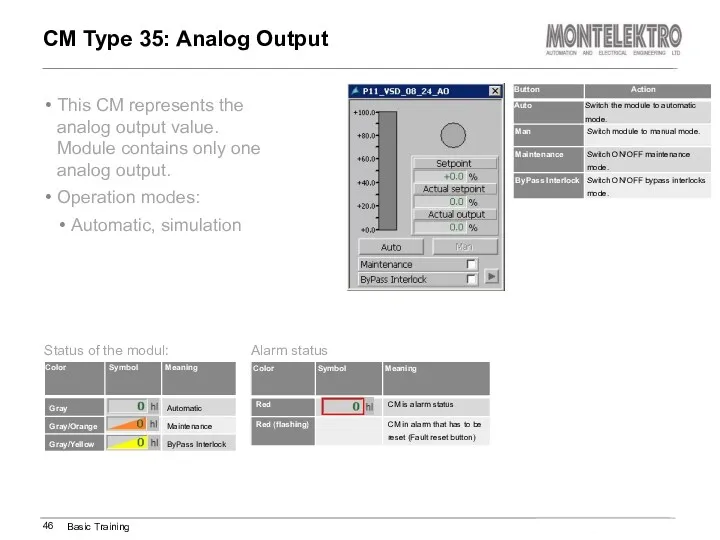
- 46. This CM represents the analog output value. Module contains only one analog output. Operation modes: Automatic,
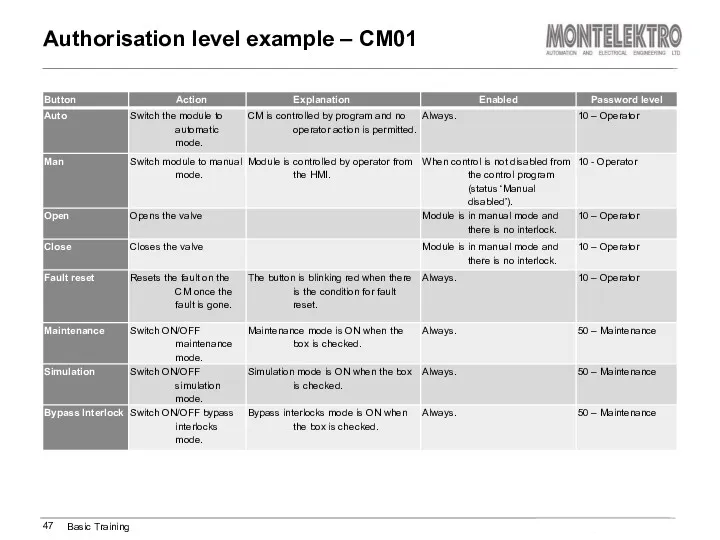
- 47. Authorisation level example – CM01 Basic Training
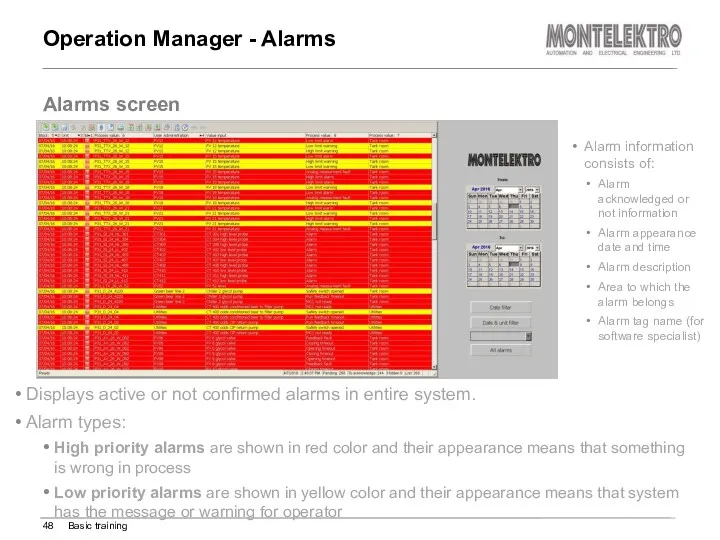
- 48. Operation Manager - Alarms Displays active or not confirmed alarms in entire system. Alarm types: High
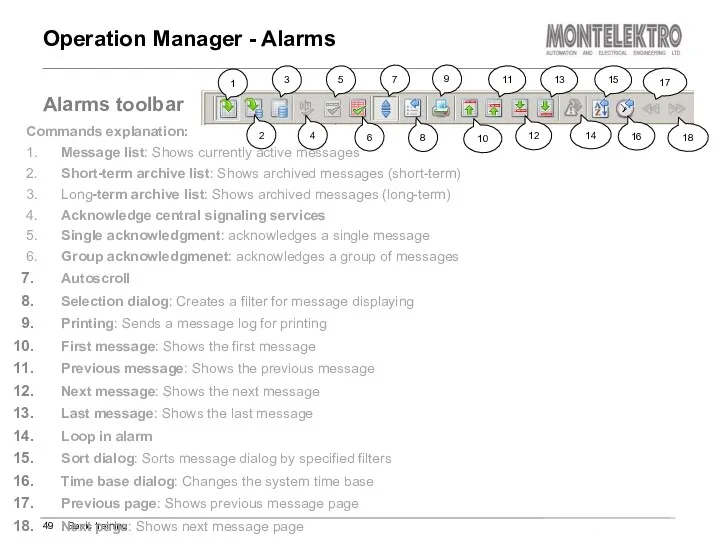
- 49. Operation Manager - Alarms Basic training Alarms toolbar Commands explanation: 1. Message list: Shows currently active
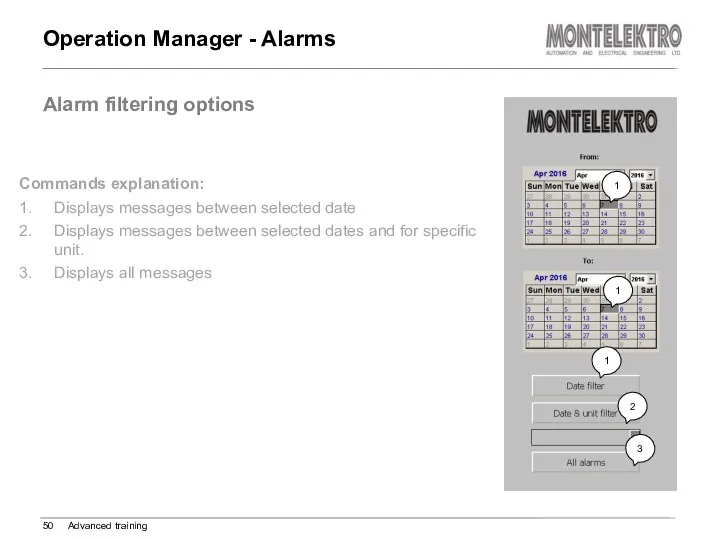
- 50. Operation Manager - Alarms Advanced training Alarm filtering options Commands explanation: 1. Displays messages between selected
- 51. Operation Manager - Trends Each process screen contains a desired number of Trend buttons. Each trend
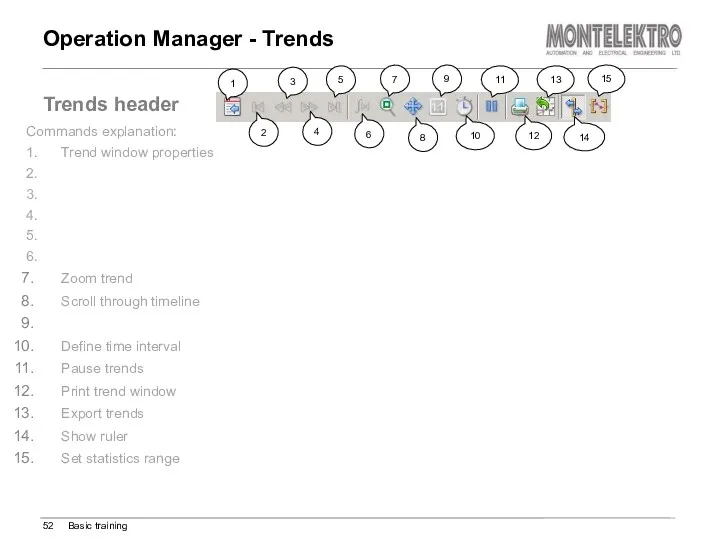
- 52. Operation Manager - Trends Basic training Trends header Commands explanation: 1. Trend window properties 2. 3.
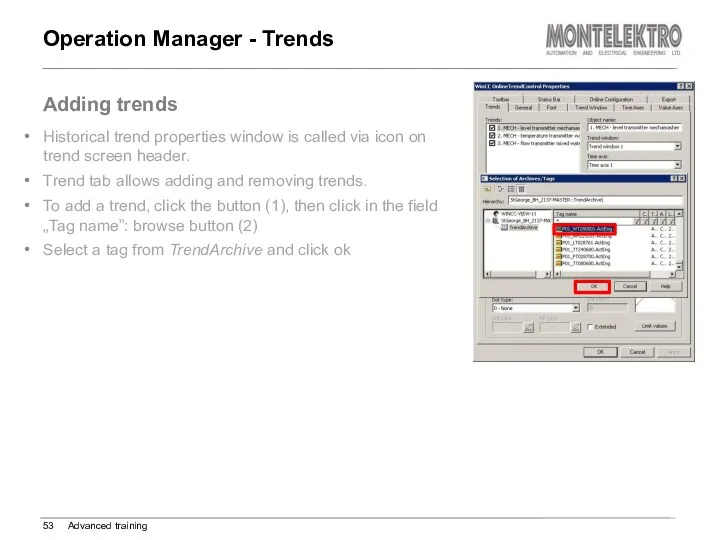
- 53. Operation Manager - Trends Advanced training Adding trends Historical trend properties window is called via icon
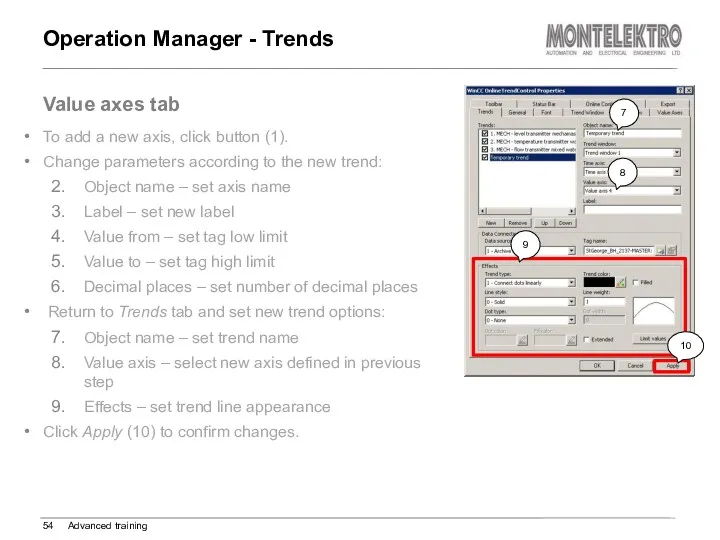
- 54. Operation Manager - Trends Advanced training Value axes tab To add a new axis, click button
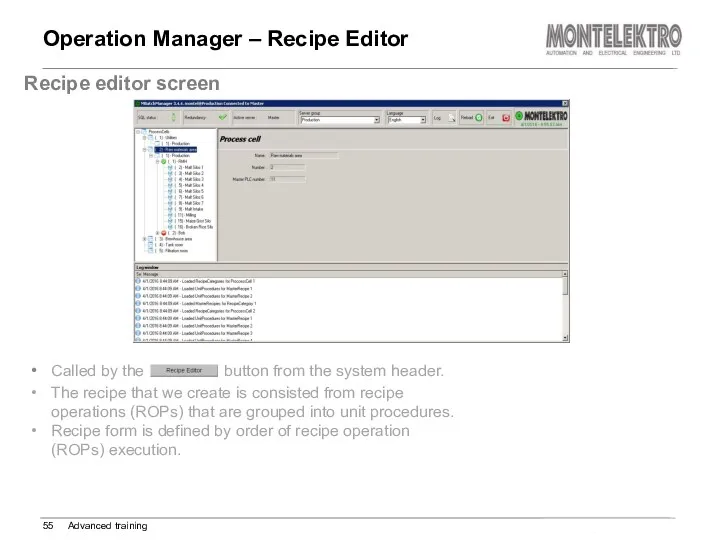
- 55. Operation Manager – Recipe Editor Advanced training Recipe editor screen Called by the button from the
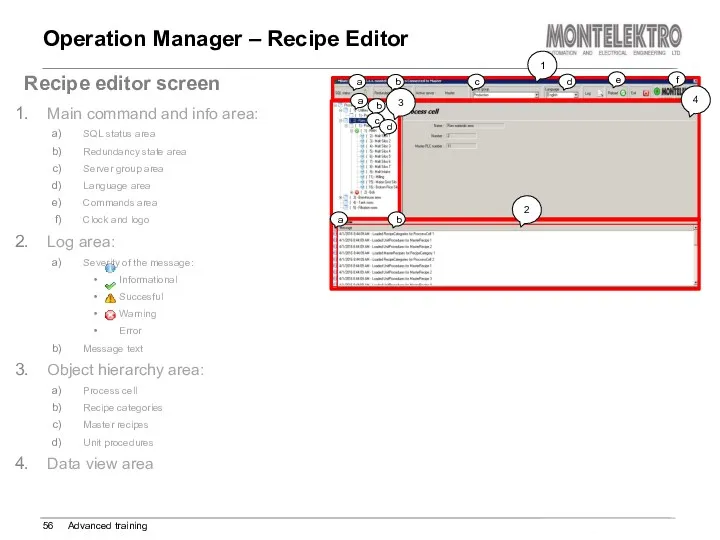
- 56. Operation Manager – Recipe Editor Advanced training Recipe editor screen Main command and info area: SQL
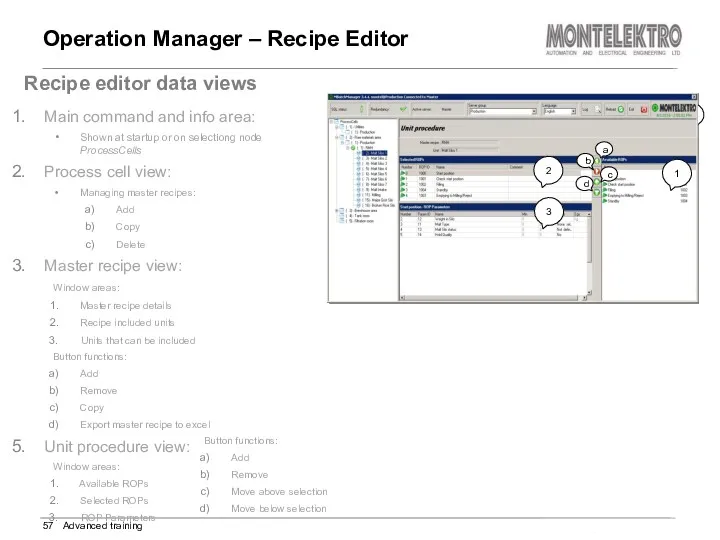
- 57. Operation Manager – Recipe Editor Advanced training Recipe editor data views Main command and info area:
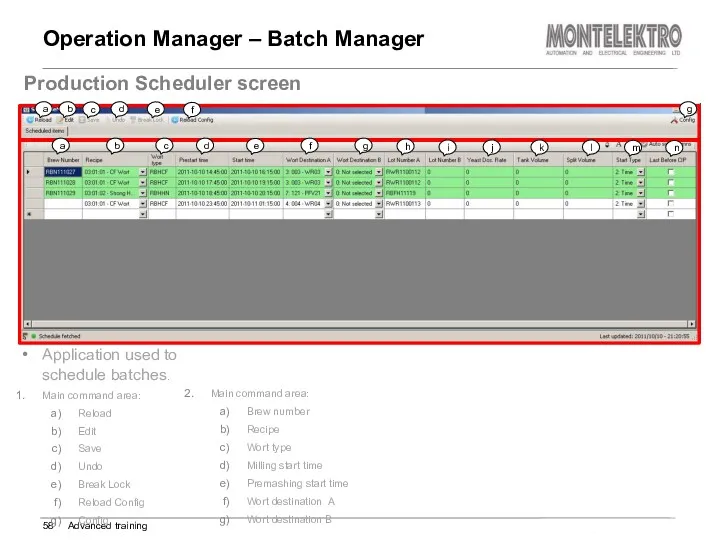
- 58. Operation Manager – Batch Manager Advanced training Production Scheduler screen Application used to schedule batches. Main
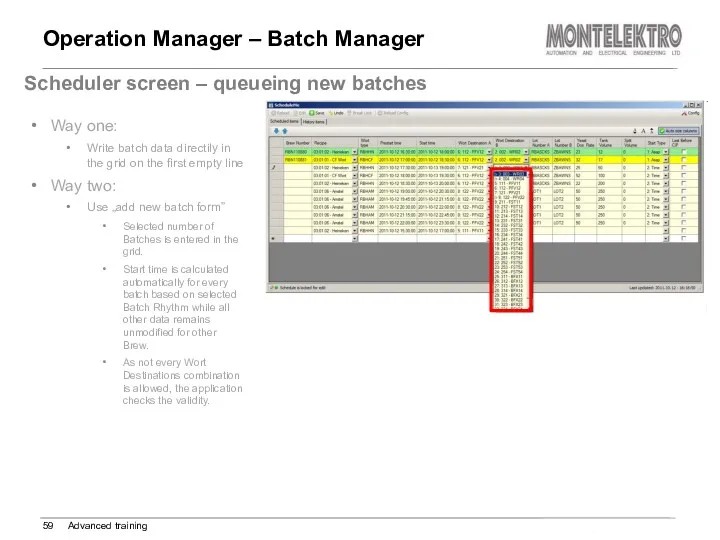
- 59. Operation Manager – Batch Manager Advanced training Scheduler screen – queueing new batches Way one: Write
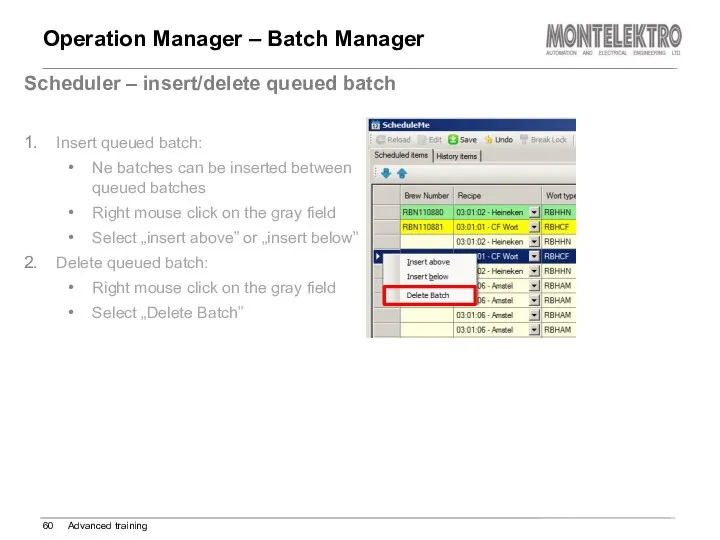
- 60. Operation Manager – Batch Manager Advanced training Scheduler – insert/delete queued batch Insert queued batch: Ne
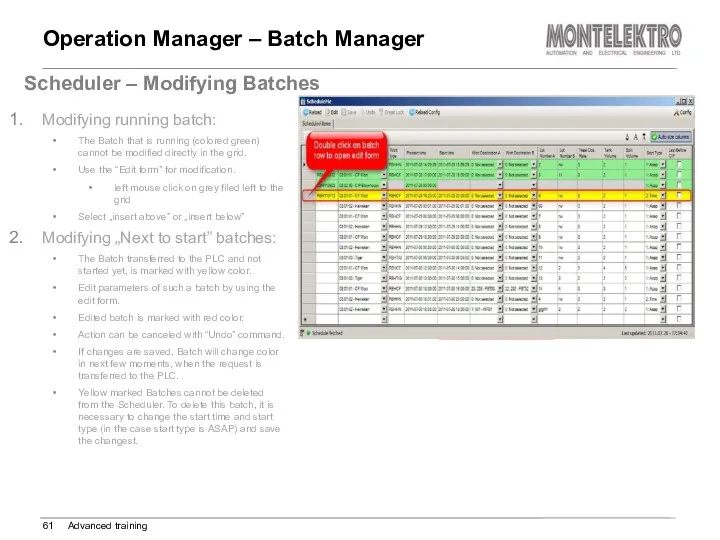
- 61. Operation Manager – Batch Manager Advanced training Scheduler – Modifying Batches Modifying running batch: The Batch
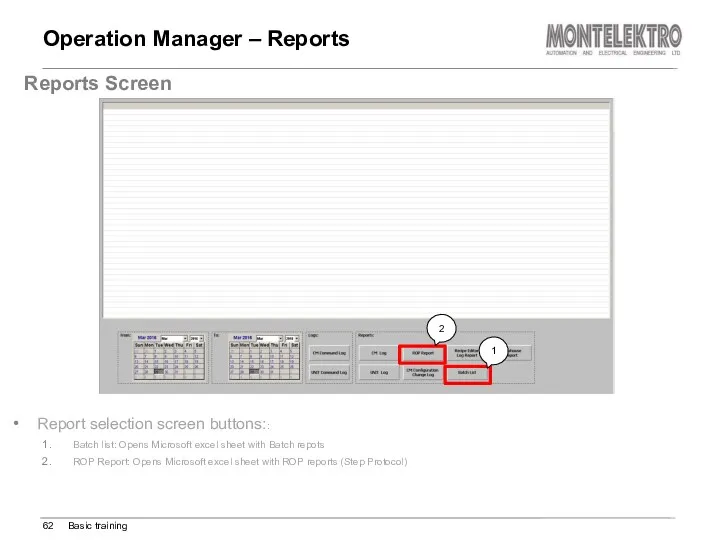
- 62. Operation Manager – Reports Basic training Reports Screen Report selection screen buttons:: Batch list: Opens Microsoft
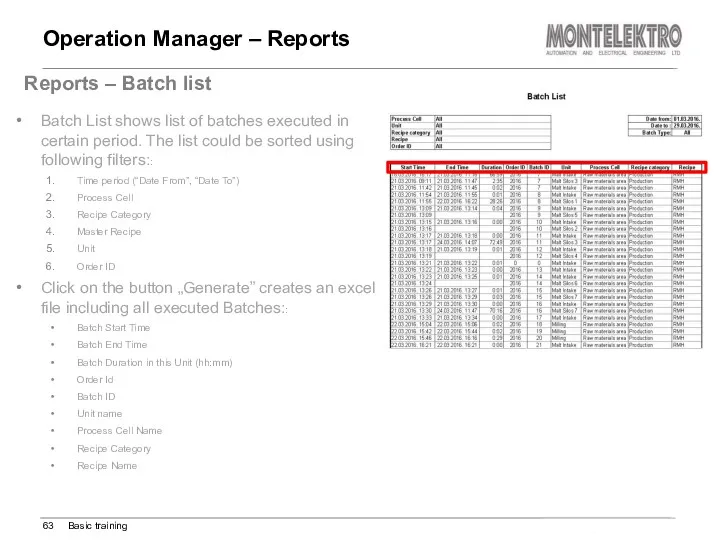
- 63. Operation Manager – Reports Basic training Reports – Batch list Batch List shows list of batches
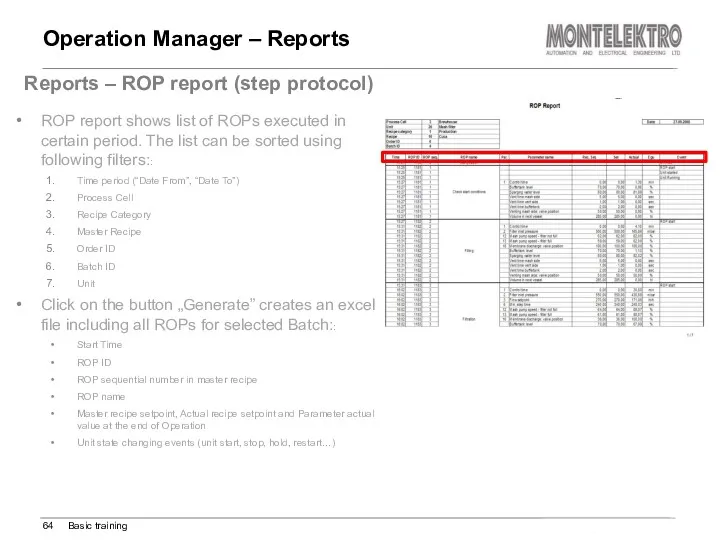
- 64. Operation Manager – Reports Basic training Reports – ROP report (step protocol) ROP report shows list
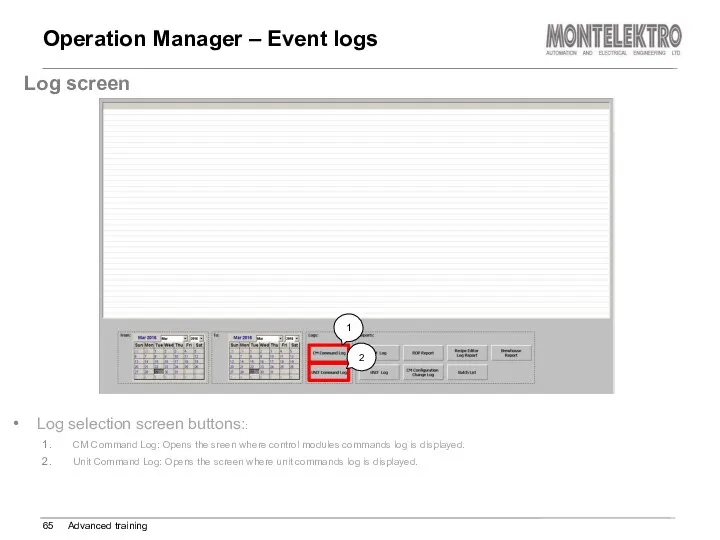
- 65. Operation Manager – Event logs Advanced training Log screen Log selection screen buttons:: CM Command Log:
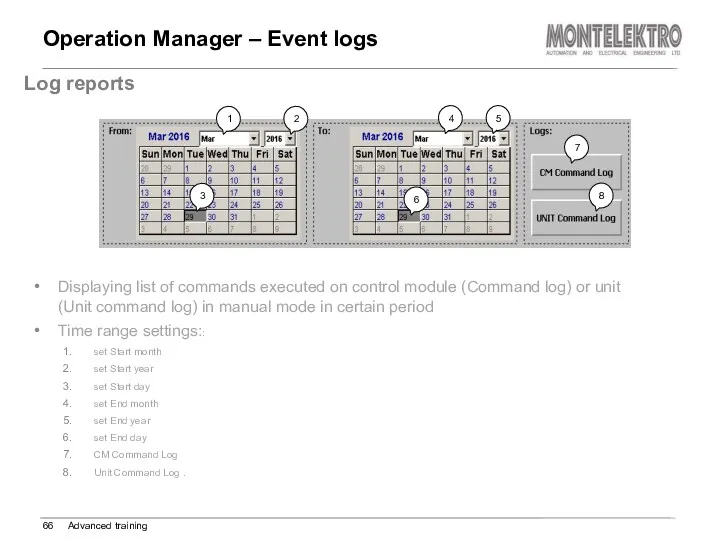
- 66. Operation Manager – Event logs Advanced training Log reports Displaying list of commands executed on control
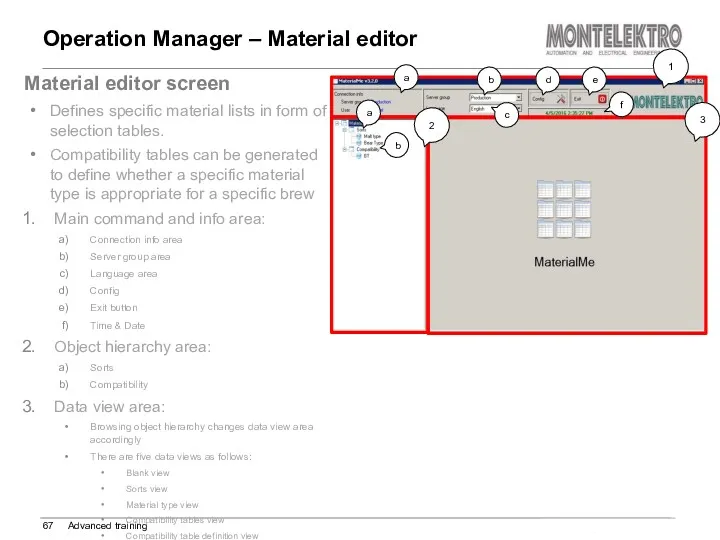
- 67. Operation Manager – Material editor Advanced training Material editor screen Defines specific material lists in form
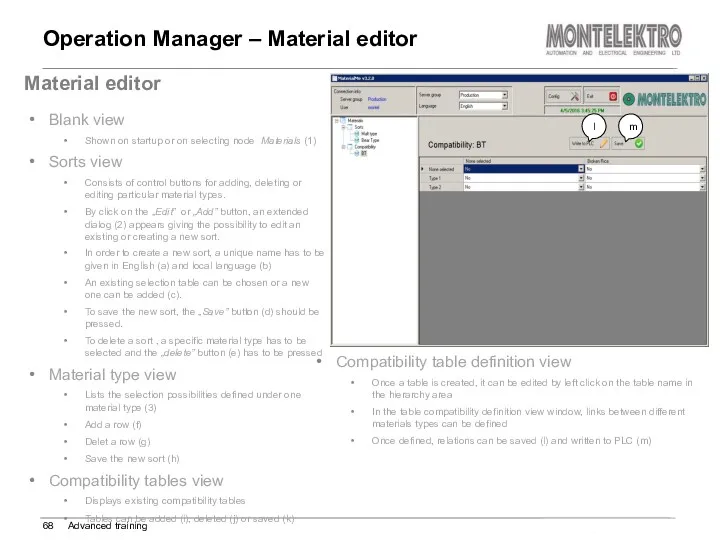
- 68. Operation Manager – Material editor Advanced training Material editor Blank view Shown on startup or on
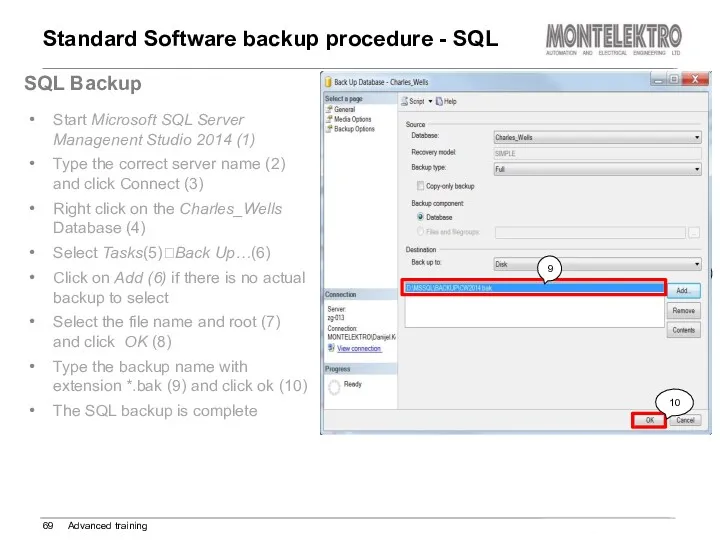
- 69. Standard Software backup procedure - SQL Advanced training SQL Backup Start Microsoft SQL Server Managenent Studio
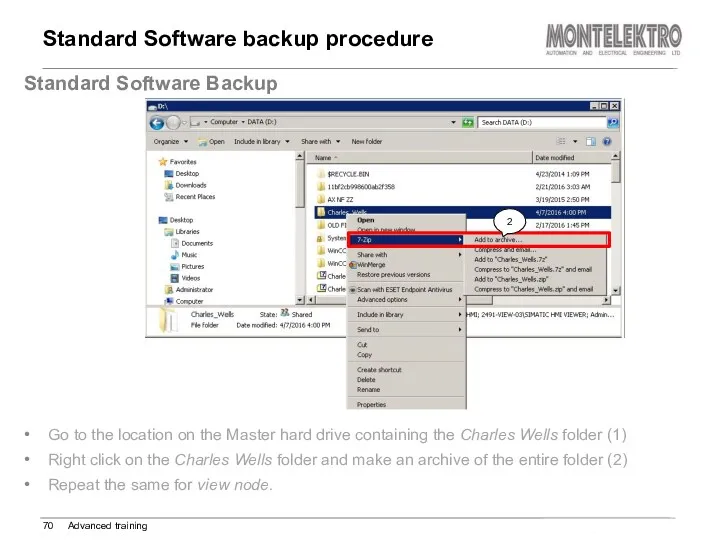
- 70. Standard Software backup procedure Advanced training Standard Software Backup Go to the location on the Master
- 72. Скачать презентацию



 Инструкция по работе с анкетой Naumen
Инструкция по работе с анкетой Naumen Пополнение карты Стрелка в мобильном приложении
Пополнение карты Стрелка в мобильном приложении нформационные ресурсы общества Информационные услуги и продукты
нформационные ресурсы общества Информационные услуги и продукты Как вебмастеру выжить в условиях кризиса
Как вебмастеру выжить в условиях кризиса Как устроена компьютерная сеть
Как устроена компьютерная сеть Анализ и синтез систем
Анализ и синтез систем Объектно-ориентированное программирование. Практические работы Pascal ABC
Объектно-ориентированное программирование. Практические работы Pascal ABC Інтернет. Громадянська освіта. 10 клас
Інтернет. Громадянська освіта. 10 клас Pro-women.ru — организация для влияния на социально-образовательные экосистемы людей
Pro-women.ru — организация для влияния на социально-образовательные экосистемы людей Производственная практика. ADO.NET и COM при работе с MS ACCESS и MS EXCEL в десктопном приложении
Производственная практика. ADO.NET и COM при работе с MS ACCESS и MS EXCEL в десктопном приложении Обработка исключительных ситуаций
Обработка исключительных ситуаций Word 2007: спецкурс
Word 2007: спецкурс Технология объектно-ориентированного проектирования ИС (разработки программного обеспечения) – Rational Unified Process (RUP)
Технология объектно-ориентированного проектирования ИС (разработки программного обеспечения) – Rational Unified Process (RUP) Инновационные модели деятельности школьного библиотекаря по формированию экологической культуры у детей
Инновационные модели деятельности школьного библиотекаря по формированию экологической культуры у детей Алгоритмизация и программирование (лекция)
Алгоритмизация и программирование (лекция) Средства общения в сети Интернет
Средства общения в сети Интернет Опыт внедрения системы электронного документооборота Правительства Ульяновской области
Опыт внедрения системы электронного документооборота Правительства Ульяновской области Урок по теме Сортировка, удаление и добавление записей 8 класс
Урок по теме Сортировка, удаление и добавление записей 8 класс Возможности 3D технологий
Возможности 3D технологий Принципы работы протоколов разных уровней. . Стеки OSI, TCP/IP, IPX/SPX, NetBIOS/SMB. (Тема 11)
Принципы работы протоколов разных уровней. . Стеки OSI, TCP/IP, IPX/SPX, NetBIOS/SMB. (Тема 11) Принципы обработки информации компьютером. Арифметические и логические основы работы компьютера. Лекция 5
Принципы обработки информации компьютером. Арифметические и логические основы работы компьютера. Лекция 5 Компьютерное моделирование
Компьютерное моделирование Кибербуллинг
Кибербуллинг C++ для ЕГЭ
C++ для ЕГЭ Электронные таблицы MS Excel
Электронные таблицы MS Excel Стандартные приложения ОС Windows. Работа с файлами и папками
Стандартные приложения ОС Windows. Работа с файлами и папками Динамические структуры данных: очереди и стеки
Динамические структуры данных: очереди и стеки Сервер DHCP и его назначение
Сервер DHCP и его назначение