Содержание
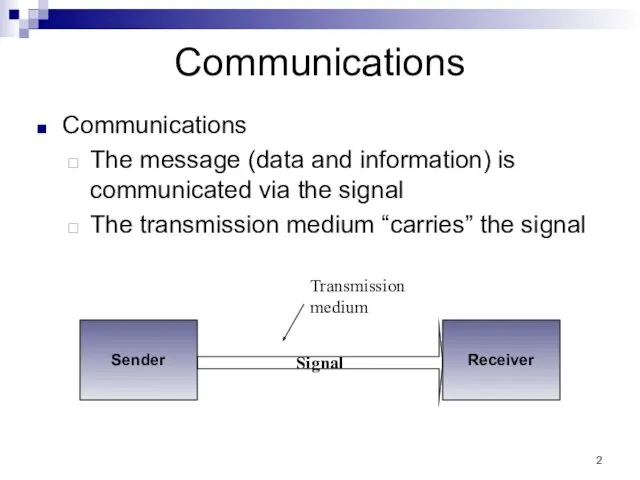
- 2. Communications Communications The message (data and information) is communicated via the signal The transmission medium “carries”
- 3. -The transmission of data from one computer to another, or from one device to another. A
- 4. Telecommunications Telecommunications The electronic transmission of signals for communications, including such means as: Telephone Radio Television
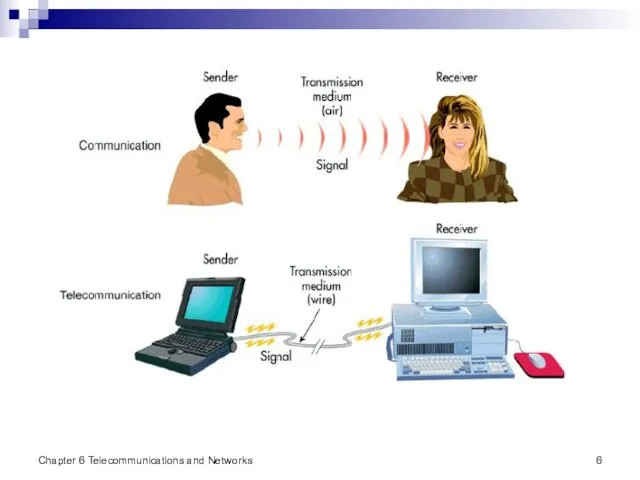
- 5. Communications and Telecommunications In human speech, the sender transmits a signal through the transmission medium of
- 6. Chapter 6 Telecommunications and Networks
- 7. Data Communications Data communications A specialized subset of telecommunications that refers to the electronic collection, processing,
- 8. Computer Network Computer network… The communications media, devices, and software needed to connect two or more
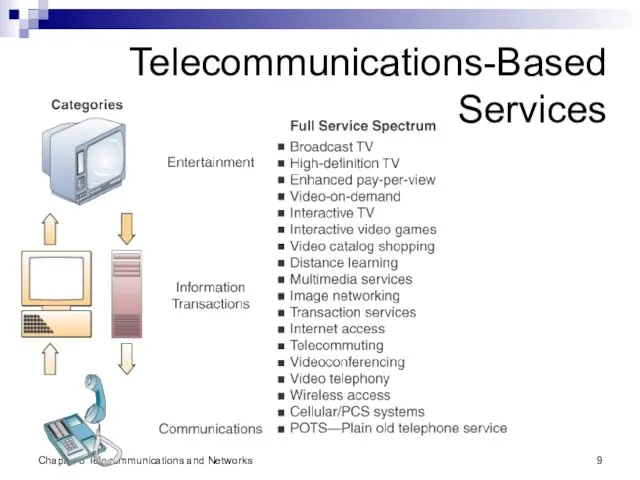
- 9. Chapter 6 Telecommunications and Networks Telecommunications-Based Services
- 10. Chapter 6 Telecommunications and Networks Internet Networking Technologies Internet networking technologies are being used as technology
- 11. Chapter 6 Telecommunications and Networks Open Systems Open systems use common standards for hardware, software, applications,
- 12. Chapter 6 Telecommunications and Networks Digital Network Technologies Telecommunications are being revolutionized by switch from analog
- 13. Chapter 6 Telecommunications and Networks Telecommunications Network Components Terminals Any input/output device that uses networks to
- 14. Chapter 6 Telecommunications and Networks Telecommunications Network Components Telecommunications control software Controls telecommunications activities Manages the
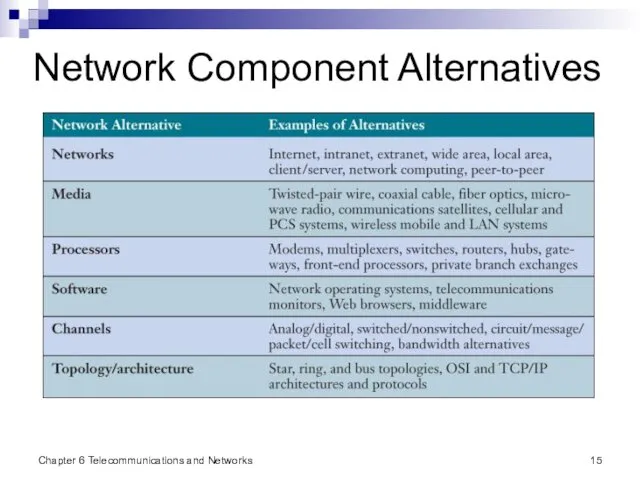
- 15. Chapter 6 Telecommunications and Networks Network Component Alternatives
- 16. Chapter 6 Telecommunications and Networks Types of Communications Networks Primary types of communications networks Wide Area
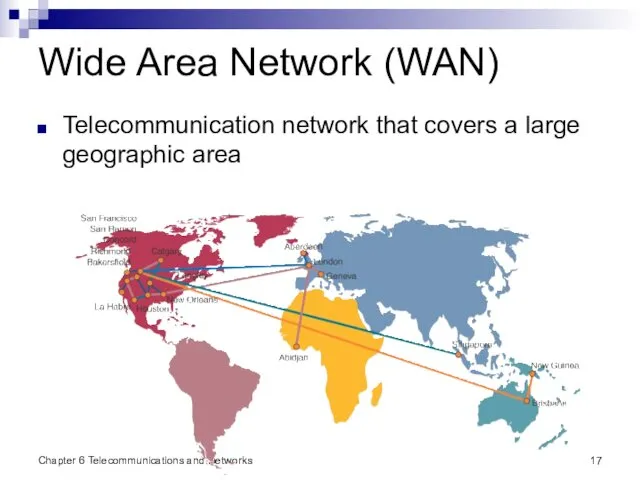
- 17. Chapter 6 Telecommunications and Networks Wide Area Network (WAN) Telecommunication network that covers a large geographic
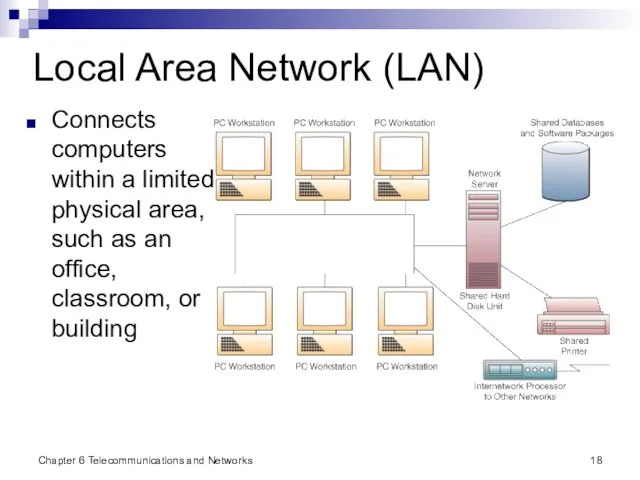
- 18. Chapter 6 Telecommunications and Networks Local Area Network (LAN) Connects computers within a limited physical area,
- 19. Chapter 6 Telecommunications and Networks Virtual Private Networks (VPN) Used to establish secure intranets and extranets
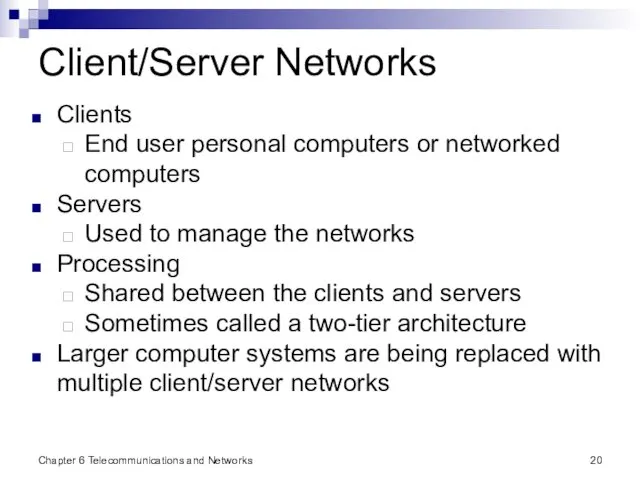
- 20. Chapter 6 Telecommunications and Networks Client/Server Networks Clients End user personal computers or networked computers Servers
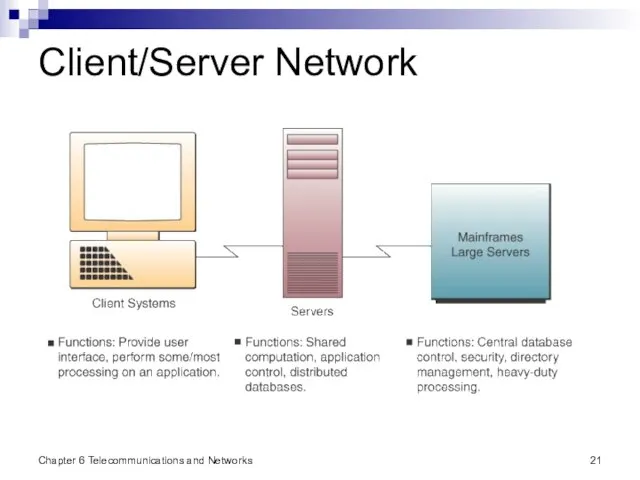
- 21. Chapter 6 Telecommunications and Networks Client/Server Network
- 22. Chapter 6 Telecommunications and Networks Peer-to-Peer Networks Central Server Architecture P2P file-sharing software connects all PCs
- 23. Chapter 6 Telecommunications and Networks Telecommunications Media Twisted-Pair Wire Ordinary telephone wire Copper wire is twisted
- 24. Chapter 6 Telecommunications and Networks Telecommunications Processors Modems The most common type of communications processor Converts
- 25. Chapter 6 Telecommunications and Networks Inter-Network Processors Switch… makes connections between telecommunications circuits in a network
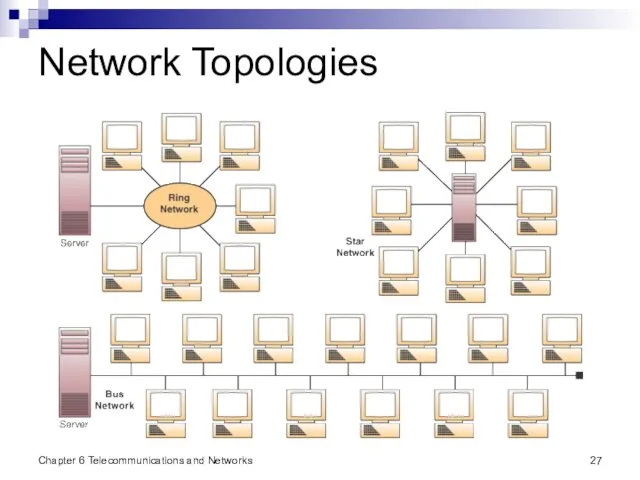
- 26. Chapter 6 Telecommunications and Networks Network Topologies Topology - The structure of a network Star Network
- 27. Chapter 6 Telecommunications and Networks Network Topologies
- 29. Скачать презентацию











 Разновидности компьютерных сетей. Сервисы интернета
Разновидности компьютерных сетей. Сервисы интернета Моделирование и формализация для 5-7 классов
Моделирование и формализация для 5-7 классов Scrum метрики
Scrum метрики Сети Ethernet городского уровня (Metro Ethernet). Протоколы канального уровня
Сети Ethernet городского уровня (Metro Ethernet). Протоколы канального уровня Электронная почта
Электронная почта Scratch: Создаем игру Лабиринт
Scratch: Создаем игру Лабиринт Центр технологической компетенции аддитивных технологий. 3D-печать
Центр технологической компетенции аддитивных технологий. 3D-печать Компетентностный подход как фактор модернизации общего образования
Компетентностный подход как фактор модернизации общего образования Системы счисления
Системы счисления Элементы алгебры логики. Математические основы информатики
Элементы алгебры логики. Математические основы информатики Основы организации научных исследований
Основы организации научных исследований Роль информационной деятельности в современном обществе
Роль информационной деятельности в современном обществе Система искусственного интеллекта
Система искусственного интеллекта Модели и моделирование
Модели и моделирование Алгоритмы
Алгоритмы Спілкування в чатах. Програми обміну миттєвими повідомленнями
Спілкування в чатах. Програми обміну миттєвими повідомленнями Разработка урока информатики по теме Моделирование информационных процессов. Корреляционные зависимости
Разработка урока информатики по теме Моделирование информационных процессов. Корреляционные зависимости Виды программного обеспечения
Виды программного обеспечения Windows XP
Windows XP Структура HTML-кода. Основы верстки. CSS. Фреймворки для создания сайтов
Структура HTML-кода. Основы верстки. CSS. Фреймворки для создания сайтов Создание Web-сайтов в программе Microsoft FrontPage
Создание Web-сайтов в программе Microsoft FrontPage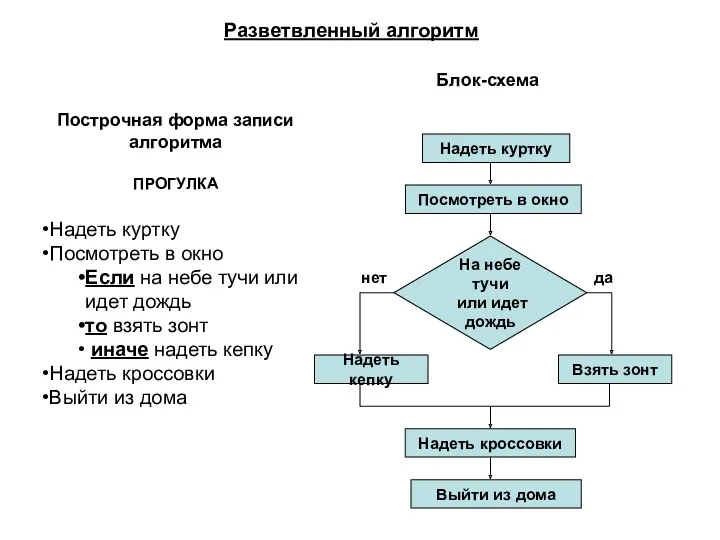 Алгоритмы
Алгоритмы Обзор операций и базовых инструкций языка Си. (Тема 3)
Обзор операций и базовых инструкций языка Си. (Тема 3) Технические средства телекоммуникационных технологий
Технические средства телекоммуникационных технологий Самые обсуждаемые темы красноярских СМИ
Самые обсуждаемые темы красноярских СМИ Агрегатор. Единый сервис заказов
Агрегатор. Единый сервис заказов Адаптивность. CSS
Адаптивность. CSS Коммерческое предложение для компании Эколас. Интернет в офис
Коммерческое предложение для компании Эколас. Интернет в офис