Содержание
- 2. Network Concepts A network is an interconnected or interrelated chain, group, or system 6-
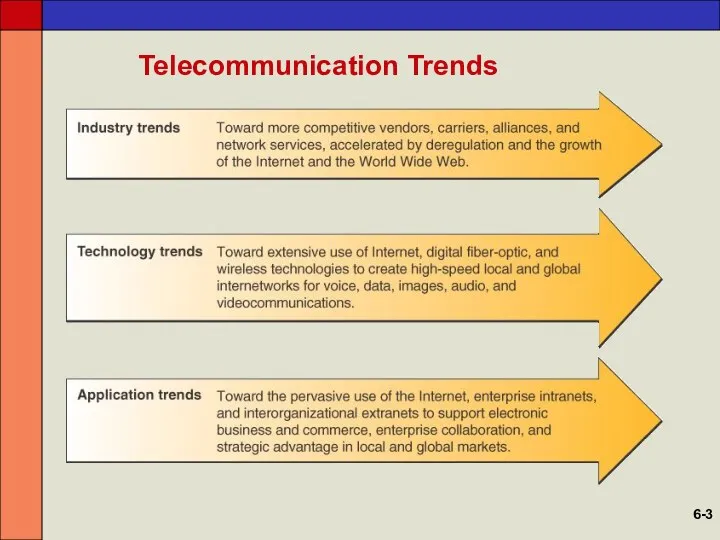
- 3. Telecommunication Trends 6-
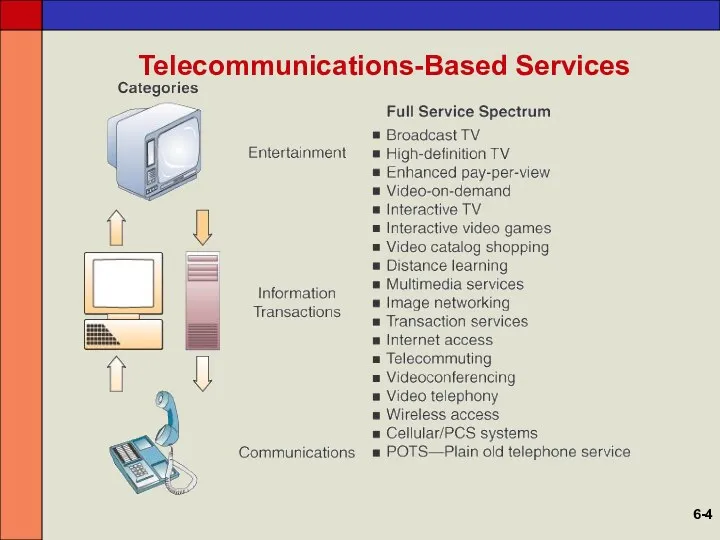
- 4. Telecommunications-Based Services 6-
- 5. Internet Networking Technologies Internet networking technologies are being used as technology platform Web browser suites HTML
- 6. Open Systems Open systems use common standards for hardware, software, applications, and networks Internet networking technologies
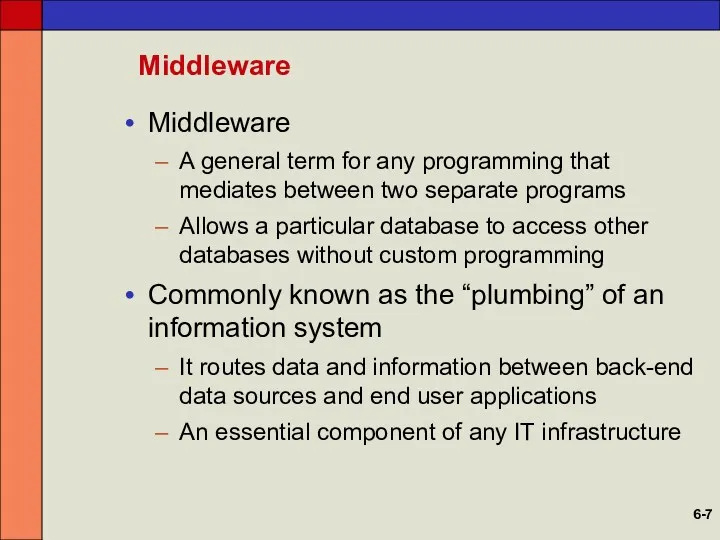
- 7. Middleware Middleware A general term for any programming that mediates between two separate programs Allows a
- 8. Wireless Technologies Fiber-optic Uses pulses of laser-generated light Reduced size and installation effort Vastly greater communication
- 9. Business Application Trends Telecommunications networks now play a vital and pervasive role in Web-enabled… E-business processes
- 10. Internet2 Next generation of the Internet High-performance Different infrastructure than the current Internet Infinite bandwidth 6-
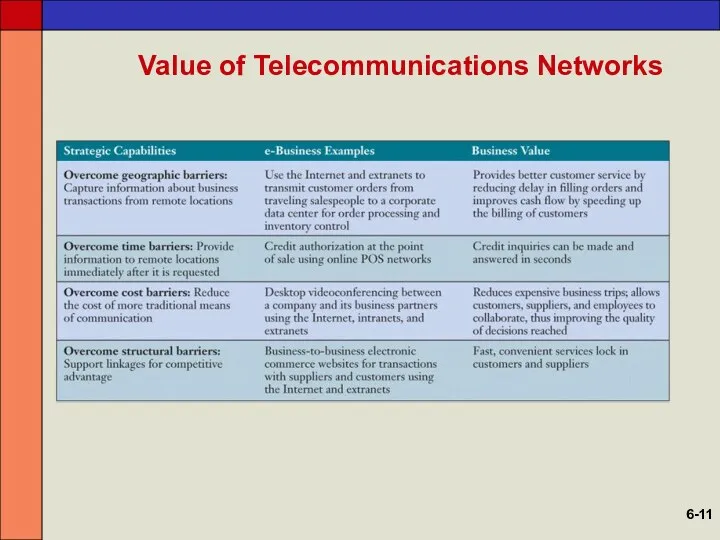
- 11. Value of Telecommunications Networks 6-
- 12. Internet Service Providers ISP A company that specializes in providing easy access to the Internet For
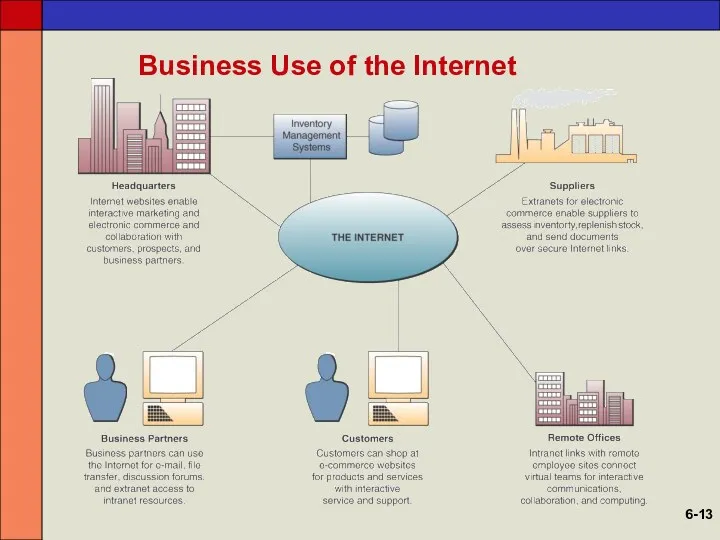
- 13. Business Use of the Internet 6-
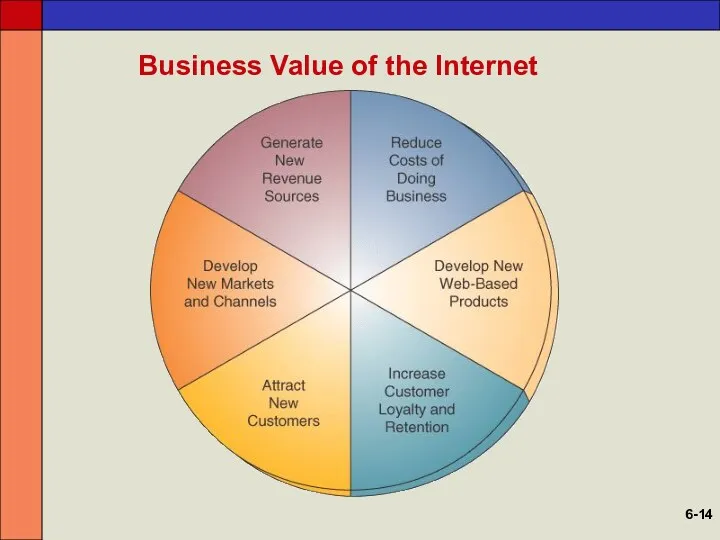
- 14. Business Value of the Internet 6-
- 15. The Role of Intranets Many companies have sophisticated and widespread intranets, offering… Detailed data retrieval Collaboration
- 16. Intranets Intranets are protected by… Passwords Encryption Firewalls Customers, suppliers, and other business partners can access
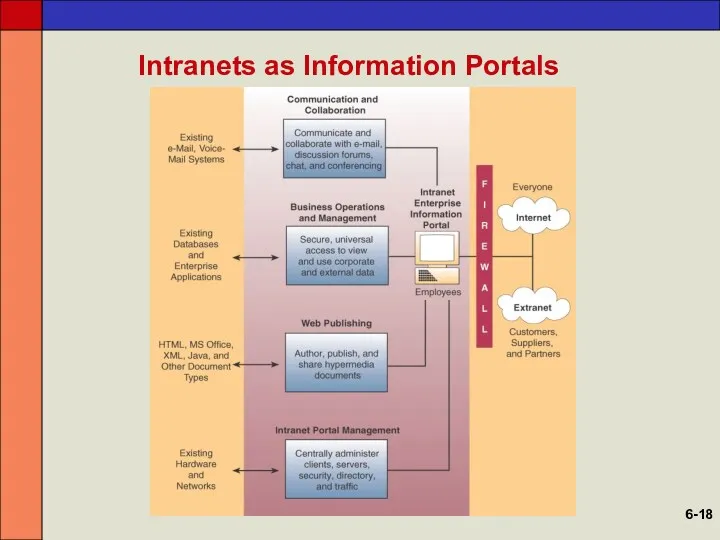
- 17. Business Value of Intranets Intranets support Communications and collaboration Business operations and management Web publishing Intranet
- 18. Intranets as Information Portals 6-
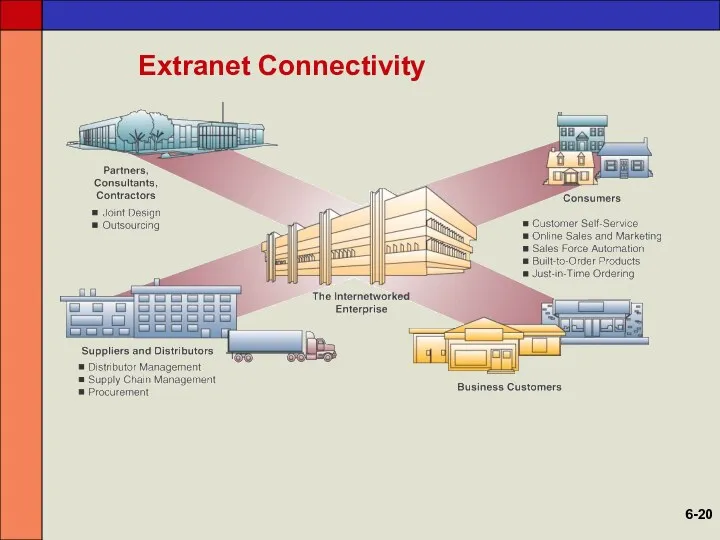
- 19. Extranets Network links that use Internet technologies to connect the intranet of a business to the
- 20. Extranet Connectivity 6-
- 21. Business Value of Extranets Web browser technology makes customer and supplier access to intranets easier and
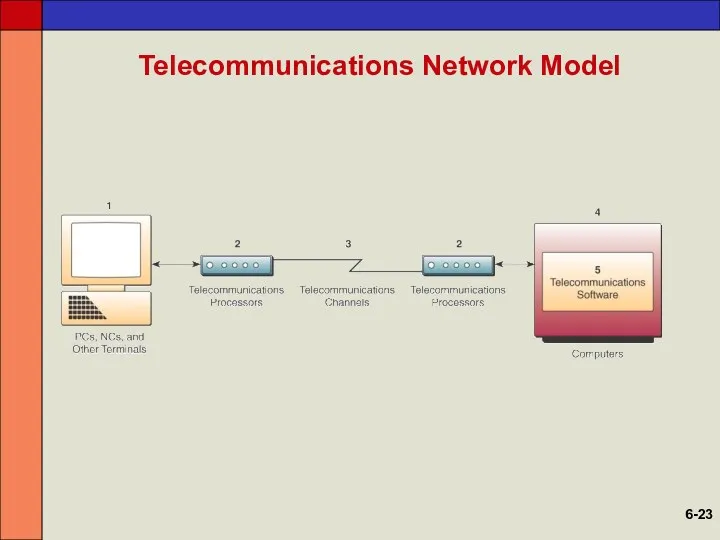
- 22. Telecommunications Network Model A telecommunications network is any arrangement where A sender transmits a message To
- 23. Telecommunications Network Model 6-
- 24. Telecommunications Network Components Terminals Any input/output device that uses networks to transmit or receive data Telecommunications
- 25. Telecommunications Network Components Telecommunications control software Controls telecommunications activities Manages the functions of telecommunications networks Includes
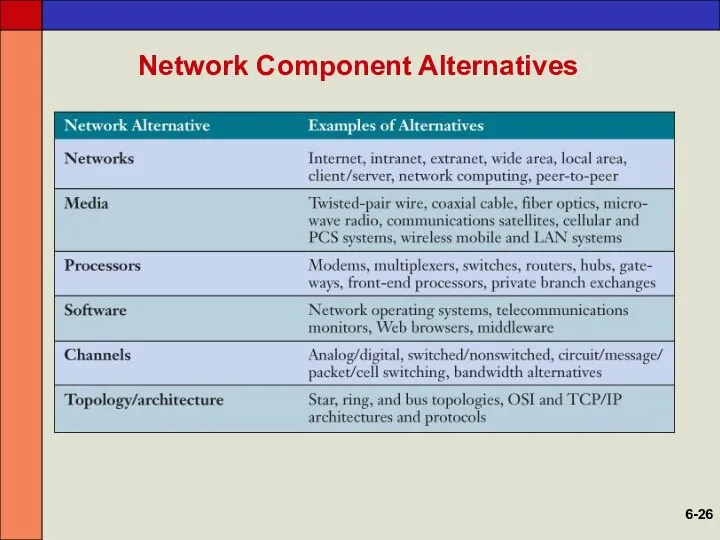
- 26. Network Component Alternatives 6-
- 27. Types of Communications Networks Primary types of communications networks Wide Area Local Area Virtual Private Client/Server
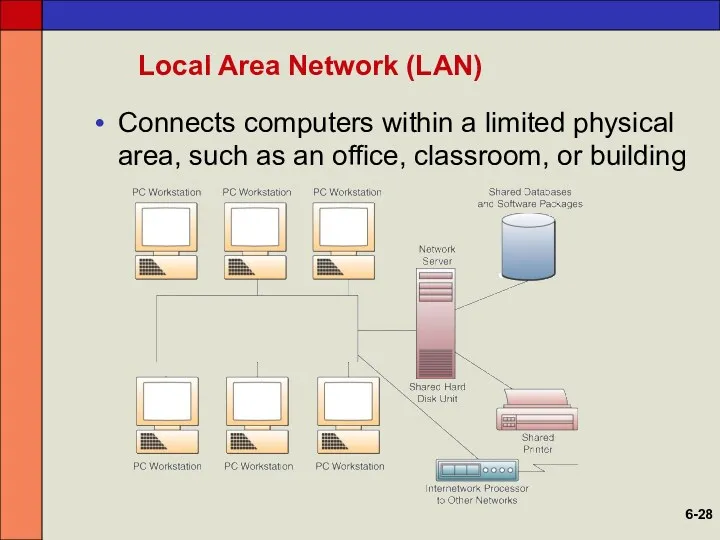
- 28. Local Area Network (LAN) Connects computers within a limited physical area, such as an office, classroom,
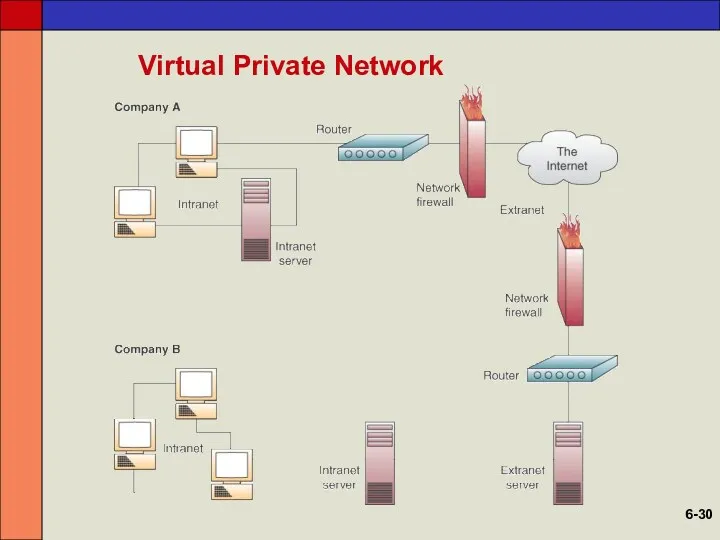
- 29. Virtual Private Networks (VPN) Used to establish secure intranets and extranets The Internet is the main
- 30. Virtual Private Network 6-
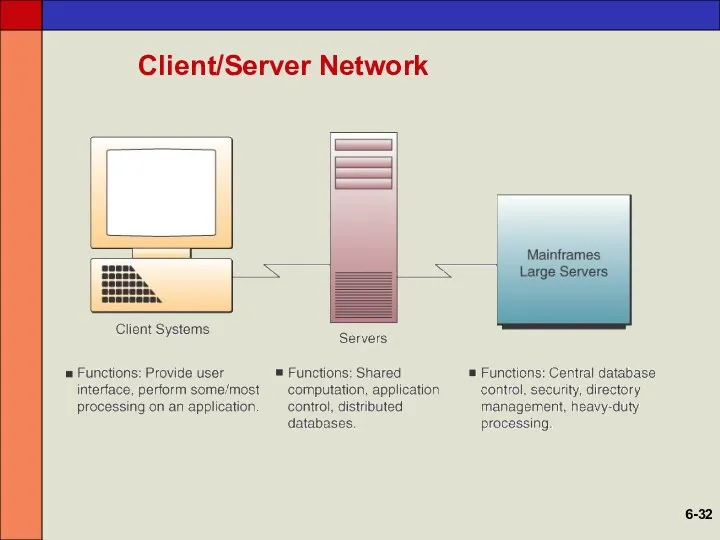
- 31. Client/Server Networks Clients End user personal computers or networked computers Servers Used to manage the networks
- 32. Client/Server Network 6-
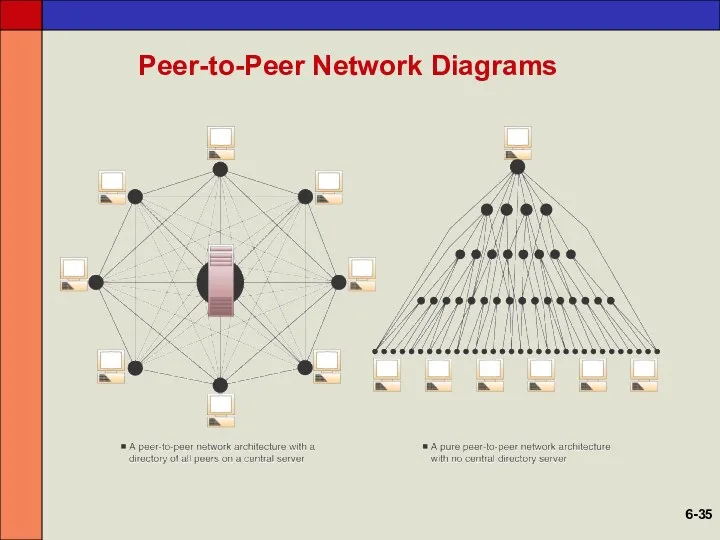
- 33. Peer-to-Peer Networks Central Server Architecture P2P file-sharing software connects all PCs to a central server When
- 34. Peer-to-Peer Networks Pure Peer-to-Peer Architecture No central directory or server File-sharing software connects one PC to
- 35. Peer-to-Peer Network Diagrams 6-
- 36. Wireless Technologies Wireless LANS Uses wireless radio-wave technology to connect PCs within an office or a
- 37. Wireless Technologies Other Wireless Systems Cellular phones Mobile radio PDAs Telecommunications networks now play vital and
- 38. The Wireless Web Wireless Internet access is growing as Web-enabled information appliances proliferate Smart telephones, pagers,
- 39. Telecommunications Processors Modems The most common type of communications processor Converts a digital signal to an
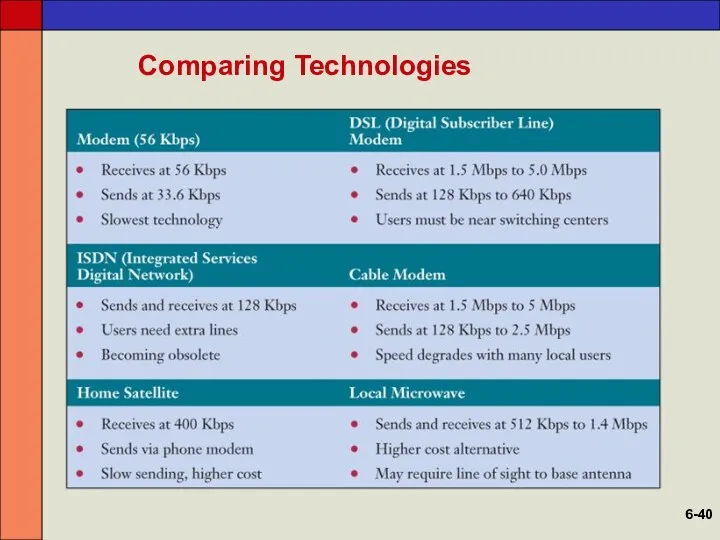
- 40. Comparing Technologies 6-
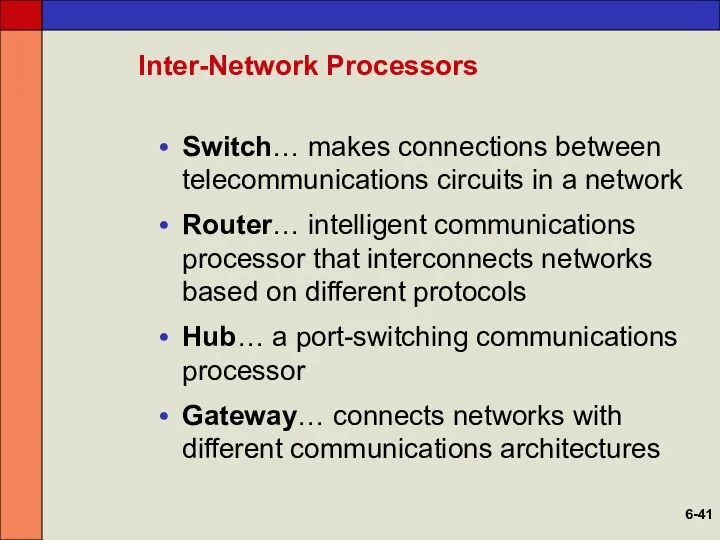
- 41. Inter-Network Processors Switch… makes connections between telecommunications circuits in a network Router… intelligent communications processor that
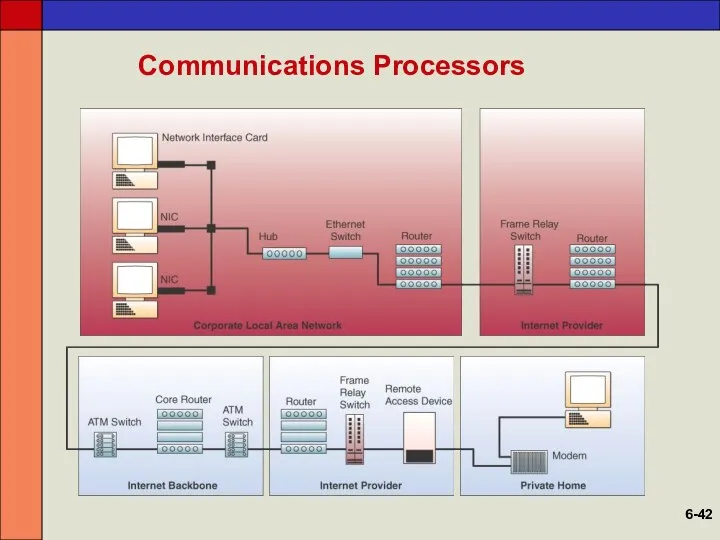
- 42. Communications Processors 6-
- 43. Communications Processors Multiplexer… allows a single communications channel to carry simultaneous data transmissions from many terminals
- 44. Telecommunications Software May reside in PCs, servers, mainframes, and communications processors Vital part of all telecommunications
- 45. Network Management Functions Traffic Management Manage network resources and traffic to avoid congestion and optimize service
- 46. Network Management Functions Capacity Planning Survey network resources, traffic patterns, and users’ needs Determine the best
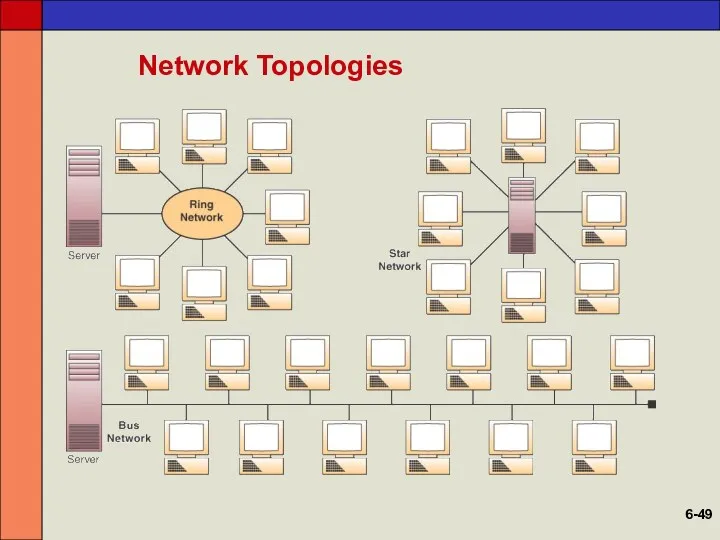
- 47. Network Topologies Topology The structure of a network Star Network Ties end user computers to a
- 48. Network Topologies Mesh Network Uses direct communications lines to connect some or all of the computers
- 49. Network Topologies 6-
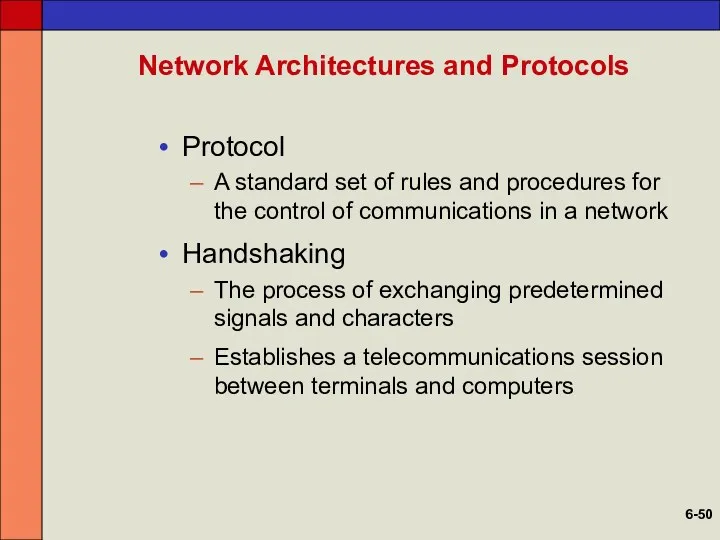
- 50. Network Architectures and Protocols Protocol A standard set of rules and procedures for the control of
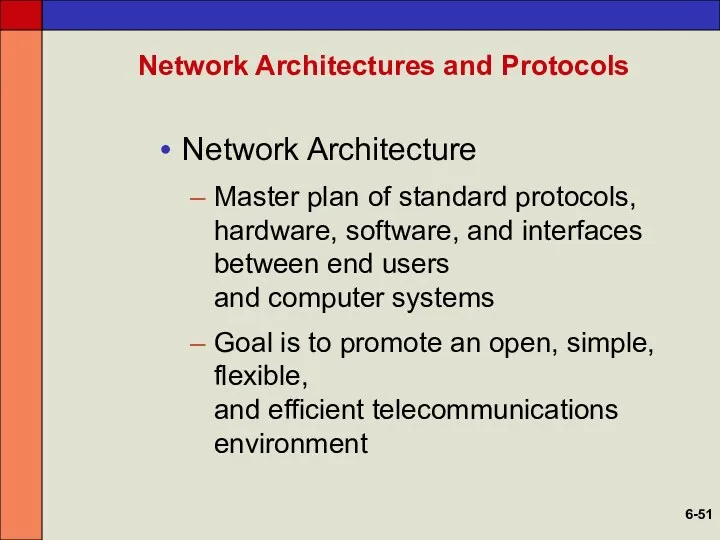
- 51. Network Architectures and Protocols Network Architecture Master plan of standard protocols, hardware, software, and interfaces between
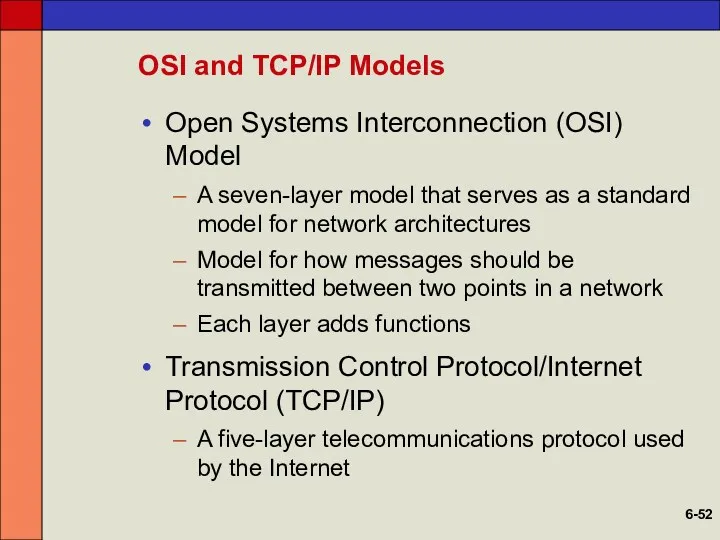
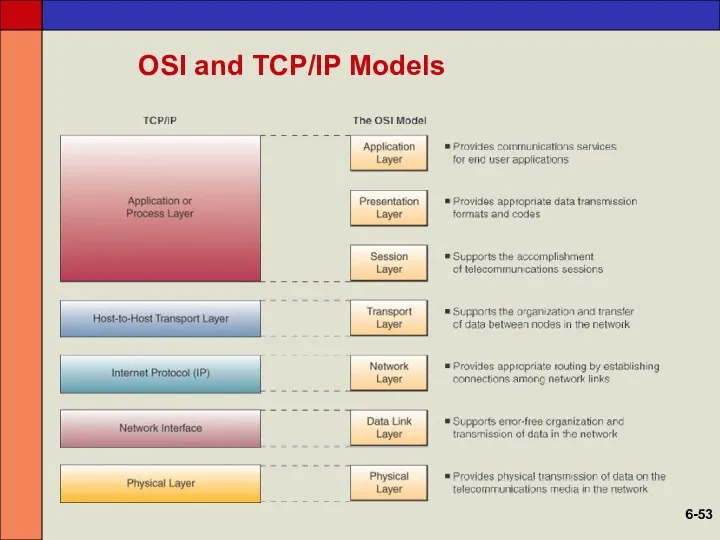
- 52. OSI and TCP/IP Models Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Model A seven-layer model that serves as a
- 53. OSI and TCP/IP Models 6-
- 54. Voice Over IP Internet Telephony Using an Internet connection to pass voice data using IP instead
- 56. Скачать презентацию




























 Mantis tickets
Mantis tickets Игровые персонажи Dota 2
Игровые персонажи Dota 2 Основы языка Pascal. Меню. Анимация
Основы языка Pascal. Меню. Анимация Презентация к докладу Образовательный web-квест
Презентация к докладу Образовательный web-квест Мережеві і розподілені операційні системи
Мережеві і розподілені операційні системи Программное обеспечение ЭВМ
Программное обеспечение ЭВМ Перспективные направления в IT
Перспективные направления в IT Гіперпосилання і елементи управління в презентаціях
Гіперпосилання і елементи управління в презентаціях Windows Movie Maker
Windows Movie Maker Информационные технологии автоматизированного проектирования
Информационные технологии автоматизированного проектирования Опасности в интернете. Мошенники в интернете
Опасности в интернете. Мошенники в интернете Локальные и глобальные сети ЭВМ. Защита информации в сетях. (Тема 6)
Локальные и глобальные сети ЭВМ. Защита информации в сетях. (Тема 6) Компютерные игры
Компютерные игры Колесо Жизни
Колесо Жизни Інтерфейс користувача бази даних
Інтерфейс користувача бази даних Алгоритм. Свойства алгоритма
Алгоритм. Свойства алгоритма Типографика. Основы графического дизайна
Типографика. Основы графического дизайна Табличный процессор Microsoft Excel
Табличный процессор Microsoft Excel Введение в курс тестирования. (Занятие 1)
Введение в курс тестирования. (Занятие 1) Файловые системы и базы данных
Файловые системы и базы данных Инструменты графического редактора. Начинаем рисовать. 5 класс
Инструменты графического редактора. Начинаем рисовать. 5 класс Базы данных. Лекция 2
Базы данных. Лекция 2 Символьный и строковый типы данных
Символьный и строковый типы данных Вредоносное программное обеспечение. Описание. Классификация
Вредоносное программное обеспечение. Описание. Классификация Информационная технология: предмет, цель, задачи, состав компонентов. Лекция 2
Информационная технология: предмет, цель, задачи, состав компонентов. Лекция 2 Файл Полное имя файла
Файл Полное имя файла Профессиональное программирование. Системно-философский подход
Профессиональное программирование. Системно-философский подход Жүйелік блок
Жүйелік блок