Содержание
- 2. Mid & New Kingdom Burial-Cham The Middle Kingdom began when pharaoh Mentuhotep united Egypt again after
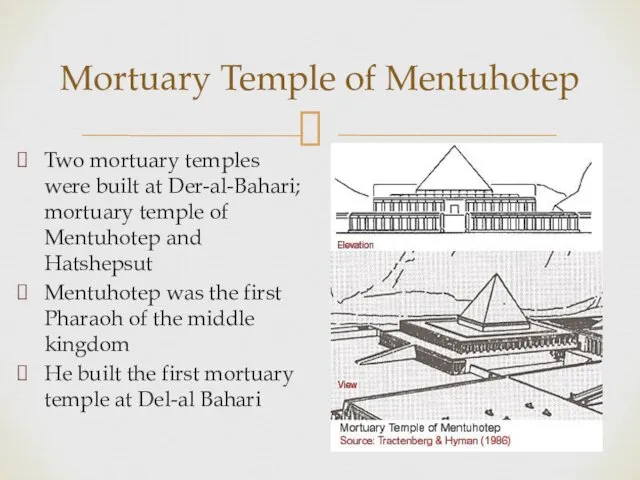
- 3. Mortuary Temple of Mentuhotep Two mortuary temples were built at Der-al-Bahari; mortuary temple of Mentuhotep and
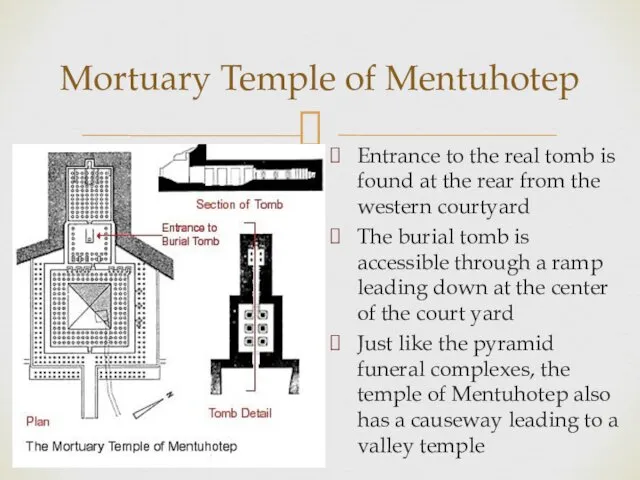
- 4. Mortuary Temple of Mentuhotep Entrance to the real tomb is found at the rear from the
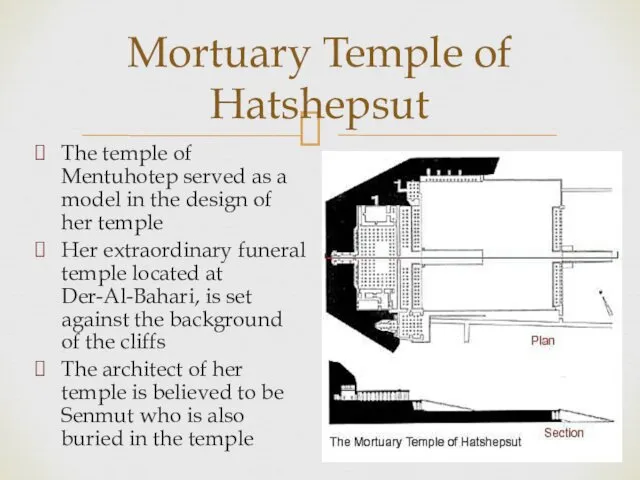
- 5. Mortuary Temple of Hatshepsut The temple of Mentuhotep served as a model in the design of
- 6. Mortuary Temple of Hatshepsut The temple of Hatshepsut is like a giant stage on three levels
- 7. Mortuary Temple of Hatshepsut Her temple was not a construction of stone masses as in the
- 11. Underground Tomb- Rock Cut Tomb Two types of Underground tombs were built by pharaohs and nobles
- 12. Underground Tomb- Rock Cut Tomb Beni Hassan consist of 3 elements: A colonnade entrance portico for
- 13. Underground Tomb- Rock Cut Tomb The columns on the exterior were shaped like a prism with
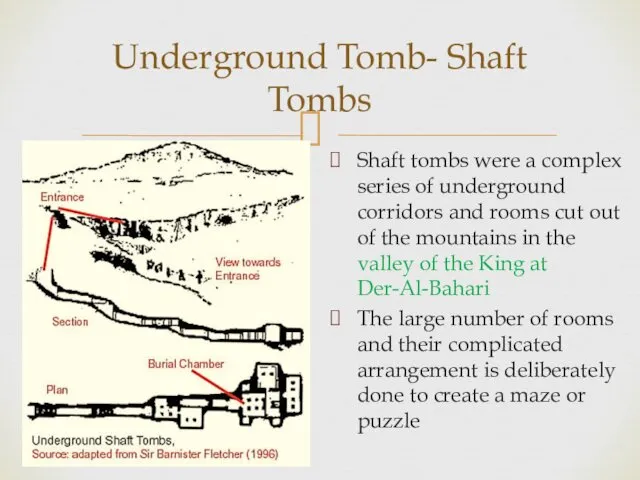
- 14. Underground Tomb- Shaft Tombs Shaft tombs were a complex series of underground corridors and rooms cut
- 15. New Kingdom Cult Temples The Middle Kingdom lasted for 275 years The New Kingdom lasted for
- 16. The most important and common architectural elements of the New Kingdom were temples Several temples were
- 17. – Long approaches – Guardian sphinxes – Colonnaded vestibules and inner courts – Darkening shrines –
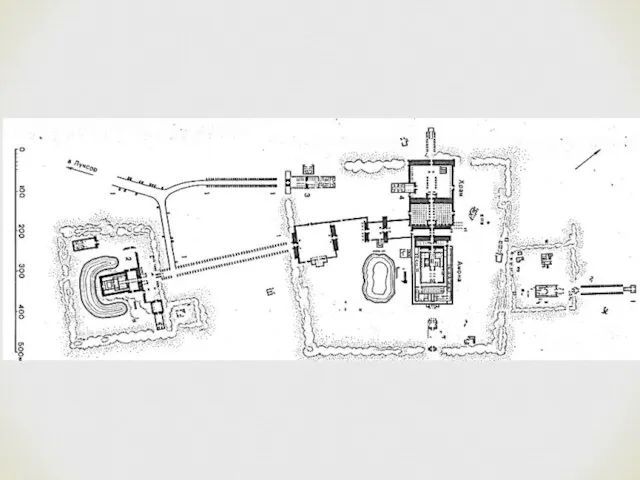
- 18. New Kingdom Cult Temples Many examples of the New Kingdom temples are found at Karnak and
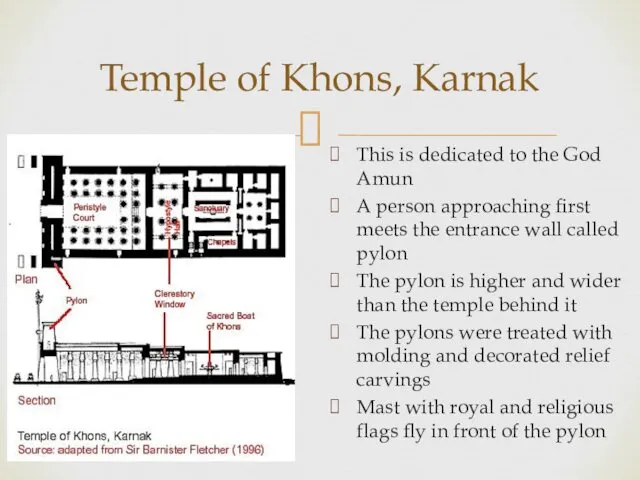
- 20. Temple of Khons, Karnak This is dedicated to the God Amun A person approaching first meets
- 21. Temple of Khons, Karnak Behind the pylon is the peristyle courtyard Made up of a row
- 23. The ceiling was usually painted blue to resemble the sky with stars twinkling The columns in
- 24. As you move from the pylon into the temple, the roof becomes lower and the floor
- 25. It is the largest of the New Kingdom temples and it grew in a haphazard way
- 26. Arrangement of the hypostyle hall consist of 134 columns arranged in 16 rows; 7 rows of
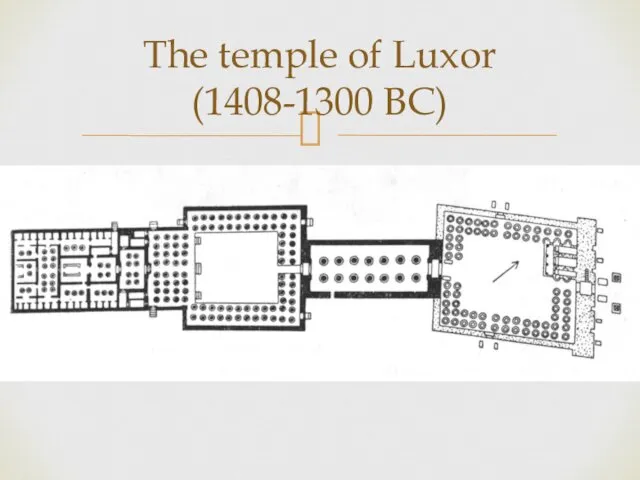
- 30. The temple of Luxor (1408-1300 BC)
- 32. The Temple of Seti (1312 BC)
- 33. The Ramesseum Thebes (1301 BC)
- 34. The Great Temple Abu Simbel (1301 BC)
- 35. Two buildings types dominated ancient Egyptian architecture; tombs and temples Minimal attention was paid to houses
- 36. Plant materials, clay and stone Plants consist of readily available material like reeds, papyrus and palm
- 37. Construction system in ancient Egypt reflected the availability of materials Two construction systems were predominant: Adobe
- 38. Ancient Egyptians contributed to technologies in the aspect of lighting Egyptians used courtyards extensively for lighting
- 40. Скачать презентацию






























 Город России - Тверь
Город России - Тверь Древний Рим
Древний Рим Москва – столица России
Москва – столица России Тайна Перевала Дятлова
Тайна Перевала Дятлова Россия в 2008-2020 гг
Россия в 2008-2020 гг Великая Отечественная война. Коренной перелом
Великая Отечественная война. Коренной перелом Февральская революция и Временное правительство
Февральская революция и Временное правительство Блокада Ленинграда
Блокада Ленинграда Сурский оборонительный рубеж
Сурский оборонительный рубеж Экономическое развитие России в начале ХХ века
Экономическое развитие России в начале ХХ века Зобалаң жылдар жаңғырығы (Қуғын-сүргін, ашаршылық құрбандарын еске алу)
Зобалаң жылдар жаңғырығы (Қуғын-сүргін, ашаршылық құрбандарын еске алу) Римский скульптурный портрет
Римский скульптурный портрет СССР в первое послевоенное десятилетие
СССР в первое послевоенное десятилетие Музей восковых фигур Мадам Тюссо в Лондоне
Музей восковых фигур Мадам Тюссо в Лондоне Московский кремль
Московский кремль Объекты Всемирного культурного наследия в России
Объекты Всемирного культурного наследия в России Реконкиста и образование централизованных государств на Пиренейском полуострове
Реконкиста и образование централизованных государств на Пиренейском полуострове Общественное движение в годы правления Николая I
Общественное движение в годы правления Николая I Память бережно храним посвящается 35-летию со дня гибели Героя Советского Союза Николая Яковлевича Анфиногенова
Память бережно храним посвящается 35-летию со дня гибели Героя Советского Союза Николая Яковлевича Анфиногенова Город Омск. Городские мотивы в картинах художников
Город Омск. Городские мотивы в картинах художников Обыкновенное чудо – люди России. Зинаида Мартыновна Портнова
Обыкновенное чудо – люди России. Зинаида Мартыновна Портнова СЕМЬ ЧУДЕС СВЕТА
СЕМЬ ЧУДЕС СВЕТА Подготовка к ЕГЭ по истории 2017 – 2018 учебный год
Подготовка к ЕГЭ по истории 2017 – 2018 учебный год История Индии
История Индии Предпосылки петровских реформ
Предпосылки петровских реформ Мир на грани ядерной войны
Мир на грани ядерной войны Манифест об отмене крепостного права как важнейшая правовая основа проведения земельной реформы в России 1861 г
Манифест об отмене крепостного права как важнейшая правовая основа проведения земельной реформы в России 1861 г День народного единства России
День народного единства России