Содержание
- 2. The Renaissance: 1485–1660 1500s Humanism 1534 Henry VIII Breaks with Church 1558–1603 Reign of Elizabeth I
- 3. Humanism Humanism—intellectual movement that greatly influenced Renaissance thinkers, writers, artists studied the Bible and the classics
- 4. Humanism English lawyer Two Friends—Two Humanists traveled throughout Europe Dutch monk Desiderius Erasmus Sir Thomas More
- 5. Humanism Around 1455 . . . printing press invented by Johannes Gutenberg press set up in
- 6. Henry VIII Breaks with the Church Henry VIII (reigned 1509—1547) “Renaissance man”—poet, musician, athlete had six
- 7. Henry VIII Breaks with the Church The Reformation in Europe reformers reject authority of pope and
- 8. Henry VIII Breaks with the Church 1533 Pope refuses Henry VIII’s request for annulment Henry appoints
- 9. Divorce was not allowed, so Henry was looking for a loophole. He asked Pope Clement VII
- 10. Henry VIII Breaks with the Church Protestant Reformation After 1534 Henry closes monasteries Protestantism begins in
- 11. the “boy king” rules in name only “Bloody Mary” restores pope’s power hunts down and executes
- 12. The Reign of Elizabeth I Elizabeth I—literary connoisseur; beloved symbol of peace, security, prosperity restores law
- 13. The Reign of Elizabeth I Mary, Queen of Scots Elizabeth’s cousin, heir to English throne initiates
- 14. Vast fleet of warships from Spain (Spanish Armada) sent to invade England 1588 The Defeat of
- 15. England set eight small frigates ablaze and sailed them into the Armada. The Armada was the
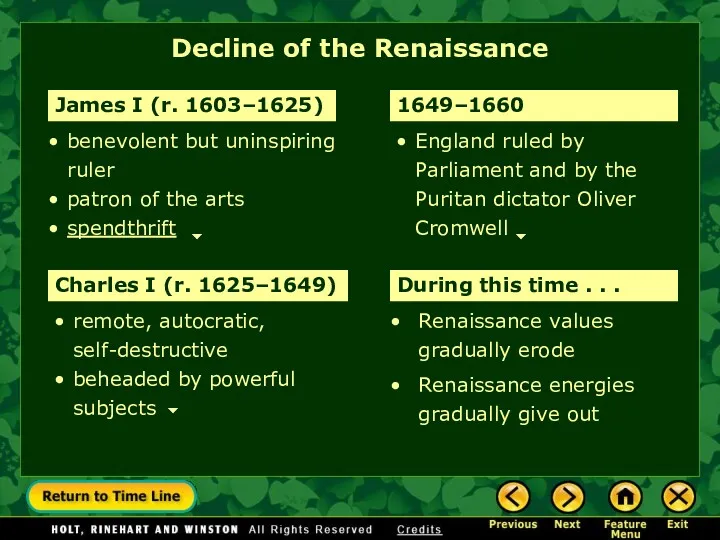
- 16. benevolent but uninspiring ruler patron of the arts spendthrift remote, autocratic, self-destructive beheaded by powerful subjects
- 17. Decline of the Renaissance spendthrift n. someone who is wasteful and lavish in his or her
- 18. _________ established the Church of England, separate from the Roman Church _________ benevolent ruler, patron of
- 19. END
- 20. Viewing the Art Renaissance Learning The instruments shown in the painting suggest that the ambassadors have
- 22. Скачать презентацию


















 Қазақ хандығына 550-жыл
Қазақ хандығына 550-жыл Страницы великой войны. Памяти павших
Страницы великой войны. Памяти павших Исследовательская работа Как делают бумагу?
Исследовательская работа Как делают бумагу? Церковні братства
Церковні братства Parizh. 6 klass
Parizh. 6 klass Образование варварских королевств. Государство франков в VI-VIII веках
Образование варварских королевств. Государство франков в VI-VIII веках Летчик Виктор Васильевич Талалихин
Летчик Виктор Васильевич Талалихин A Dictator in the Soviet Union (U.S.S.R)
A Dictator in the Soviet Union (U.S.S.R) День народного единства
День народного единства Петер Симон Паллас
Петер Симон Паллас Бій під Крутами
Бій під Крутами Войны граждан и рабов
Войны граждан и рабов Вавилонский царь Хаммурапи и его законы
Вавилонский царь Хаммурапи и его законы О неизвестных героях войны…
О неизвестных героях войны… Средневековый город Венеция. 6 класс
Средневековый город Венеция. 6 класс Индия в 19 веке
Индия в 19 веке Презентация по истории Древнего мира Библейские сказания (для Office 2007)
Презентация по истории Древнего мира Библейские сказания (для Office 2007) Роль кружковой работы в деятельности школьного музея.
Роль кружковой работы в деятельности школьного музея. Великая Отечественная война (1941-1945)
Великая Отечественная война (1941-1945) Презентация для 6 класса Рыцарские традиции и обычаи
Презентация для 6 класса Рыцарские традиции и обычаи Святитель Лука
Святитель Лука Религия древних египтян
Религия древних египтян БССР в годы новой экономической политики. Участие в образовании СССР. Укрупнение территории
БССР в годы новой экономической политики. Участие в образовании СССР. Укрупнение территории Журнал Time, как элемент американской культуры
Журнал Time, как элемент американской культуры Jews in Spain, 14th century
Jews in Spain, 14th century Александр III (продолжение)
Александр III (продолжение) Реформы патриарха Никона и возникновение старообрядчества
Реформы патриарха Никона и возникновение старообрядчества История с образования государства Киевская Русь до Великих реформ Александра II ( в двух частях)
История с образования государства Киевская Русь до Великих реформ Александра II ( в двух частях)