- Главная
- Культурология
- Types of culture

Содержание
- 2. Introduction When talking about different cultures, people typically refer to “national” culture. However, our behaviour and
- 3. From universal to regional culture (Reisinger, 2009) Universal culture (culture of all nationalities and humans); Civilisation
- 4. From generation to functional culture (Reisinger, 2009) Generation culture (culture of a particular generation; for example,
- 5. From religious to individual culture Religious culture (e.g. the culture of Christians, Jews or Muslims); Gender
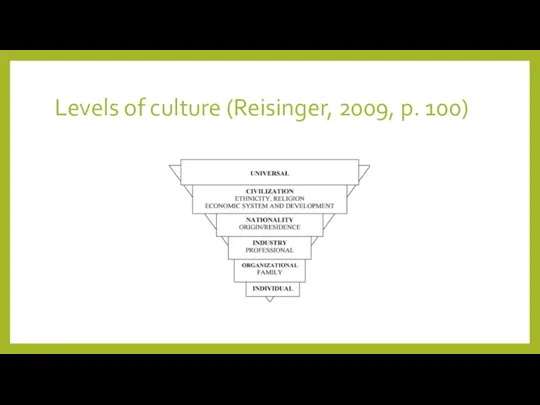
- 6. Levels of culture (Reisinger, 2009, p. 100)
- 7. Levels of culture – interdependent and affected The particular levels are interdependent and influence each other.
- 9. Скачать презентацию
Слайд 2
Introduction
When talking about different cultures, people typically refer to “national” culture.
Introduction
When talking about different cultures, people typically refer to “national” culture.
However, our behaviour and preferences are affected by several other cultures, such as ethnicity, race, religion or occupation.
For example, people of a certain profession, such as business people or lawyers, are influenced by the culture of the industry and the profession itself, as well as the culture of the organisation they work for.
For example, people of a certain profession, such as business people or lawyers, are influenced by the culture of the industry and the profession itself, as well as the culture of the organisation they work for.
Слайд 3
From universal to regional culture (Reisinger, 2009)
Universal culture (culture of all
From universal to regional culture (Reisinger, 2009)
Universal culture (culture of all
nationalities and humans);
Civilisation culture (culture of a particular civilisation comprising different nationalities with similar political systems, economic development, ethnic roots, and religious values);
Ethnic culture (culture of an ethnic group the members of which share a language, religion, colour, etc.);
Race culture (culture of a particular race, for example, African-American, etc.);
National culture (culture of a national group, often referred to as ‘‘country’’ culture. However, within the geographic boundaries of a given country several nationalities and cultures may live, for example, Serbs, Croatians, Kosovars and Macedonians in the former Yugoslavia, or Slovaks, Hungarians, Roma people and Rusyns living in Slovakia)
Regional culture (culture of a specific geographical region, such as the culture of Southern Italy)
Civilisation culture (culture of a particular civilisation comprising different nationalities with similar political systems, economic development, ethnic roots, and religious values);
Ethnic culture (culture of an ethnic group the members of which share a language, religion, colour, etc.);
Race culture (culture of a particular race, for example, African-American, etc.);
National culture (culture of a national group, often referred to as ‘‘country’’ culture. However, within the geographic boundaries of a given country several nationalities and cultures may live, for example, Serbs, Croatians, Kosovars and Macedonians in the former Yugoslavia, or Slovaks, Hungarians, Roma people and Rusyns living in Slovakia)
Regional culture (culture of a specific geographical region, such as the culture of Southern Italy)
Слайд 4
From generation to functional culture (Reisinger, 2009)
Generation culture (culture of a
From generation to functional culture (Reisinger, 2009)
Generation culture (culture of a
particular generation; for example, “Baby Boomers”, Zen generation)
Industry culture (culture of a specific industry, such as tourism, banking, or pharmaceuticals)
Professional culture (culture of a particular profession, e.g. doctors, lawyers, engineers)
Organisational / corporate culture (culture of a specific organisation, e.g. IBM);
Functional culture (culture of a specific department within an organisation e.g. finance, marketing, human resources)
Industry culture (culture of a specific industry, such as tourism, banking, or pharmaceuticals)
Professional culture (culture of a particular profession, e.g. doctors, lawyers, engineers)
Organisational / corporate culture (culture of a specific organisation, e.g. IBM);
Functional culture (culture of a specific department within an organisation e.g. finance, marketing, human resources)
Слайд 5
From religious to individual culture
Religious culture (e.g. the culture of Christians,
From religious to individual culture
Religious culture (e.g. the culture of Christians,
Jews or Muslims);
Gender culture (culture of men, women, LGBTQIA+ etc.);
Class culture (culture of the upper, upper-middle, middle, working and lower class);
(Benčíková,2007)
Family culture (structure and cohesion of a particular family, the roles and responsibilities of the wife and husband, etc.);
Individual culture (value system, beliefs, or attitudes of an individual);
(Reisinger, 2009)
Gender culture (culture of men, women, LGBTQIA+ etc.);
Class culture (culture of the upper, upper-middle, middle, working and lower class);
(Benčíková,2007)
Family culture (structure and cohesion of a particular family, the roles and responsibilities of the wife and husband, etc.);
Individual culture (value system, beliefs, or attitudes of an individual);
(Reisinger, 2009)
Слайд 6
Levels of culture (Reisinger, 2009, p. 100)
Levels of culture (Reisinger, 2009, p. 100)
Слайд 7
Levels of culture – interdependent and affected
The particular levels are interdependent
Levels of culture – interdependent and affected
The particular levels are interdependent
and influence each other.
For example, national culture is affected by the economic development or religion of a particular civilisation. National culture influences industry and professional cultures, as well as organisational and family culture.
Individuals can be affected by the different types of culture they belong to (Camerer & Mader, 2016).
For example, a Christian female advocate living in Slovakia may be influenced by the attributes of the given religion, gender, professional and national culture.
For example, national culture is affected by the economic development or religion of a particular civilisation. National culture influences industry and professional cultures, as well as organisational and family culture.
Individuals can be affected by the different types of culture they belong to (Camerer & Mader, 2016).
For example, a Christian female advocate living in Slovakia may be influenced by the attributes of the given religion, gender, professional and national culture.
- Предыдущая
Экономический рост




 Рюш как современный вид отделки одежды
Рюш как современный вид отделки одежды Импрессионизм. Символизм. Постимпрессионизм
Импрессионизм. Символизм. Постимпрессионизм Художественная культура пореформенной России
Художественная культура пореформенной России Художественная культура XVII в. Школы и стили
Художественная культура XVII в. Школы и стили Одежда говорит о человеке
Одежда говорит о человеке Ласковый и нежный зверь. Электронная викторина по мифу о зверобое. 12+
Ласковый и нежный зверь. Электронная викторина по мифу о зверобое. 12+ История бисероплетения
История бисероплетения Функции социально-культурной деятельности
Функции социально-культурной деятельности Пасха в Германии
Пасха в Германии Мода, культура и ты. Композиционно-конструктивные принципы дизайна одежды
Мода, культура и ты. Композиционно-конструктивные принципы дизайна одежды Карнавал. История карнавалов
Карнавал. История карнавалов Костюм XIX века
Костюм XIX века Мифифеские существа мира
Мифифеские существа мира Любимый эффект наших клиентов. Варианты и его усиление
Любимый эффект наших клиентов. Варианты и его усиление Самые известные музеи Италии
Самые известные музеи Италии Творческий проект. Малахитовая сказка
Творческий проект. Малахитовая сказка Марли Мэтлин
Марли Мэтлин Все народы воспевают мудрость старости. 4 класс
Все народы воспевают мудрость старости. 4 класс Stand-Up - сольное юмористическое выступление перед аудиторией, где комик высмеивает проблемы общества, пороки людей
Stand-Up - сольное юмористическое выступление перед аудиторией, где комик высмеивает проблемы общества, пороки людей Сохранение и развитие казачьей культуры
Сохранение и развитие казачьей культуры Картины исторические и бытовые
Картины исторические и бытовые Шедевры мировой архитектуры
Шедевры мировой архитектуры Мир византийской культуры
Мир византийской культуры Особенности национального костюма
Особенности национального костюма Способы складывания салфеток для сервировки праздничного стола
Способы складывания салфеток для сервировки праздничного стола Звонкие и тихие цвета. Рисунок Весна идет
Звонкие и тихие цвета. Рисунок Весна идет Живопись первой половины 19 века в России
Живопись первой половины 19 века в России Синтез искусств в театре, кино, на телевидении
Синтез искусств в театре, кино, на телевидении