Содержание
- 2. Chapter Outline 1) Overview 2) Concept of Causality 3) Conditions for Causality 4) Definition of Concepts
- 3. 9) A Classification of Experimental Designs 10) Pre-experimental Designs 11) True Experimental Designs 12) Quasi Experimental
- 4. 18) Determining a Test Marketing Strategy 19) International Marketing Research 20) Ethics in Marketing Research 21)
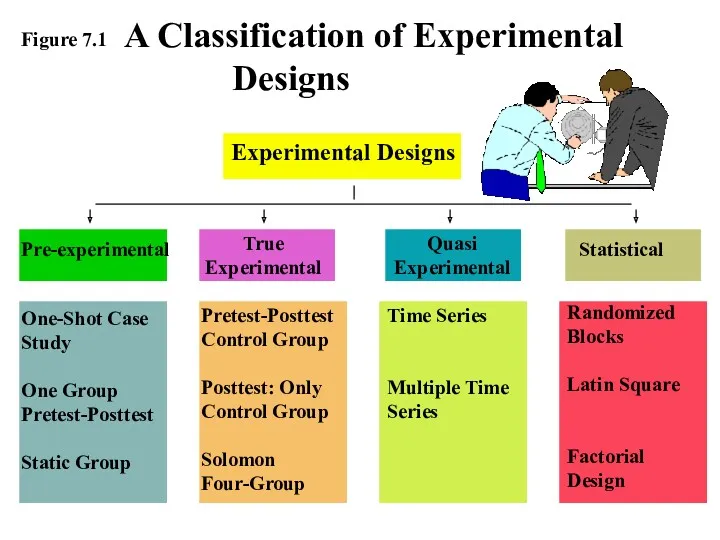
- 5. A Classification of Experimental Designs Experimental Designs Pre-experimental True Experimental Quasi Experimental Statistical One-Shot Case Study
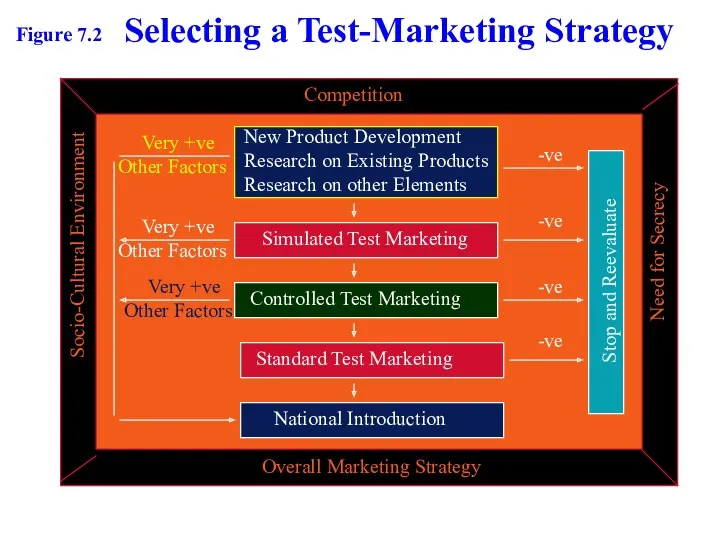
- 6. Selecting a Test-Marketing Strategy Competition Overall Marketing Strategy Socio-Cultural Environment Need for Secrecy New Product Development
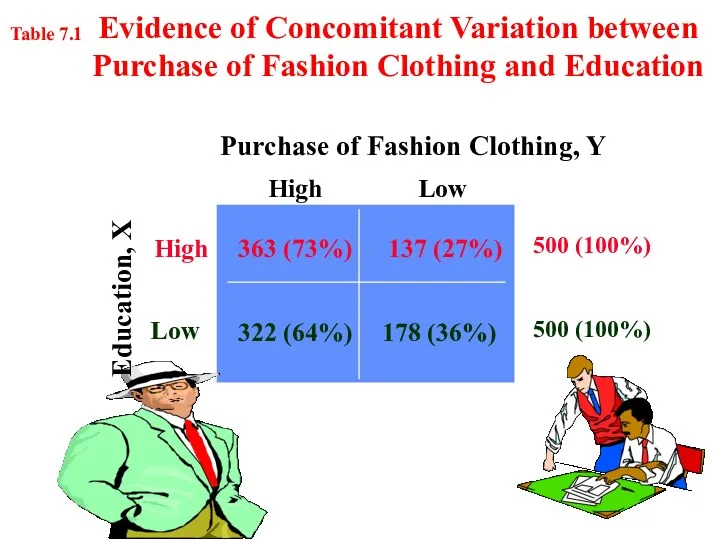
- 7. Evidence of Concomitant Variation between Purchase of Fashion Clothing and Education High High Low 363 (73%)
- 8. Purchase of Fashion Clothing by Income and Education Low Income Purchase High Low High Low Education
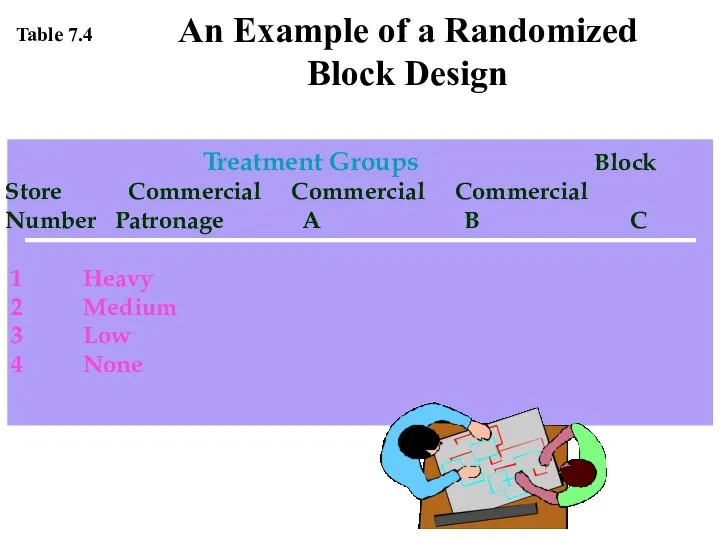
- 9. Treatment Groups Block Store Commercial Commercial Commercial Number Patronage A B C 1 Heavy 2 Medium
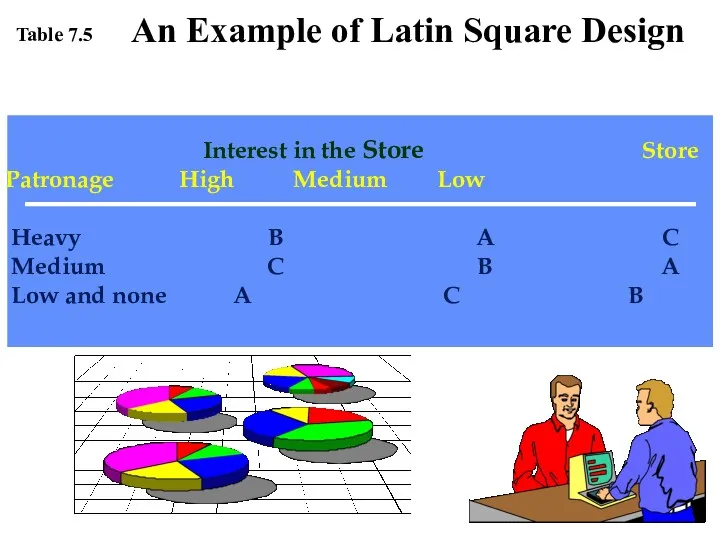
- 10. Interest in the Store Store Patronage High Medium Low Heavy B A C Medium C B
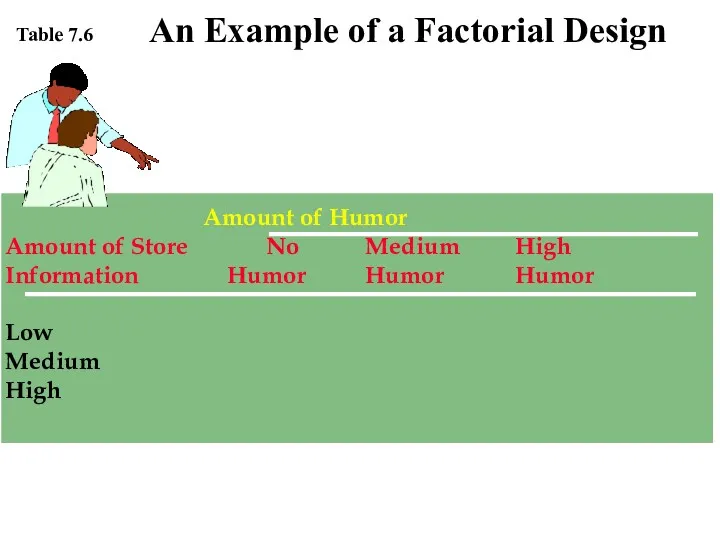
- 11. Amount of Humor Amount of Store No Medium High Information Humor Humor Humor Low Medium High
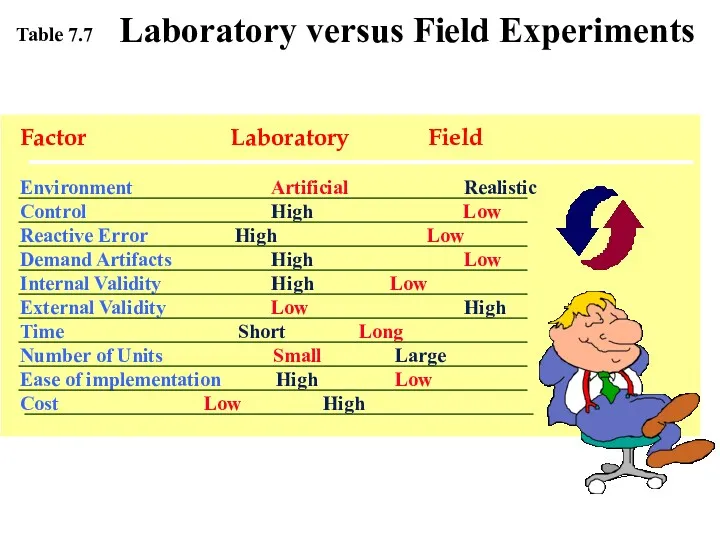
- 12. Factor Laboratory Field Environment Artificial Realistic Control High Low Reactive Error High Low Demand Artifacts High
- 13. Criteria for the Selection of Test Markets RIP 7.1 Test Markets should have the following qualities:
- 14. Dancer Fitzgerald’s Sample List of Recommended Test Markets RIP 7.2 Albany-Schenectady-Troy, N Knoxville, TN Boise, ID
- 16. Скачать презентацию






 Приемы увеличения среднего чека. Семинар для заведений общественного питания
Приемы увеличения среднего чека. Семинар для заведений общественного питания Seldon – универсальный бизнес-инструмент
Seldon – универсальный бизнес-инструмент Advertising - Logos and Commercial Techniques (quiz) NLC
Advertising - Logos and Commercial Techniques (quiz) NLC Порядкодом. Марка товаров для порядка в доме
Порядкодом. Марка товаров для порядка в доме Lifan - лидер на российском рынке
Lifan - лидер на российском рынке Маркетинговые исследования спазмолитических лекарственных препаратов с углубленным товароведческим анализом
Маркетинговые исследования спазмолитических лекарственных препаратов с углубленным товароведческим анализом Уход за окрашенными волосами на примере фирмы Londa Proffesional и Kerastase
Уход за окрашенными волосами на примере фирмы Londa Proffesional и Kerastase Выездные игры на праздник
Выездные игры на праздник Институт развития молодежи. Проект YOUTH BUSINESS CLUB
Институт развития молодежи. Проект YOUTH BUSINESS CLUB Реклама – особый вид потребительской информации
Реклама – особый вид потребительской информации Маркетинг взаимоотношений с потребителями (МВП)
Маркетинг взаимоотношений с потребителями (МВП) Разработка рекламной кампании для малого предприятия
Разработка рекламной кампании для малого предприятия HERBALIFE. Мы меняем жизни людей к лучшему
HERBALIFE. Мы меняем жизни людей к лучшему Цвет в логотипе. Что цвета бренда говорят о бизнесе
Цвет в логотипе. Что цвета бренда говорят о бизнесе Салон Аlua. Yйлену той койлектерi
Салон Аlua. Yйлену той койлектерi Центры доставки. Оформление офисов. Яндекс Доставка
Центры доставки. Оформление офисов. Яндекс Доставка Обновленный сайт представителя Avon
Обновленный сайт представителя Avon Встраиваемая техника Samsung
Встраиваемая техника Samsung Специальность маркетинг в практической деятельности компании
Специальность маркетинг в практической деятельности компании Метод экспертных оценок Дельфи
Метод экспертных оценок Дельфи Поисковое продвижение
Поисковое продвижение Имидж. Консалтинговый бизнес
Имидж. Консалтинговый бизнес Cronwell Resort Югорская Долина
Cronwell Resort Югорская Долина Охрана труда в автосалоне МАКС - Моторс Гранд. Ассортиментная характеристика товаров
Охрана труда в автосалоне МАКС - Моторс Гранд. Ассортиментная характеристика товаров Интернет-предпринимательство
Интернет-предпринимательство La Mia Italia
La Mia Italia Rodeker DOB 360 beam bulbs dats. Lighting for future
Rodeker DOB 360 beam bulbs dats. Lighting for future Коммуникационная политика
Коммуникационная политика