Содержание
- 2. LICENSING Make a legally protected asset available to another company. Parties: licensor / licensee Assets: brand
- 3. LICENSING Disadvantages: -Limited market control -Short life -Licensees may turn into competition Remedy: -agreements that contemplate
- 4. LICENSING Q1: What did Pilkington did wrong when licensing to Glaverbel? Q2: Which are 3 other
- 5. LICENSING A1: They did not include cross tech exchange in the contract. A2: -Create export market
- 6. It is used to get partial or full ownership of operations outside the home country. Foreign
- 7. GLOBAL STRATEGIC PARTNERSHIPS To succed in global markets cannot rely only on their technological superiority or
- 8. THE NATURE OF GLOBAL STRATEGIC PARTNERSHIPS Linkages between companies to jointly pursue a common goal. Strategic
- 9. THE NATURE OF GLOBAL STRATEGIC PARTNERSHIPS Attributes of strategic alliances: 1: Joint long term strategy to
- 10. THE NATURE OF GLOBAL STRATEGIC PARTNERSHIPS A4: -High product development costs -Lacking the skills, capital, know-how
- 11. SUCCESS FACTORS -Mission -Strategy -Governance -Culture -Organization -Management Remember that outside the agreement: Partners are still
- 12. INTERNATIONAL PARTNERSHIPS IN DEVELOPING COUNTRIES Q5: Which markets are attractive because of their big size and
- 13. COOPERATIVE STRATEGIES IN JAPAN: KEIRETSU It is an interbusiness alliance or an enterprise group that cooperates
- 14. COOPERATIVE STRATEGIES IN SOUTH KOREA: CHAEBOL It is composed by dozens of companies centered around a
- 15. XXI CENTURY COOPERATIVE STRATEGIES: TARGETING THE DIGITAL FUTURE Companies are forming strategic alliances to make the
- 16. MARKET EXPANSION STRATEGIES Strategy 1: Country and market concentration Strategy 2: Country concentration and market diversification
- 18. Скачать презентацию















 Системы контроля и управления доступом
Системы контроля и управления доступом Пробковый герметик ISOCORK
Пробковый герметик ISOCORK Вводное обучение сотрудников
Вводное обучение сотрудников Маркетинговые коммуникации. Коммуникационный процесс
Маркетинговые коммуникации. Коммуникационный процесс Цели, задачи и принципы социальной рекламы
Цели, задачи и принципы социальной рекламы Мультиварка невероятно экономит время
Мультиварка невероятно экономит время Светильники для Ваших проектов
Светильники для Ваших проектов Торговое оборудование IKEA сегодня
Торговое оборудование IKEA сегодня Возвращаем 10 % бонусами при покупке смартфонов, планшетов Samsung
Возвращаем 10 % бонусами при покупке смартфонов, планшетов Samsung Шампуни Маленькая Фея
Шампуни Маленькая Фея Новые ароматы. Alan Bray Mademoiselle Delice
Новые ароматы. Alan Bray Mademoiselle Delice Маркетинговые стратегии выхода российских банков на зарубежные рынки, на примере ПАО ВТБ 24
Маркетинговые стратегии выхода российских банков на зарубежные рынки, на примере ПАО ВТБ 24 Три метра над уровнем неба
Три метра над уровнем неба Программа по трудоустройству для студентов от компании СОФТКЛУБ
Программа по трудоустройству для студентов от компании СОФТКЛУБ Causal Research Design: Experimentation
Causal Research Design: Experimentation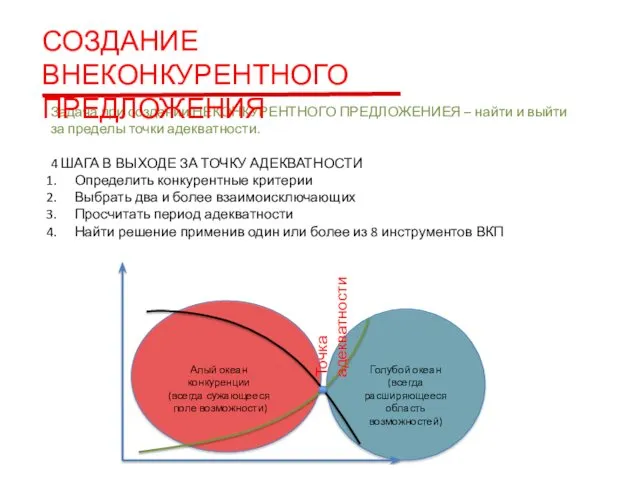 Создание внеконкурентного предложения
Создание внеконкурентного предложения Тема 3. Обзор маркетплейсов
Тема 3. Обзор маркетплейсов Натуральные масла в социальной сети ВКонтакте (интернет-магазин)
Натуральные масла в социальной сети ВКонтакте (интернет-магазин) Заработок на Ютуб
Заработок на Ютуб Немецкая школа футбола fc stuttgart
Немецкая школа футбола fc stuttgart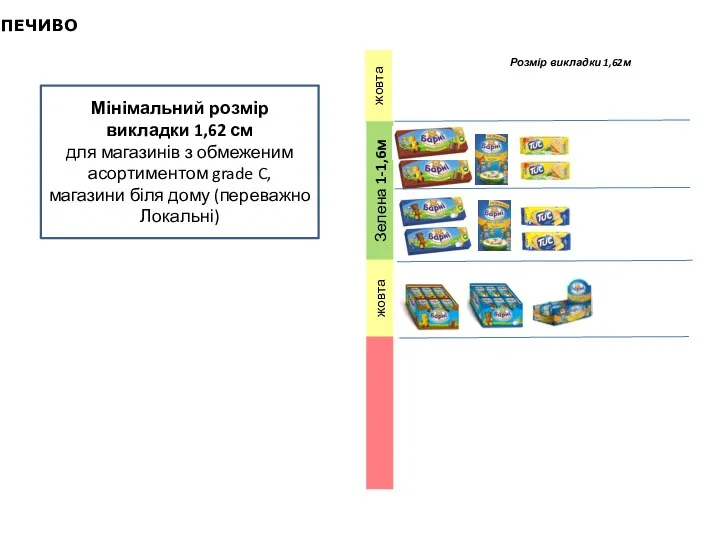 Планограми викладки печива
Планограми викладки печива The Walt Pr
The Walt Pr Косметический прибор Секрет красоты. La Beauté Secrète Portable Apparatus
Косметический прибор Секрет красоты. La Beauté Secrète Portable Apparatus Информированность. Ноябрь 2023. СДЭК
Информированность. Ноябрь 2023. СДЭК Рекламный проект для чипсов марки Pringles
Рекламный проект для чипсов марки Pringles Создание собственных онлайн-курсов
Создание собственных онлайн-курсов Разработчик компьютерных игр компания Mysticism Games
Разработчик компьютерных игр компания Mysticism Games Компания Добрый квест. Организация мероприятий на природе
Компания Добрый квест. Организация мероприятий на природе