Содержание
- 2. Industry analysis (Five Forces Model) Competitive advantage and strategy Global competition
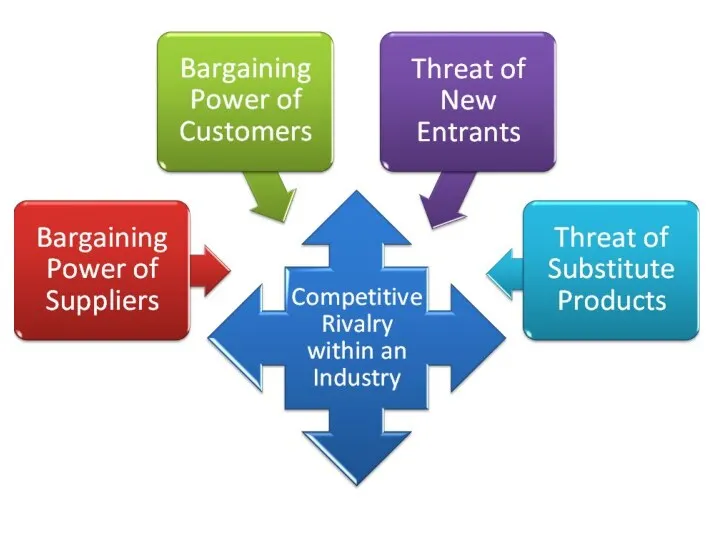
- 4. A. .Industry analysis Five Forces model Michael Porter's famous Five Forces of Competitive Position model provides
- 6. The five forces are environmental forces that impact on a company’s ability to compete in a
- 7. Q1: For what reasons.the rivalry among the industry will be increased? Q2: How to set barriers
- 8. 1. Rivalry Among Existing Competitors What cause the increase of rivalry among the industry? A larger
- 9. Low swithing cost Low level of product differentiation Strategic stakes are high High exit barriers
- 10. In pursuring anadvantage over its rivals. A firm can choose from several competitive moves: Changing prices
- 11. 2.Threat of New Entrants Profitable markets that yield high returns will attract new firms. This results
- 12. Capital Requirements Patented or proprietary know-how Difficult in brand switching Restricted distribution channels High economies of
- 13. 3. Bargaining Power of Suppliers Suppliers are likely to be powerful if : High cost to
- 14. 4. Bargaining Power of Buyers Buyer groups are likely to be powerful if : Buyers are
- 15. 5.Threat of Substitute Products Products with improving price/performance tradeoffs relative to present industry products A threat
- 16. Factors that determine the threat of substitute products? Buyer propensity to substitute Relative price performance of
- 17. Number of substitute products available in the market Ease of substitution. Information-based products are more prone
- 18. B. Competitive advantage An advantage that a firm has over its competitors, allowing it to generate
- 19. CASE
- 20. 1. Cost advantage strategy It is a firm's ability to produce a good or service at
- 21. CASE
- 23. CASE 2
- 24. Any benefit? Higher profit margin.achieve more earnings from its products Increased market share Sustainability Capital for
- 25. Risky? Focusing on price can make the company lose sight of evolving customer tastes and preferences.
- 26. 2. Differential advantage strategy A differential advantage is created when a firm's products or services differ
- 27. A product or service that differs from its rivals: Differences in quality which are usually accompanied
- 28. CASE 1
- 29. The key to differential advantage is that the customer should not only appreciate the benefit it
- 30. CASE 2
- 31. Differential advantage = High cost?
- 32. C. Global competition Strategic initiatives should address competitiveness issues not only at the level of the
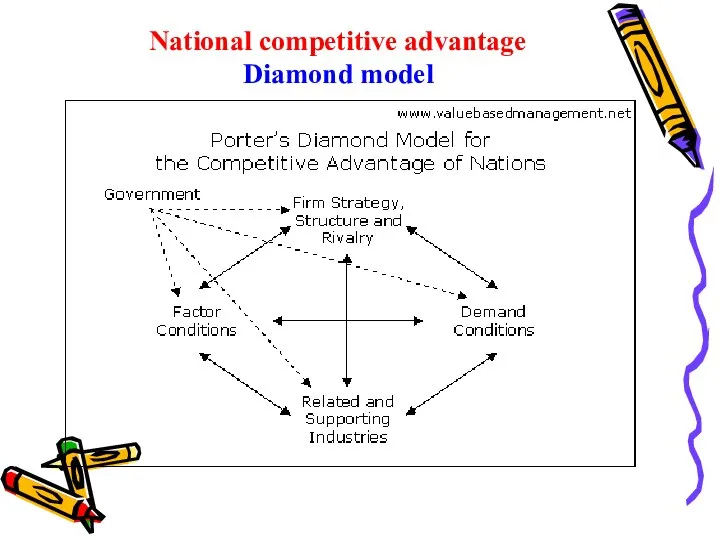
- 33. National competitive advantage Diamond model
- 34. It analyzing why some nations are more competitive than others are, and why some industries within
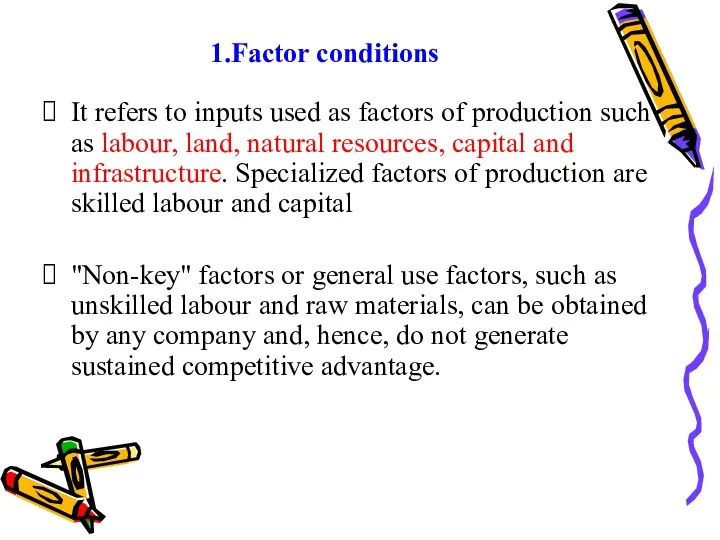
- 35. 1.Factor conditions It refers to inputs used as factors of production such as labour, land, natural
- 36. 2. Demand Conditions Demand conditions in the domestic market provide the primary driver of growth, innovation
- 37. CASE 1 The French are sophisticated wine consumers. These consumers force and help French wineries to
- 38. CASE 2
- 39. CASE 3
- 40. CASE 4
- 41. 3. Related and Supporting Industries a set of strong related and supporting industries is important to
- 42. CASE 1 The shoe and leather industry in Italy. Italy is not only successful with shoes
- 43. CASE 2
- 44. 4. Firm Strategy, Structure and Rivalry National performance in particular sectors is inevitably related to the
- 45. CASE It provide intense competition in the domestic market, as well as the foreign markets in
- 46. ALSO.Cultural aspects play an important role. In different nations, factors like management structures, working morale between
- 47. CASE Germany tends to have hierarchical management structures composed of managers with strong technical backgrounds and
- 48. 5. Government The government plays an important role in diamond model. "Government’s proper role is as
- 49. Governments can influence all four of determinants through a variety of actions: Subsidies to firms Tax
- 50. Summary Five Forces Model: Rivalry Among Existing Competitors. Threat of New Entrants. Bargaining Power of Suppliers.
- 51. Reference 竞争战略 迈克尔·波特 华夏出版社 竞争优势 迈克尔·波特 华夏出版社 国家竞争优势 迈克尔·波特 华夏出版社 竞争的资本 Stuart Crainer,中国青年出版社 海尔中国造之竞争战略与核心能力 胡泳 海南出版社
- 53. Скачать презентацию















































 Что такое маркетинг? Обязанности маркетолога
Что такое маркетинг? Обязанности маркетолога Маркетинг–менеджмент – фундамент успешного бизнеса
Маркетинг–менеджмент – фундамент успешного бизнеса Услуга Бесплатный вызов 8-800
Услуга Бесплатный вызов 8-800 External and internal PR at аviation сompany
External and internal PR at аviation сompany Эффективные продажи
Эффективные продажи Продажа товаров через терминал. Основные ошибки
Продажа товаров через терминал. Основные ошибки Кровати от фабрики Мелодия сна
Кровати от фабрики Мелодия сна Бонусная программа лояльности Клуб покупателей
Бонусная программа лояльности Клуб покупателей Маркетинг – план Lambre
Маркетинг – план Lambre Как правильно выбрать крем
Как правильно выбрать крем Hotel Ring. Услуги
Hotel Ring. Услуги Линейка тарифных планов Престижный+. Билайн
Линейка тарифных планов Престижный+. Билайн Зимняя коллекция 2017 Ritter Sport
Зимняя коллекция 2017 Ritter Sport Система товародвижения в маркетинге
Система товародвижения в маркетинге Карьера в Digital, непопулярный путь в IT или что делать в IT, когда ты не программист
Карьера в Digital, непопулярный путь в IT или что делать в IT, когда ты не программист Задачи транспортного обеспечения коммерческой деятельности
Задачи транспортного обеспечения коммерческой деятельности Выкладка и размещение товара
Выкладка и размещение товара Первый аромаотель в Крыму
Первый аромаотель в Крыму Анализ аптечного ассортимента лекарственных средств на основе лекарственного растительного сырья слабительного действия
Анализ аптечного ассортимента лекарственных средств на основе лекарственного растительного сырья слабительного действия Недвижимость. Индустриальный парк Союз-монолит. Московская область, г.о. Домодедово, мкрн. Барыбино, владение Росмонолит
Недвижимость. Индустриальный парк Союз-монолит. Московская область, г.о. Домодедово, мкрн. Барыбино, владение Росмонолит Матрица НТИ 2.0
Матрица НТИ 2.0 Шаблон презентации на Demo Day
Шаблон презентации на Demo Day Суперсила сочных фруктов и редких масел в упаковке Саше
Суперсила сочных фруктов и редких масел в упаковке Саше Линия DSD OPIUM (двойного действия)
Линия DSD OPIUM (двойного действия) Products of the past: One Size Fits All
Products of the past: One Size Fits All Уход от Curex
Уход от Curex Лабораторна робота №3. Морями Скандинавії
Лабораторна робота №3. Морями Скандинавії Нейминг – профессиональная разработка названий фирм, товаров и услуг
Нейминг – профессиональная разработка названий фирм, товаров и услуг