Содержание
- 2. Learning Objectives 1.1 Why is marketing important? 1.2 What is the scope of marketing? 1.3 What
- 3. The Value of Marketing Financial success often depends on marketing ability Successful marketing builds demand for
- 4. The Scope of Marketing Marketing is about identifying and meeting human and social needs Marketing is
- 5. Marketing Management The art and science of choosing target markets and getting, keeping, and growing customers
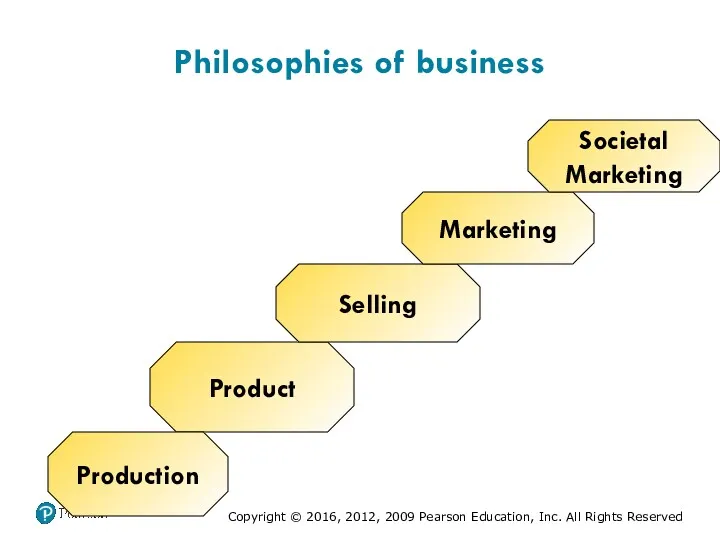
- 6. Philosophies of business Product Selling Marketing Production Societal Marketing
- 7. What is Marketing? a business philosophy (a perspective/an orientation) alternative approaches/orientations an organizational function of creating,
- 8. What is Marketed? (1 of 2) Goods Services Events Experiences Persons
- 9. What is Marketed? (2 of 2) Places Properties Organizations Information Ideas
- 10. Who Markets? A marketer is someone who seeks a response—attention, a purchase, a vote, a donation—from
- 11. 8 Demand States Negative Nonexistent Latent Declining Irregular Unwholesome Full Overfull
- 12. Key Customer Markets Consumer markets Business markets Global markets Nonprofit & governmental markets
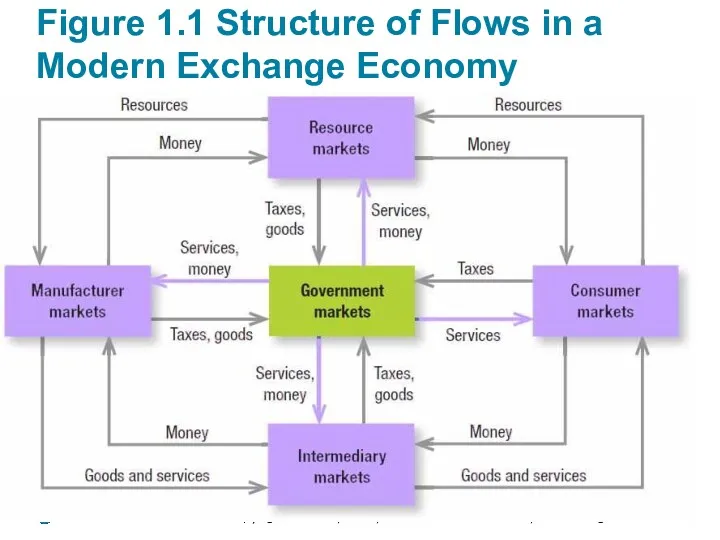
- 13. Figure 1.1 Structure of Flows in a Modern Exchange Economy
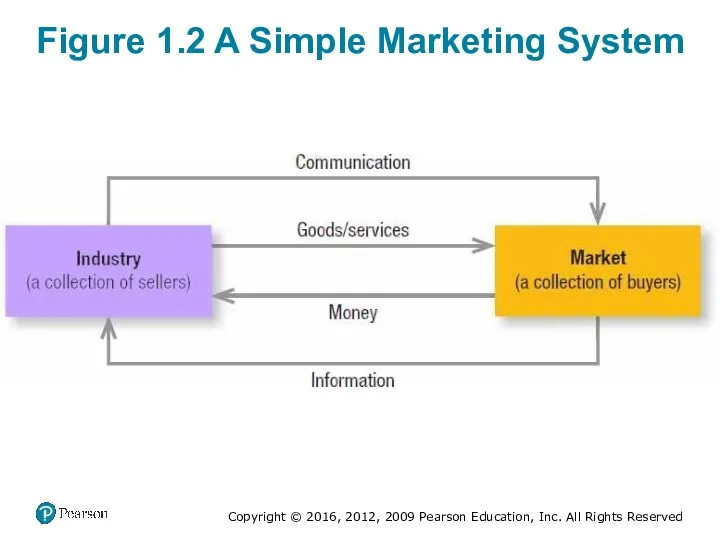
- 14. Figure 1.2 A Simple Marketing System
- 15. Core Marketing Concepts (1 of 10) Needs: the basic human requirements such as for air, food,
- 16. Types of Needs Stated needs (The customer wants an inexpensive car.) Real needs (The customer wants
- 17. Core Marketing Concepts (2 of 10) Target markets Positioning Segmentation
- 18. Core Marketing Concepts (3 of 10) Value proposition: a set of benefits that satisfy those needs
- 19. Core Marketing Concepts (4 of 10) Marketing channels Communication (media) Distribution (deliver and or sell the
- 20. Core Marketing Concepts (5 of 10) Paid media: TV, magazine and display ads, paid search, and
- 21. Core Marketing Concepts (6 of 10) Impressions: occur when consumers view a communication Engagement: the extent
- 22. Core Marketing Concepts (7 of 10) Value: a combination of quality, service, and price (qsp: the
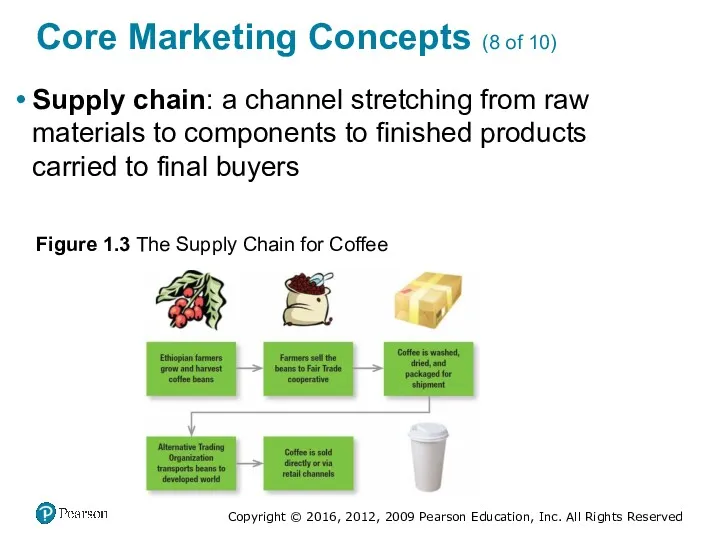
- 23. Core Marketing Concepts (8 of 10) Supply chain: a channel stretching from raw materials to components
- 24. Core Marketing Concepts (9 of 10) Competition: all the actual and potential rival offerings and substitutes
- 25. Core Marketing Concepts (10 of 10) Marketing environment Task environment - the actors engaged in producing,
- 26. The New Marketing Realities Technology Globalization Social responsibility
- 27. A Dramatically Changed Marketplace (1 of 6) New consumer capabilities Can use the internet as a
- 28. A Dramatically Changed Marketplace (2 of 6) New consumer capabilities Can actively interact with companies Can
- 29. A Dramatically Changed Marketplace (3 of 6) New company capabilities Can use the internet as a
- 30. A Dramatically Changed Marketplace (4 of 6) New company capabilities Can improve purchasing, recruiting, training, and
- 31. A Dramatically Changed Marketplace (5 of 6) Changing channels Retail transformation Disintermediation
- 32. A Dramatically Changed Marketplace (6 of 6) Heightened competition Private brands Mega-brands Deregulation Privatization
- 33. Marketing in Practice Marketing balance Marketing accountability Marketing in the organization
- 34. Company Orientation Toward the Marketplace Production Product Selling Marketing
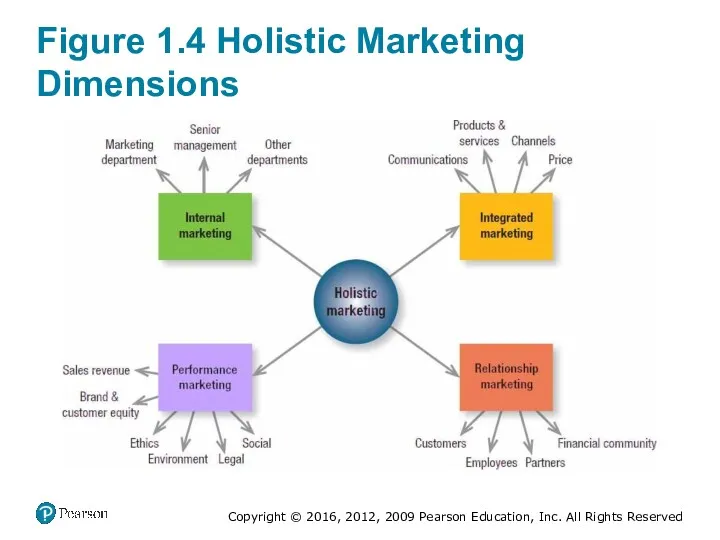
- 35. Figure 1.4 Holistic Marketing Dimensions
- 36. Relationship Marketing Customers Employees Marketing partners Financial community
- 37. Integrated Marketing Devise marketing activities and programs that create, communicate, and deliver value such that “the
- 38. Internal Marketing The task of hiring, training, and motivating able employees who want to serve customers
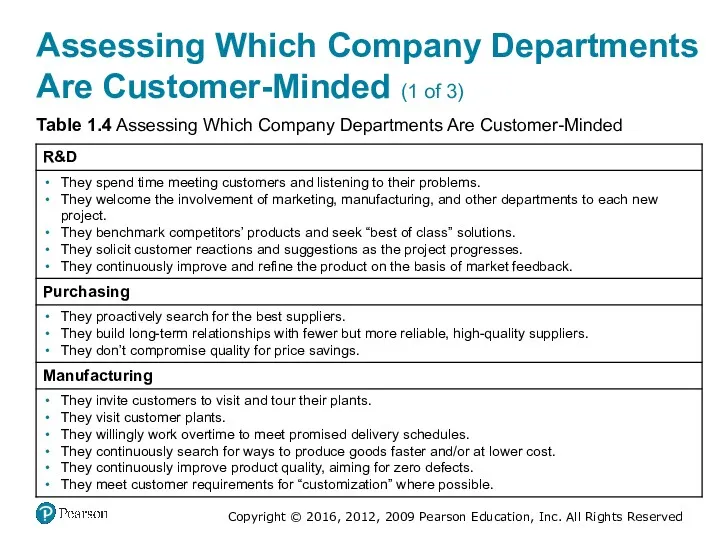
- 39. Assessing Which Company Departments Are Customer-Minded (1 of 3) Table 1.4 Assessing Which Company Departments Are
- 40. Assessing Which Company Departments Are Customer-Minded (2 of 3) [Table 1.4 continued]
- 41. Assessing Which Company Departments Are Customer-Minded (3 of 3) [Table 1.4 continued]
- 42. Performance Marketing Financial accountability Environmental impact Social impact
- 43. Figure 1.5 Marketing Mix Components (4 Ps)
- 44. Modern Marketing Management People Processes Programs Performance
- 45. Figure 1.6 The Evolution of Marketing Management
- 46. Marketing Management Tasks (1 of 2) Developing market strategies and plans Capturing marketing insights Connecting with
- 47. Marketing Management Tasks (2 of 2) Creating value Delivering value Communicating value Creating successful long-term growth
- 49. Скачать презентацию
































![Assessing Which Company Departments Are Customer-Minded (2 of 3) [Table 1.4 continued]](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/293287/slide-39.jpg)
![Assessing Which Company Departments Are Customer-Minded (3 of 3) [Table 1.4 continued]](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/293287/slide-40.jpg)






 Бриф и предложение. Структура предложения на проведение маркетинговых исследований. Пример предложения
Бриф и предложение. Структура предложения на проведение маркетинговых исследований. Пример предложения Відділ стандартів та розвитку торгового персоналу
Відділ стандартів та розвитку торгового персоналу Бизнес-план. Кинотеатр Киноскоп
Бизнес-план. Кинотеатр Киноскоп President - бренд средств по уходу за полостью рта
President - бренд средств по уходу за полостью рта Корпорация Tancha. Подарки из конфет
Корпорация Tancha. Подарки из конфет Корпорация Apple
Корпорация Apple Прайс радио Рекорд
Прайс радио Рекорд Marketing offer Dinamicka Development
Marketing offer Dinamicka Development Анализ имиджа компании New Balance
Анализ имиджа компании New Balance Экомерчандайзер. Экологические товары
Экомерчандайзер. Экологические товары Сканди 2 (1)
Сканди 2 (1) Создание внеконкурентного предложения
Создание внеконкурентного предложения Наставничество. Первые 100 к. на Ozon
Наставничество. Первые 100 к. на Ozon Мастер-класс. 42 канала рекламы для бизнеса или как быстро получить заявки - бесплатно
Мастер-класс. 42 канала рекламы для бизнеса или как быстро получить заявки - бесплатно Сеть фитнес-клубов Вертикаль
Сеть фитнес-клубов Вертикаль Прототип сайта
Прототип сайта Анкетирования, как форма маркетинговых исследований
Анкетирования, как форма маркетинговых исследований Приглашение на концерт Её величество - женщина!
Приглашение на концерт Её величество - женщина! Потенциал маркетинговых технологий в управлении человеческими ресурсами
Потенциал маркетинговых технологий в управлении человеческими ресурсами Продающая группа для фотографа
Продающая группа для фотографа Эксперт по развитию рекламных агентств
Эксперт по развитию рекламных агентств Физиотерапия. Что предлагает BTL для физиотерапии
Физиотерапия. Что предлагает BTL для физиотерапии Продукция компании Heineken®
Продукция компании Heineken® Анализ рекламного ролика Chanel
Анализ рекламного ролика Chanel Услуги. Быстросервис
Услуги. Быстросервис Свадебное агентство Свадьба в России
Свадебное агентство Свадьба в России Бонусная программа лояльности Клуб покупателей
Бонусная программа лояльности Клуб покупателей Оценка общего впечатления от сотрудничества с Диалайн
Оценка общего впечатления от сотрудничества с Диалайн