Содержание
- 2. 08/03/2022 Назначение СОЖ Обеспечивать охлаждение, смазку и защиту инструмента и обрабатываемой поверхности
- 3. 08/03/2022 Îáúåì ðûíêà 50000 - 100000 ò Ïîòðåáëåíèå ïðîìûøëåííîãî ïðåäïðèÿòèÿ îò …êã äî 5000 òîíí
- 4. 08/03/2022 Îòðàñëè ïðîìûøëåííîñòè -ïîòðåáèòåëè ÑÎÆ - Àâòîìîáèëüíàÿ - Ïîäøèïíèêîâàÿ - Ìîòîðíûå ïðåäïðèÿòèÿ - Ìàøèíîñòðîèòåëüíûå çàâîäû -
- 5. 08/03/2022 Êîíêóðåíòû Øåëë - Castrol - Stuart - Fuchs - Quaker - Blazer
- 6. 08/03/2022 Ñèëüíûå ñòîðîíû Øåëë Ðàçâåòâëåííàÿ ñåòü äèñòðèáüþòîðîâ Îòëàæåíà ñõåìà ïîñòàâîê ÷åðåç ôèíñêèé ñêëàä Óíèâåðñàëüíûé ïîðòôåëü ïðîäóêòîâ
- 7. 08/03/2022 Ïðîöåññû îáðàáîòêè ìåòàëëîâ Îñíîâíûå ïðîöåññû Ðåçàíèå (îáðàçîâàíèå ñòðóæêè) ÎÌÄ Ýëåêòðîýðîçèîííàÿ îáðàáîòêà ìåòàëëîâ Çàùèòà îò êîððîçèè
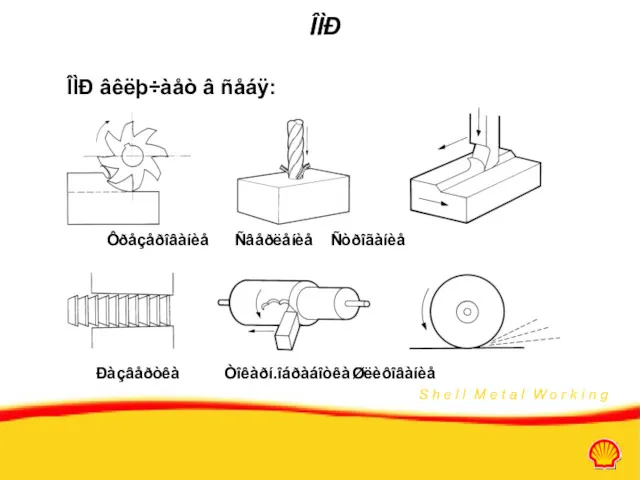
- 8. ÎÌÐ ÎÌÐ âêëþ÷àåò â ñåáÿ:
- 9. Îáðàçîâàíèå ñòðóæêè Îáðàçîâàíèå ñòðóæêè - êàê ñäâèã êàðò â êîëîäå (òðåíèå ñêîëüæåíèÿ) Â çàâèñèìîñòè îò ìàòåðèàëà
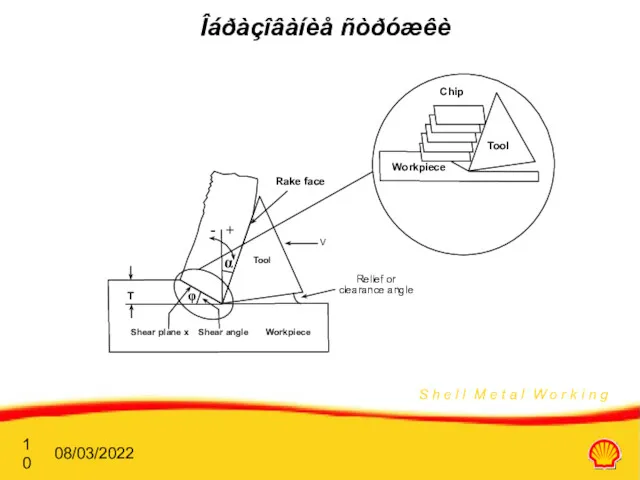
- 10. 08/03/2022 Îáðàçîâàíèå ñòðóæêè - + Shear plane x Shear angle Workpiece Relief or clearance angle V
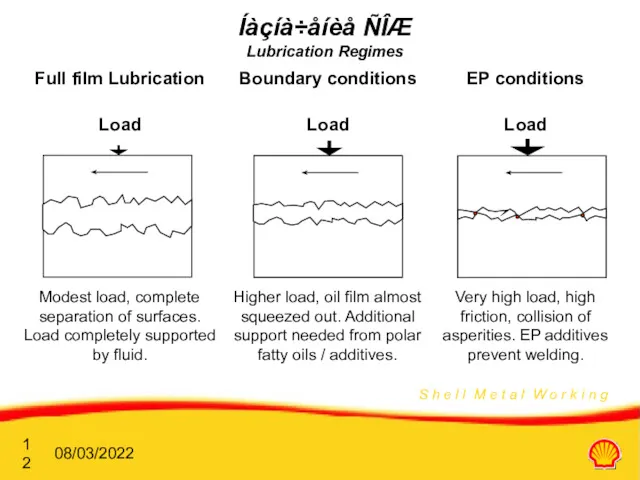
- 11. Íàçíà÷åíèå ÑÎÆ Reduce friction and wear thus (See lubrication regimes): Improving tool life and surface finish
- 12. 08/03/2022 Íàçíà÷åíèå ÑÎÆ Lubrication Regimes Full film Lubrication Load Modest load, complete separation of surfaces. Load
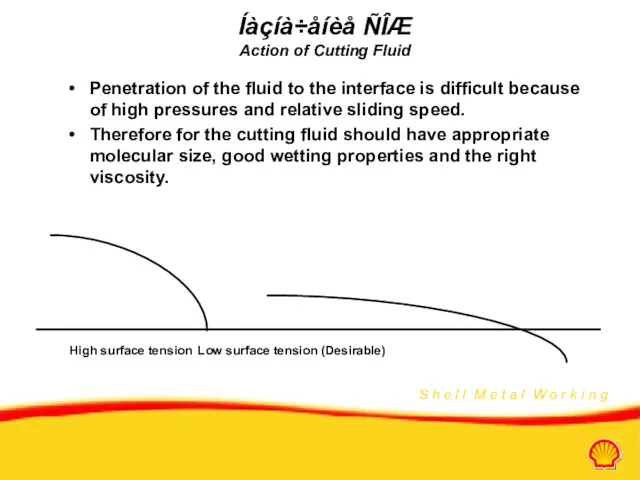
- 13. Íàçíà÷åíèå ÑÎÆ Action of Cutting Fluid Penetration of the fluid to the interface is difficult because
- 14. 08/03/2022 Íàçíà÷åíèå ÑÎÆ Key Parameters Machining process: Work piece material: Tooling: Cutting conditions: Quality required: Turning,
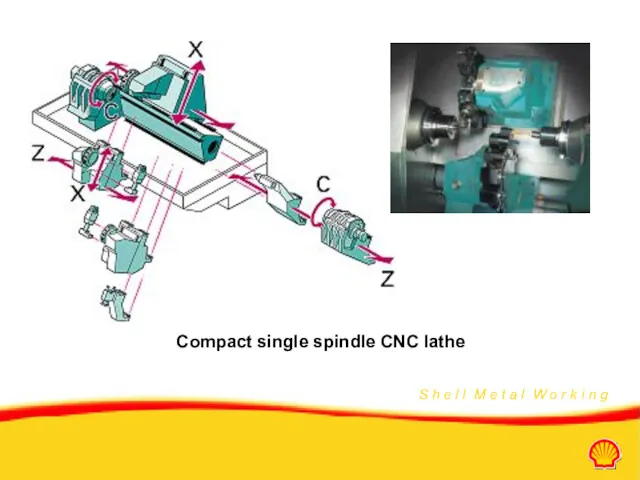
- 15. Compact single spindle CNC lathe
- 16. Ïðîöåññû ÎÌÐ Ôðåçåðîâàíèå Among the most versatile machine tools because of the variety of cutting operations.
- 17. Ïðîöåññû ÎÌÐ Ãëóáîêîå ñâåðëåíèå, Ñâåðëåíèå è êîëüöåâîå ñâåðëåíèå (1) Deep hole drilling: the production of holes
- 18. Ïðîöåññû ÎÌÐ Ãëóáîêîå ñâåðëåíèå, Ñâåðëåíèå è êîëüöåâîå ñâåðëåíèå (2) Boring: Used to enlarge a hole to
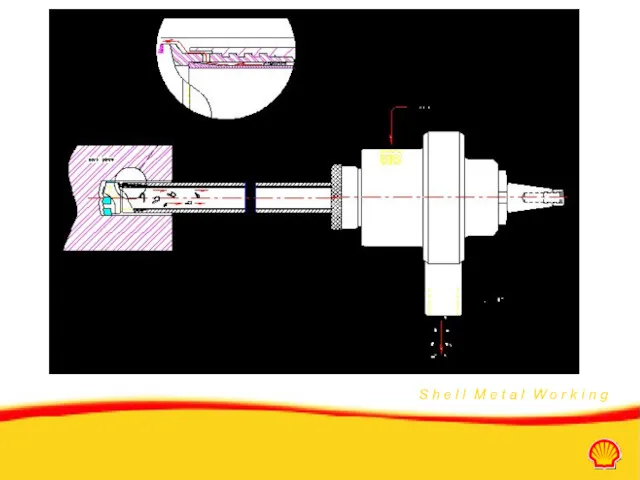
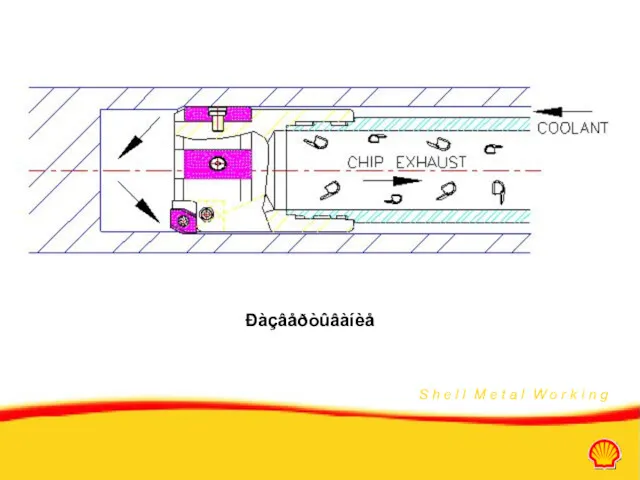
- 19. Double tube system
- 20. Ðàçâåðòûâàíèå
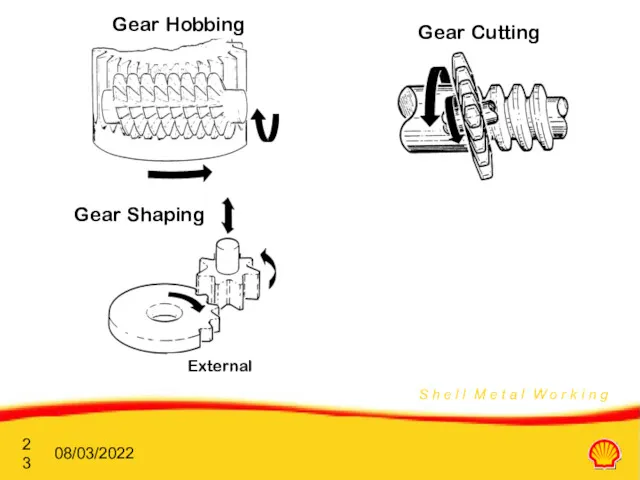
- 21. Ïðîöåññû ÎÌÐ Çóá÷àòûå êîëåñà / ìåòîäû ðåçàíèÿ Several methods of gear making: Íàêàòêà: Favoured for high-volume
- 22. 08/03/2022 Ïðîöåññû ÎÌÐ Çóá÷àòûå êîëåñà / ìåòîäû ðåçàíèÿ Gear Shaving: Used as a finishing operation and
- 23. 08/03/2022
- 24. Worm Gear Cutting
- 25. Ïðîöåññû ÎÌÐ Ðàçâåðòêà The most severe of machining operations - Used to produce holes, grooves and
- 26. Ïðîöåññû ÎÌÐ Øëèôîâàíèå The grinding process is usually employed to impart a high standard of finish
- 27. 08/03/2022 Ïðîöåññû ÎÌÐ Õîíèíãîâàíèå, Ñóïåðôèíèøèðîâàíèå, Äîâîäêà Honing: special type of grinding, combined linear and rotating movement
- 28. 08/03/2022 Ïðîöåññû ÎÌÐ Ïèëåíèå Very common Three options: Circular saw: very common Belt saw: faster but
- 29. Îïåðàöèè îáðàáîòêè ìåòàëëîâ Operation Most severe Internal Broaching, Surface or External broaching Sawing Tapping Gear Cutting
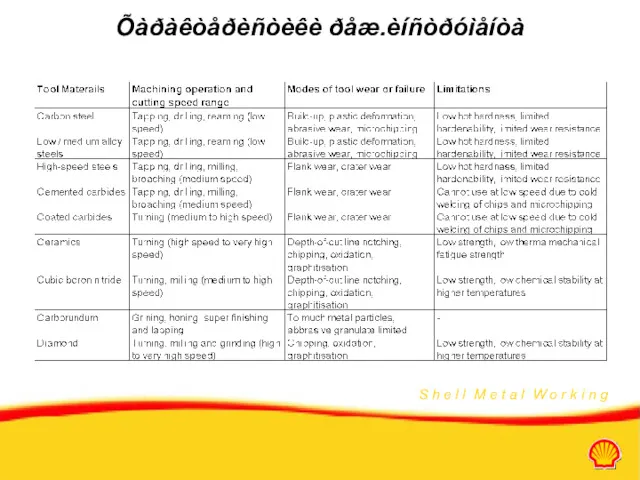
- 30. Õàðàêòåðèñòèêè ðåæ.èíñòðóìåíòà
- 31. Òåõíîëîãè÷íîñòü ìàòåðèàëîâ Material Brass Steel Titanium alloys Aluminium alloys Cast iron Tensile strength N/mm² 500 500
- 32. Òåõíîëîãè÷íîñòü ìàòåðèàëîâ Magnesium alloys Brass (Cu/Zn alloy) Bronze (Cu/Sn alloy) Aluminium alloys Mild steel Low /
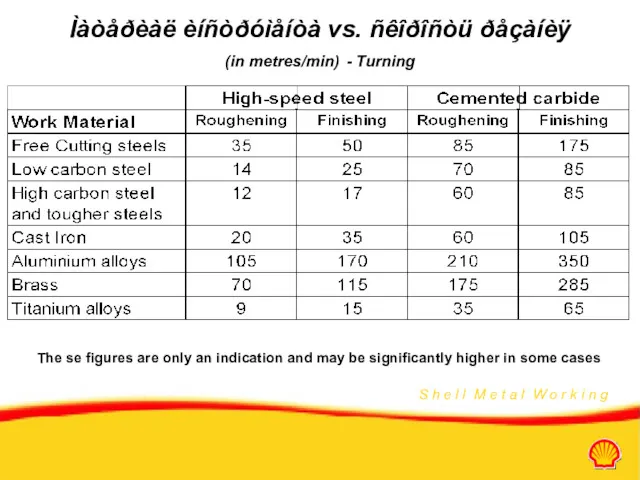
- 33. Ìàòåðèàë èíñòðóìåíòà vs. ñêîðîñòü ðåçàíèÿ (in metres/min) - Turning The se figures are only an indication
- 34. 03-Aug-22 SHELL Ïðîäóêòû Øåëë äëÿ ìåòàëëîîáðàáîòêè
- 36. Скачать презентацию























 Деятельность агентства Remar Group
Деятельность агентства Remar Group Агрегатопонные автоматизированные осветительные вегетационные модули АОВМ-2
Агрегатопонные автоматизированные осветительные вегетационные модули АОВМ-2 Бізнес-план. Повстяники
Бізнес-план. Повстяники Авиационный комплекс им. С.В. Ильюшина. Целевой набор
Авиационный комплекс им. С.В. Ильюшина. Целевой набор Маркетинговый анализ международной деятельности компании AUDI
Маркетинговый анализ международной деятельности компании AUDI Наружная реклама
Наружная реклама Формирование ассортимента круп на предприятии розничной торговли на примере магазина Спар ООО Универмаг
Формирование ассортимента круп на предприятии розничной торговли на примере магазина Спар ООО Универмаг Реклама – это любая информация о фирме, ее товарах и услугах
Реклама – это любая информация о фирме, ее товарах и услугах Бесплатный аудит сайта и аудит компании для всех новых пользователей Seopult
Бесплатный аудит сайта и аудит компании для всех новых пользователей Seopult Построение карт восприятия. Образ бренда
Построение карт восприятия. Образ бренда Пояснительная записка по Офису (нежилое помещение № 5)
Пояснительная записка по Офису (нежилое помещение № 5) Маркетинговые технологии в аптечной организации
Маркетинговые технологии в аптечной организации Средства массовой информации
Средства массовой информации Технология продаж дополнительных услуг
Технология продаж дополнительных услуг Товар и товарная политика. Качество товара
Товар и товарная политика. Качество товара Menu Italian Cuisine Victoria
Menu Italian Cuisine Victoria Belavia Belarusian Airlines
Belavia Belarusian Airlines Nissan
Nissan Canal Home In Paradise Point
Canal Home In Paradise Point Планирование маркетинговой деятельности на примере British Airways
Планирование маркетинговой деятельности на примере British Airways Мотивация курьеров Wildberries
Мотивация курьеров Wildberries группа компаний СМУ-8
группа компаний СМУ-8 Омега 3, Омега 6 и Омега 9. Незаменимые жирные кислоты
Омега 3, Омега 6 и Омега 9. Незаменимые жирные кислоты Протезирование на имплантах за один день. Стоматология Anestik
Протезирование на имплантах за один день. Стоматология Anestik Программа-практикума Работа с возражениями клиентов. Рабочая тетрадь
Программа-практикума Работа с возражениями клиентов. Рабочая тетрадь Рекламное агенство Gallery
Рекламное агенство Gallery Oferta świąteczno-sylwestrowa „Ki`Ko Team Studio”
Oferta świąteczno-sylwestrowa „Ki`Ko Team Studio” Project: Global Social Media Plan // June Topic: Fruit Drops Format: image Date: Flexible Content
Project: Global Social Media Plan // June Topic: Fruit Drops Format: image Date: Flexible Content