Estimation of permissible nitrogen content in the protective gas of the sodium circuit. Rosatom презентация
- Главная
- Без категории
- Estimation of permissible nitrogen content in the protective gas of the sodium circuit. Rosatom

Содержание
- 2. With an increased concentration of nitrogen in the protective gas of the sodium circuits of the
- 3. Thermodynamic analysis shows that the formation of iron nitrides in nitrogen is almost impossible. When nitriding
- 4. There are some patterns of the effect of nitrogen on the behavior of unstabilized steels in
- 5. In the atmosphere of technical nitrogen, weak nitriding of steel at 973 K is noticeable after
- 6. The allowable partial pressure of nitrogen in the gas phase is determined based on the reduction
- 7. Dependence of permissible nitrogen pressure in the gas cavity above steel 0Х16Н15МЗБ on the exposure time,
- 8. The permissible nitrogen content in the protective gas of the reactor was normalized to a value
- 9. The solubility of molecular nitrogen in sodium is extremely low ((1–4) 10–9 wt.% At 450–600 °
- 11. Скачать презентацию
With an increased concentration of nitrogen in the protective gas
With an increased concentration of nitrogen in the protective gas
Nitrogen as an impurity introduction into structural materials has a significant impact on the mechanical and technological properties of steel. The main negative effect that occurs with increasing nitrogen concentration is the loss of plastic properties of steels.
Thermodynamic analysis shows that the formation of iron nitrides in nitrogen
Thermodynamic analysis shows that the formation of iron nitrides in nitrogen
Nitriding of most austenitic steels does not allow to obtain a layer with a depth of more than 0.12–0.15 mm. With increasing temperature, the total depth of the nitrided layer increases. The hardness of the nitrated layer decreases with increasing temperature.
There are some patterns of the effect of nitrogen on the
There are some patterns of the effect of nitrogen on the
1) steel with a high (up to 0.12%) nitrogen content has a maximum corrosion rate, assessed by weight change, and an increased tendency to lose nitrogen and carbon;
2) nitrogen in the steel increases the activity of carbon and enhances the decarburization of steel;
3) the introduction of molybdenum into the composition of the steel (along with chromium) reduces the transfer of both carbon and nitrogen.
In the atmosphere of technical nitrogen, weak nitriding of steel at
In the atmosphere of technical nitrogen, weak nitriding of steel at
Under the same conditions in sodium, nitriding occurred more intensively, but especially quickly in the gas phase over sodium.
Increasing the pressure of nitrogen over sodium causes accelerated nitriding of steel in sodium and in nitrogen in the presence of sodium vapor.
The decrease in the effect of nitrogen on the mechanical properties of samples immersed in sodium, compared with the effect on samples over sodium, is due to the low solubility of nitrogen in sodium.
The allowable partial pressure of nitrogen in the gas phase is
The allowable partial pressure of nitrogen in the gas phase is
It is assumed that the change in the relative elongation of steel samples also correlates with the depth of penetration of nitrogen. Therefore, assuming that the allowable partial pressure of nitrogen corresponds to the allowable relative elongation of steel, the calculated dependence is obtained, which for steel in protective gas saturated with sodium vapor has the form
δ = 259 ехр(-75300/RT) (P τ)0.5
where: τ is the time, h;
T is temperature, K;
P is the partial pressure of nitrogen, atm.
Nevzorov B.A., Zotov V.V., Ivanov V.A. and others. Corrosion of structural materials in liquid alkali metals. / Ed. prof. Nevzorov B.A. - M .: Atomizdat, 1977.
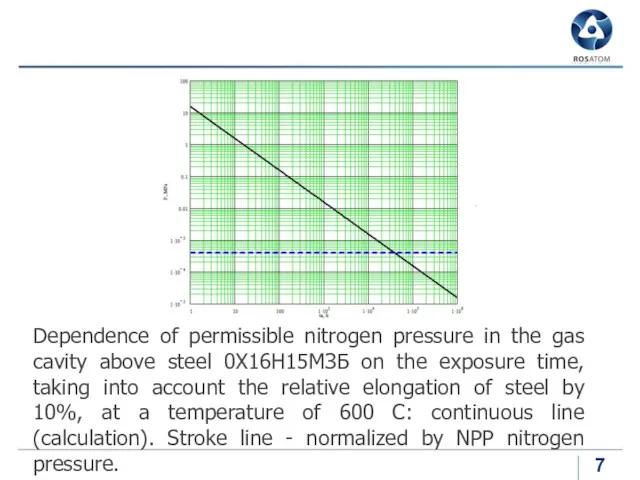
Dependence of permissible nitrogen pressure in the gas cavity above steel
Dependence of permissible nitrogen pressure in the gas cavity above steel
The permissible nitrogen content in the protective gas of the reactor
The permissible nitrogen content in the protective gas of the reactor
Substantiation of the range of regulated impurities in sodium coolant of the primary and secondary circuits of the reactor BN-600. Technical Note, IPPE, 2010.
The solubility of molecular nitrogen in sodium is extremely low ((1–4)
The solubility of molecular nitrogen in sodium is extremely low ((1–4)
Zagorulko Yu. Status of sodium coolant in BN600, at present time // WG4 "Liquid Metal Technology" Meeting, Cadarache 2007 October 15th to 19th.





 Презентация открытого мероприятия для начинающих воспитателей по познавательному развитию
Презентация открытого мероприятия для начинающих воспитателей по познавательному развитию Акцентологические ошибки в современной речи
Акцентологические ошибки в современной речи Лето 2015. Фотоальбом
Лето 2015. Фотоальбом Санаторий Березовая Роща. Стилевое решение 4 этажа
Санаторий Березовая Роща. Стилевое решение 4 этажа Кафе Цезарь
Кафе Цезарь Дидактическая игра. Автоматизация и определение места звука [р] в словах
Дидактическая игра. Автоматизация и определение места звука [р] в словах Буква Э
Буква Э презентация Солдатский треугольник
презентация Солдатский треугольник Свойства древесины
Свойства древесины Презентация Простые вещества металлы
Презентация Простые вещества металлы Презентация Технология коррекции письма
Презентация Технология коррекции письма Социальный проект
Социальный проект Machine-tools - a measure of Man’s progress
Machine-tools - a measure of Man’s progress Суғару каналдарының конструкциялары және есебі
Суғару каналдарының конструкциялары және есебі урок 10.02.22
урок 10.02.22 Реконструкция технологического процесса погрузочно-разгрузочных работ с комплексной переработкой пиловочного сырья
Реконструкция технологического процесса погрузочно-разгрузочных работ с комплексной переработкой пиловочного сырья Мастер-класс для учителей-логопедов Роль интерактивных технологий в коррекционной работе учителя-логопеда ДОУ Диск Диск Диск
Мастер-класс для учителей-логопедов Роль интерактивных технологий в коррекционной работе учителя-логопеда ДОУ Диск Диск Диск презентация Ориентирование на местности
презентация Ориентирование на местности Психология тарихы. Психологияның даму кезеңдері. (Часть 3)
Психология тарихы. Психологияның даму кезеңдері. (Часть 3) Организация вахтенной службы
Организация вахтенной службы Мой родной поселок Мари-Турек.
Мой родной поселок Мари-Турек. Теория. Медитация. Образ жизни
Теория. Медитация. Образ жизни Отчет об исследовании Значение специально организованного процесса обучения дошкольников с амблиопией и косоглазием
Отчет об исследовании Значение специально организованного процесса обучения дошкольников с амблиопией и косоглазием Физические приборы
Физические приборы Портфилио. Обучение и организация различных видов деятельности и общения детей с сохранным развитием
Портфилио. Обучение и организация различных видов деятельности и общения детей с сохранным развитием Дереворежущие инструменты. Тема 1.2
Дереворежущие инструменты. Тема 1.2 Родовища та фабрики металургії в Україні
Родовища та фабрики металургії в Україні Историческая геология
Историческая геология