Содержание
- 2. Essential Math for Games Collisions Up to this point, objects just pass through each other Two
- 3. Essential Math for Games Computational Geometry Algorithms for solving geometric problems Object intersections Object proximity Path
- 4. Essential Math for Games Distance Testing Useful for computing intersection between simple objects E.g. sphere intersection
- 5. Essential Math for Games Point-Point Distance Compute length of vector between two points P0 and P1,
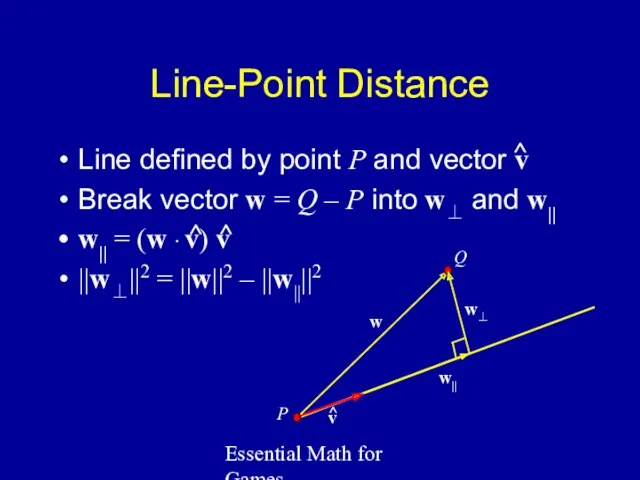
- 6. Essential Math for Games Line-Point Distance Line defined by point P and vector v Break vector
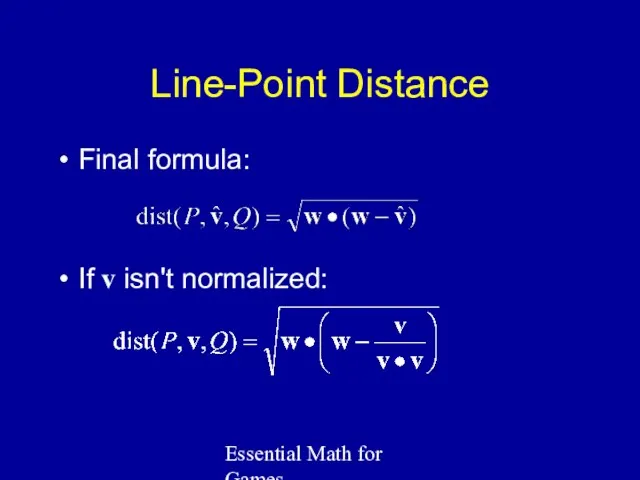
- 7. Essential Math for Games Line-Point Distance Final formula: If v isn't normalized:
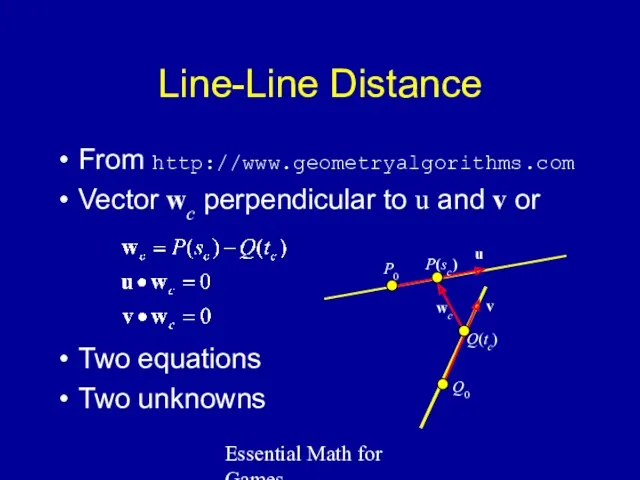
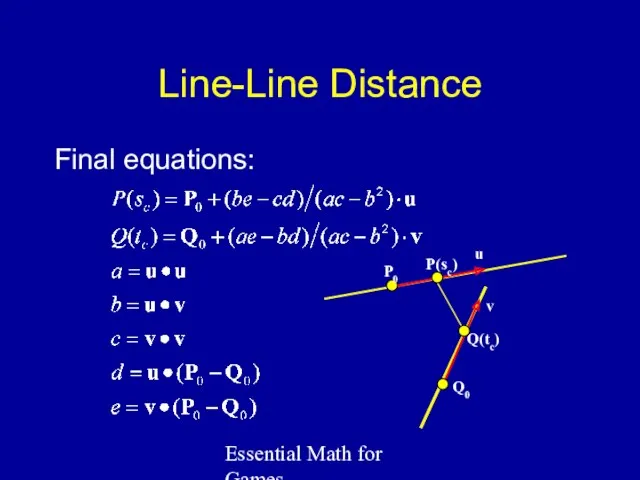
- 8. Essential Math for Games Line-Line Distance From http://www.geometryalgorithms.com Vector wc perpendicular to u and v or
- 9. Essential Math for Games Line-Line Distance Final equations: P0 u Q0 v P(sc) Q(tc)
- 10. Essential Math for Games Segment-Segment Distance Determine closest point between lines If lies on both segments,
- 11. Essential Math for Games Bounding Objects Detecting intersections with complex objects expensive Provide simple object that
- 12. Essential Math for Games Bounding Sphere Tightest sphere that surrounds model For each point, compute distance
- 13. Essential Math for Games Bounding Sphere (Cont’d) What to use for center? Local origin of model
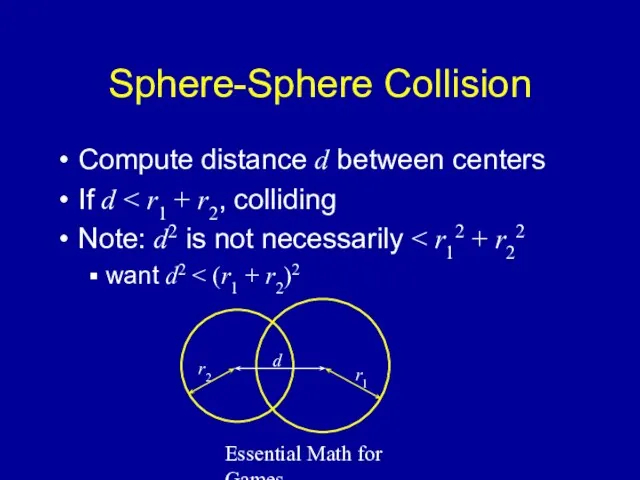
- 14. Essential Math for Games Sphere-Sphere Collision Compute distance d between centers If d Note: d2 is
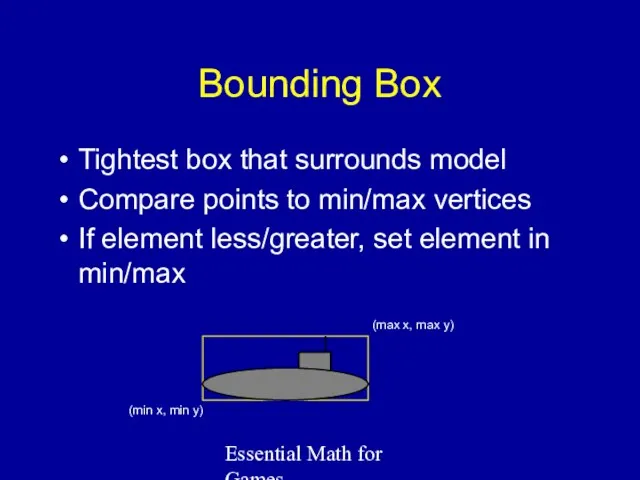
- 15. Essential Math for Games Bounding Box Tightest box that surrounds model Compare points to min/max vertices
- 16. Essential Math for Games Axis-Aligned Bounding Box Box edges aligned to world axes Recalc when object
- 17. Essential Math for Games Axis-Aligned Box-Box Collision Compare x values in min,max vertices If min2 >
- 18. Essential Math for Games Object-Oriented Bounding Box Box edges aligned with local object coordinate system Much
- 19. Essential Math for Games OBB Collision Idea: determine if separating plane between boxes exists Project box
- 20. Essential Math for Games OBB Collision To ensure maximum extents, take dot product using only absolute
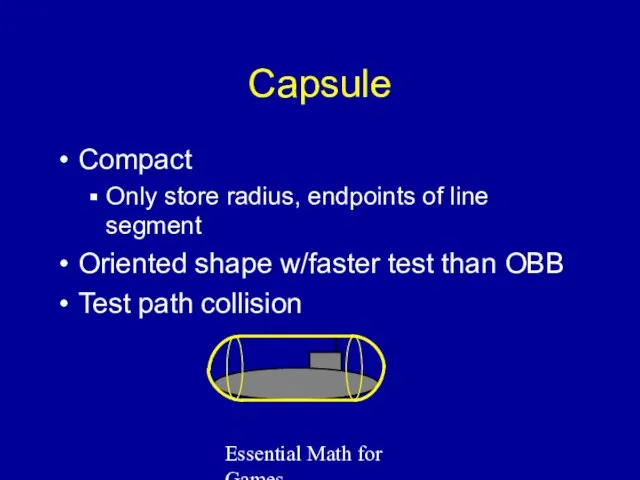
- 21. Essential Math for Games Capsule Cylinder with hemispheres on ends One way to compute Calc bounding
- 22. Essential Math for Games Capsule Compact Only store radius, endpoints of line segment Oriented shape w/faster
- 23. Essential Math for Games Capsule-Capsule Collision Key: swept sphere axis is line segment with surrounding radius
- 24. Essential Math for Games Caveat Math assumes infinite precision Floating point is not to be trusted
- 25. Essential Math for Games Which To Use? As many as necessary Start with cheap tests, move
- 26. Essential Math for Games Recap Sphere -- cheap, not a good fit AABB -- still cheap,
- 27. Essential Math for Games Collision Detection Naïve: n2 checks! Two part process Broad phase Cull out
- 28. Essential Math for Games Broad Phase Obvious steps Only check each pair once Flag object if
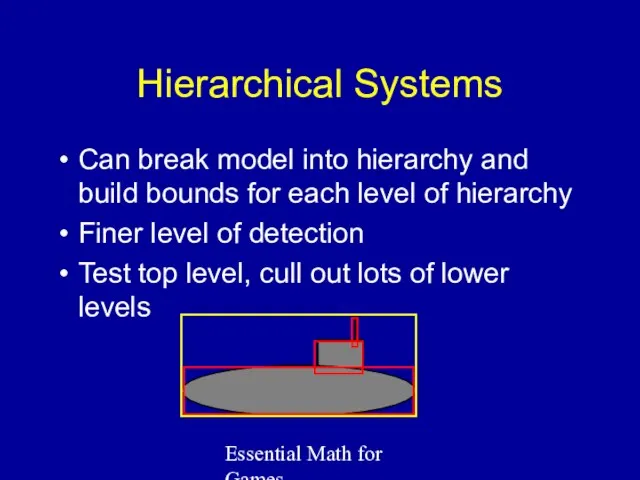
- 29. Essential Math for Games Hierarchical Systems Can break model into hierarchy and build bounds for each
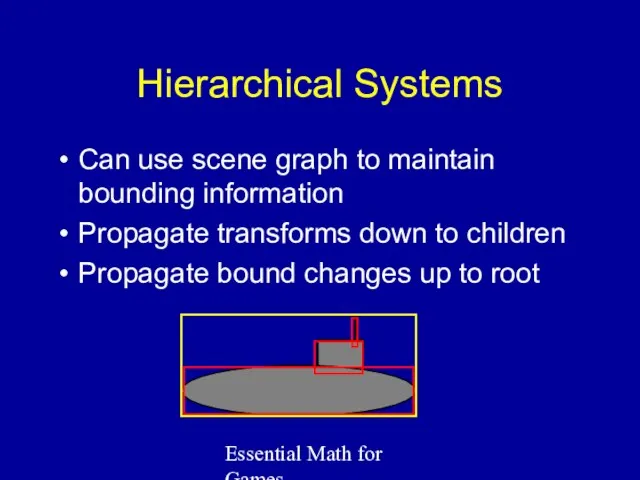
- 30. Essential Math for Games Hierarchical Systems Can use scene graph to maintain bounding information Propagate transforms
- 31. Essential Math for Games Spatial Subdivision Break world into separate areas Only check your area and
- 32. Essential Math for Games Sweep and Prune Store sorted x extents of objects Sweep from min
- 33. Essential Math for Games Spatial Subdivision Other methods: Quadtrees, octrees BSP trees, kd-trees Room-portal Choice depends
- 34. Essential Math for Games Temporal Coherence Objects nearby generally stay nearby Check those first Can take
- 35. Essential Math for Games Narrow Phase Have culled object pairs Need to find Contact point Normal
- 36. Essential Math for Games Contact Region Two objects interpenetrate, have one (or more) regions A bit
- 37. Essential Math for Games Contact Features Faceted objects collide at pair of contact features Only consider
- 38. Essential Math for Games Contact Features For E-E: Point is intersection of edges Normal is cross
- 39. Essential Math for Games Contact Points Can have multiple contact points Ex: two concave objects Store
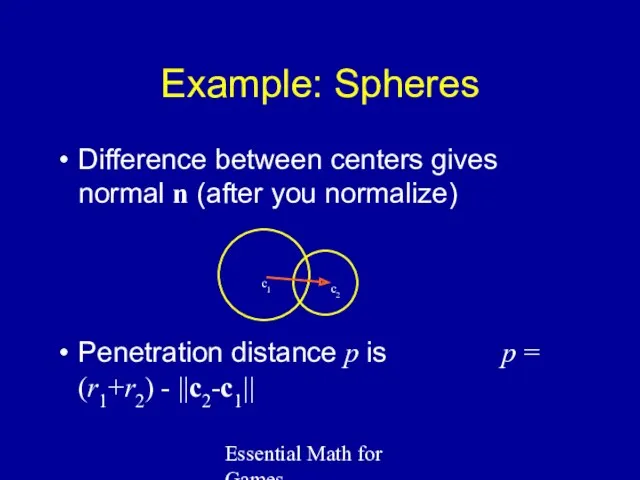
- 40. Essential Math for Games Example: Spheres Difference between centers gives normal n (after you normalize) Penetration
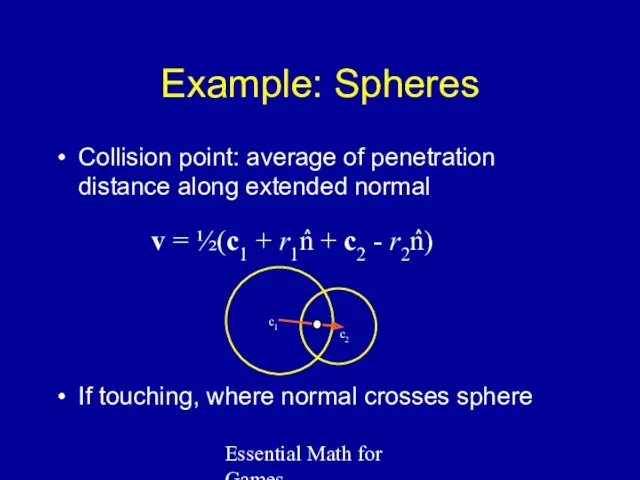
- 41. Essential Math for Games Example: Spheres Collision point: average of penetration distance along extended normal If
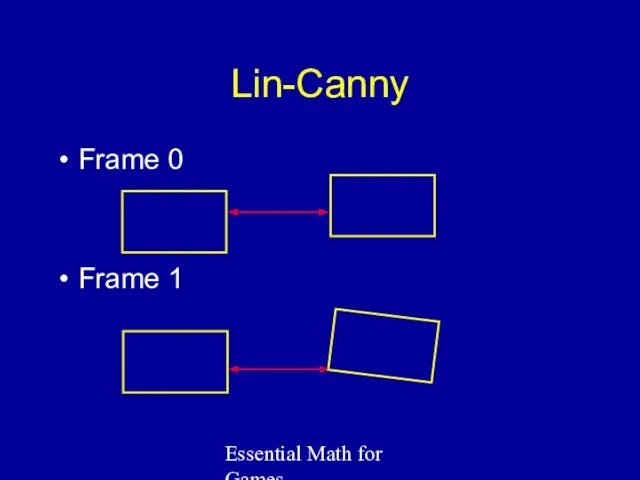
- 42. Essential Math for Games Lin-Canny For convex objects Easy to understand, hard to implement Closest features
- 43. Essential Math for Games Lin-Canny Frame 0 Frame 1
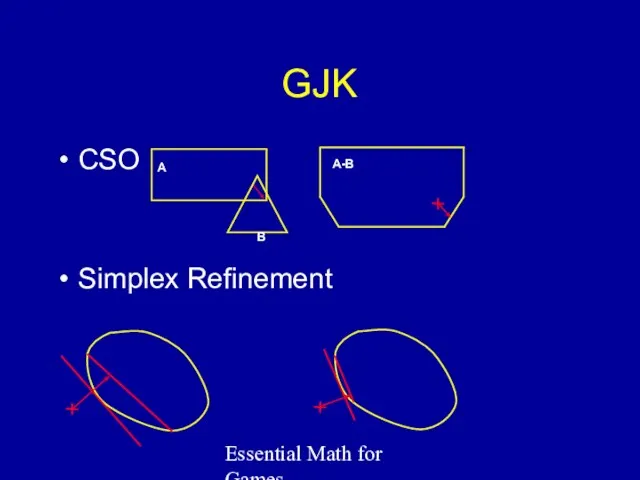
- 44. Essential Math for Games GJK For Convex Objects Hard to understand, easy to implement Finds point
- 45. Essential Math for Games GJK CSO Simplex Refinement
- 46. Essential Math for Games Missing Collision If time step is too large for object speed, two
- 47. Essential Math for Games Missing Collision One solution: slice time interval Simulate between slices Same problem,
- 48. Essential Math for Games Missing Collision Another solution: use swept volumes If volumes collide, may collide
- 49. Essential Math for Games Recap Collision detection complex Combo of math and computing Break into two
- 50. Essential Math for Games References Preparata, Franco P. and Michael Ian Shamos, Computational Geometry: An Introduction,
- 52. Скачать презентацию



































 Дифференциальное исчисление
Дифференциальное исчисление Решение задач с помощью уравнений
Решение задач с помощью уравнений Определение арифметической прогрессии. Формула n-го члена арифметической прогрессии. 9 класс
Определение арифметической прогрессии. Формула n-го члена арифметической прогрессии. 9 класс Деление чисел. Делимое, делитель, частное
Деление чисел. Делимое, делитель, частное Письменное деление многозначных чисел на трехзначное число
Письменное деление многозначных чисел на трехзначное число Аналитическая геометрия
Аналитическая геометрия Стандартный вид числа. 8 класс
Стандартный вид числа. 8 класс Сумма углов треугольника. Внешний угол треугольника (7 класс)
Сумма углов треугольника. Внешний угол треугольника (7 класс) Деление дробей
Деление дробей Итоговый тест по математике, 5 класс
Итоговый тест по математике, 5 класс Простейшие уравнения. Задание В 6
Простейшие уравнения. Задание В 6 Тест по математике для 4 класса(Программа Школа России)
Тест по математике для 4 класса(Программа Школа России) Десятичные дроби. Путешествие на математическом поезде
Десятичные дроби. Путешествие на математическом поезде Брейн-ринг по теме Алгебра логики
Брейн-ринг по теме Алгебра логики Сумма и разность кубов двух выражений
Сумма и разность кубов двух выражений задачи на разностное сравнение
задачи на разностное сравнение Мониторинг по математике в 7-8 классах
Мониторинг по математике в 7-8 классах Геометриялық прогрессия
Геометриялық прогрессия Выражения с дробями
Выражения с дробями Синус, косинус и тангенс острого угла прямоугольного треугольника
Синус, косинус и тангенс острого угла прямоугольного треугольника Гармонизация статистических доказательств и предсказаний
Гармонизация статистических доказательств и предсказаний Игры для детей
Игры для детей Графическое решение показательных уравнений и неравенств
Графическое решение показательных уравнений и неравенств Подобные треугольники. Геометерия. 8 класс
Подобные треугольники. Геометерия. 8 класс План-конспект урока и презентация, по математике 2 класс.
План-конспект урока и презентация, по математике 2 класс. Формулы сложения
Формулы сложения Теорема Виета. 8 класс
Теорема Виета. 8 класс Арифметическая прогрессия
Арифметическая прогрессия