Содержание
- 2. Practical information My office: A 202 IYBF-building Office hours: Tuesdays: 11:00 – 12:00 and 17:00 –
- 3. C Course syllabus Basic course in statistical thinking and analysis. The primary goals are to help
- 4. Class attendance policy Students are expected to attend all scheduled classes as well as to bring
- 5. Tardiness Policy Students are permitted to arrive to the class in the first 15 minutes after
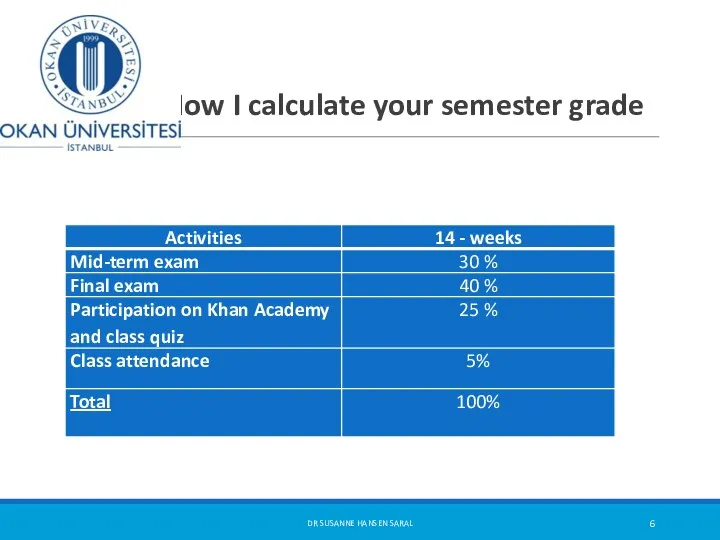
- 6. How I calculate your semester grade DR SUSANNE HANSEN SARAL
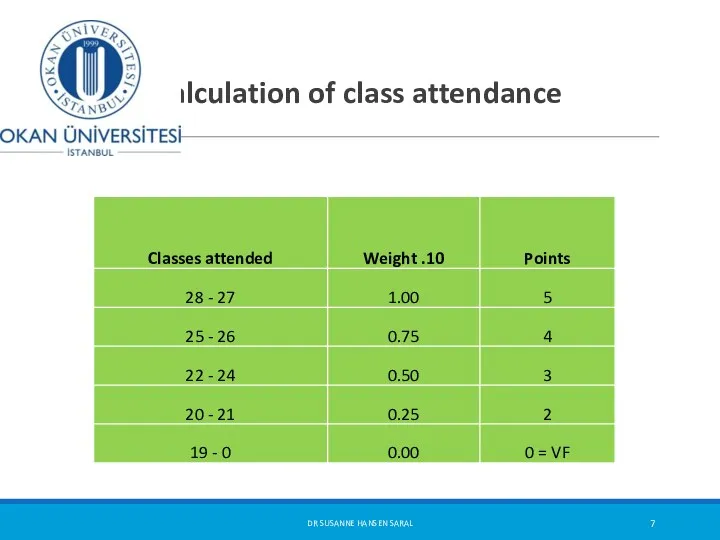
- 7. Calculation of class attendance DR SUSANNE HANSEN SARAL
- 8. Course textbook Sharpe: Business Statistics, 3/e, Global Edition, Pearson Newbold, Carlson, Thorne, Statistics for Business and
- 9. Homework on Khan Academy Every week I will assign new homework on www.khanacademy.org I give you
- 10. Create your account in Khan Academy Go to www.khanacademy.org create an account with your email address
- 11. PIAZZA.COM Piazza.com – class platform for: Posting class lectures, course syllabus, class announcement DR SUSANNE HANSEN
- 12. Send me an email to the following address: susanne.saral@okan.edu.tr DR SUSANNE HANSEN SARAL
- 13. What is statistics? What is the average age of the students in this class-room? DR SUSANNE
- 14. What is statistics? Every statistical problem starts with a question! What was the overall customer satisfaction
- 15. What is statistics? Every statistical problem starts with a question! Why would companies or individuals want
- 16. What is statistics? To make good business decisions to help improve company revenues DR SUSANNE HANSEN
- 17. What is statistics? How in Statistics do we go about answering such questions? What was the
- 18. What is statistics? We need to collect information from the source we are interested in to
- 19. What is statistics? Statistics concern populations In the former examples the populations are : All customers
- 20. Statistical key definitions POPULATION A population is the collection of all items of interest under investigation.
- 21. Examples of Populations Incomes of all families in Izmir All children in all elementary schools of
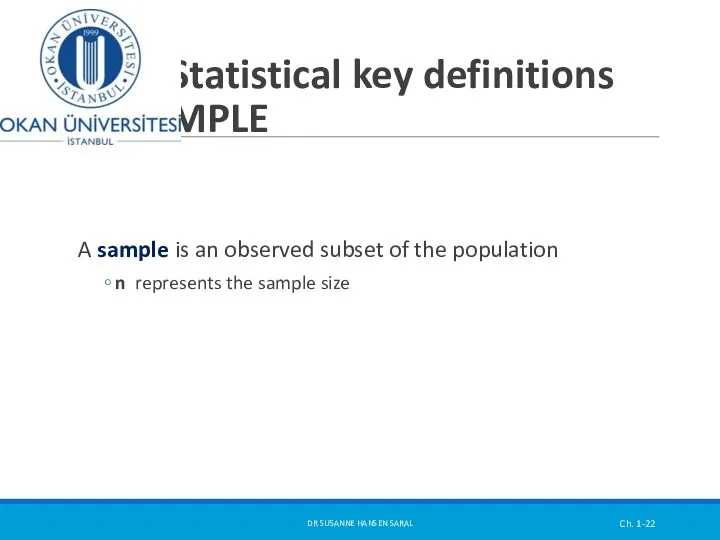
- 22. Statistical key definitions SAMPLE A sample is an observed subset of the population n represents the
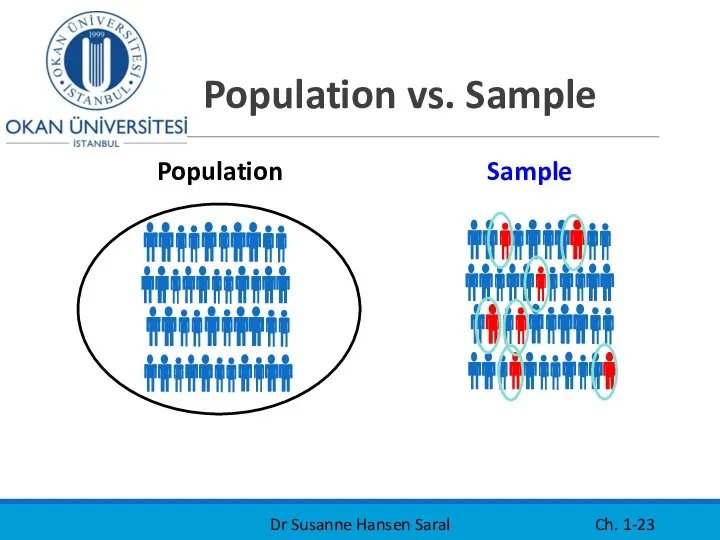
- 23. Population vs. Sample Dr Susanne Hansen Saral Ch. 1- Population Sample
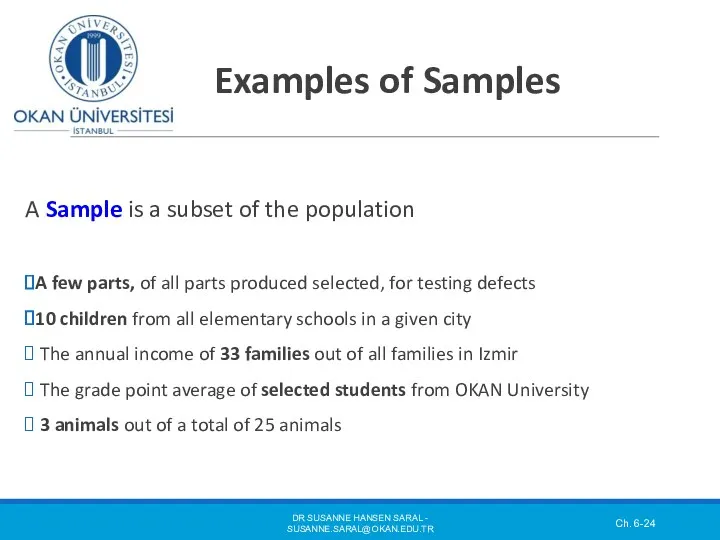
- 24. Examples of Samples A Sample is a subset of the population A few parts, of all
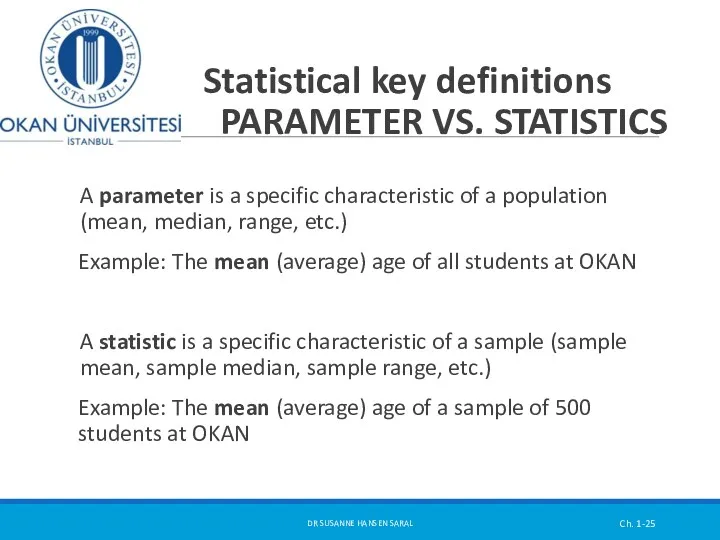
- 25. Statistical key definitions PARAMETER VS. STATISTICS A parameter is a specific characteristic of a population (mean,
- 26. Why is it necessary to collect samples? Populations are indefinite and their parameters are rarely known.
- 27. Why is it necessary to collect samples? Populations are usually infinite. Therefore impossible to investigate the
- 28. Randomness (Turkish: Rasgelelik) Our final objective in statistics is to make valid and reliable statements about
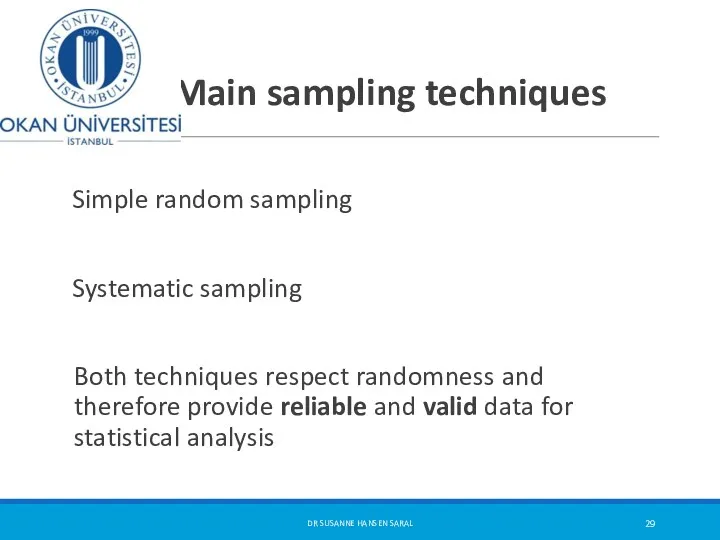
- 29. Main sampling techniques Simple random sampling Systematic sampling Both techniques respect randomness and therefore provide reliable
- 30. Random Sampling Simple random sampling is a procedure in which: Each member/item in the population is
- 31. Sampling error In statistics we make decision about a population based on sample data, because the
- 32. Non-sampling error Non-sampling errors: Are errors not connected to the sampling procedure Population is not properly
- 33. Inferential statistics Drawing conclusion about a population based a sample information. DR SUSANNE HANSEN SARAL Ch.
- 34. Inferential statistics To draw conclusions about the population based on a sample we need to collect
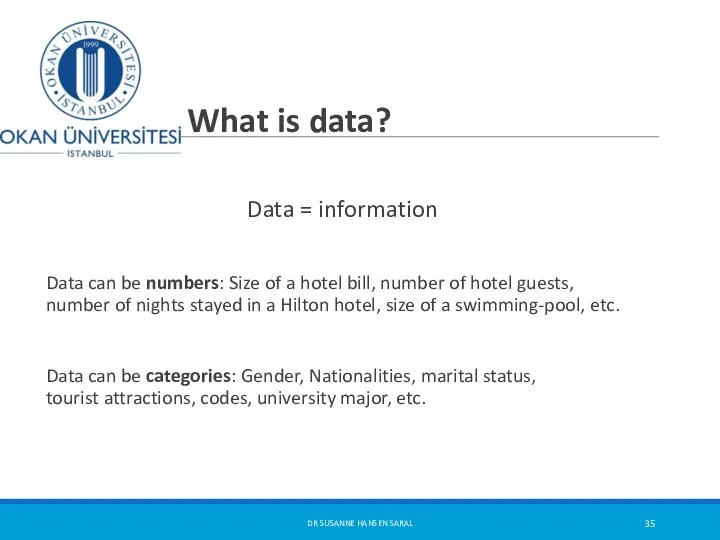
- 35. What is data? Data = information Data can be numbers: Size of a hotel bill, number
- 36. Data and context Data are useless without a context. When we deal with data we need
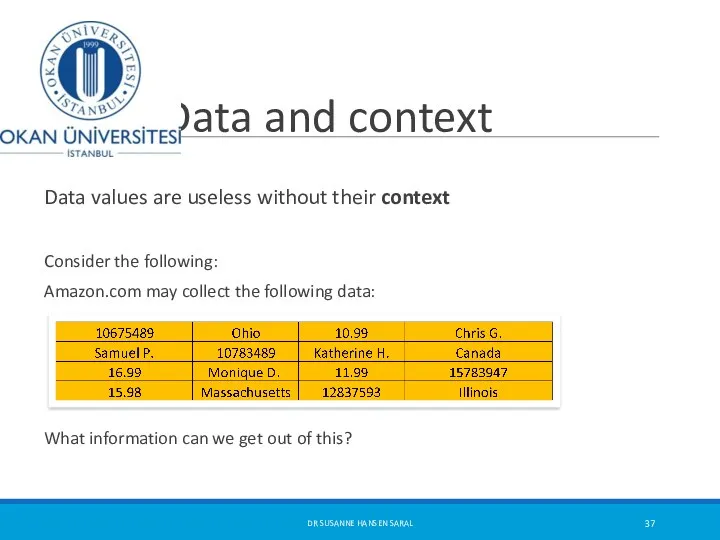
- 37. Data and context Data values are useless without their context Consider the following: Amazon.com may collect
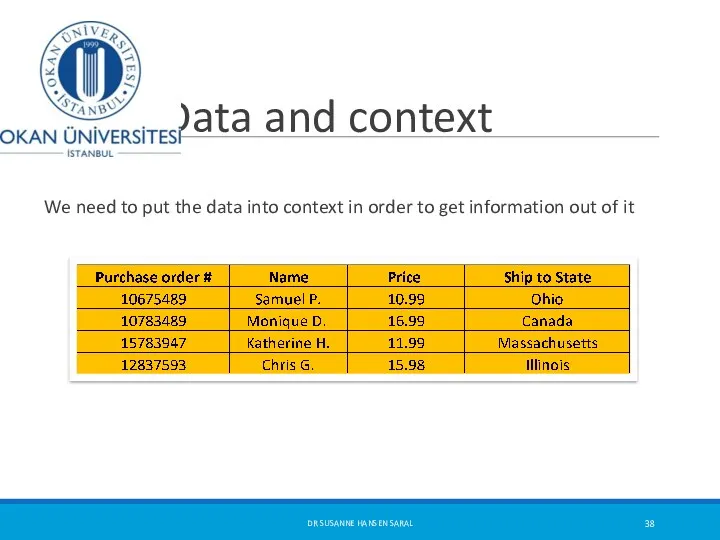
- 38. Data and context We need to put the data into context in order to get information
- 39. What is statistics? It is a basic study of transforming data into information : how to
- 40. Where does data come from? Market research Survey (online questionnaires, paper questionnaires, etc.) Interviews Research experiments
- 42. Скачать презентацию





























 Правило умножения. Перестановки и факториалы
Правило умножения. Перестановки и факториалы Урок математики.Решение задач и выражений
Урок математики.Решение задач и выражений Числовые и буквенные выражения
Числовые и буквенные выражения Подобные треугольники. Пропорциональные отрезки
Подобные треугольники. Пропорциональные отрезки График квадратичной функции
График квадратичной функции Задачи повышенной сложности .
Задачи повышенной сложности . Повторение и закрепление изученного материала по математике (1 класс)
Повторение и закрепление изученного материала по математике (1 класс) Дидактическая игра -Собери грибы
Дидактическая игра -Собери грибы Как собрать кубик Рубика (и другие головоломки)
Как собрать кубик Рубика (и другие головоломки) Математика 6 класс. Обыкновенные дроби
Математика 6 класс. Обыкновенные дроби Решение задач на применение аксиом стереометрии
Решение задач на применение аксиом стереометрии Математические ребусы
Математические ребусы Открытый урок (презентация)
Открытый урок (презентация) Автокорреляция
Автокорреляция Внеклассное мероприятие по математике Звездный час
Внеклассное мероприятие по математике Звездный час Санау жұйесі
Санау жұйесі Пирамида. Правильная пирамида
Пирамида. Правильная пирамида Презентация к уроку математики во 2 классе по теме: Час.Минута. Определение времени по часам
Презентация к уроку математики во 2 классе по теме: Час.Минута. Определение времени по часам Системы нелинейных уравнений с двумя неизвестными
Системы нелинейных уравнений с двумя неизвестными Презентация к уроку математики в 3 классе по теме Закрепление. Решение задач.
Презентация к уроку математики в 3 классе по теме Закрепление. Решение задач. Презентация Лесенка неделька (Учим дни недели)
Презентация Лесенка неделька (Учим дни недели) Приближение десятичных дробей
Приближение десятичных дробей Деление с остатком
Деление с остатком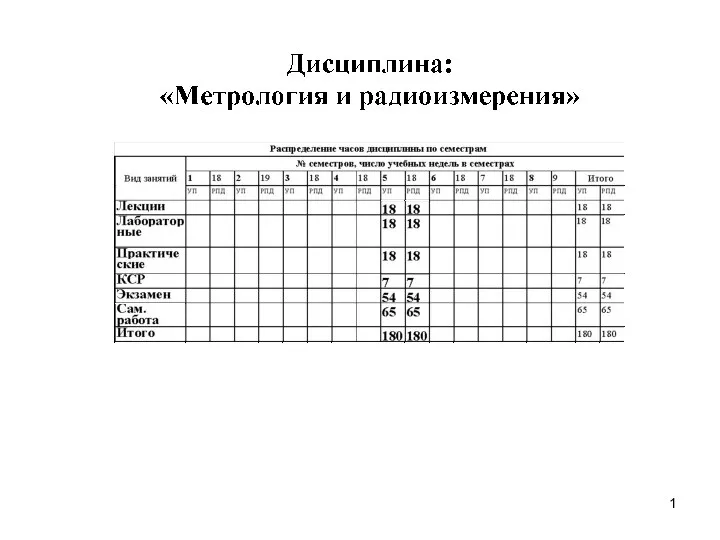 Основные понятия и термины метрологии
Основные понятия и термины метрологии Внеклассное мероприятие по математике в 6 классе
Внеклассное мероприятие по математике в 6 классе Работа по геометрии по теме Тела вращения - Гиперсфера (пояснительная записка + презентация)
Работа по геометрии по теме Тела вращения - Гиперсфера (пояснительная записка + презентация) Анимашки для оформления презентаций в Microsoft Power Point. Сборник №3
Анимашки для оформления презентаций в Microsoft Power Point. Сборник №3 Дружок. Правила по математике для учащихся 1 класса
Дружок. Правила по математике для учащихся 1 класса