Содержание
- 2. Change of scale Inch to centimeter: cm= inch times 2.54 pound to kilogram: kg=lb times 2.2
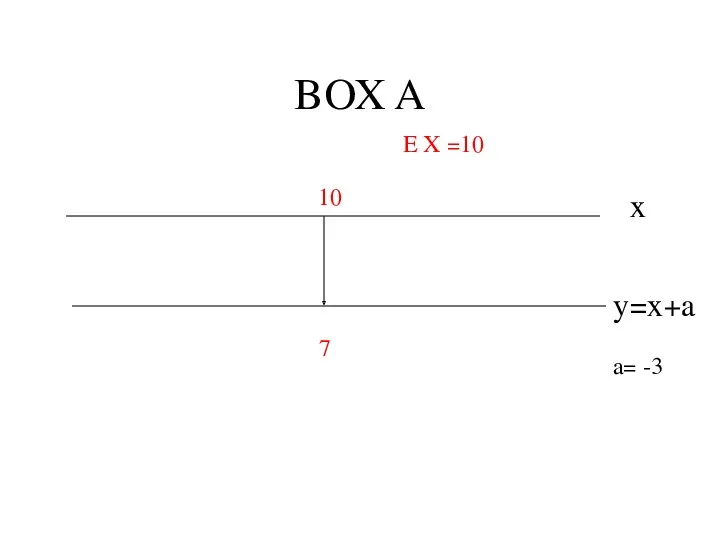
- 3. BOX A x y=x+a 10 7 a= -3 E X =10
- 4. Two Boxes A and B ; independence Independence means that neither positive nor negative dependence; any
- 5. E (X+ Y) = E X + E Y; always holds E ( X Y) =
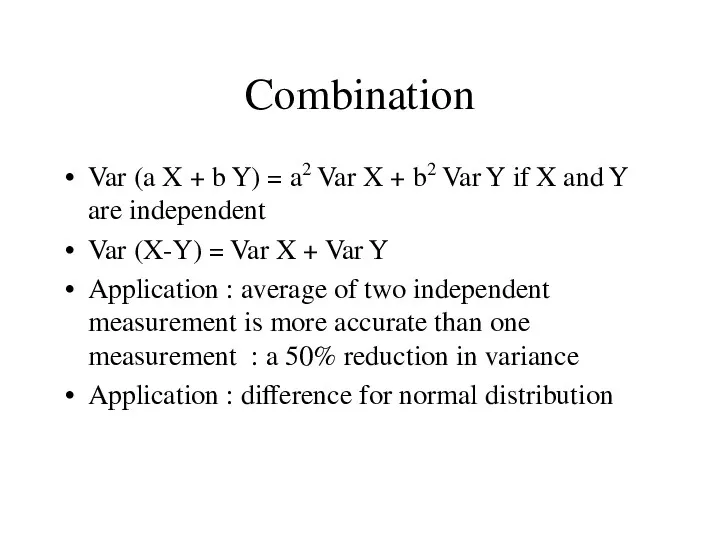
- 6. Combination Var (a X + b Y) = a2 Var X + b2 Var Y if
- 7. x: 2, 3, 4, 5 y: 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15 (2,5) (2,7) (2, 9)
- 8. Example Phone call charge : 40 cents per minute plus a fixed connection fee of 50
- 9. Example Stock A and Stock B Current price : both the same, $10 per share Predicted
- 11. Скачать презентацию






 Квадратные неравенства
Квадратные неравенства Занимательная арифметика
Занимательная арифметика Единицы времени (2 класс)
Единицы времени (2 класс) Действия с обыкновенными дробями. Создание ОАО
Действия с обыкновенными дробями. Создание ОАО Ықтималдылықтар теориясының элементтері дегеніміз не
Ықтималдылықтар теориясының элементтері дегеніміз не Наглядное представление статистической информации
Наглядное представление статистической информации Необычное в привычном
Необычное в привычном Вторая производная и ее физический смысл
Вторая производная и ее физический смысл Дивовижне число Пі
Дивовижне число Пі Таблиця ділення на 3. Збери букет для Попелюшки
Таблиця ділення на 3. Збери букет для Попелюшки Площадь. Многоугольник
Площадь. Многоугольник Презентация к НОД ФЭМП Путешествие в сказку Цветик-семицветик
Презентация к НОД ФЭМП Путешествие в сказку Цветик-семицветик Измерение углов. Транспортир
Измерение углов. Транспортир Новые открытия в математике
Новые открытия в математике Арифметический диктант к уроку математика 4 класс
Арифметический диктант к уроку математика 4 класс Умножение на трехзначное число. 3 класс
Умножение на трехзначное число. 3 класс Магия числа 7.
Магия числа 7. Королевство знаний. Четные числа
Королевство знаний. Четные числа Случайные события и их вероятность
Случайные события и их вероятность Корреляциялык анализ
Корреляциялык анализ Интерактивный тест для проведения контрольного среза за 1 четверть в 6 классе по учебнику Н.Я.Виленкин
Интерактивный тест для проведения контрольного среза за 1 четверть в 6 классе по учебнику Н.Я.Виленкин Презентация Мышь-малютка
Презентация Мышь-малютка Побудова графіків тригонометричних функцій
Побудова графіків тригонометричних функцій Обратная функция
Обратная функция Цилиндр. Площадь его поверхности
Цилиндр. Площадь его поверхности Эпюр №1. Точка, прямая, плоскость
Эпюр №1. Точка, прямая, плоскость Среднее арифметическое, размах, мода и медиана. Алгебра. 7 класс
Среднее арифметическое, размах, мода и медиана. Алгебра. 7 класс Округление результатов расчета доверительного интервала
Округление результатов расчета доверительного интервала