Содержание
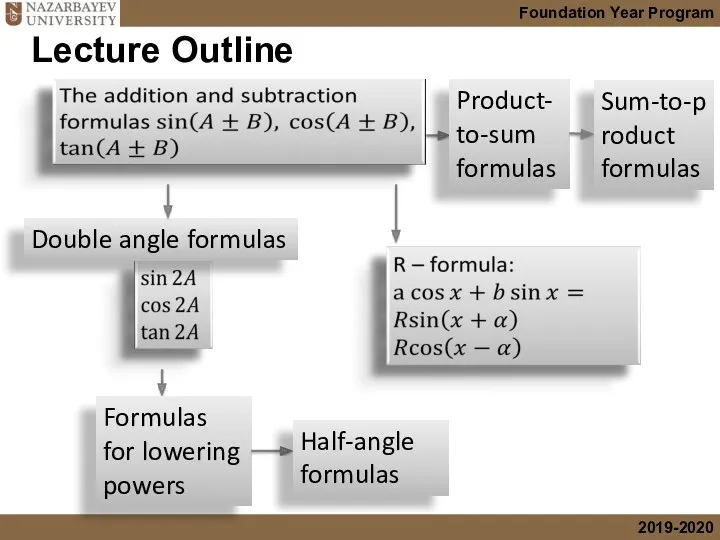
- 2. Lecture Outline Formulas for lowering powers Half-angle formulas Double angle formulas Product-to-sum formulas Sum-to-product formulas
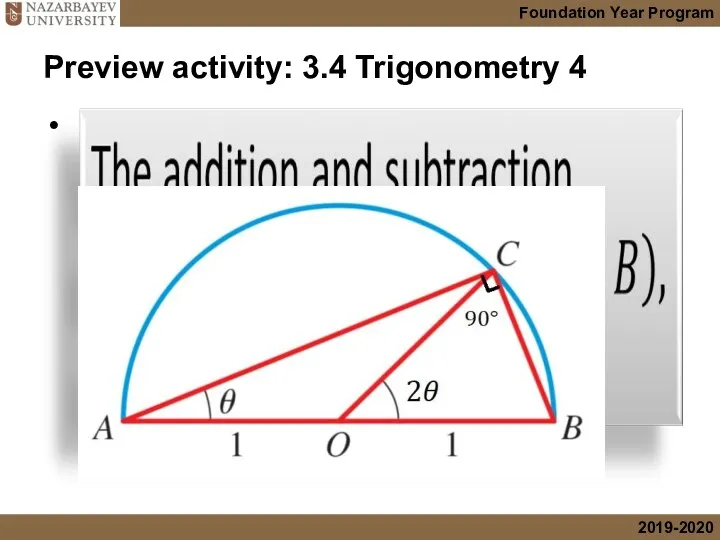
- 3. Preview activity: 3.4 Trigonometry 4
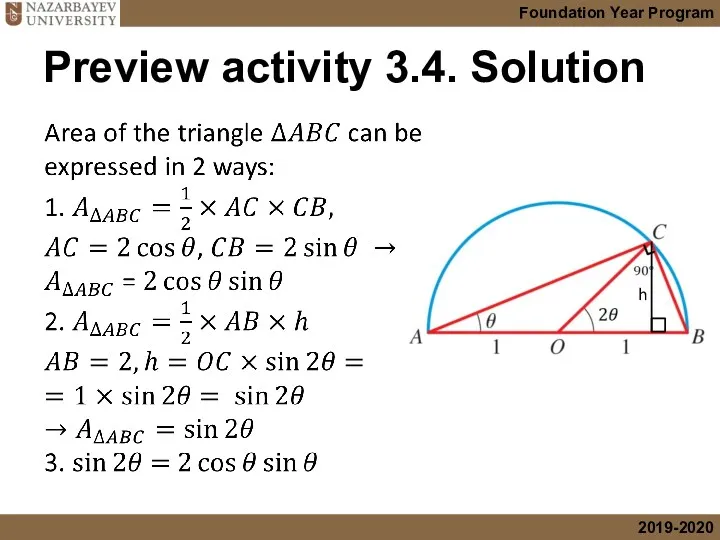
- 4. Preview activity 3.4. Solution h
- 5. Introduction Analytic trigonometry combines the use of a coordinate system with algebraic manipulation of the various
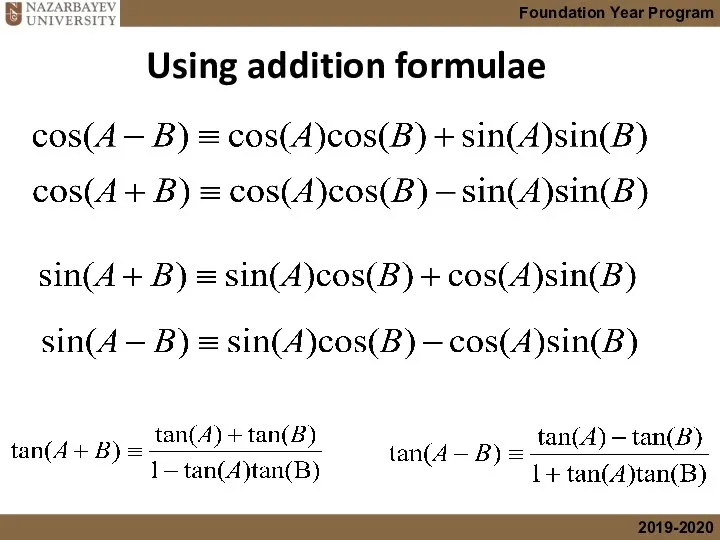
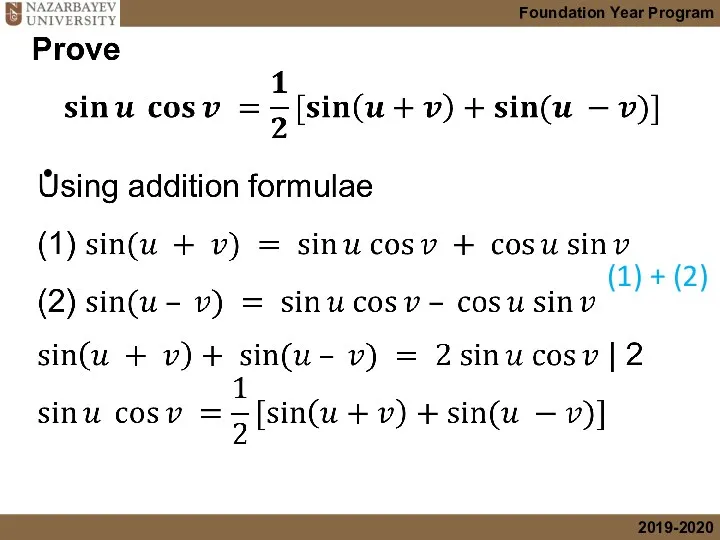
- 6. Using addition formulae
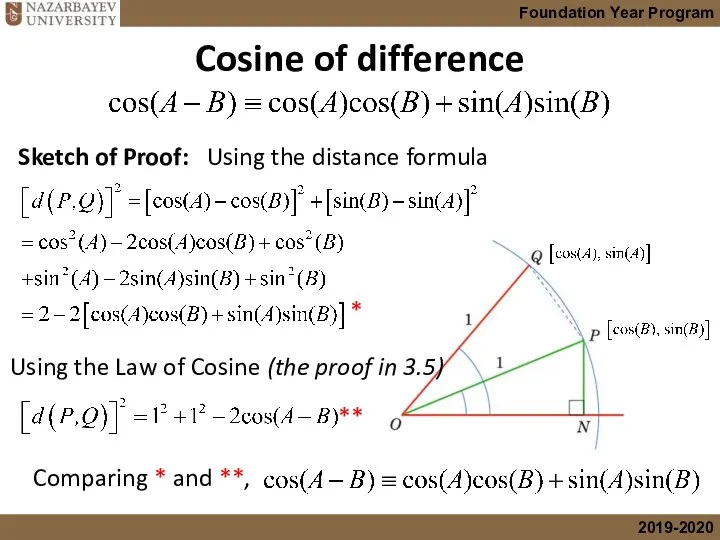
- 7. Cosine of difference Sketch of Proof: Using the distance formula Using the Law of Cosine (the
- 8. Proofs of Cosine of sum, Sine of sum and difference, tangent of sum and difference formulae
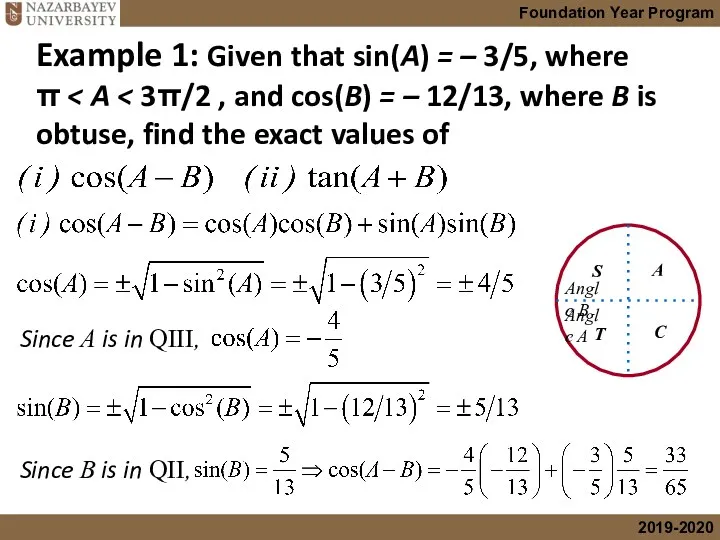
- 9. Example 1: Given that sin(A) = – 3/5, where π Since A is in QIII, Since
- 10. Example 1: Given that sin(A) = – 3/5, where π
- 11. Your turn!
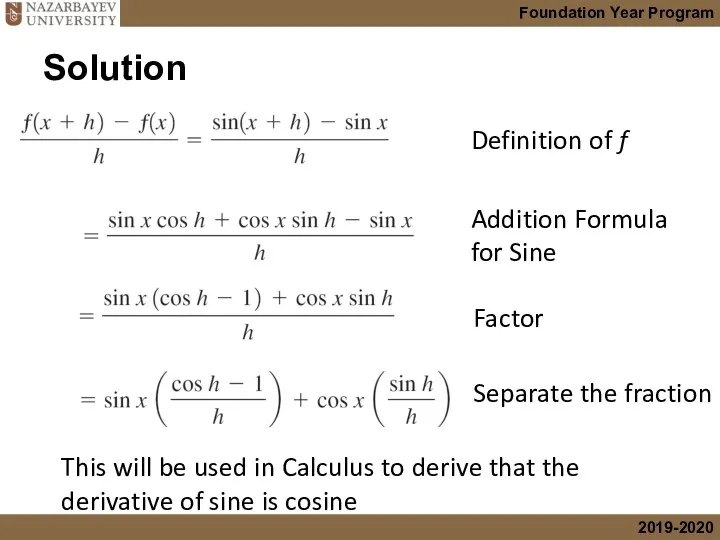
- 12. Solution Definition of f Addition Formula for Sine Factor Separate the fraction This will be used
- 13. Example 2
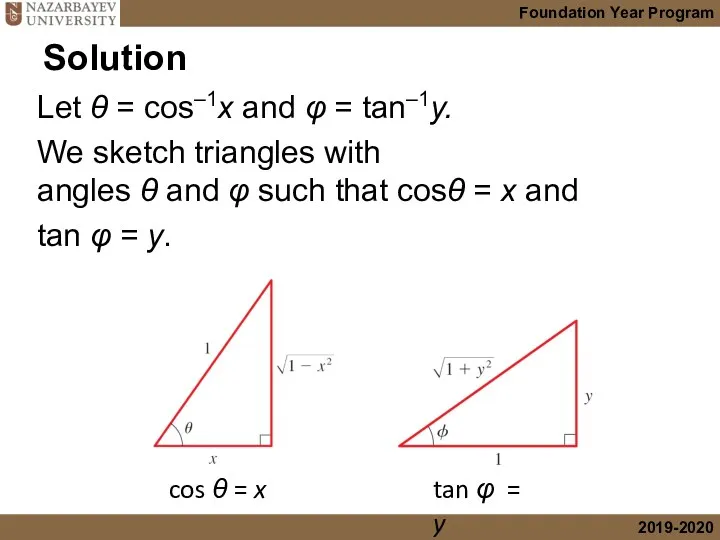
- 14. Let θ = cos–1x and φ = tan–1y. We sketch triangles with angles θ and φ
- 16. Double angle formulae
- 17. Prove double angle for sine Prove Using addition formula for sin(A + A):
- 18. Proofs for Cosine and tangent of double angle formulae are given in additional questions 6-7
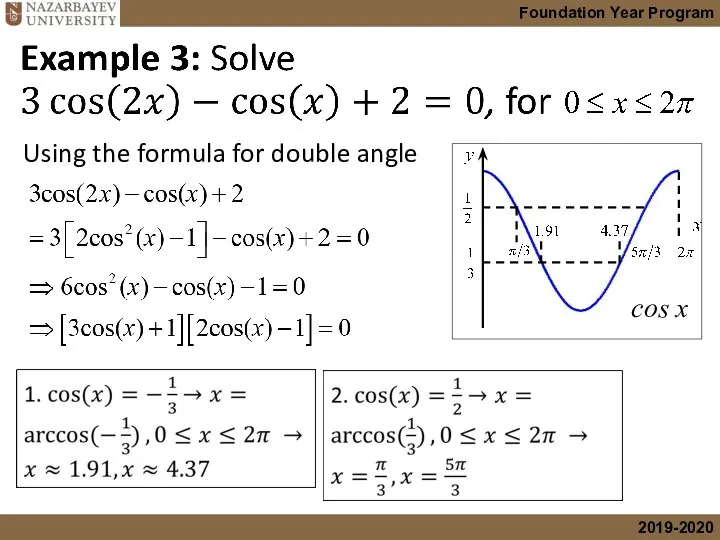
- 19. Using the formula for double angle
- 20. Example 4: By writing the following equations as quadratic in tan(x/2) solve , for Using the
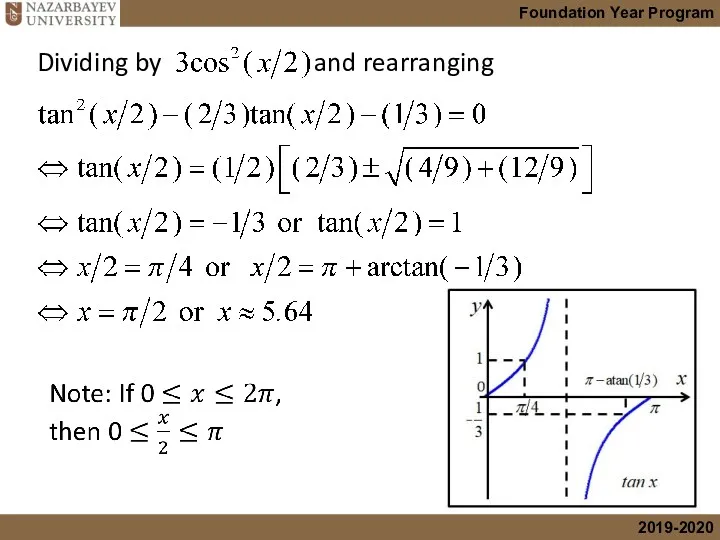
- 21. Dividing by and rearranging
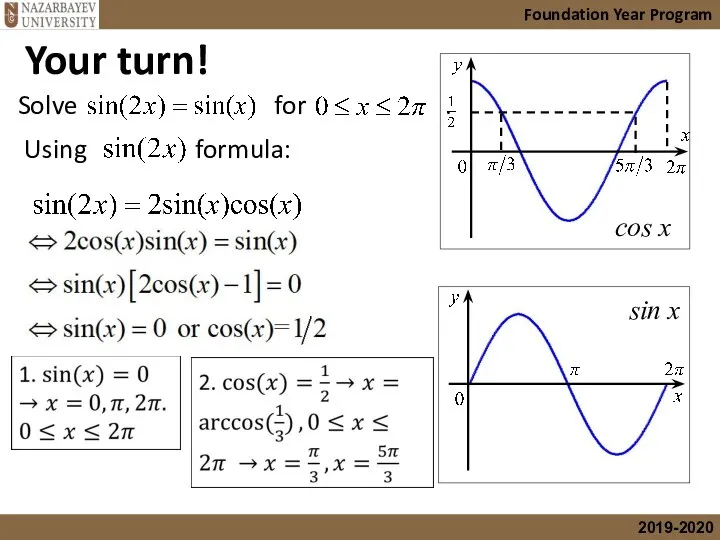
- 22. Your turn! Solve for .
- 23. Foundation Year Program Using formula: cos x sin x Your turn! Solve for .
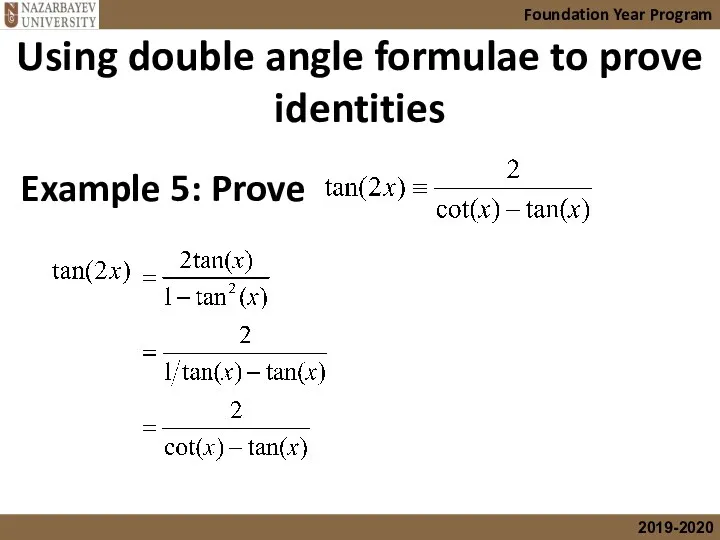
- 24. Using double angle formulae to prove identities Foundation Year Program Example 5: Prove
- 25. Foundation Year Program Example 6: Prove
- 26. Foundation Year Program Your turn! Prove
- 27. Foundation Year Program Your turn! Prove
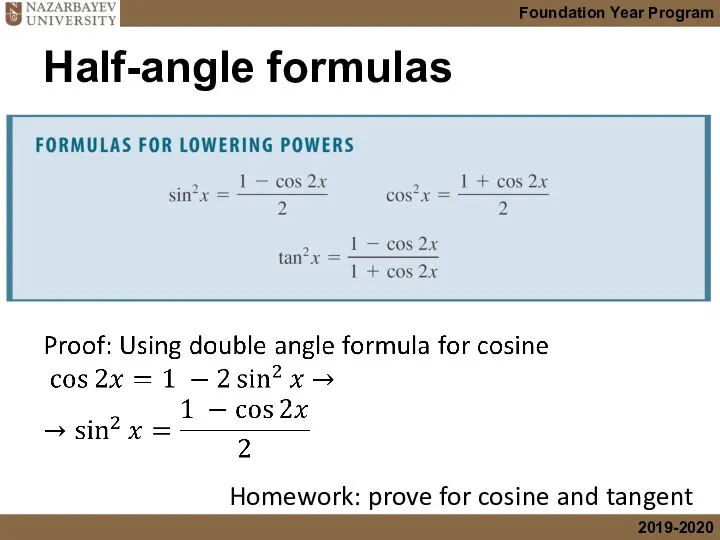
- 28. Half-angle formulas Homework: prove for cosine and tangent
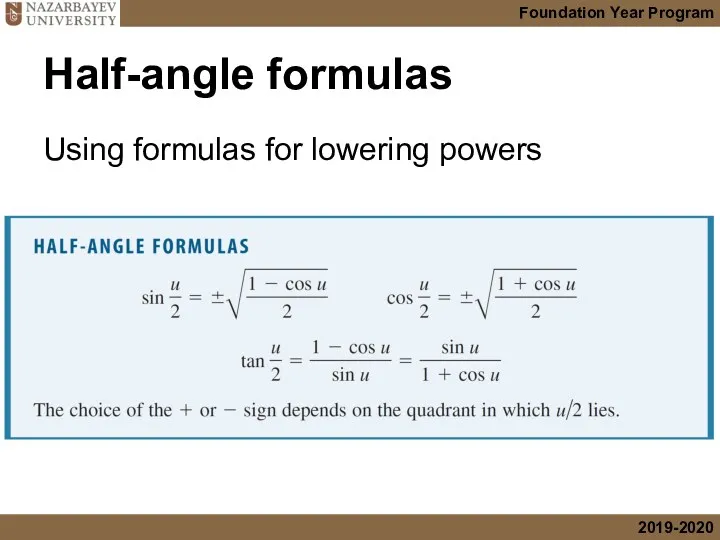
- 29. Half-angle formulas Using formulas for lowering powers
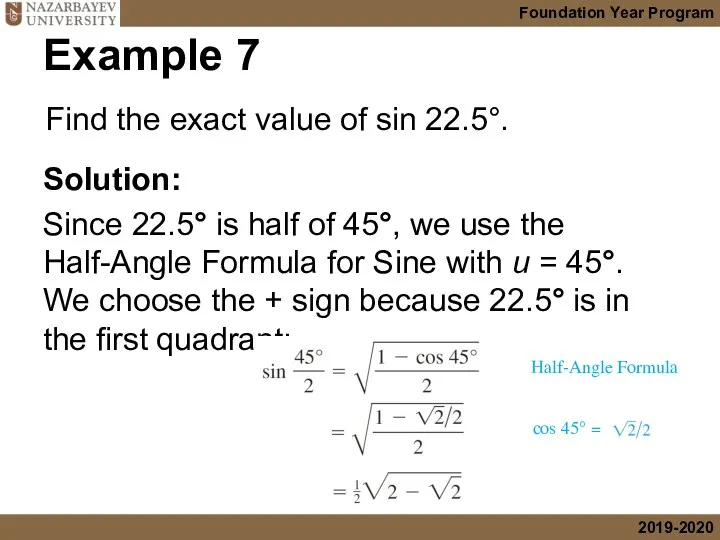
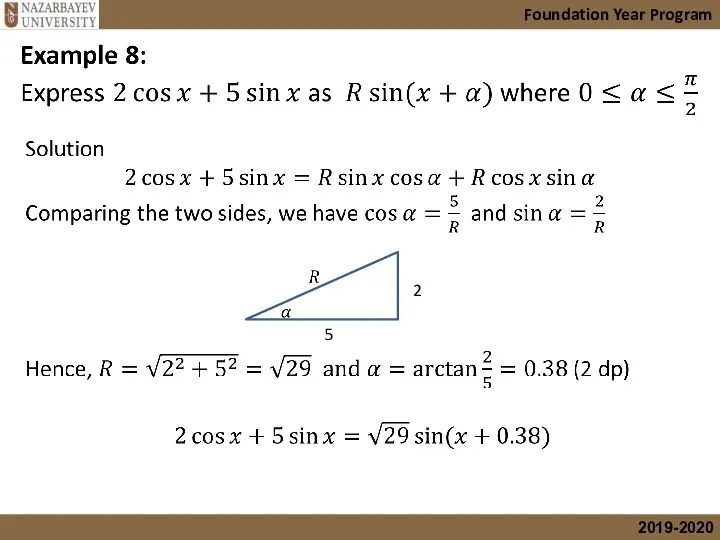
- 30. Example 7 Solution: Since 22.5° is half of 45°, we use the Half-Angle Formula for Sine
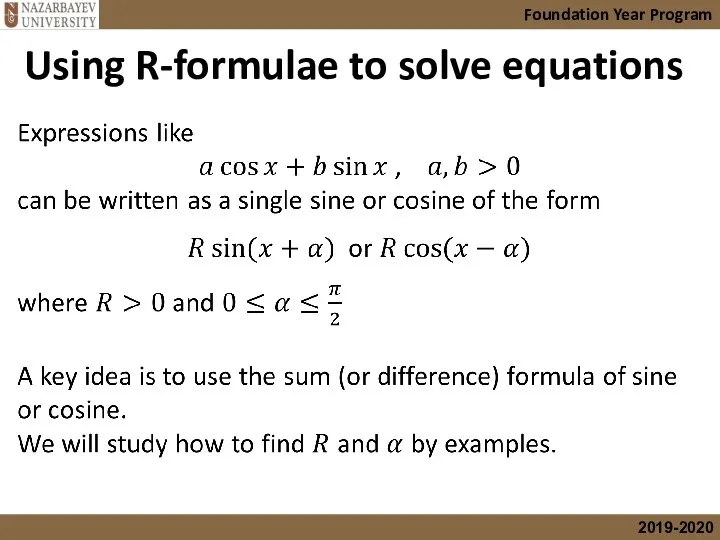
- 31. Using R-formulae to solve equations Foundation Year Program
- 32. Foundation Year Program
- 33. Foundation Year Program
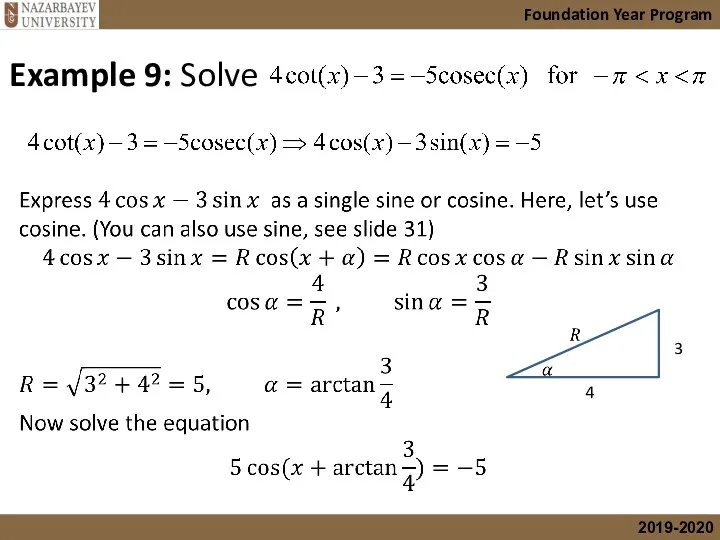
- 34. Foundation Year Program Example 9: Solve
- 35. Foundation Year Program
- 36. Foundation Year Program Alternative expression for the previous example
- 37. Without differentiating find the maximum value of Example 10
- 38. Foundation Year Program Without differentiating find the maximum value of Example 10. Solution Therefore, the maximum
- 39. Foundation Year Program Your turn! Solve
- 40. Foundation Year Program Your turn! Solve
- 41. Foundation Year Program OR But since , the only solutions are
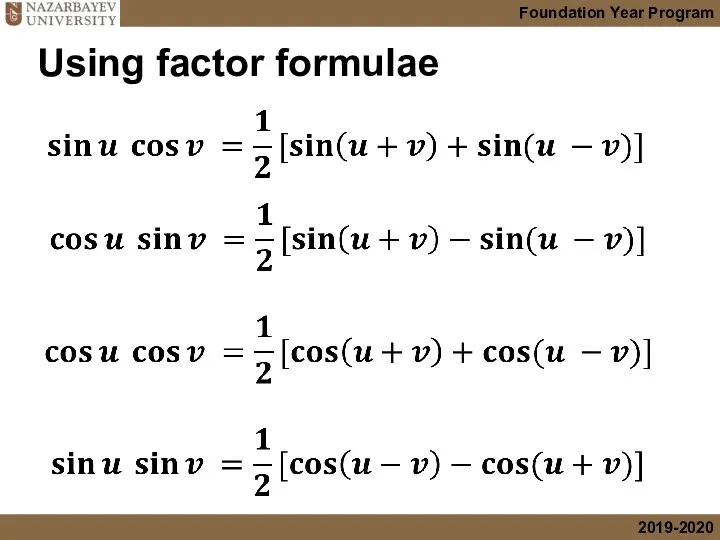
- 42. Using factor formulae
- 43. (1) + (2)
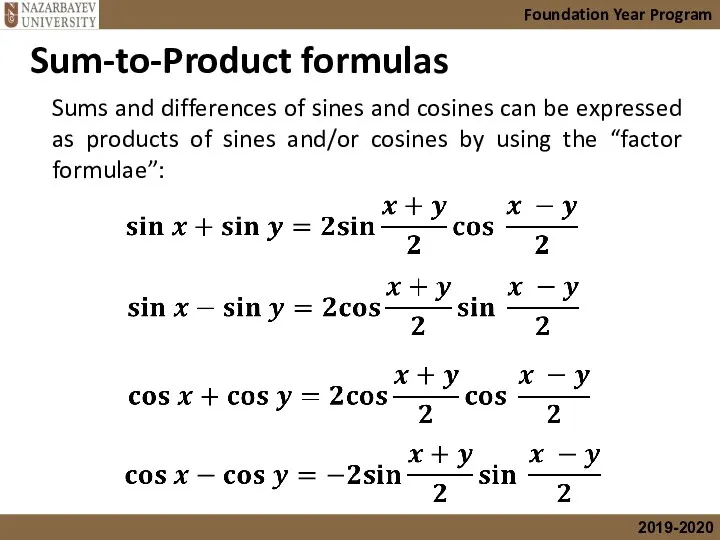
- 44. Sum-to-Product formulas Foundation Year Program Sums and differences of sines and cosines can be expressed as
- 46. Example 11
- 47. Example 11. Solution
- 48. Foundation Year Program Example 12: Solve
- 49. Foundation Year Program OR
- 50. Foundation Year Program Prove that Using factor formula for sines Using factor formula for cosines Example
- 51. Foundation Year Program Your turn! Prove that
- 52. Foundation Year Program Your turn! Prove that Using factor formula for sines Using factor formula for
- 53. Prove Additional Question 1
- 54. Additional Question 2 Prove
- 55. Additional Question 3 Prove
- 56. Additional Question 4 Prove
- 57. Additional Question 5 Prove
- 58. Additional Question 6 Prove
- 59. Additional Question 6
- 60. Additional Question 7 Prove
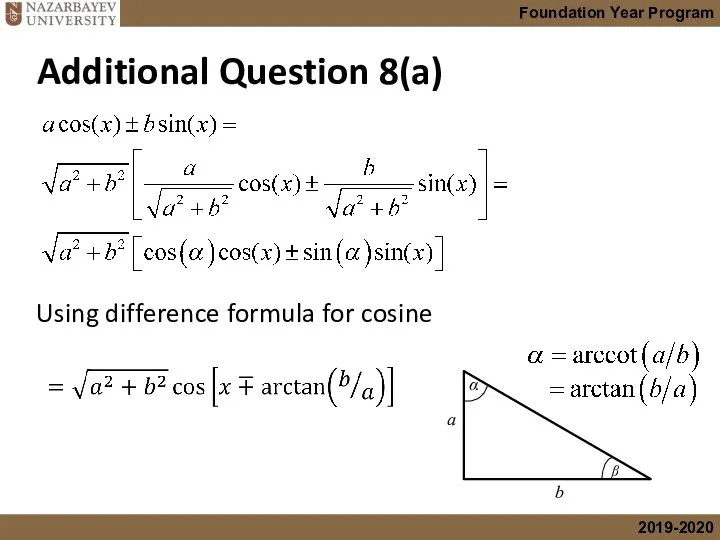
- 61. Prove that expressions of the form where a>0 and b>0, can be expressed in the following
- 62. a b α ᵝ Using difference formula for cosine Additional Question 8(a)
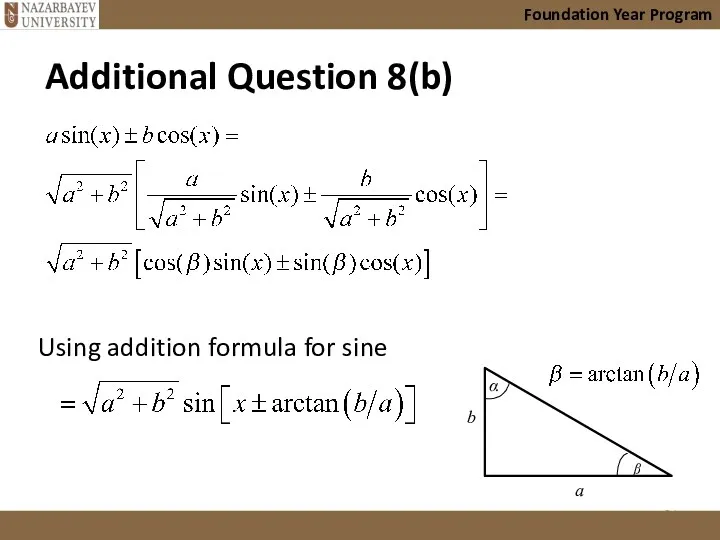
- 63. Prove that expressions of the form where a>0 and b>0, can be expressed in the following
- 64. Foundation Year Program Using addition formula for sine b a α ᵝ Additional Question 8(b)
- 65. Learning outcomes 3.4.1 Apply the addition and subtraction formulas, the half angle and double angle formulas,
- 67. Скачать презентацию








































 Формирование метапредметного умения Решать проблемы и задачи на уроках математики
Формирование метапредметного умения Решать проблемы и задачи на уроках математики Числові характеристики випадкових величин. Модуль 1, Лекція 5
Числові характеристики випадкових величин. Модуль 1, Лекція 5 Геометрия вокруг нас
Геометрия вокруг нас Елементи теорії виміру. Шкали виміру. Лекція 6. Тема 3
Елементи теорії виміру. Шкали виміру. Лекція 6. Тема 3 20230924_chetyryohugolniki
20230924_chetyryohugolniki Построение сечений тетраэдра и параллелепипеда
Построение сечений тетраэдра и параллелепипеда Отношения и предикаты. (Лекция 7)
Отношения и предикаты. (Лекция 7) Статистическая обработка данных. (Лекция 2)
Статистическая обработка данных. (Лекция 2) Презентация ТАНГРАМ Животные
Презентация ТАНГРАМ Животные обыкновенные дроби. дробь - результат деления натуральных чисел
обыкновенные дроби. дробь - результат деления натуральных чисел Параллельность прямых и плоскостей. Параллельные прямые в пространстве
Параллельность прямых и плоскостей. Параллельные прямые в пространстве Объем прямоугольного параллелепипеда
Объем прямоугольного параллелепипеда Счастливый случай. Игра
Счастливый случай. Игра Внеклассное занятие. Математический брейн-ринг. 5 класс
Внеклассное занятие. Математический брейн-ринг. 5 класс Признаки возрастания и убывания функции
Признаки возрастания и убывания функции Деление десятичной дроби на 10, 100, 1000
Деление десятичной дроби на 10, 100, 1000 Взаимное расположение графиков линейных функций
Взаимное расположение графиков линейных функций Конспект урока математики в первом классе Тема: Сложение в пределах 10.
Конспект урока математики в первом классе Тема: Сложение в пределах 10. Готовимся к ГИА, 9 класс. Тест 1, часть 1
Готовимся к ГИА, 9 класс. Тест 1, часть 1 Предел функции
Предел функции Умножение многочлена на одночлен
Умножение многочлена на одночлен Таблица сложения
Таблица сложения Фрактальная графика на языке Turbo Pascal
Фрактальная графика на языке Turbo Pascal Статистические данные
Статистические данные Презентация урока математики в 1 классе
Презентация урока математики в 1 классе Системы уравнений с двумя переменными
Системы уравнений с двумя переменными Решение уравнений. Задание №21 по материалам открытого банка задач ОГЭ по математике
Решение уравнений. Задание №21 по материалам открытого банка задач ОГЭ по математике Закрепление изученного
Закрепление изученного