Содержание
- 2. Contents Linear dependence of vectors Basis on the plane and in space Decomposition of a vector
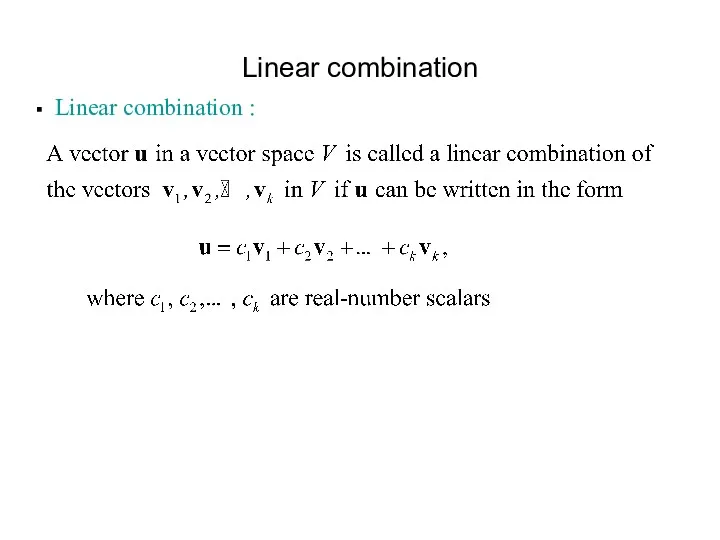
- 3. Linear combination Linear combination :
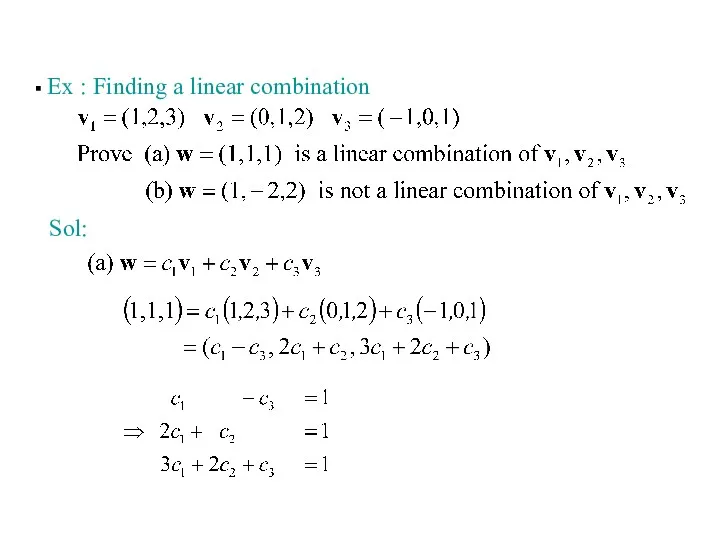
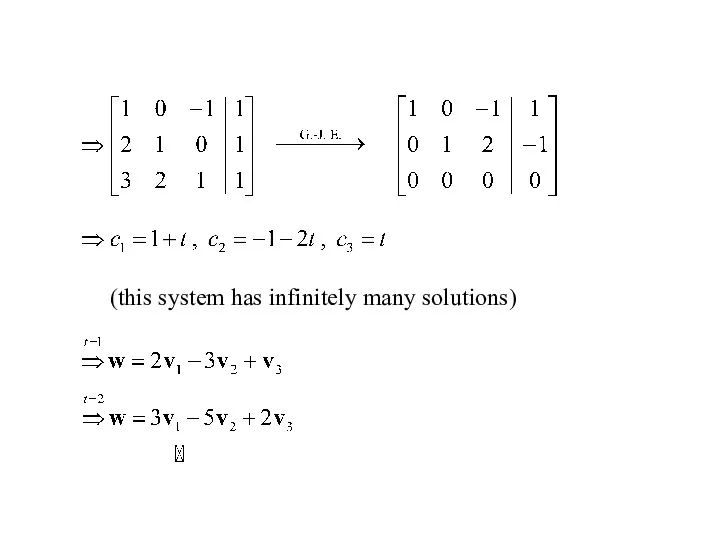
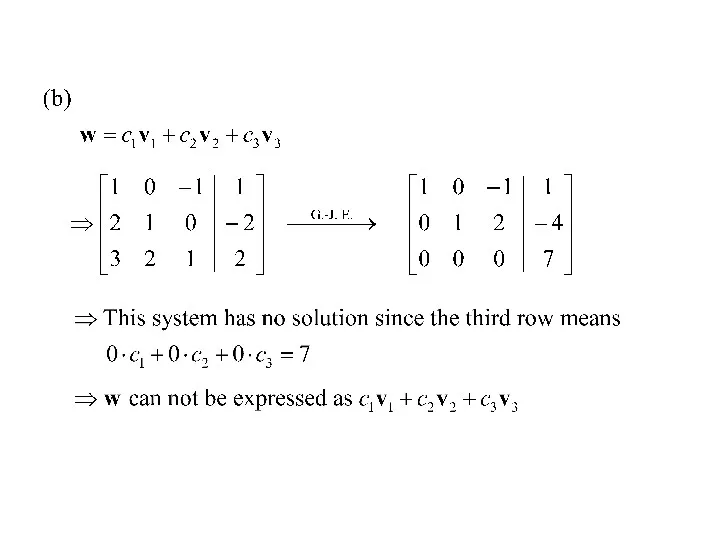
- 4. Ex : Finding a linear combination Sol:
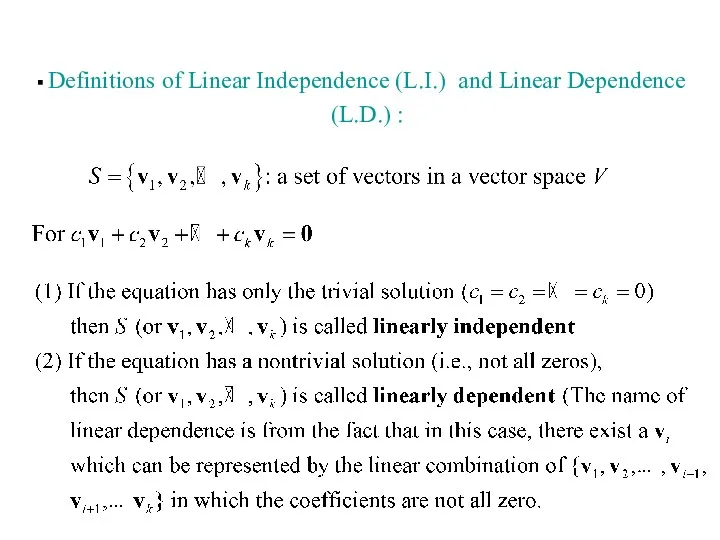
- 8. Definitions of Linear Independence (L.I.) and Linear Dependence (L.D.) :
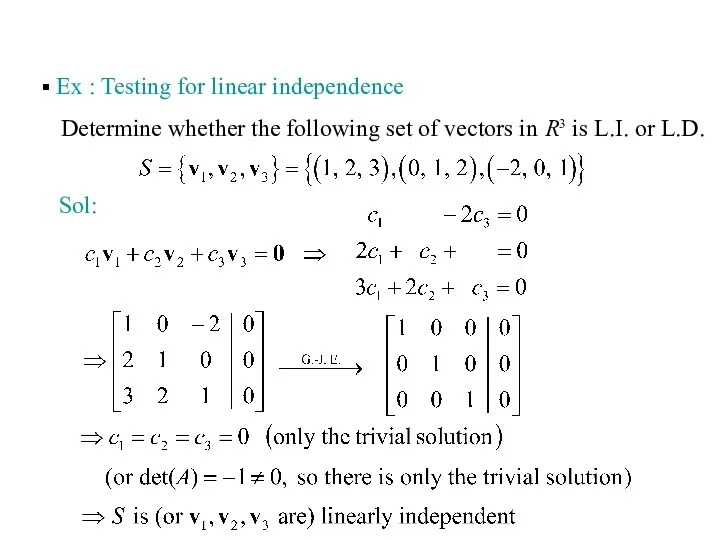
- 9. Ex : Testing for linear independence Sol: Determine whether the following set of vectors in R3
- 10. EX: Testing for linear independence Determine whether the following set of vectors in P2 is L.I.
- 11. Basis Basis : V: a vector space S is linearly independent - S is called a
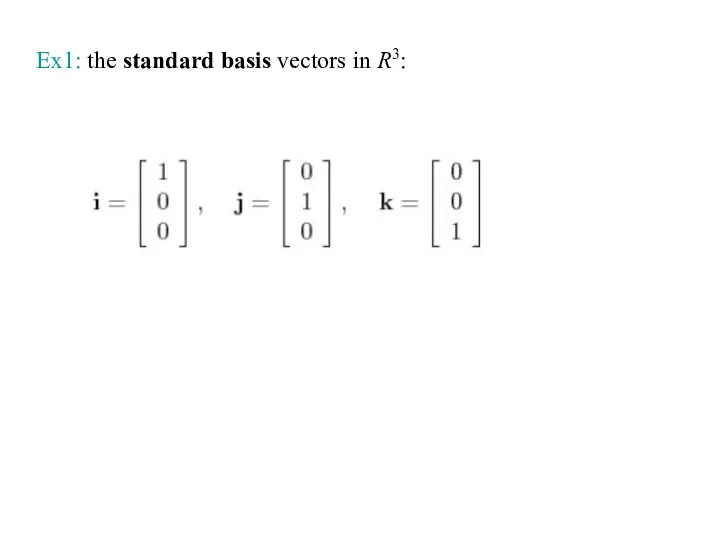
- 12. Ex1: the standard basis vectors in R3:
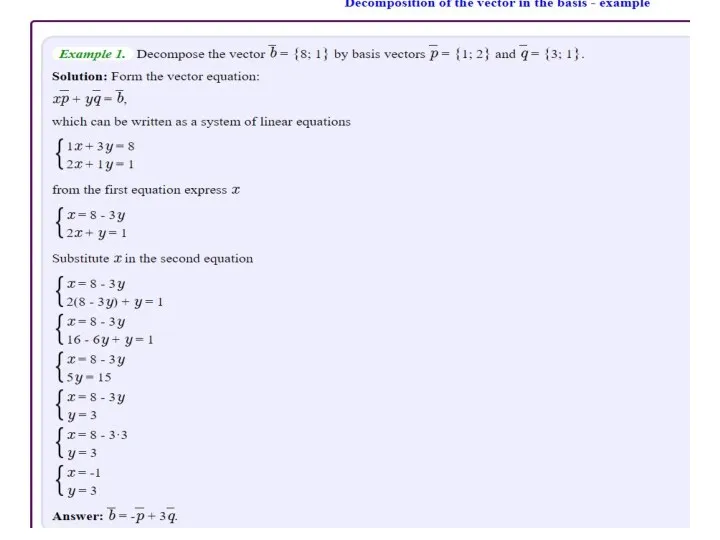
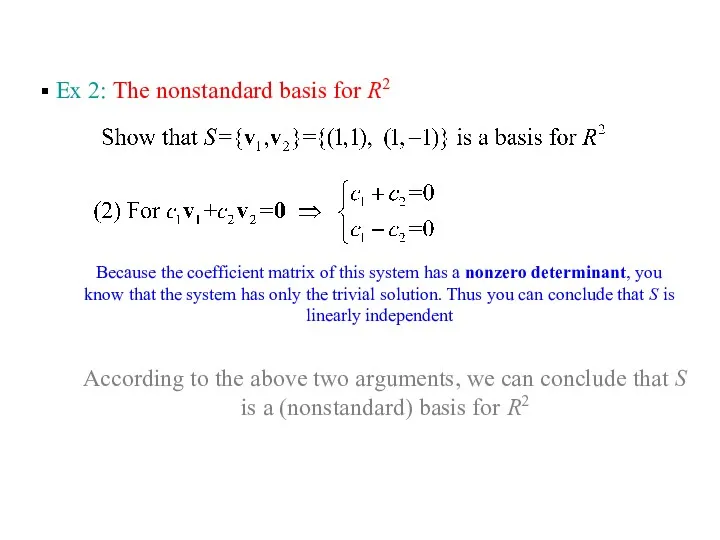
- 13. Ex 2: The nonstandard basis for R2 Because the coefficient matrix of this system has a
- 20. Скачать презентацию



 Угол между скрещивающимися прямыми. 10 класс
Угол между скрещивающимися прямыми. 10 класс Случаи сложения вида +6
Случаи сложения вида +6 Касательная к окружности. Решение задач
Касательная к окружности. Решение задач Сложение чисел с разными знаками
Сложение чисел с разными знаками Работа в программе Excel на уроках математики. Составление таблиц и диаграмм, анализ статистических данных
Работа в программе Excel на уроках математики. Составление таблиц и диаграмм, анализ статистических данных Тригонометрические функции y = sin x и y = cos x . Их свойства и графики
Тригонометрические функции y = sin x и y = cos x . Их свойства и графики Умножение и деление на 10
Умножение и деление на 10 Математика в поэзии
Математика в поэзии Векторная алгебра
Векторная алгебра Розв'язування задач за допомогою рівнянь
Розв'язування задач за допомогою рівнянь Методическая разработка урок математики Единицы длины 3 класс
Методическая разработка урок математики Единицы длины 3 класс Задания для устного счёта Помогите Незнайке (математика, 2 класс)
Задания для устного счёта Помогите Незнайке (математика, 2 класс) Функция. Область определения и область значений функции
Функция. Область определения и область значений функции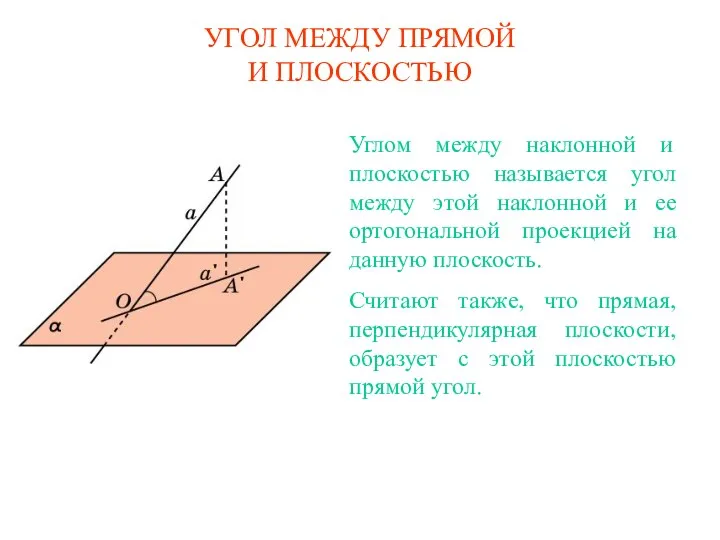 5.Угол между прямой и плоскостью (куб), задачи
5.Угол между прямой и плоскостью (куб), задачи Действия над конечными случайными величинами
Действия над конечными случайными величинами Презентация к уроку математики в 4 классе по теме ПОСТРОЕНИЕ ТОЧЕК ПО ИХ КООРДИНАТАМ.
Презентация к уроку математики в 4 классе по теме ПОСТРОЕНИЕ ТОЧЕК ПО ИХ КООРДИНАТАМ. Решение задач на проценты. Урок математики в 5 классе
Решение задач на проценты. Урок математики в 5 классе Теріс сандарды қосу
Теріс сандарды қосу Прямоугольная система координат
Прямоугольная система координат Определение квадратичной функции. Упражнение 5
Определение квадратичной функции. Упражнение 5 Координаты на прямой
Координаты на прямой Экстремумы функции
Экстремумы функции Комплексные числа
Комплексные числа Деление многозначного числа на двузначное
Деление многозначного числа на двузначное Статистическая обработка информации
Статистическая обработка информации Объемы многогранников и тел вращения
Объемы многогранников и тел вращения Математический морской бой
Математический морской бой Урок математики 2 класс УМК Планета знаний Тема: Наглядная геометрия
Урок математики 2 класс УМК Планета знаний Тема: Наглядная геометрия