Содержание
- 2. OBJECTIVES At the end of this presentation the participant will be able to: Discuss Operation Smile
- 3. Operation Smile’s Commitment Safe quality surgical care for every child, every time
- 4. Perioperative Nursing Provide safe, efficient, and caring environment for each surgical patient. Minimize patient risk for
- 5. Infection Risk Contaminated instruments Inadequately cleaned and sterilized Contaminated after sterilization. Safe practice recommendations Apply principles
- 6. Operation Smile Ensuring Safe Surgery Global Standards of Care Standard 3.6 Requires equipment for proper sterilization
- 7. Purpose of Operation Smile Sterilization Policy Ensure that recommended standards of practice with regards to infection
- 8. Medical Policy 5.6 Sterilization All critical items such as instruments, supplies and equipment used during surgical
- 9. Policy - 2 Items are considered sterile that have undergone one of several sterilization methods including
- 10. Policy - 3 All facility processed re-useable critical items will be considered unsterile after being packed
- 11. Policy - 4 All manufactured sterile supplies must be stored within a closed container in a
- 12. Policy - 5 During missions saturated steam under pressure will be the method of sterilization for
- 13. How do we accomplish all this in a mission setting?
- 14. Quality Assurance Procedures Let’s all get on the same page!!
- 15. Implementation Common problems Achieving sterilization between cases Monitoring sterilization processes Adjusting to local hospital policy Preparation
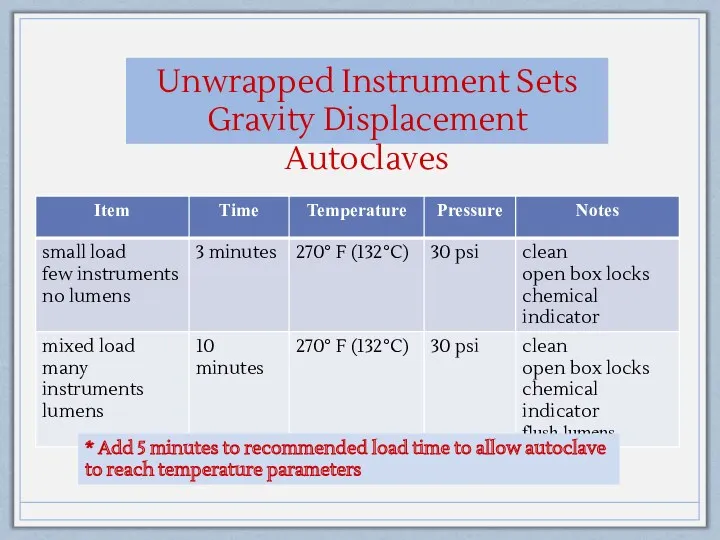
- 16. Unwrapped Instrument Sets Gravity Displacement Autoclaves * Add 5 minutes to recommended load time to allow
- 17. Load time unwrapped items Operation Smile Autoclaves Reach parameters – 5 minutes Exposure time – 10
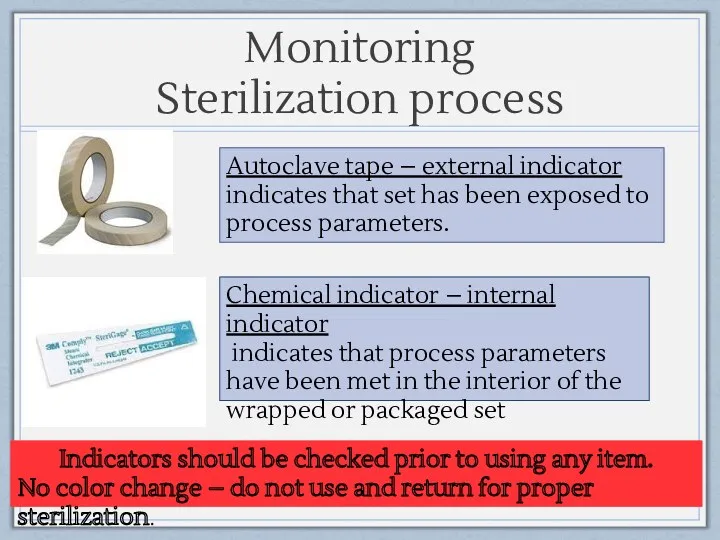
- 18. Monitoring Sterilization process Autoclave tape – external indicator indicates that set has been exposed to process
- 19. Wrapped Instrument Sets Operation Smile Autoclave Wrapped sets require drying time. Drying time requires 15-60 minutes
- 20. Wrapped or Packaged Instrument Sets in Operation Smile Autoclave *Not recommended without use of minimum drying
- 21. Soft Tissue Surgical Set Cleaning and Inspection Guidelines Keith Ballance August 2014
- 22. Instrument wrap Usually supplied by hospital Should be square wrap with a 6 inch border around
- 23. Rigid containers Place manufacturer approved unidirectional filter paper in disc holder in the bottom and top
- 24. Hospital sterilization At the end of day instruments sets are cleaned, assembled and wrapped, then taken
- 25. Wet packs? If the exterior wrap is damp or wet or if condensate/water droplets are found
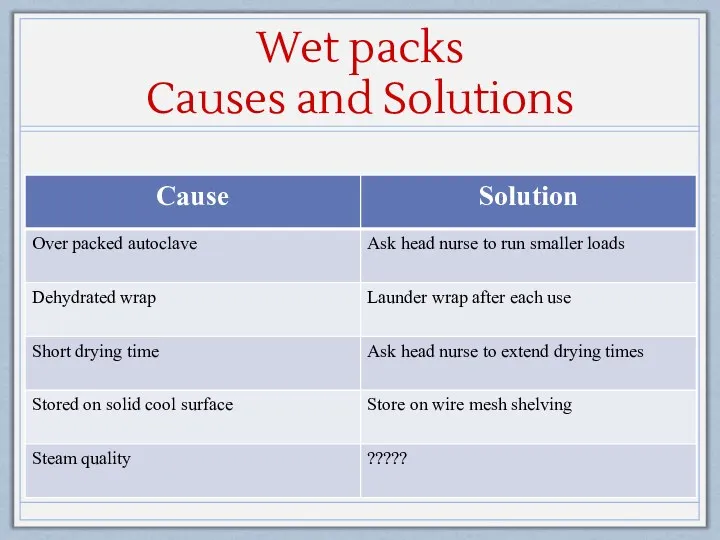
- 26. Wet packs Causes and Solutions
- 27. High Level Disinfection (HLD) Process of destroying or inhibiting growth of pathogenic microorganisms on inanimate objects.
- 28. HLD Policy All semi-critical items that will be re-used for patient care will undergo high level
- 29. HLD is NOT Sterilization
- 30. Purpose of HLD Disinfect semi-critical items, which are those that come into contact with non-intact skin
- 31. Preparation of Disinfectant Solution Diluted household bleach: 1:20 dilution 1 part bleach to 20 parts water.
- 32. HLD Procedure Prepare disinfectant solution Submerge item in solution Soak/contact time 12-30 minutes Minimum contact time
- 34. WON’T DO
- 35. TRUST Patients and surgeons TRUST that we have provided a sterile environment. Surgical Conscience
- 36. Future Goals Monitoring the effectiveness of sterilization processes with biological indicator testing Unidirectional filter paper for
- 37. Summary Sterilization and disinfection is a nursing responsibility that involves the trust of the patient and
- 38. Resources Alexander’s Care of the Patient in Surgery, Jane C. Rothrock, 15th edition, Mosby Elsevier, 2015.
- 40. Скачать презентацию


































 Виды переломов плоских костей
Виды переломов плоских костей Физиология сенсорных систем. Физиология боли
Физиология сенсорных систем. Физиология боли Структура и функции пульпы. Этиология и патогенез пульпита у детей. Классификация пульпита. Лекция 1
Структура и функции пульпы. Этиология и патогенез пульпита у детей. Классификация пульпита. Лекция 1 Эндометриоз. Актуальность проблемы
Эндометриоз. Актуальность проблемы Коклюш
Коклюш International Federation of Medical Students’ Associations
International Federation of Medical Students’ Associations Бронхиальная астма
Бронхиальная астма Хроническая сердечна недостаточность
Хроническая сердечна недостаточность Патологія серцево-судинної системи
Патологія серцево-судинної системи Лекарственные растения
Лекарственные растения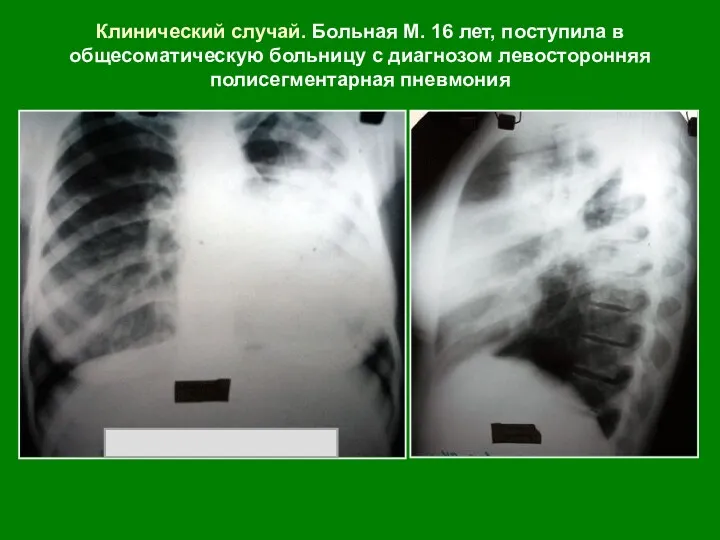 Инфильтративный туберкулез легких. Казеозная пневмония
Инфильтративный туберкулез легких. Казеозная пневмония Дәрілік өсімдіктер
Дәрілік өсімдіктер Основы гомеопатии
Основы гомеопатии Эвтаназия
Эвтаназия Участие в диагностике и лечении заболеваний сельскохозяйственных животных
Участие в диагностике и лечении заболеваний сельскохозяйственных животных Болезнь Пертеса у детей
Болезнь Пертеса у детей Work of cardiologist
Work of cardiologist Патология беременности
Патология беременности Жатыр мойны және денесінің обыры тақырыбына презентация
Жатыр мойны және денесінің обыры тақырыбына презентация Стоматологическая заболеваемость. Эпидемиологические методы обследования и их роль в профилактике. (Лекция 3)
Стоматологическая заболеваемость. Эпидемиологические методы обследования и их роль в профилактике. (Лекция 3)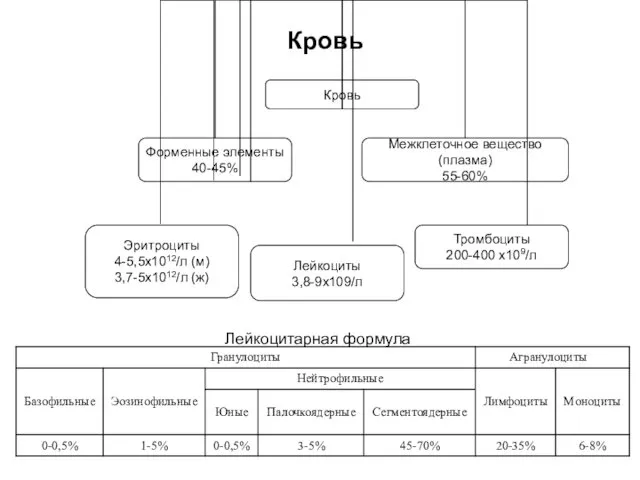 Кровь. Форменные элементы крови
Кровь. Форменные элементы крови Пародонт. Аурулары. Жіктелісі. Этиологиясы. Патогенезі
Пародонт. Аурулары. Жіктелісі. Этиологиясы. Патогенезі Адаптация – определение, видове, значение. Дезадаптация – разстройства на различните психични функции
Адаптация – определение, видове, значение. Дезадаптация – разстройства на различните психични функции Дифференциальная диагностика кровохарканья и легочного кровотечения
Дифференциальная диагностика кровохарканья и легочного кровотечения Elizabeth Blackwell (1821-1910)
Elizabeth Blackwell (1821-1910) The hormonal regulation of the body
The hormonal regulation of the body Сахарный диабет, как социально-значимое заболевание
Сахарный диабет, как социально-значимое заболевание Біріншілік туберкулез
Біріншілік туберкулез