Содержание
- 3. Antianginal Agents 1.Organic Nitrates 2. β-Blockers 3. Calcium Channel Blockers 4. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors
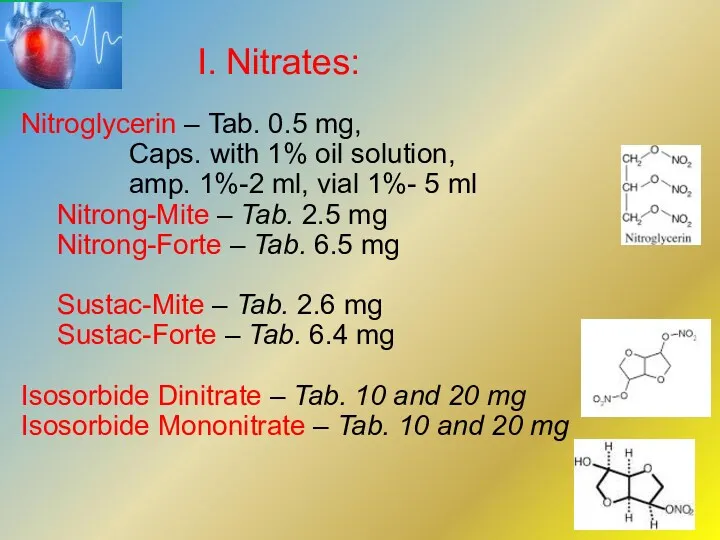
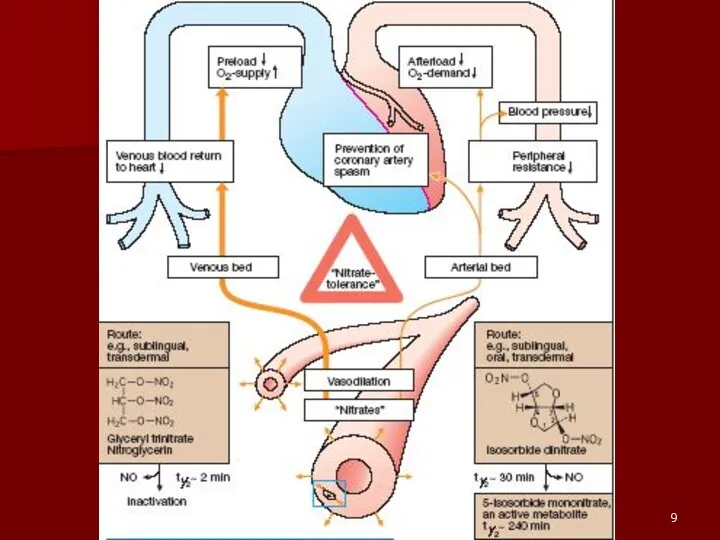
- 4. I. Nitrates: Nitroglycerin – Tab. 0.5 mg, Caps. with 1% oil solution, amp. 1%-2 ml, vial
- 6. Nitroglycerin - tab. 0.0005 g (0.5 mg), amp. 1%-2 ml, vial 1% spirituous sol. - 5
- 8. Clinucal uses of Nitroglycerine: Prophylaxis and Control of Angina Attack IV Infusion in Myocardial Infarction Pulmonary
- 10. Overdose With Nitroglycerine: Vasodilation and Methemoglobinemia - ⮚ Hypotension, Throbbing Headache, Palpitations, ⮚ Visual disturbances, Flushing
- 11. Treatment of overdose with nitroglycerine: Gastric Lavage; Activated Charcoal Oxygen therapy (Hyperbaric Oxygenation) Antidotes: Ascorbic acid
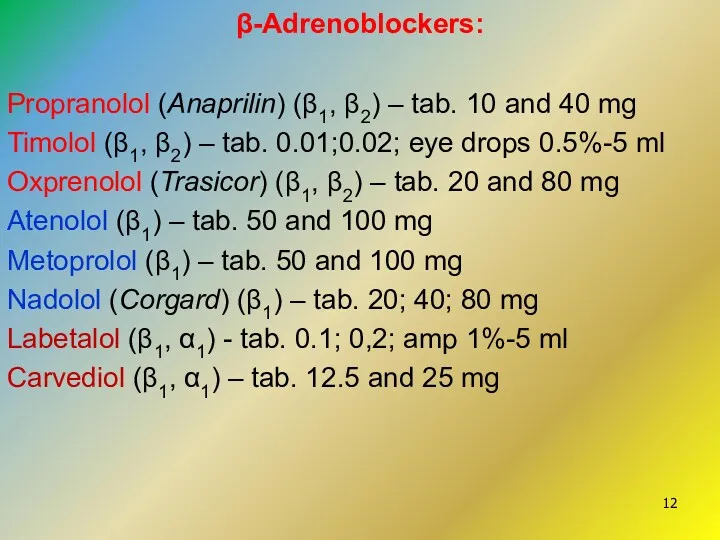
- 12. β-Adrenoblockers: Propranolol (Anaprilin) (β1, β2) – tab. 10 and 40 mg Timolol (β1, β2) – tab.
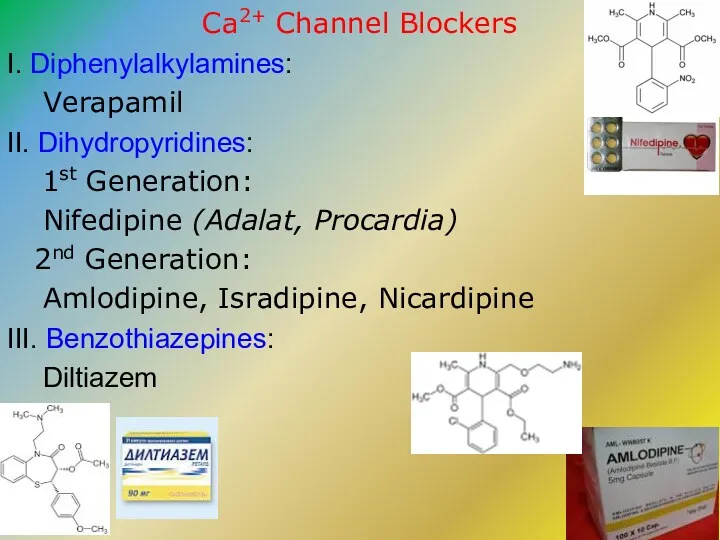
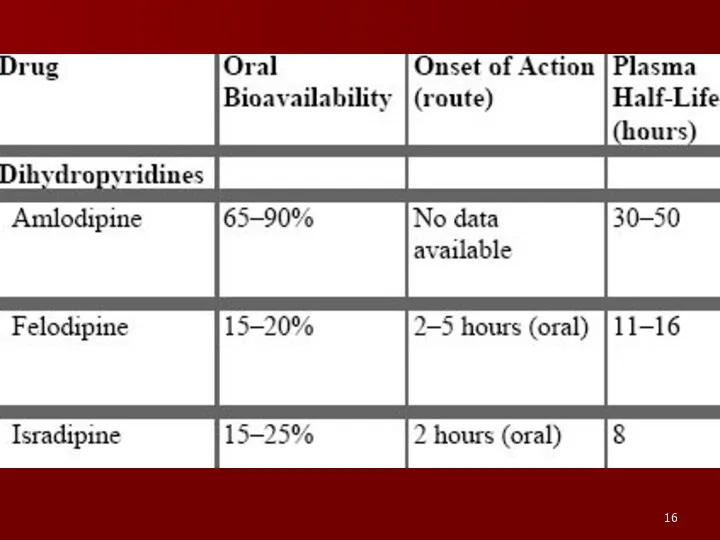
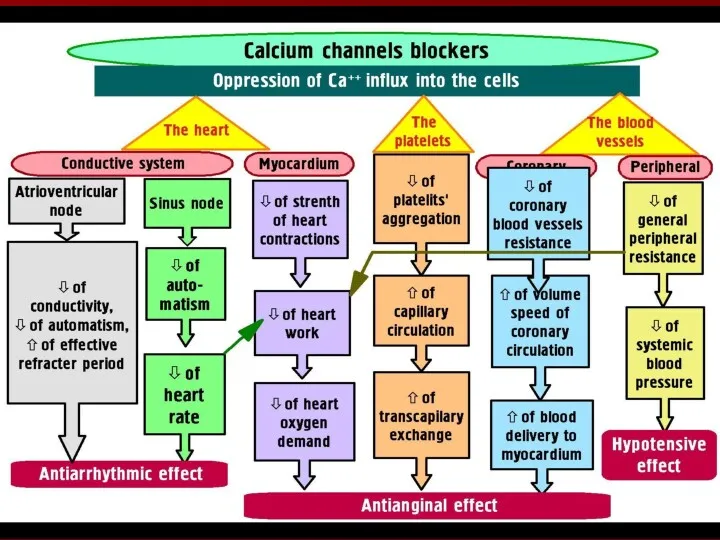
- 13. Ca2+ Channel Blockers I. Diphenylalkylamines: Verapamil II. Dihydropyridines: 1st Generation: Nifedipine (Adalat, Procardia) 2nd Generation: Amlodipine,
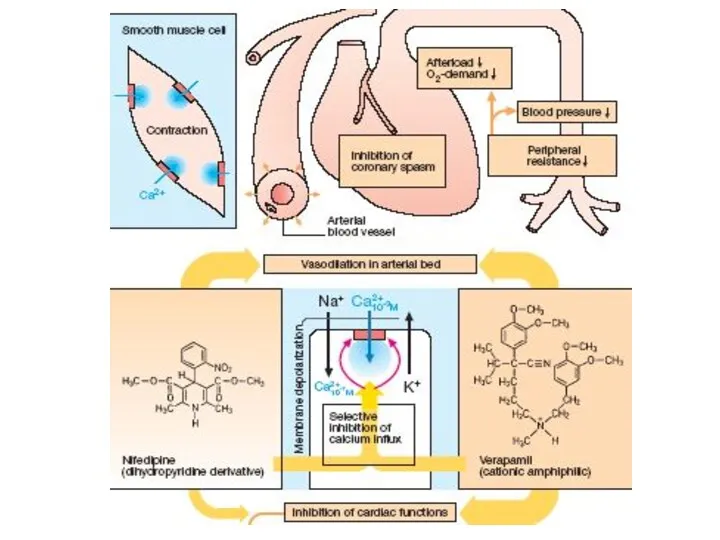
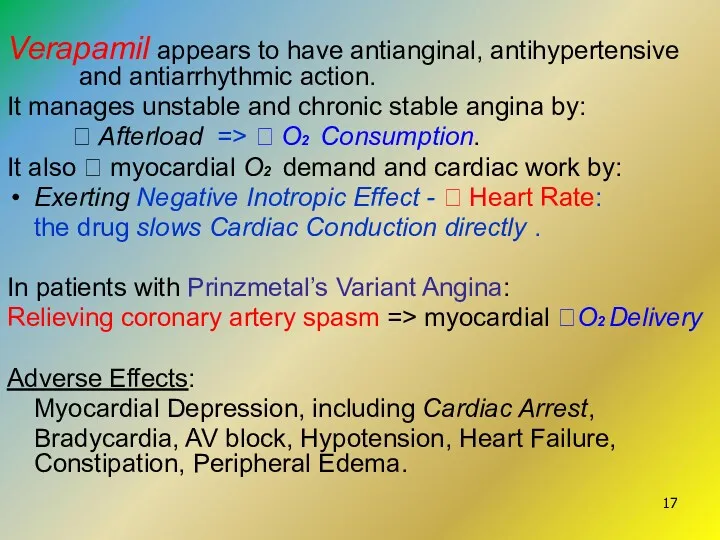
- 17. Verapamil appears to have antianginal, antihypertensive and antiarrhythmic action. It manages unstable and chronic stable angina
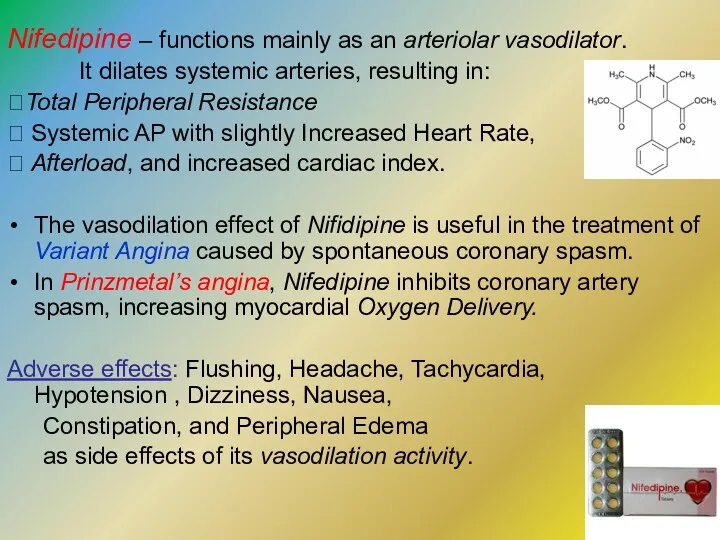
- 19. Nifedipine – functions mainly as an arteriolar vasodilator. It dilates systemic arteries, resulting in: ?Total Peripheral
- 20. Amlodipine is a Dihydropyridine compound – the 2nd Generation long-acting Ca2+ antagonist. It blocks the inward
- 21. The Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors: Captopril, Lisinopril, Enalapril block the ACE that cleaves Angiotensin I to
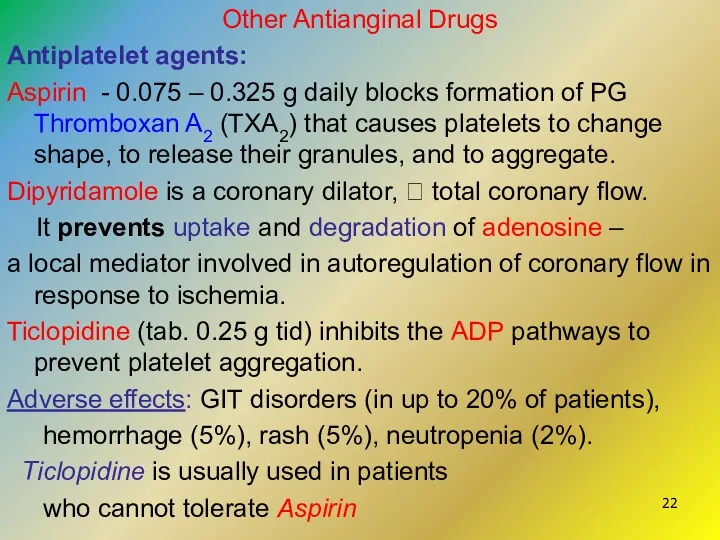
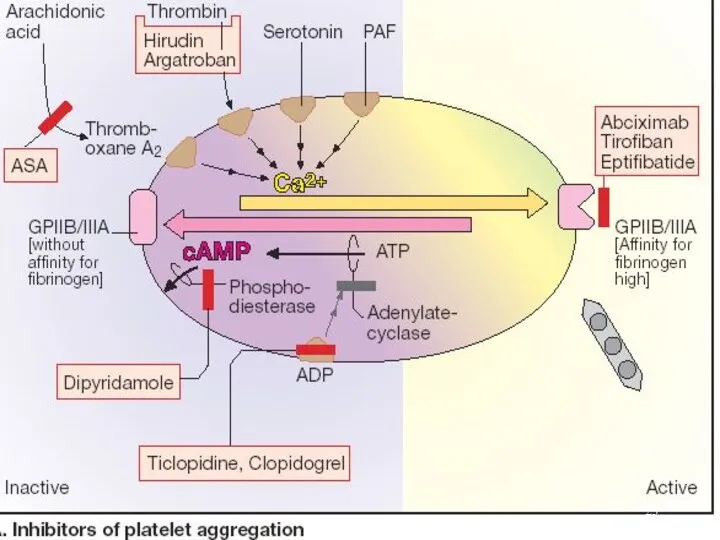
- 22. Other Antianginal Drugs Antiplatelet agents: Aspirin - 0.075 – 0.325 g daily blocks formation of PG
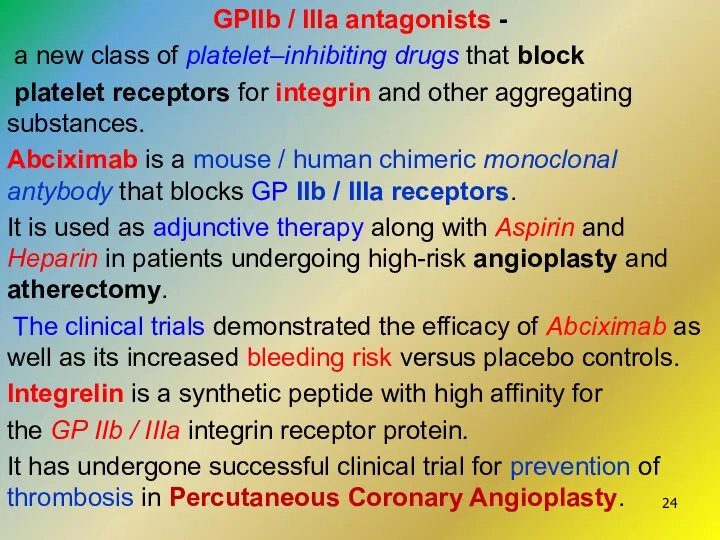
- 24. GPIIb / IIIa antagonists - a new class of platelet–inhibiting drugs that block platelet receptors for
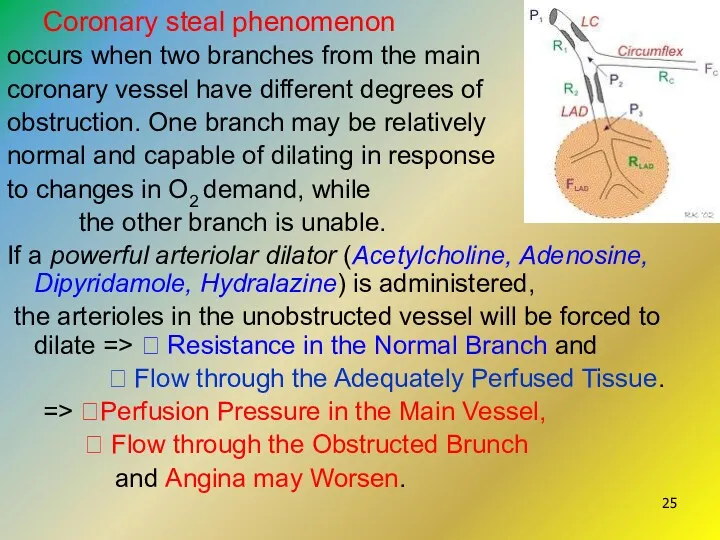
- 25. Coronary steal phenomenon occurs when two branches from the main coronary vessel have different degrees of
- 26. Drugs for the Treatment of Acute Myocardial Infarction The major principles treatment of AMI: Pain syndrome
- 27. Neuroleptanalgesia with Fentanyl 0.005% 2-4 ml Droperidol 0.25%-1-4 ml - is a base of all schemes
- 28. Thrombolytic Therapy: Alteplase or Streptokinase to dissolve the thrombus pharmacologically Heparin is given to prevent a
- 29. Agents Regulating Cerebral Circulation I. Agents affecting the platelet aggregation and coagulation 1. Antiaggregants (Antitplatelet Drugs):
- 30. 2. Derivatives of Vinca alkaloids - derived from the Lesser Periwinkle plant (Vinca minor): Vinpocetin (Cavinton)
- 31. Pentoxiphylline - Tab. 0.1 g, amp. 2% solution 5 ml - a Methylxanthine derivative. Mechanism of
- 32. Instenon is a combined drug for the treatment of Ischemic Cerebrovascular Diseases. It contains: Methylxanthine Ethophylline,
- 33. Vinpocetin (Cavinton) tab. 5 mg, amp. 0.5%-2 ml is an alkaloid derivative from Periwinkle (Vinca minor).
- 34. Nicergolin (Sermion) – tab. 5 mg, 10 mg; vial 4 mg IM combines the structures of
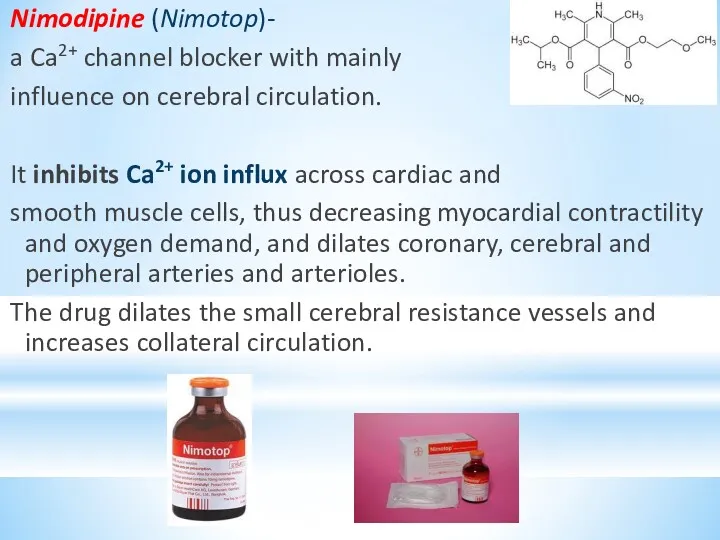
- 35. Nimodipine (Nimotop)- a Ca2+ channel blocker with mainly influence on cerebral circulation. It inhibits Ca2+ ion
- 37. Скачать презентацию















 Дегенерация сетчатки глаза
Дегенерация сетчатки глаза Определение ССГ, данное на международном симпозиуме по сухому глазу (DEWS)
Определение ССГ, данное на международном симпозиуме по сухому глазу (DEWS) ДВС-синдром
ДВС-синдром Тоқ ішектің қатерлі ісігі
Тоқ ішектің қатерлі ісігі Гнойная хирургия у детей
Гнойная хирургия у детей Ортодонтическое лечение. Общий план
Ортодонтическое лечение. Общий план Ведение послеоперационных больных со стриктурой уретры
Ведение послеоперационных больных со стриктурой уретры Третичный период сифилиса
Третичный период сифилиса Грипп
Грипп Нефротический синдром
Нефротический синдром Починка, коррекция и реставрация полных съемных протезов
Починка, коррекция и реставрация полных съемных протезов Апластические анемии
Апластические анемии Противоопухолевой иммунитет. Теории канцерогенеза
Противоопухолевой иммунитет. Теории канцерогенеза Нервная анорексия и булимия
Нервная анорексия и булимия Вступ в курс інфектології. Поняття про інфекційні хвороби. Особливості інфекційних хвороб. Класифікація
Вступ в курс інфектології. Поняття про інфекційні хвороби. Особливості інфекційних хвороб. Класифікація Тромботические микроангиопатии. Большая проблема или интересная задача
Тромботические микроангиопатии. Большая проблема или интересная задача Особенности работы медицинской сестры общей практики с пациентами детского возраста в амбулаторно-поликлинических условиях
Особенности работы медицинской сестры общей практики с пациентами детского возраста в амбулаторно-поликлинических условиях Трихинеллез. Эпизоотологические данные
Трихинеллез. Эпизоотологические данные Эволюция хирургического лечения рака молочной железы
Эволюция хирургического лечения рака молочной железы Гравидограмма
Гравидограмма Алалияның симптоматикасы мен механизмі
Алалияның симптоматикасы мен механизмі Дәрілік өсімдік шикізаттың химиялық құрамы
Дәрілік өсімдік шикізаттың химиялық құрамы How does your body gain immunity
How does your body gain immunity Особенности ведения пациента с ожирением: взгляд эндокринолога
Особенности ведения пациента с ожирением: взгляд эндокринолога Открытый прикус
Открытый прикус Экстремальные состояния. Шок, коллапс, кома. Причины, механизмы развития, последствия
Экстремальные состояния. Шок, коллапс, кома. Причины, механизмы развития, последствия Введения лекарственных веществ через рот - жидких форм разным видам животных
Введения лекарственных веществ через рот - жидких форм разным видам животных Практические аспекты трахеостомии
Практические аспекты трахеостомии