Слайд 2
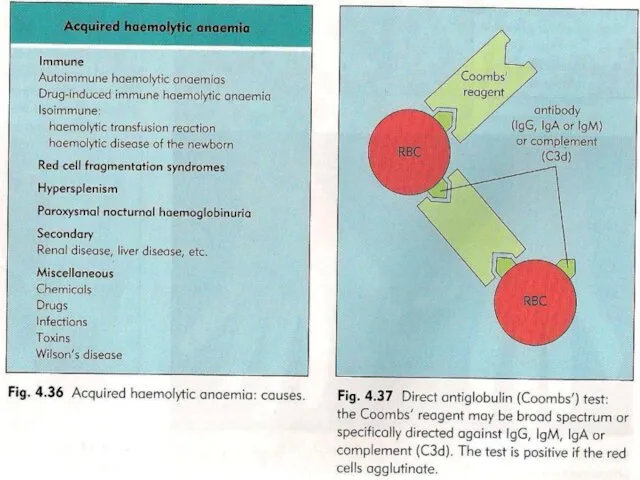
Слайд 3

Слайд 4

EPIDEMIOLOGY
Incidence: 10:1000000 population
Women>men
Usually midlife, can occur at any age
50% idiopathic
Can be
associated with autoimmune diseases, drugs, B-lymphoproliferative disorders – CLL, NHL
Слайд 5

CLINICAL FINDINGS
Jaundice, usually mild
Signs and symptoms of anemia – acute or
chronic
30% splenomegaly
Lymphadenopathy, fever, renal falure, rash, petechiae or echymoses – alert of other underlying disease
Evan’s syndrome – AIHA and Imuune Thrombocytopenia
Слайд 6

LABORATORY EVALUATION
Anemia with enhanced erythropoesis
Reticulocytosis
Blood smear: spherocytes, occasional fragments, nucleated RBC
Bone
marrow – erythroid hyperplasia, megaloblastosis with folate deficiency
Слайд 7

LABORATORY EVALUATION
Unconjugated bilirubinemia, increased LDH, low haptoglobin
Intravascular hemolysis – free Hb
in plasma, hemosiderin in urine
DAT + IgG or Complement on patient’s RBC - in 80% of AIHA positive
Слайд 8
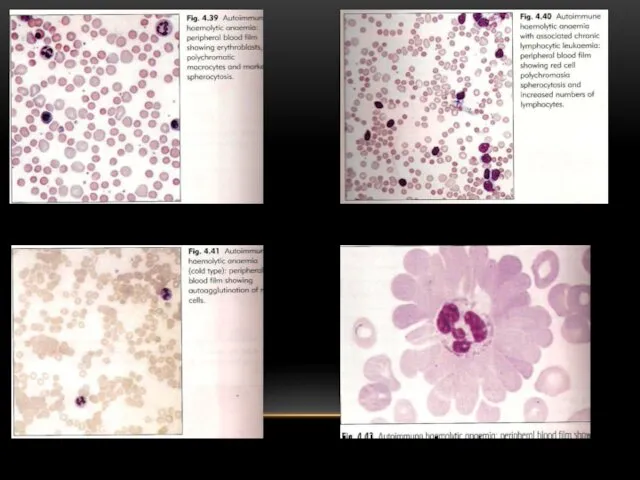
Слайд 9

TREATMENT
Transfusion, if severe symptomatic anemia, with steroids, close follow up and
monitoring
Corticosteroids – prednisone 1-2 mg/kg/day in two divided doses, continue until Hb≥10, than slow tapering down
Splenectomy in steroid refractory or dependent cases, 50-60% response
IVIG 0.4 gr/kg/day for 5 days
Cytotoxic: azathioprine, cytoxane, vincristine
Danazol
Слайд 10

COLD AGGLUTININ DISEASE
Antibodies that bind RBC at cold temperature (5-18°C), usually
IgM
Chronic – idiopathic or associated with B cell lymphoma
Transient – post infectious Mycoplasma Pneumonia, EBV, HIV, collagen vascular disease
Слайд 11

THERAPY
Warming, warmed blood transfusion
Prednisone, splenectomy - mostly non beneficial
Plasma exchange
- temporal relief
Chemotherapy – azathioprine, CVP
Immune suppression – Ciclosporin A, etc.
Treatment of the underlying disease










 Современная концепция естественного вскармливания
Современная концепция естественного вскармливания Deontology. Introduction
Deontology. Introduction Фармакология витамина Е
Фармакология витамина Е Разбор клинического случая. Демонстрация пациента
Разбор клинического случая. Демонстрация пациента Рак лёгкого
Рак лёгкого Тағамдық аллергия
Тағамдық аллергия Сестринская помощь пациентам с впервые выявленной бронхиальной астмой
Сестринская помощь пациентам с впервые выявленной бронхиальной астмой Онкогенні папіломавіруси
Онкогенні папіломавіруси Тістердің бұзылуы және олардың жоғалту кезіндегі морфологиялық және функционалды өзгерістер
Тістердің бұзылуы және олардың жоғалту кезіндегі морфологиялық және функционалды өзгерістер Нарушения ритма сердца. Синдром нарушения ритма
Нарушения ритма сердца. Синдром нарушения ритма Tratamentul Diabetului zaharat 2
Tratamentul Diabetului zaharat 2 Розацеа. Этиология и патогенез
Розацеа. Этиология и патогенез Энтеробактерии. Эшерихии
Энтеробактерии. Эшерихии Лечение опухолей толстого кишечника: лучевая и химиотерапия
Лечение опухолей толстого кишечника: лучевая и химиотерапия Лечебная физкультура при инфаркте миокарда
Лечебная физкультура при инфаркте миокарда Проводящие пути центральной нервной системы
Проводящие пути центральной нервной системы Факторы иммунитета. Новый мир COVID-19. Инфекции и прививки
Факторы иммунитета. Новый мир COVID-19. Инфекции и прививки Патофизиология эндокринной системы
Патофизиология эндокринной системы Целиакия у детей. Дифференциальный диагноз
Целиакия у детей. Дифференциальный диагноз Вирус бешенства
Вирус бешенства Лазеры в хирургии
Лазеры в хирургии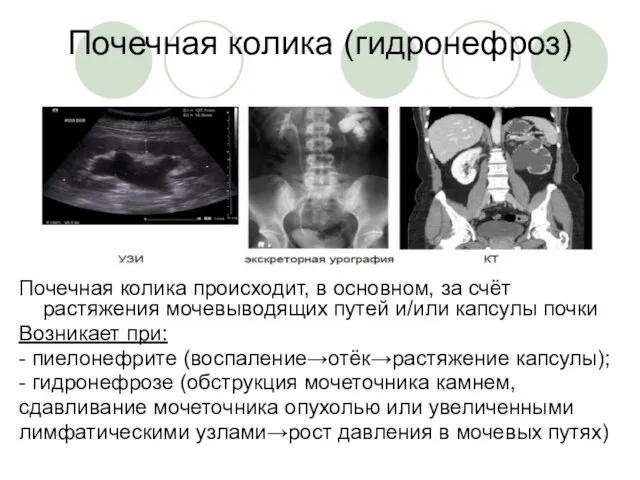 Неотложная радиология в урологии. Почечная колика
Неотложная радиология в урологии. Почечная колика Протиста (только жгутиковые)
Протиста (только жгутиковые) Акне (Угри)
Акне (Угри) Фиброз и цирроз печени. Гемахроматоз. Болезнь Вильсона
Фиброз и цирроз печени. Гемахроматоз. Болезнь Вильсона Методы диагностики микобактерий туберкулеза
Методы диагностики микобактерий туберкулеза Чорна смерть. Чума
Чорна смерть. Чума Хронический панкреатит. Диагностика и лечение
Хронический панкреатит. Диагностика и лечение