Содержание
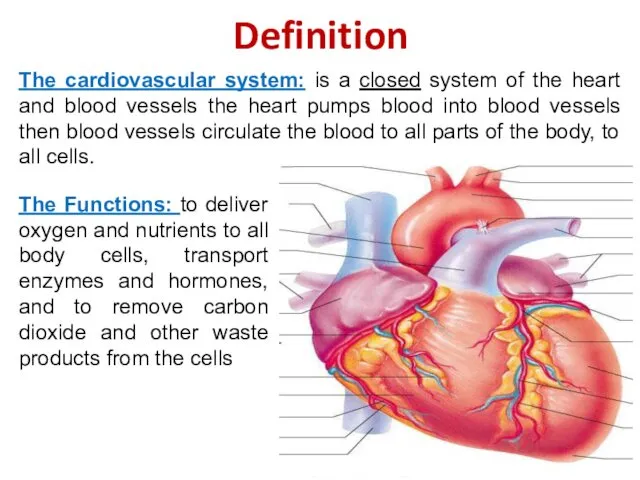
- 2. Definition The cardiovascular system: is a closed system of the heart and blood vessels the heart
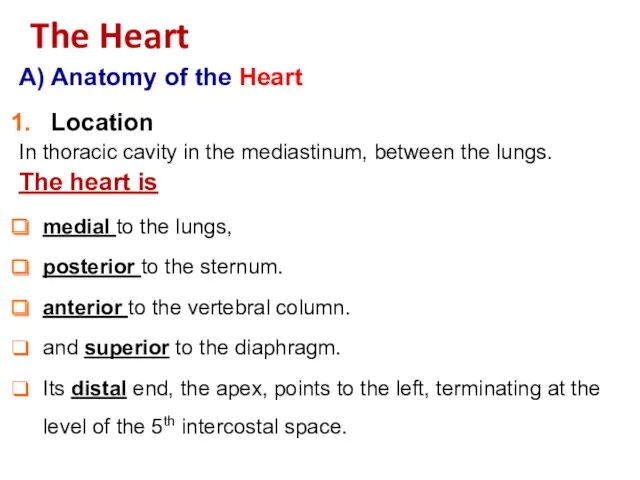
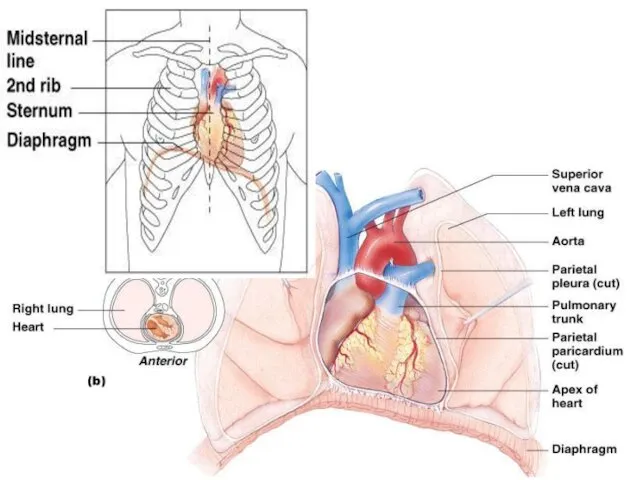
- 3. A) Anatomy of the Heart Location In thoracic cavity in the mediastinum, between the lungs. The
- 5. Coverings of the Heart: Anatomy The Function of the Pericardium: Protects and anchors the heart Prevents
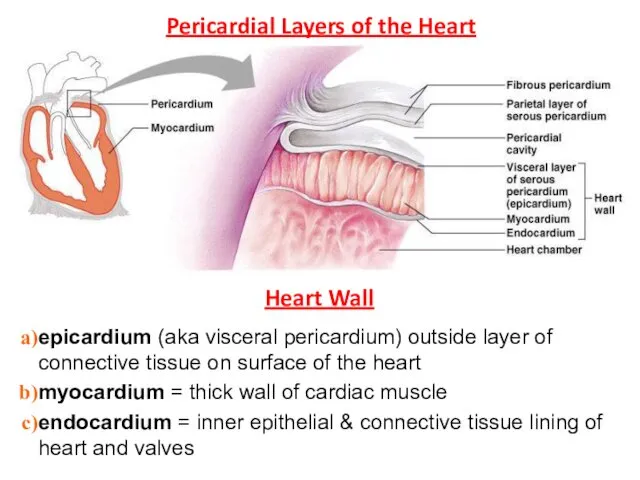
- 6. Pericardial Layers of the Heart Heart Wall epicardium (aka visceral pericardium) outside layer of connective tissue
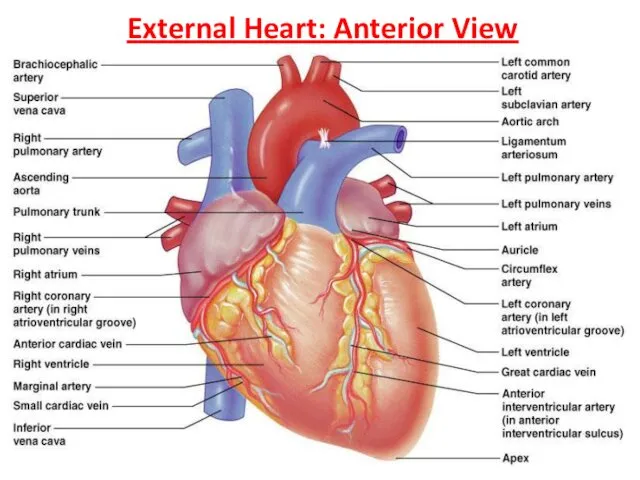
- 7. Chambers of the heart (4) atrium (R & L)—receive blood each atria extends into a smaller,
- 8. External Heart: Major Vessels of the Heart Vessels returning blood to the heart include: Superior and
- 9. External Heart: Anterior View
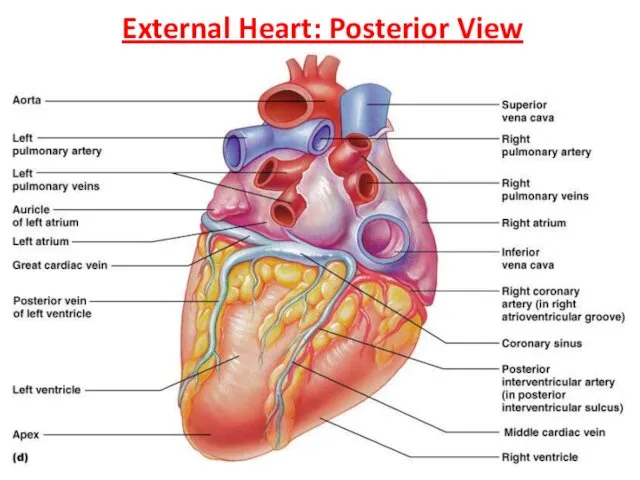
- 10. External Heart: Posterior View
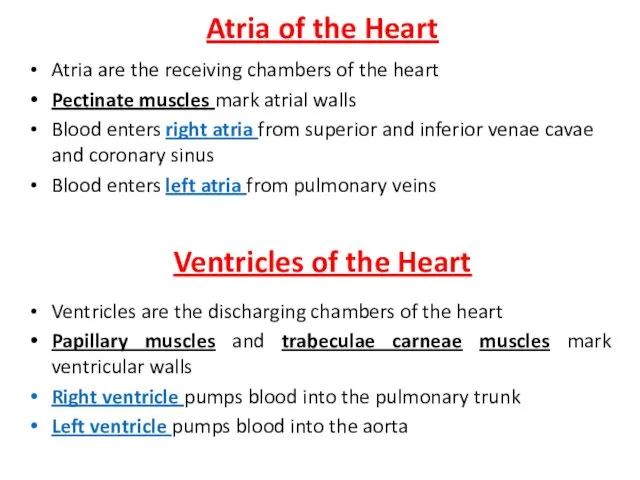
- 11. Atria of the Heart Atria are the receiving chambers of the heart Pectinate muscles mark atrial
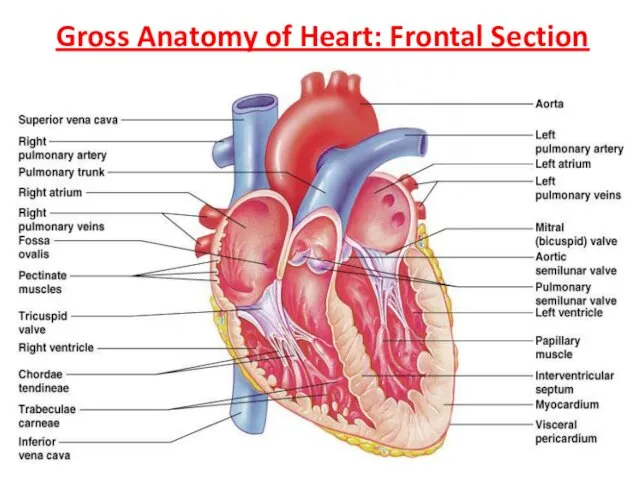
- 12. Gross Anatomy of Heart: Frontal Section
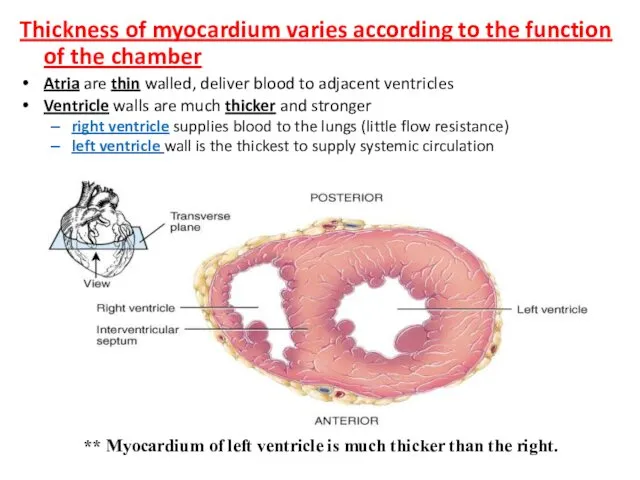
- 13. Thickness of myocardium varies according to the function of the chamber Atria are thin walled, deliver
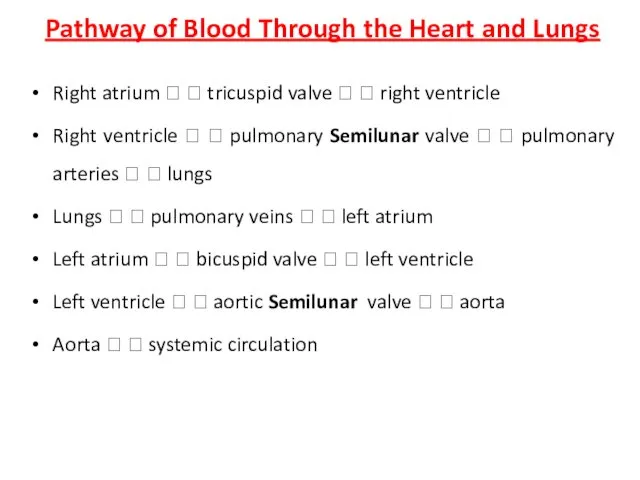
- 14. Pathway of Blood Through the Heart and Lungs Right atrium ? ? tricuspid valve ? ?
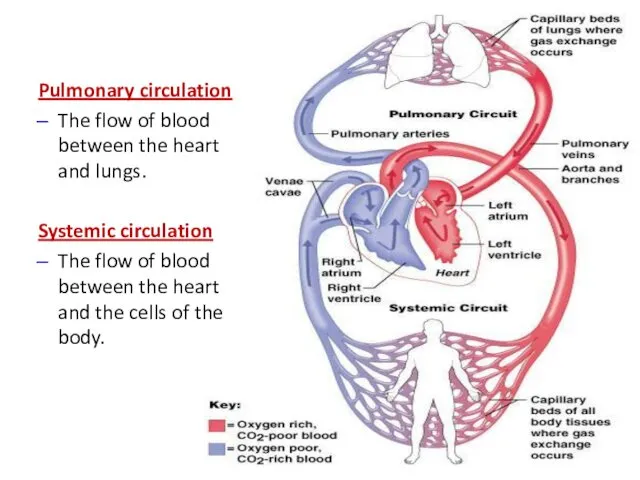
- 15. Pulmonary circulation The flow of blood between the heart and lungs. Systemic circulation The flow of
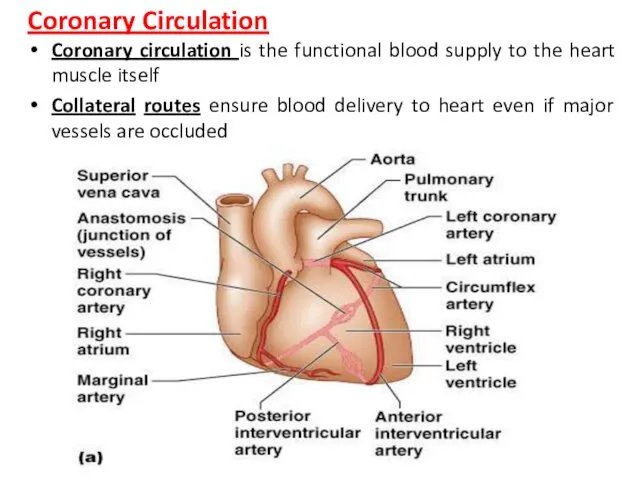
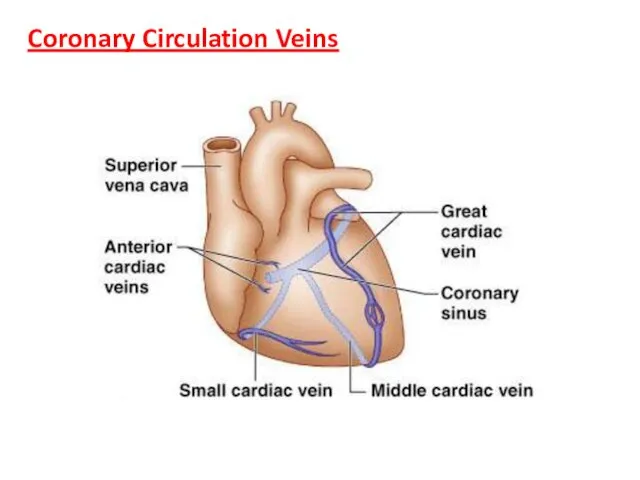
- 16. Coronary Circulation Coronary circulation is the functional blood supply to the heart muscle itself Collateral routes
- 17. Coronary Circulation Veins
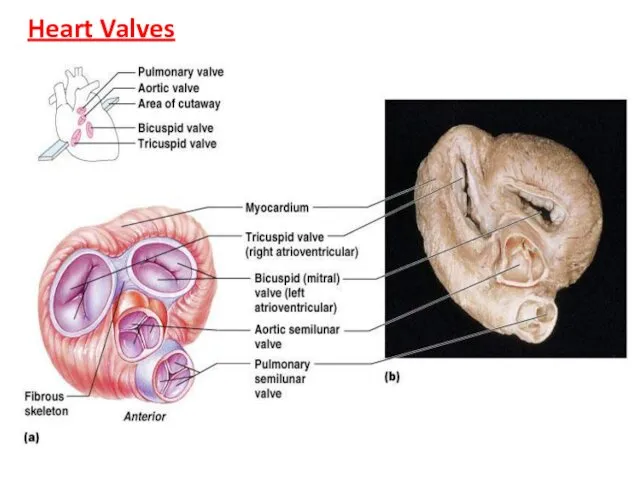
- 18. Heart Valves Heart valves ensure uni-directional blood flow through the heart Atrioventricular (AV) valves lie between
- 19. Heart Valves
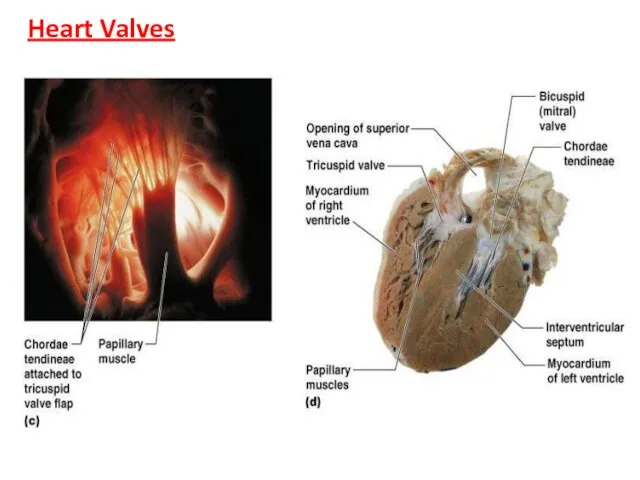
- 20. Heart Valves
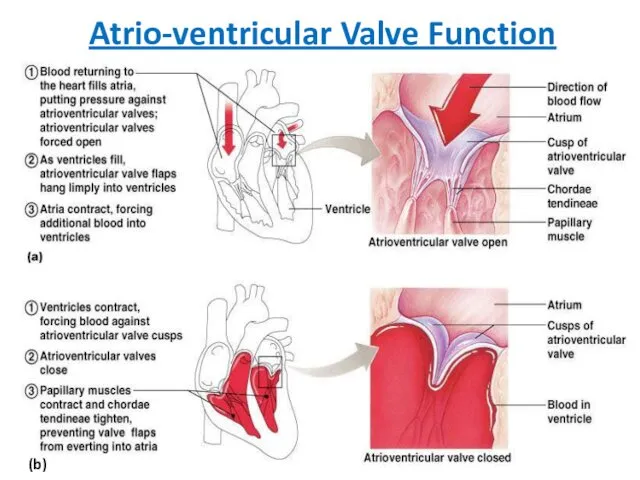
- 21. Atrio-ventricular Valve Function (b)
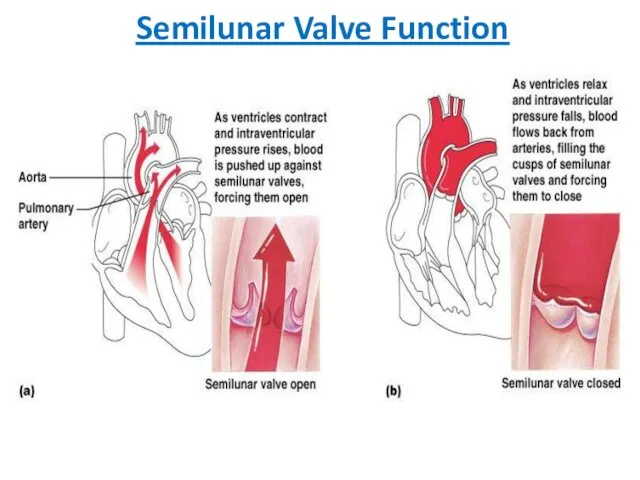
- 22. Semilunar Valve Function
- 24. Скачать презентацию




 Наркоз (общее обезболивание)
Наркоз (общее обезболивание) Sistem nervos - generalitati
Sistem nervos - generalitati Законы движения крови по сосудам. Основные гемодинамические показатели
Законы движения крови по сосудам. Основные гемодинамические показатели Medical insurance for employees and their family members
Medical insurance for employees and their family members Лихорадка Эбола
Лихорадка Эбола Заболеваемость населения как медико-социальная проблема. Эпидемиологические методы изучения заболеваемости
Заболеваемость населения как медико-социальная проблема. Эпидемиологические методы изучения заболеваемости Государственное автономное учреждение здравоохранения Московской области Центральная городская клиническая больница г. Реутов
Государственное автономное учреждение здравоохранения Московской области Центральная городская клиническая больница г. Реутов Патология и физиология климактерия. Индивидуализация ЗГТ
Патология и физиология климактерия. Индивидуализация ЗГТ Миоксигенирующий массаж лица
Миоксигенирующий массаж лица Фізіологічний післяпологовий період
Фізіологічний післяпологовий період Радиобиологические основы лучевой терапии. Реакции и осложнения при лучевой терапии. Лучевая терапия неопухолевых заболеваний
Радиобиологические основы лучевой терапии. Реакции и осложнения при лучевой терапии. Лучевая терапия неопухолевых заболеваний Кишечная непроходимость. Динамическая кишечная непроходимость
Кишечная непроходимость. Динамическая кишечная непроходимость Медициналық – генетикалық кеңес беру
Медициналық – генетикалық кеңес беру Фотометрические методы биохимического анализа. Турбидиметрия и нефелометрия
Фотометрические методы биохимического анализа. Турбидиметрия и нефелометрия Распорядок дня для здорового образа жизни: основы правильного режима дня
Распорядок дня для здорового образа жизни: основы правильного режима дня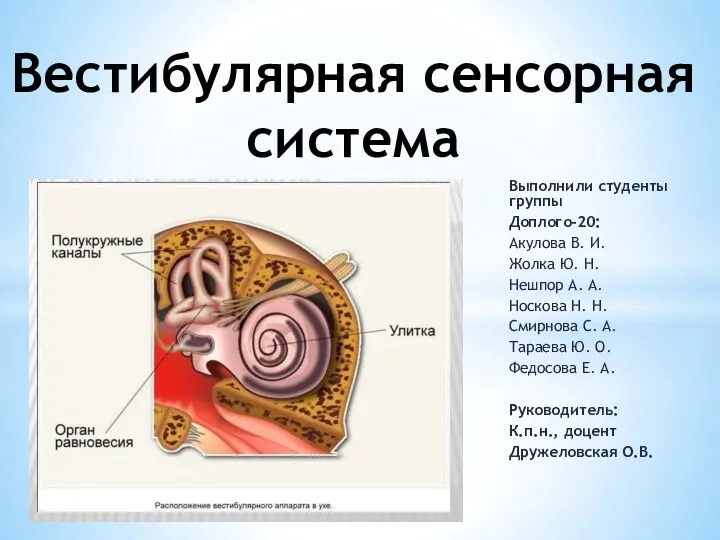 Вестибулярная сенсорная система
Вестибулярная сенсорная система Сенситивные периоды детей раннего возраста
Сенситивные периоды детей раннего возраста Қант диабеті
Қант диабеті Миокардиты. Этиология
Миокардиты. Этиология Серологические реакции
Серологические реакции Чувствительность: общие понятия
Чувствительность: общие понятия Профилактика некариозных поражений:флоороза, гипоплазия эмали. Факторы риска возникновения флюороза, местной и системной
Профилактика некариозных поражений:флоороза, гипоплазия эмали. Факторы риска возникновения флюороза, местной и системной Бруцеллез (сарып) ауруы
Бруцеллез (сарып) ауруы Неязвенные желудочные диспепсии
Неязвенные желудочные диспепсии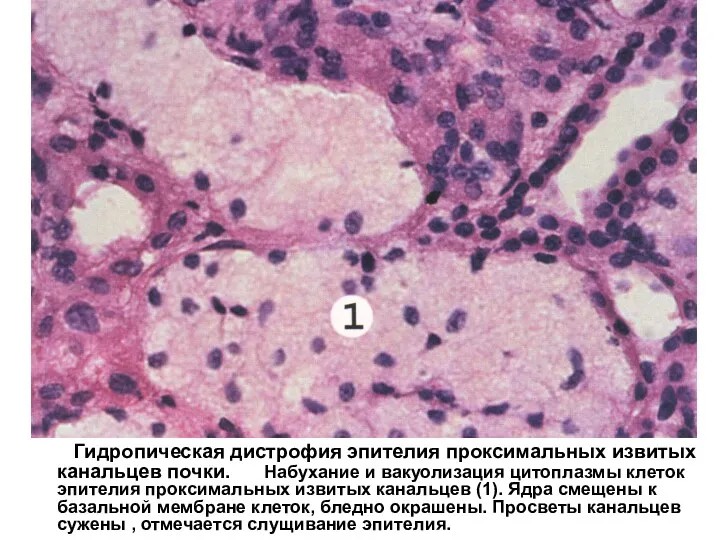 Гидропическая дистрофия эпителия проксимальных извитых канальцев почки
Гидропическая дистрофия эпителия проксимальных извитых канальцев почки Классификация энцефалитов. Аутоиммунные энцефалиты
Классификация энцефалитов. Аутоиммунные энцефалиты Выхаживание детей с экстремально низкой массой тела
Выхаживание детей с экстремально низкой массой тела Мектептегі оқу жұмысының кейбір түрлеріне қойылатын гигиеналық талаптар
Мектептегі оқу жұмысының кейбір түрлеріне қойылатын гигиеналық талаптар