Слайд 2
What is CAH?
It is a familial disorder of adrenal steroid biosynthesis
due to adrenal enzyme deficiency with autosomal recessive mode of inheritance.
Classical CAH is a sever homozygotic disorder with an incidence of 1 : 7,000-15,000
Non-classical CAH is less sever heterozygotic disorder with an incidence of 1 : 500-1,000
3 major enzymes deficiency are clinically important
21-Hydroxylase deficiency (90%-95%)
11-b-Hydroxylase deficiency
17-a-Hydroxylase deficiency
Слайд 3
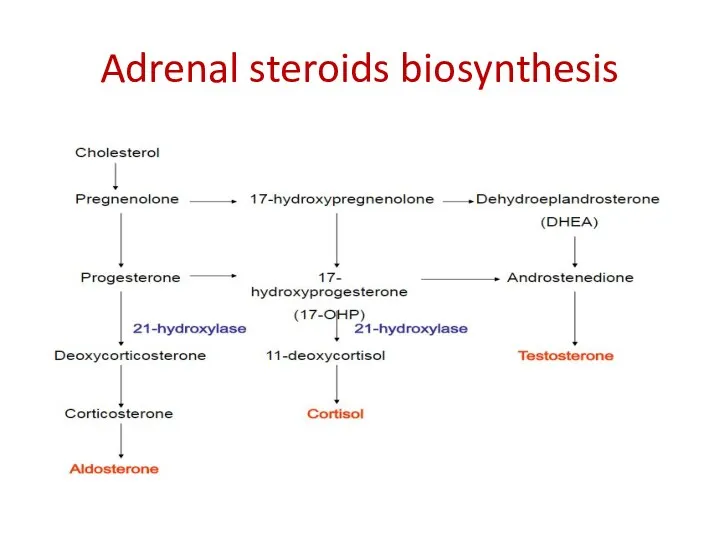
Adrenal steroids biosynthesis
Слайд 4
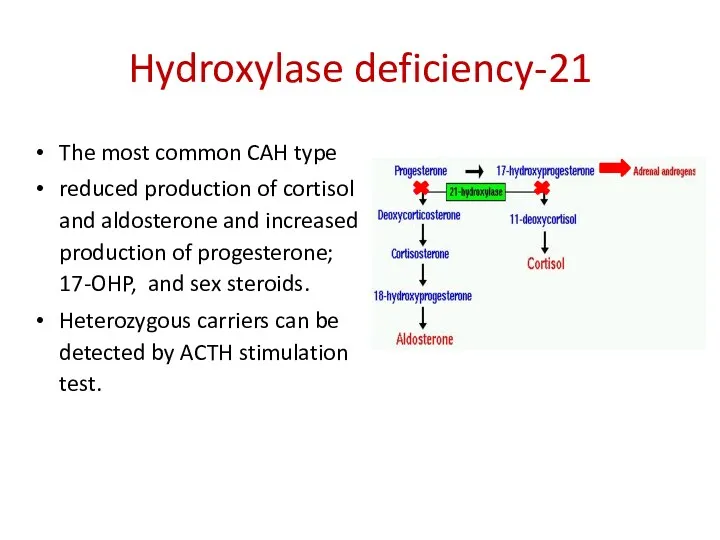
21-Hydroxylase deficiency
The most common CAH type
reduced production of cortisol and
aldosterone and increased production of progesterone; 17-OHP, and sex steroids.
Heterozygous carriers can be detected by ACTH stimulation test.
Слайд 5
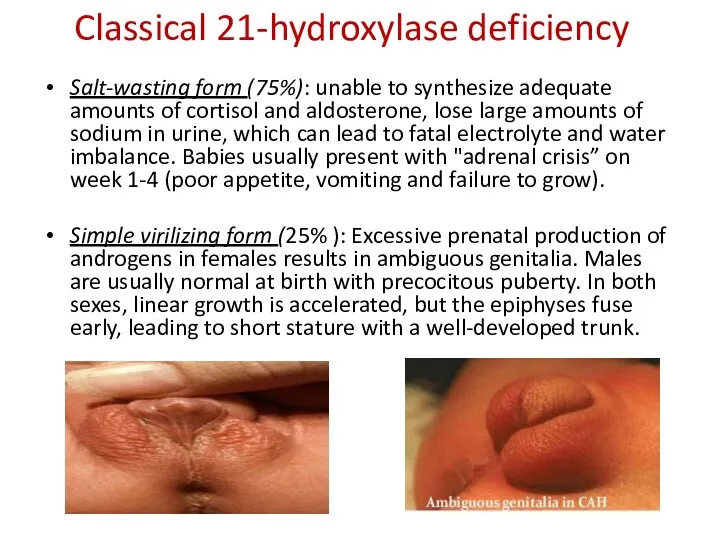
Classical 21-hydroxylase deficiency
Salt-wasting form (75%): unable to synthesize adequate amounts of
cortisol and aldosterone, lose large amounts of sodium in urine, which can lead to fatal electrolyte and water imbalance. Babies usually present with "adrenal crisis” on week 1-4 (poor appetite, vomiting and failure to grow).
Simple virilizing form (25% ): Excessive prenatal production of androgens in females results in ambiguous genitalia. Males are usually normal at birth with precocitous puberty. In both sexes, linear growth is accelerated, but the epiphyses fuse early, leading to short stature with a well-developed trunk.
Слайд 6

Non-classical 21-hydroxylase deficiency
Usually is mild and manifest as an androgen excess
later in life. Aldosterone and cortisol deficiency isn’t usually observed.
Female manifestations: hirsutism, acne, male-pattern balding, oligomenorrhea, infertility.
Male manifestations: general asymptomatic, short stature, sometimes oligospermia.
Слайд 7
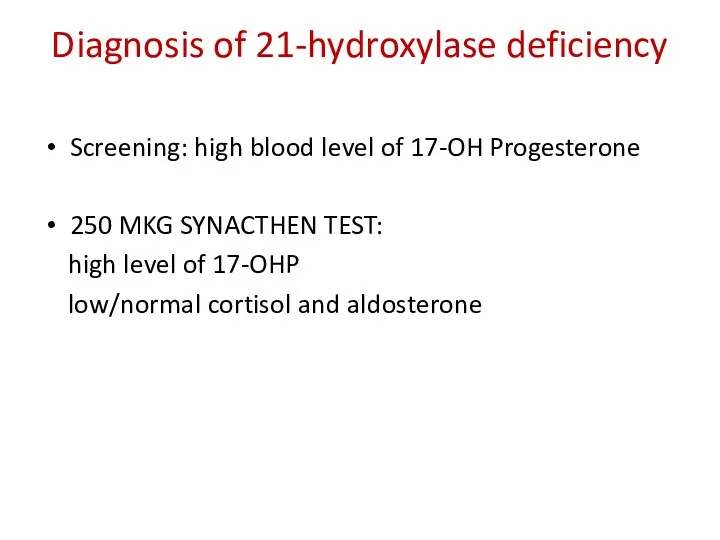
Diagnosis of 21-hydroxylase deficiency
Screening: high blood level of 17-OH Progesterone
250 MKG
SYNACTHEN TEST:
high level of 17-OHP
low/normal cortisol and aldosterone
Слайд 8
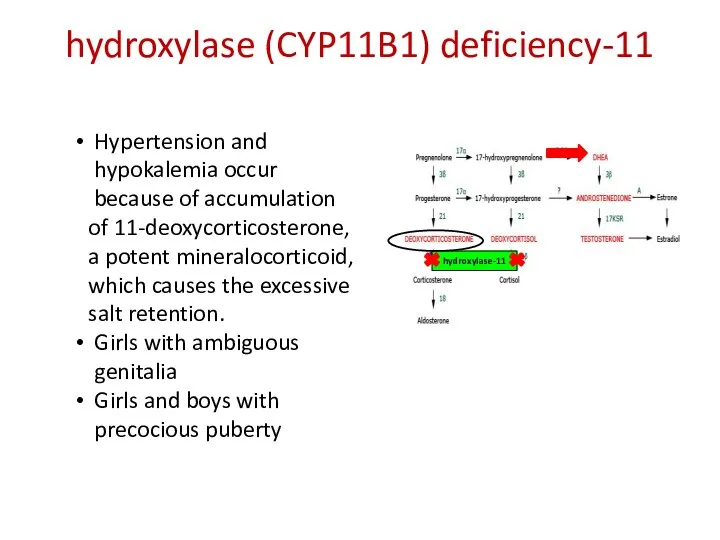
11-hydroxylase (CYP11B1) deficiency
11-hydroxylase
Hypertension and hypokalemia occur
because of accumulation
of 11-deoxycorticosterone,
a potent mineralocorticoid,
which causes the excessive
salt retention.
Girls with ambiguous genitalia
Girls and boys with precocious puberty
Слайд 9
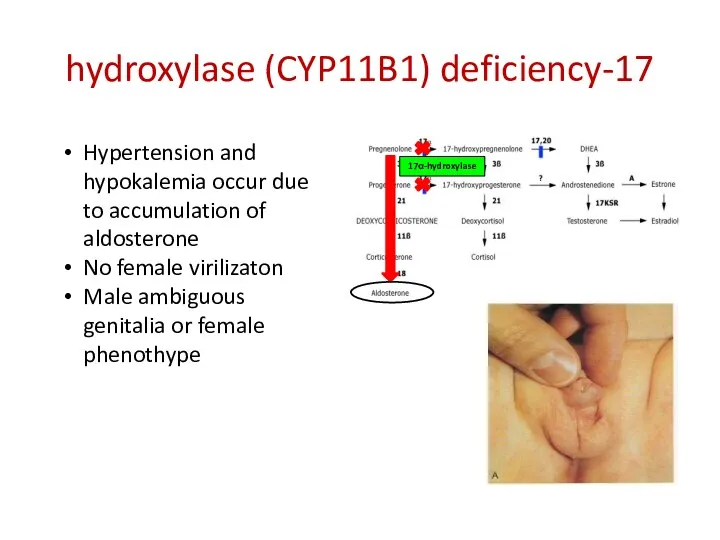
17-hydroxylase (CYP11B1) deficiency
17α-hydroxylase
Hypertension and hypokalemia occur due to accumulation of aldosterone
No
female virilizaton
Male ambiguous genitalia or female phenothype
Слайд 10
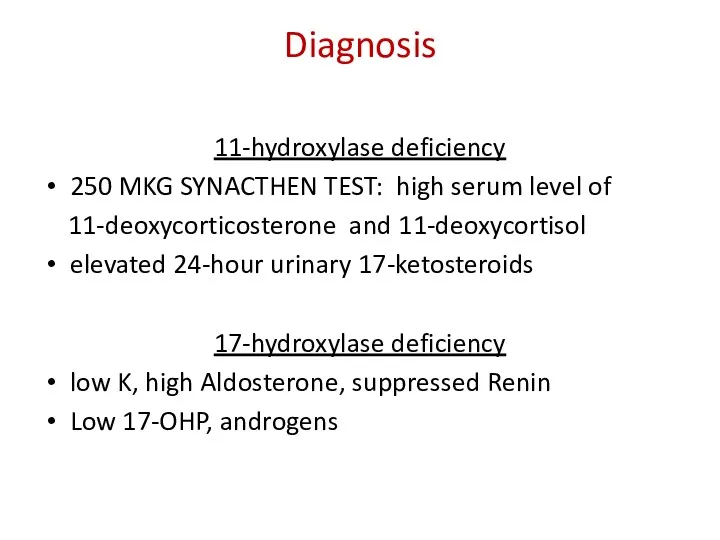
Diagnosis
11-hydroxylase deficiency
250 MKG SYNACTHEN TEST: high serum level of
11-deoxycorticosterone and 11-deoxycortisol
elevated 24-hour urinary 17-ketosteroids
17-hydroxylase deficiency
low K, high Aldosterone, suppressed Renin
Low 17-OHP, androgens
Слайд 11

TREATMENT PRINCIPLES
In classical CAH treatment is life-long
Treatment goals are:
to maintain
growth velocity & skeletal maturation.
to normalize electrolytes & hormone levels using the smallest dose of glucocorticoids.
mineralocorticoid replacement may be needed to sustain normal electrolyte homeostasis.
Plastic surgery for ambiguous genitalia at early age
Genetic counseling
Psychological support
Слайд 12

Prenatal diagnosis and treatment
Done by chorionic villus sampling at 8-12 wk
& amniocentesis at 18-20 wk.
Prenatal treatment of 21-hydroxylase deficiency prevents intrauterine virilization of female fetuses.
The mother with nonclassical CAH is treated with dexamethasone as soon as the pregnancy is recognized until fetus sex determination.











 Ортопедиялық (ортодентия tel tedavi̇si̇) стоматологияда қолданылатын полимерлер
Ортопедиялық (ортодентия tel tedavi̇si̇) стоматологияда қолданылатын полимерлер Сүйектің эктопиялық дамуы
Сүйектің эктопиялық дамуы Гендік терапия
Гендік терапия Гестационный сахарный диабет
Гестационный сахарный диабет Средства, влияющие на функции органов дыхания
Средства, влияющие на функции органов дыхания Основы онкологии
Основы онкологии Этика и медицинская деонтология. Биоэтика
Этика и медицинская деонтология. Биоэтика Первая помощь при кровотечении
Первая помощь при кровотечении Организация санитарно-противоэпидемического обеспечения и медицинского снабжения в чрезвычайных ситуациях
Организация санитарно-противоэпидемического обеспечения и медицинского снабжения в чрезвычайных ситуациях Медицинская информатика: основы защиты данных. Лекция 3
Медицинская информатика: основы защиты данных. Лекция 3 Қант диабетінің емі
Қант диабетінің емі 1 жасқа дейінгі балаларды табиғи тамақтандыру
1 жасқа дейінгі балаларды табиғи тамақтандыру Туберкулинді диагностика
Туберкулинді диагностика Экопаталогии. Экология человека
Экопаталогии. Экология человека Основные понятия и категории социальной медицины
Основные понятия и категории социальной медицины Коррекция кальций-фосфорного обмена у пациентов на гемодиализе
Коррекция кальций-фосфорного обмена у пациентов на гемодиализе Остеоартроз (остеоартрит)
Остеоартроз (остеоартрит) Опыт хирургического лечения опухолей надпочечников у детей
Опыт хирургического лечения опухолей надпочечников у детей Микобактерии – возбудители микобактериозов, туберкулеза и лепры
Микобактерии – возбудители микобактериозов, туберкулеза и лепры Өңештің бөгде заттары
Өңештің бөгде заттары Клінічні та ЕКГ-ознаки порушень збудливості та провідності
Клінічні та ЕКГ-ознаки порушень збудливості та провідності Преждевременная отслойка нормально расположенной плаценты
Преждевременная отслойка нормально расположенной плаценты Общий уход за больными в предоперационный и послеоперационный период
Общий уход за больными в предоперационный и послеоперационный период Ми қыртысы. Ми қыртысының цитоархитектоникасы
Ми қыртысы. Ми қыртысының цитоархитектоникасы Психология сложного дефекта
Психология сложного дефекта Расслоение аорты, диагностика, неотложная помощь
Расслоение аорты, диагностика, неотложная помощь Социофобия. Панические атаки. Агрофобия. ВСД
Социофобия. Панические атаки. Агрофобия. ВСД Пороки митрального клапана
Пороки митрального клапана