Содержание
- 2. Dental caries is a breakdown of teeth due to activities of bacteria. The cavities may be
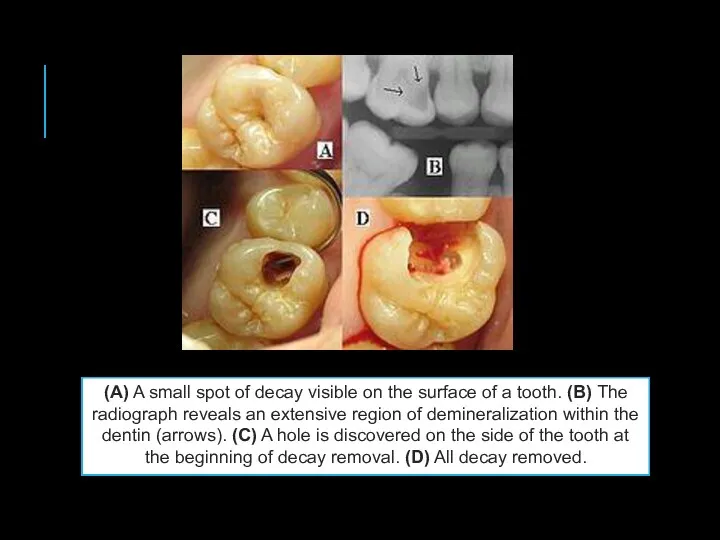
- 3. (A) A small spot of decay visible on the surface of a tooth. (B) The radiograph
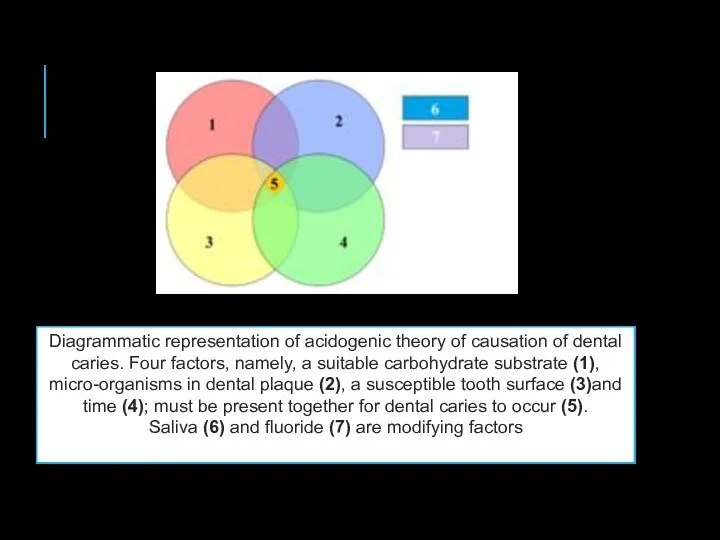
- 4. Diagrammatic representation of acidogenic theory of causation of dental caries. Four factors, namely, a suitable carbohydrate
- 5. SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS A person experiencing caries may not be aware of the disease. The earliest
- 6. CAUSE There are four things required for caries formation: a tooth surface (enamel or dentin), caries-causing
- 7. PREVENTION Oral hygiene Personal hygiene care consists of proper brushing and flossing daily. The purpose of
- 8. Zero Conditional Uses: Use the zero conditional to talk about scientific facts, constant laws of nature,
- 9. First Conditional Uses: Use the first conditional to talk about probable/possible conditions in the future, or
- 10. Second Conditional Uses: Use the second conditional to talk about unreal or hypothetical situations in the
- 11. Third Conditional Uses: Use the third conditional to talk about past events that are untrue. Formula:
- 12. MIXED CONDITIONALS When we talk about mixed conditionals, we are referring to conditional sentences that combine
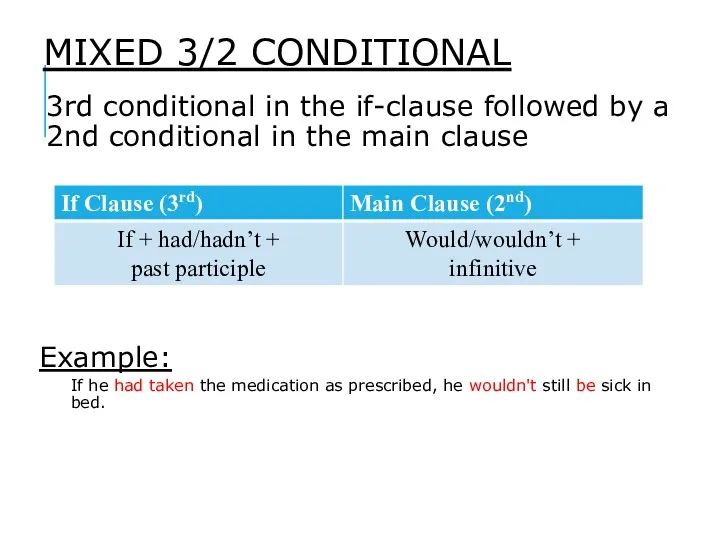
- 13. MIXED 3/2 CONDITIONAL 3rd conditional in the if-clause followed by a 2nd conditional in the main
- 14. MIXED 3/2 CONDITIONAL With this combination we are describing what the outcome would be in the
- 15. WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN THE THIRD CONDITIONAL AND THE MIXED CONDITIONAL? 3rd Conditional Describes what
- 16. MIXED 3/2 CONDITIONAL 2nd conditional in the if-clause followed by a 3rd conditional in the main
- 18. Скачать презентацию











 Магнитно-резонансная томография
Магнитно-резонансная томография Аллергия
Аллергия Рак. Эпидемиология. Классификация рака
Рак. Эпидемиология. Классификация рака Пародонт ауруларын ортопедиялық емдеу тәсілдері
Пародонт ауруларын ортопедиялық емдеу тәсілдері Электрокардиограмма при гипертрофии различных отделов миокарда
Электрокардиограмма при гипертрофии различных отделов миокарда Невынашивание. Преждевременные роды
Невынашивание. Преждевременные роды Своды стопы. Плоскостопие
Своды стопы. Плоскостопие Основи безпечного харчування
Основи безпечного харчування Организация психиатрической помощи в РФ
Организация психиатрической помощи в РФ Кардиогенный шок
Кардиогенный шок Урогенитальный хламидиоз
Урогенитальный хламидиоз 5_6_Средства_на_дыхательную_систему
5_6_Средства_на_дыхательную_систему Әріптестермен өзара қарым-қатынастың ерекшеліктері
Әріптестермен өзара қарым-қатынастың ерекшеліктері Химиятерапиялық заттар. Антибиотиктер
Химиятерапиялық заттар. Антибиотиктер Bronchial asthma
Bronchial asthma Нейросифилис. Органические поражения ЦНС и ПНС, вызванные инвазией бледной трепонемы
Нейросифилис. Органические поражения ЦНС и ПНС, вызванные инвазией бледной трепонемы Кариес зубов. Эпидемиология, распространенность, интенсивность
Кариес зубов. Эпидемиология, распространенность, интенсивность Здоровье как состояние и свойство организма
Здоровье как состояние и свойство организма Питание детей 1 года жизни (лекция № 27 для интернов)
Питание детей 1 года жизни (лекция № 27 для интернов) Трансплантация легких
Трансплантация легких Синдром поражения миокарда
Синдром поражения миокарда Гипертонический криз: современное состояние проблемы, алгоритмы диагностики и лечения
Гипертонический криз: современное состояние проблемы, алгоритмы диагностики и лечения Послеродовые болезни
Послеродовые болезни Синдром портальной гипертензии
Синдром портальной гипертензии Острая вирусная инфекция - полиомиелит
Острая вирусная инфекция - полиомиелит Тактична медицина. Головні принципи надання допомоги під час бойових дій
Тактична медицина. Головні принципи надання допомоги під час бойових дій Виды кровотечений и оказание первой помощи
Виды кровотечений и оказание первой помощи Депрессия. Факторы, повышающие вероятность депрессии
Депрессия. Факторы, повышающие вероятность депрессии