Содержание
- 2. Endometriosis is a disease in which endometrial glands and stroma implant and grow in areas outside
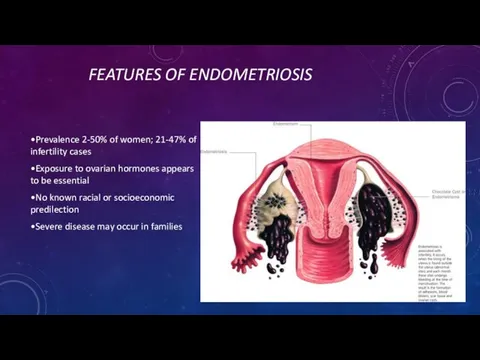
- 3. FEATURES OF ENDOMETRIOSIS •Prevalence 2-50% of women; 21-47% of infertility cases •Exposure to ovarian hormones appears
- 4. IS ENDOMETRIOSIS INCREASING? •1965-1984, endometriosis rose from 10 to 19% as primary indication for hysterectomy •Simultaneously,
- 5. ETIOLOGIES OF ENDOMETRIOSIS •Sampson's theory: Retrograde menses and peritoneal implantation –Most women retrograde menstruate •Meyer's theory:
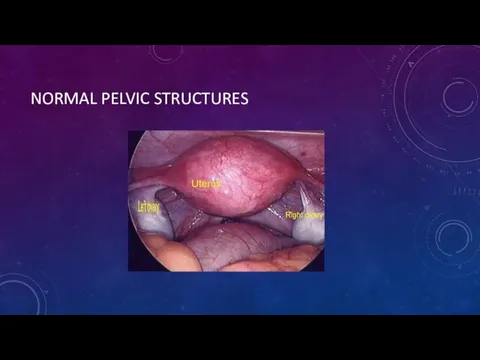
- 6. NORMAL PELVIC STRUCTURES
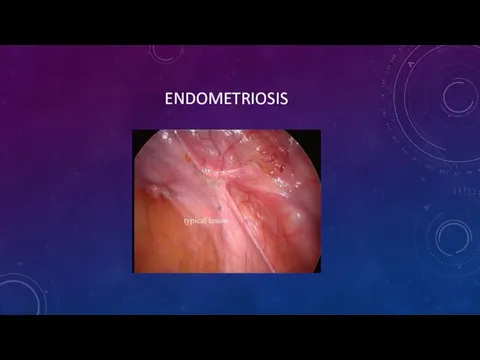
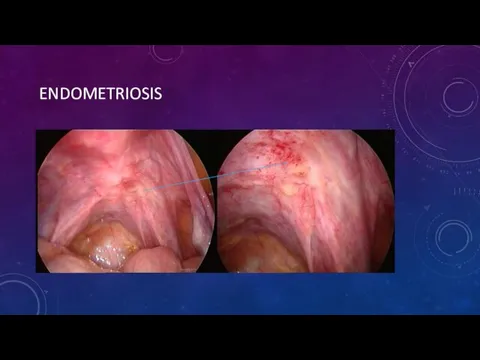
- 7. ENDOMETRIOSIS
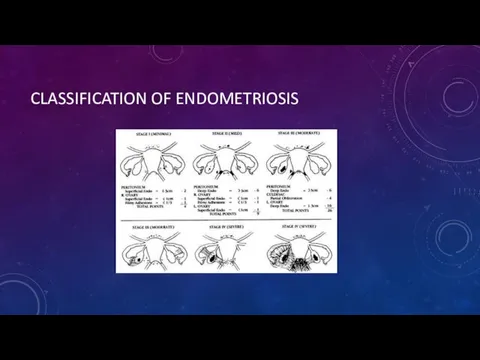
- 8. CLASSIFICATION OF ENDOMETRIOSIS
- 9. CLINICAL PRESENTATION Pelvic pain •Infertility •Pelvic mass
- 10. PHYSICAL FINDINGS Tender nodules along the uterosacral ligaments or in the cul-de-sac, especially just before menses
- 11. DIAGNOSIS OF ENDOMETRIOSIS Diagnosis of Endometriosis •Direct visualization of implants – Laparoscopically – Conscious pain mapping
- 12. ENDOMETRIOSIS
- 13. TREATMENT OF ENDOMETRIOSIS Management of pain – Surgery – Medical therapy •Treatment of infertility – Surgery
- 14. MANAGEMENT OF PAIN Surgical treatment – Ablation of endometrial implants – Lysis of adhesions – Ablation
- 15. LOCALIZATION on or under the ovaries behind the uterus on the tissues that hold the uterus
- 16. PROPHYLAXIS Research suggests that frequent and early pregnancy, use of oral contraceptives, and daily exercise may
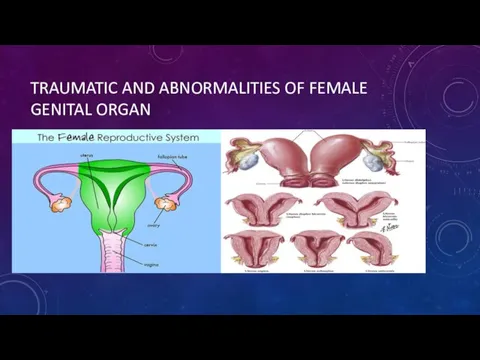
- 17. TRAUMATIC AND ABNORMALITIES OF FEMALE GENITAL ORGAN
- 18. UTERINE ABNORMALITIES double vagina, double cervix and double uterus single vagina, single cervix and double single-horned
- 19. INVESTIGATIONS Ultrasound Hysterosalpingography, which allows evaluation of the uterine cavity and tubal patency. MRI scan, which
- 20. MANAGEMENT Decision for surgical intervention will depend on the effect of the abnormality on enabling a
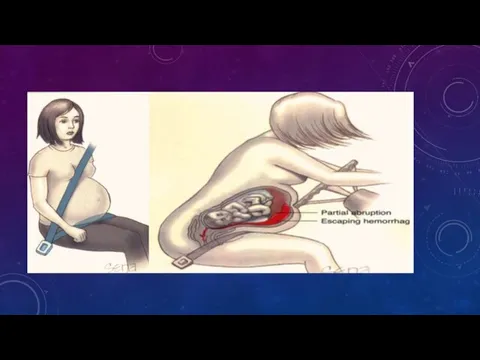
- 21. GENITAL TRAUMATIC A _ Obstetric Trauma Uterus (Blunt & Penetration) Genital Tract (delivery trauma) B _
- 23. DELIVERY TRAUMA Lacerations of the birth canal Raptures Hematomas Injuries to the cervix Vaginal laceration
- 24. GENITAL TRACT TRAUMA ?FOREIGN BODY ?SEXUAL ASSULT ?HEMATOMA
- 26. Скачать презентацию
















 Хирургическое лечение переломов костей голени
Хирургическое лечение переломов костей голени Физиология возбуждимых тканей
Физиология возбуждимых тканей Гипертонический криз
Гипертонический криз Строение органов дыхания у новорожденных и детей
Строение органов дыхания у новорожденных и детей Жүкті әйелдерді амбулаториялық жағдайда жүргізу
Жүкті әйелдерді амбулаториялық жағдайда жүргізу Особености травматологии детского возраста
Особености травматологии детского возраста Эмбриогенез, анатомо-физиологические особенности почек и мочевыделительной системы у детей
Эмбриогенез, анатомо-физиологические особенности почек и мочевыделительной системы у детей Special issues. Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in adults and adolescents
Special issues. Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in adults and adolescents Здоровье и болезнь. Факторы, определяющие здоровье. Методика сбора анамнеза. Периоды детского возраста. Оценка здоровья
Здоровье и болезнь. Факторы, определяющие здоровье. Методика сбора анамнеза. Периоды детского возраста. Оценка здоровья Физиология боли
Физиология боли ИБС. Стенокардия. Инфаркт миокарда
ИБС. Стенокардия. Инфаркт миокарда Основы травматологии и ортопедии
Основы травматологии и ортопедии Пародонтоз. Идиопатические заболевания пародонта
Пародонтоз. Идиопатические заболевания пародонта Filling’s material: permanent & temporary
Filling’s material: permanent & temporary Симптомы и методы обследования в урологии
Симптомы и методы обследования в урологии Организация гинекологической помощи детям
Организация гинекологической помощи детям Введение в медицинскую рецептуру
Введение в медицинскую рецептуру Опухоли головного и спинного мозга
Опухоли головного и спинного мозга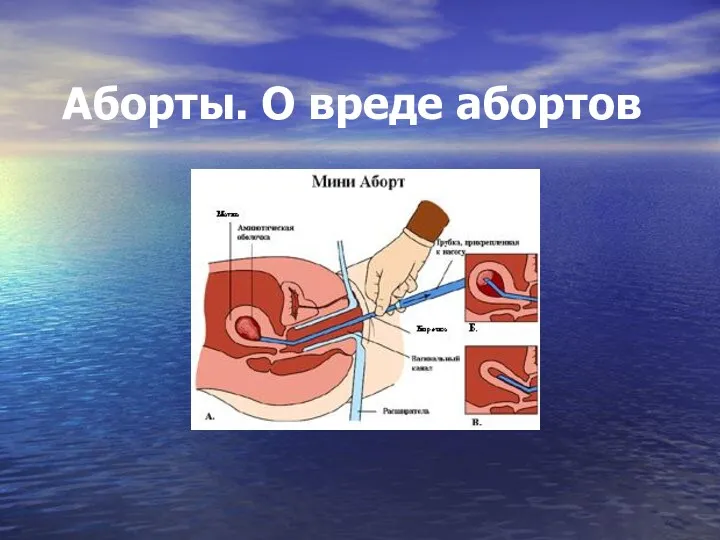 Аборты. О вреде абортов
Аборты. О вреде абортов Эмоциональные расстройства
Эмоциональные расстройства Гепатит В
Гепатит В Общая фармакология. Фармакодинамика
Общая фармакология. Фармакодинамика Информатизация медицины
Информатизация медицины Методы иммунодиагностики и иммунопрофилактики инфекционных болезней
Методы иммунодиагностики и иммунопрофилактики инфекционных болезней Қабыну ауруларының асқынулары. Сепсис
Қабыну ауруларының асқынулары. Сепсис Дифференциальная диагностика абдоминального болевого синдрома у детей
Дифференциальная диагностика абдоминального болевого синдрома у детей Чума. Симптомы. Клиника. Лечение
Чума. Симптомы. Клиника. Лечение Мұрынның артқы тампонадасы
Мұрынның артқы тампонадасы